Use the DB Query Action
In many scenarios, your test data doesn't live inside the test tool itself, but can be present in databases. The DB Query action in Harness AI Test Automation (AIT) allows you to fetch live data directly from your database during test execution.
This becomes extremely useful when you want your tests or actions to adapt dynamically based on real-time data, for example, reading customer records, account balances, or transactional states before deciding what to do next.
Rather than hardcoding values, you can query, process, and reuse those results across multiple steps. This helps create data-driven intelligent automation.
Prerequisites
Platform Setup
Harness Account with AI Test Automation enabled
Resource Setup
Ensure you have the database details you want to test or query from.
You'll need:
- Database type (PostgreSQL or MongoDB; support for Oracle, MS SQL, and MySQL coming soon)
- Host and port
- Database name
- Username and password (preferably a read-only user)
- Connection string or credentials available to your test runner
Databases are often behind a firewall and may not be accessible from the Harness cloud. To access these databases, you'll need to set up a tunnel that allows access to the database from Harness cloud. Learn more about setting up tunnels for firewall-protected applications.
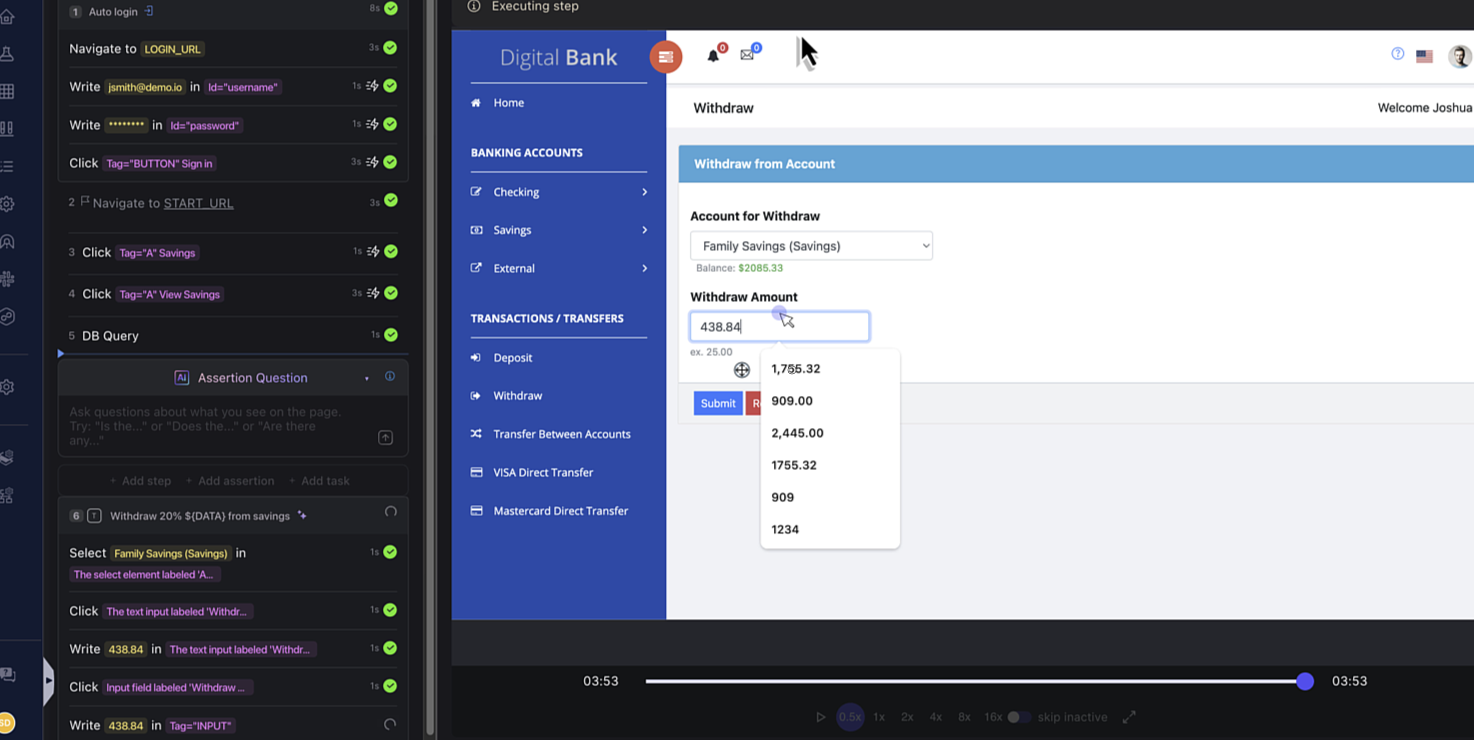
In this tutorial, we will perform a scenario where you will fetch a user’s account details from the database, extract a specific value (like the amount to withdraw) using a small script, and use that amount dynamically in a natural language multi-step task.
Step 1: Add a DB Query Action
Inside Harness AIT, select DB Query from the action list.
