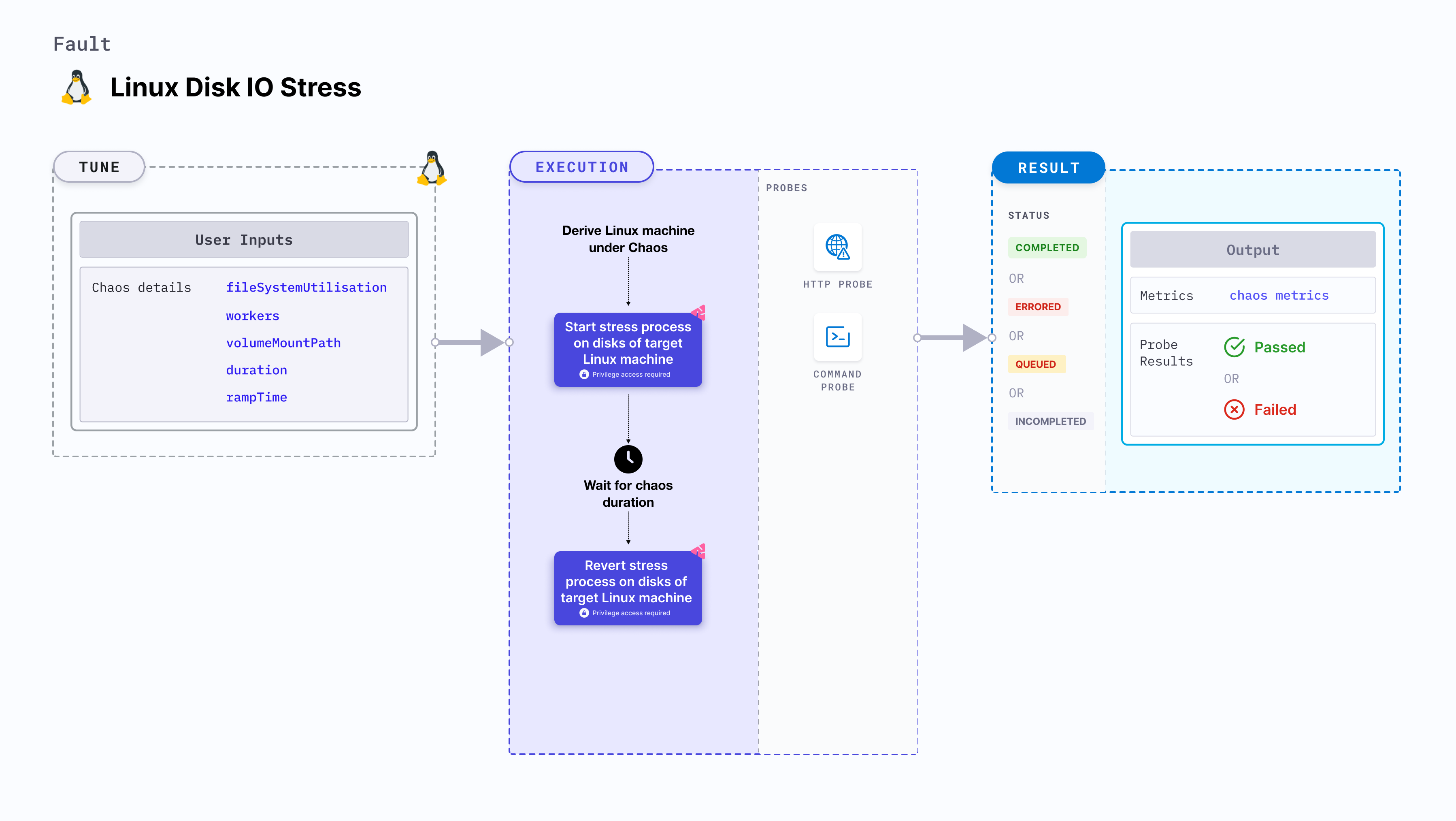
Linux disk IO stress
Linux disk IO stress applies stress on the disk of the target Linux machines over I/O operations for a specific duration.
It aims to consume the I/O bandwidth by performing frequent writes and reads to and from the disk, respectively. Consequently, the size of the file created for this operation changes frequently.
To understand the impact of the fault, check the available I/O bandwidth before and during chaos.
Use cases
- Simulates slower disk operations for the applications.
- Simulates noisy neighbour problems by exhausting the disk bandwidth.
- Verifies the disk performance on increasing I/O threads and varying I/O block sizes.
- Checks how the application functions under high disk latency conditions, when I/O traffic is high and includes large I/O blocks, and when other services monopolize the I/O disks.
- This fault can be executed on Ubuntu 16 or higher, Debian 10 or higher, CentOS 7 or higher, RHEL 7 or higher, Fedora 30 or higher, and openSUSE LEAP 15.4 or higher.
- The
linux-chaos-infrastructuresystemd service should be in an active state, and the infrastructure should be inCONNECTEDstate.
Fault permissions
The fault uses the root Linux user and root user group.
External packages
This fault uses stress-ng, which is installed as part of the infrastructure installation.
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| fileSystemUtilisation | File size consumed during the disk I/O operations. | Can be specified in bytes (b/B), kilobytes (k/K), megabytes (m/M), gigabytes (g/G), or percentage (%) of available storage. If no unit is provided, the value is assumed to be in bytes. Example values: 30m, 1G, 35%, etc. Default: 10%. |
| workers | Number of worker processes to start. | Default: 1 |
| volumeMountPath | Volume mount path used for the disk I/O operations. | Default: user HOME directory |
| duration | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 30s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
| rampTime | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 0s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
Workers
The workers input variable utilizes a specific number of workers during the disk I/O stress.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# workers to utilize
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-disk-io-stress
labels:
name: disk-io-stress
spec:
stressChaos/inputs:
workers: 1
fileSystemUtilisation: 10%
File system utilisation
The fileSystemUtilisation input variable utilizes a specific amount of file system disk space or bandwidth as a part of the disk I/O operations in bytes.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# file system amount to be utilized
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-disk-io-stress
labels:
name: disk-io-stress
spec:
stressChaos/inputs:
workers: 3
fileSystemUtilisation: 50g
Volume mount path
The volumeMountPath input variable utilizes the volume mount path where the disk I/O operations are performed.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# configure volume mount path
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-disk-io-stress
labels:
name: disk-io-stress
spec:
stressChaos/inputs:
workers: 1
fileSystemUtilisation: 50%
volumeMountPath: "/tmp"