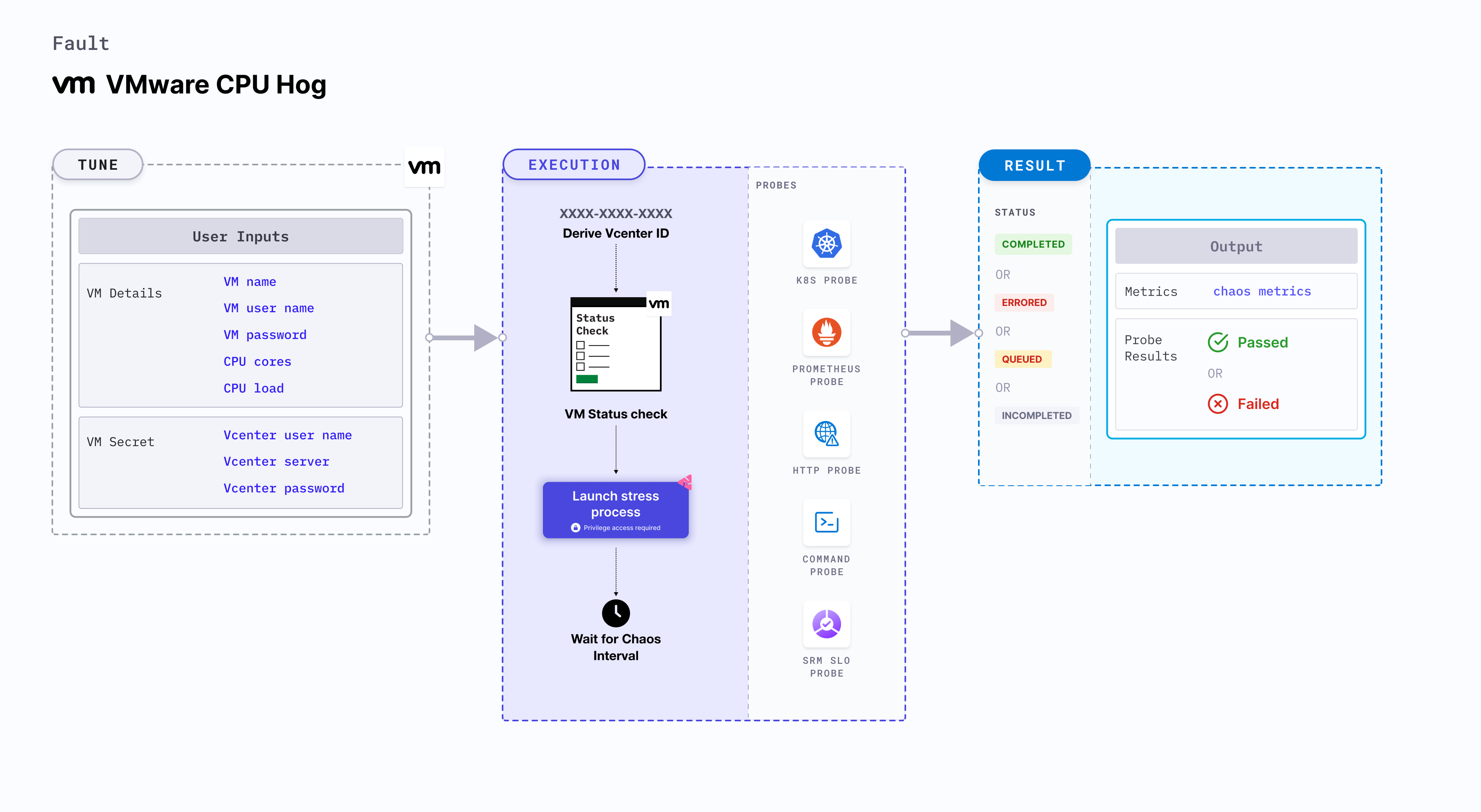
VMware CPU hog
VMware CPU hog applies stress on the CPU resources on Linux OS based VMware VM. It checks the performance of the application running on the VMware VMs.
HCE doesn't support injecting VMWare Windows faults on Bare metal server.
Use cases
- VMware CPU hog determines the resilience of an application when stress is applied on the CPU resources of a VMware virtual machine.
- VMware CPU hog simulates the situation of lack of CPU for processes running on the application, which degrades their performance.
- It also helps verify metrics-based horizontal pod autoscaling as well as vertical autoscale, that is, demand based CPU addition.
- It verifies the autopilot functionality of cloud managed clusters.
- It verifies multi-tenant load issues, that is, when the load on one container increases, it should not cause downtime in other containers.
Prerequisites
-
Kubernetes > 1.16 is required to execute this fault.
-
Execution plane should be connected to vCenter and host vCenter on port 443.
-
VMware tool should be installed on the target VM with remote execution enabled.
-
Adequate vCenter permissions should be provided to access the hosts and the VMs.
-
The VM should be in a healthy state before and after injecting chaos.
-
Run the fault with a user possessing admin rights, preferably the built-in Administrator, to guarantee permissions for memory stress testing. See how to enable the built-in Administrator in Windows.
-
Kubernetes secret has to be created that has the Vcenter credentials in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. VM credentials can be passed as secrets or as aChaosEngineenvironment variable. Below is a sample secret file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vcenter-secret
namespace: litmus
type: Opaque
stringData:
VCENTERSERVER: XXXXXXXXXXX
VCENTERUSER: XXXXXXXXXXXXX
VCENTERPASS: XXXXXXXXXXXXX
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VM_NAME | Name of the target VM. | For example, ubuntu-vm-1 |
| VM_USER_NAME | Username of the target VM. | For example, vm-user. |
| VM_PASSWORD | User password for the target VM. | For example, 1234. Note: You can take the password from secret as well. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CPU_CORES | Number of CPU cores subject to CPU stress. | Default to 1. For more information, go to CPU cores. |
| CPU_LOAD | Load exerted on each CPU core (in percentage). | Defaults to 100%. For more information, go to CPU load. |
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Defaults to 30s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | Time interval between two successive instance terminations (in seconds). | Defaults to 30s. For more information, go to chaos interval. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
| SEQUENCE | Sequence of chaos execution for multiple instances. | Defaults to parallel. Supports serial sequence as well. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution. |
| DEFAULT_HEALTH_CHECK | Determines if you wish to run the default health check which is present inside the fault. | Default: 'true'. For more information, go to default health check. |
CPU cores
It specifies the number of CPU cores of the target VM on which stress is applied. Tune it by using the CPU_CORE environment variable.
Use the following example to tune it:
# CPU hog in the VMware VM
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: VMware-cpu-hog
spec:
components:
env:
# Name of the VM
- name: VM_NAME
value: 'test-vm-01'
# CPU cores for stress
- name: CPU_CORES
value: '1'
CPU load
It specifies the load exerted on each VM CPU core (in percentage). Tune it by using the CPU_LOAD environment variable.
Use the following example to tune it:
# CPU hog in the VMware VM
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: VMware-cpu-hog
spec:
components:
env:
# Name of the VM
- name: VM_NAME
value: 'test-vm-01'
# CPU load in percentage for the stress
- name: CPU_LOAD
value: '100'