Create a Runbook Trigger
Triggers determine when and how your runbooks execute automatically in Harness AI SRE. Proper trigger configuration ensures your runbooks respond to the right conditions at the right time, enabling seamless automation for incident response and operational workflows.
Overview
Runbook triggers help you:
- Automate runbook execution based on specific conditions
- Respond to incidents, alerts, and key events automatically
- Set up event-driven workflows for faster incident resolution
- Configure conditional logic to prevent unnecessary executions
- Establish reliable automation that scales with your operations
Trigger Configuration Basics
Runbook triggers can be created based on various conditions and events. The trigger system allows you to:
- Incident-Based Automation: Execute runbooks when incidents are created, updated, or when specific field changes occur
- Key Event Responses: Trigger runbooks when key events are created in the incident timeline
- Conditional Logic: Use ALL or ANY condition types with field comparisons to create precise trigger criteria
- Field-Specific Triggers: Monitor changes to specific incident fields and trigger based on old values, new values, or field changes
Best Practices for Trigger Creation
Consider these scenarios when creating runbook triggers:
- Incident Severity Changes: Trigger escalation runbooks when incident severity increases
- Assignment Changes: Execute notification runbooks when incidents are assigned to specific teams
- Status Updates: Activate communication runbooks when incident status changes to resolved
- Key Milestones: Trigger documentation runbooks when key events are added to incident timelines
Creating Triggers
- Interactive Guide
- Step by Step
Follow this interactive guide to configure triggers that automatically execute your runbooks based on specific conditions and events.
Step 1: Access Trigger Configuration
- Open your existing runbook in the Harness AI SRE platform
- Click the Triggers tab in your runbook editor
- This opens the trigger configuration interface
Step 2: Create New Trigger
- Click + New Trigger to begin the trigger setup process
- This opens the trigger creation wizard
Step 3: Choose Trigger Template
- Select the Incident Type template from the available options
- Choose the specific Incident Type from the dropdown menu
- The selected incident type determines which fields and values will be available for condition configuration
- This selection affects what data you can use when setting up trigger conditions
Step 4: Define Trigger Conditions
- Choose Condition Type: Select either ALL or ANY for your condition logic:
- ALL: All conditions must be met for the trigger to activate
- ANY: Any one of the conditions can activate the trigger
- Set Frequency: Choose when the trigger should evaluate:
- Activity Created: Trigger when new incidents are created
- Activity Updated: Trigger when incidents are updated
- Key Event Created: Trigger when key events are added to incidents
- Add Conditions: Click to add specific field-based conditions for more precise triggering
Step 5: Configuring Additional Conditions
To add more specific conditions beyond the basic frequency setting:
- Select Field: Choose the incident field you want to monitor from the dropdown
- Fields available depend on the incident type selected in Step 3
- Options include standard incident fields and custom fields for that incident type
- Choose Comparison Type: Select what aspect of the field to monitor:
- Old Values: Compare against the previous value of the field
- New Values: Compare against the current/new value of the field
- Changed Field: Trigger when the field value changes (regardless of specific values)
- Select Comparator: Choose how to compare the field value:
- Equals: Exact match with the specified value
- Contains: Field contains the specified text
- Greater Than/Less Than: Numeric comparisons
- Other operators: Based on field type and requirements
- Enter Value: Provide the value to compare against
- Repeat: Add multiple conditions as needed using the ALL/ANY logic set in Step 4
Step 6: Save and Activate
- Review Configuration: Verify all trigger settings are correct