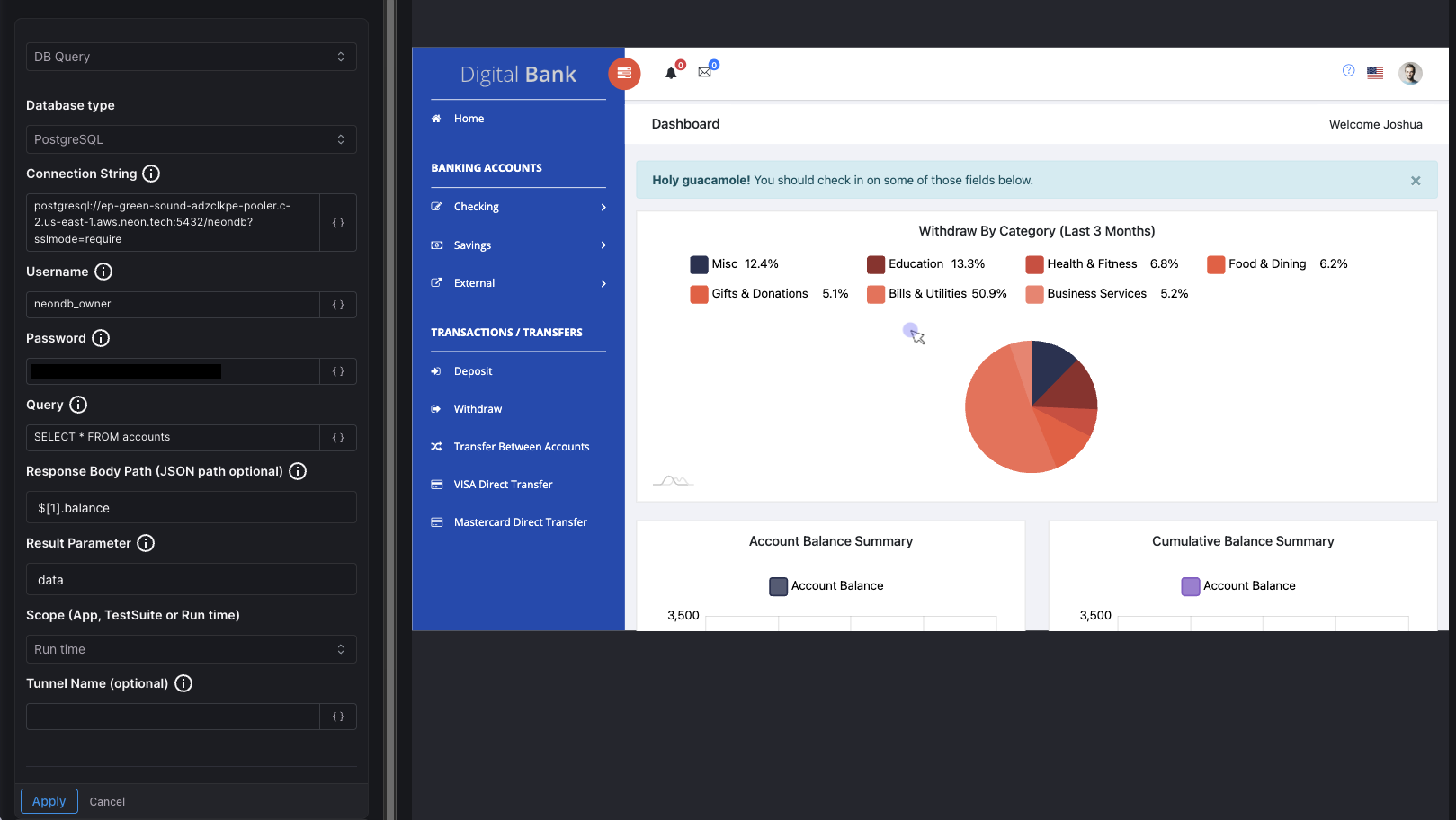
Configure the following fields to set up your database query:
Database type
Select the type of database you want to connect to. Currently supported options include:
- PostgreSQL
- MongoDB
Support for Oracle, MS SQL, and MySQL is coming soon.
Connection String : Provide the full connection string to your database. This typically includes the protocol, host, port, and database name. Follows the pattern: protocol://host:port/database_name?options
Username : Enter the database username with appropriate read permissions. For security best practices, use a read-only user account when possible.
Password : Provide the password for the database user. This field is masked for security.
Query : Write the SQL query you want to execute against the database. This should be a valid SQL statement for your database type.
Response Body Path (JSON path optional) : Specify a JSON path expression to extract specific data from the query response. This is optional but useful when you want to filter or transform the result. For instance, $[1].balance would extract the balance field from the second record (index 1) in the result set. Leave this empty if you want to capture the entire response.
Result Parameter : Define the name of the parameter where the query result will be stored. This parameter can be referenced in subsequent steps of your workflow using the syntax ${parameter_name}.
Tunnel Name (optional)
If your database is behind a firewall and requires tunnel access, specify the tunnel name here. This should match the tunnel configuration you've set up in Harness.
Once configured, click Apply to save the DB Query action. The result from this query will be stored in your specified result parameter (e.g., data), ready to be reused in upcoming steps.
Step 2: Use the Parameter in a Natural Language Task
Now comes the smart part.
You can feed that DATA parameter into a natural language action.
For instance:
Withdraw 20% ${DATA} from savings
Harness AIT interprets this statement and automatically performs the step with the actual value fetched and processed from your database creating an easy, context-aware automation flow.