- Save Trigger: Click Save to create the trigger
- Test Trigger: Test the trigger by creating dummy conditions that match your configuration
- Monitor Execution: Track trigger performance and effectiveness once activated
Trigger Configuration Best Practices
Design Principles
- Specific Conditions: Create precise trigger conditions to avoid false positives
- Logical Grouping: Organize related triggers for easier management
- Performance Optimization: Design efficient conditions that don't overload the system
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive names that clearly indicate trigger purpose
Operational Excellence
- Avoid Trigger Overlap: Ensure multiple runbooks don't trigger simultaneously for the same event
- Use Appropriate Delays: Add delays between related triggers to prevent conflicts
- Test Thoroughly: Validate trigger conditions in non-production environments first
- Monitor Execution: Track trigger effectiveness and adjust conditions as needed
Security Considerations
- Access Control: Ensure triggers have appropriate permissions for their actions
- Data Validation: Validate all input data before trigger execution
- Audit Logging: Maintain comprehensive logs of trigger activations
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling for failed trigger executions
Advanced Trigger Scenarios
Multi-Condition Triggers
Configure complex triggers that respond to multiple conditions:
- Incident Severity + Service: Trigger only for high-severity incidents affecting critical services
- Time + Alert Volume: Activate during business hours when alert volume exceeds thresholds
- Team Assignment + Escalation: Execute when incidents are escalated to specific teams
Conditional Execution
Implement smart trigger logic:
- Environment-Specific: Different triggers for production vs. development environments
- Service-Aware: Triggers that behave differently based on affected services
- Context-Sensitive: Triggers that adapt based on incident context and history
Troubleshooting Triggers
Common Issues
Trigger Not Activating
- Solution: Verify trigger conditions match actual event data
- Prevention: Test triggers with realistic scenarios before deployment
Performance Issues
- Solution: Optimize trigger conditions and reduce evaluation frequency
- Prevention: Regular performance monitoring and condition refinement
Integration with Key Events
Key Event Trigger Configuration
When using Key Events as trigger sources:
- Set Trigger Condition: In the Triggers section, set the condition to "Key Event Created"
- Map Event to Input: Configure how event data maps to runbook input variables
- Dynamic Execution: Enable automatic execution when specified Key Events occur
- Data Validation: Ensure event data meets runbook input requirements
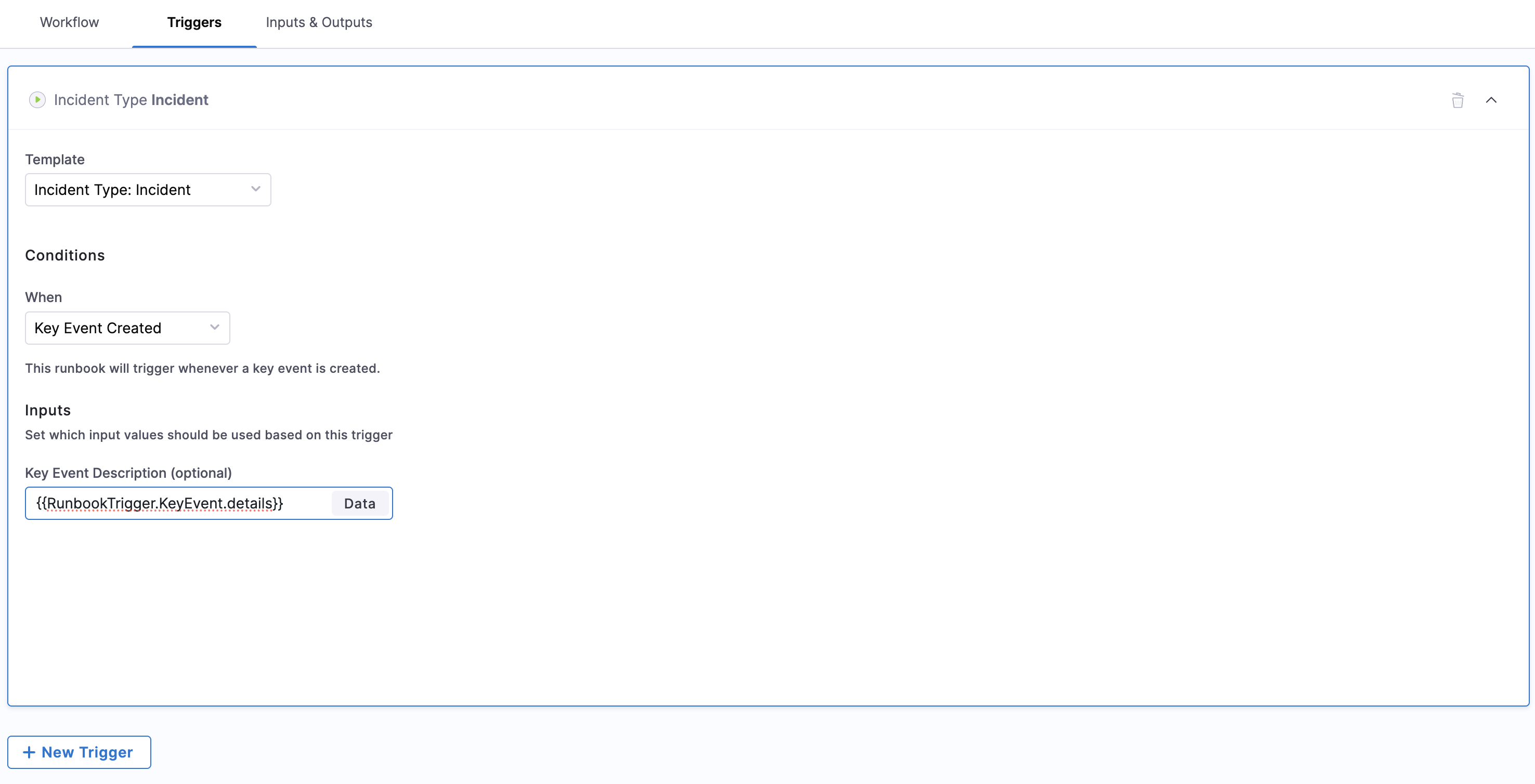
This approach allows for seamless integration between event detection and automated response, without requiring manual configuration of input variables for each execution.
Benefits
- Automated Response: Immediate response to incidents and alerts without manual intervention
- Consistent Execution: Standardized response procedures triggered by specific conditions
- Scalable Operations: Handle increasing incident volumes without additional manual effort
- Reduced MTTR: Faster incident resolution through automated trigger-based responses
- Operational Efficiency: Free up team members to focus on complex issues requiring human intervention
- Audit Trail: Complete tracking of automated actions and their triggers
- Flexible Configuration: Adapt trigger behavior to changing operational requirements
Next Steps
Getting Started
- Create a Runbook to attach triggers to
- Configure Authentication for secure trigger execution
- Set Up Incident Types to configure the fields available for trigger conditions
Advanced Configuration
- Configure Incident Fields for trigger condition data
- Set Up Project Connectors for external system integration
- Return to Runbook Overview for additional automation capabilities
Best Practices Resources
Need Help? Contact our support team by email at support@harness.io or visit the Harness Documentation for additional resources and troubleshooting guides.