Namespace considerations
This section discusses the steps required to run chaos experiments on specific namespaces.
Kubernetes clusters are vast, multi-layered, and customizable. A simple misconfiguration or vulnerability introduced by libraries poses a threat to the Kubernetes environment. These threats allow users with malicious intent to gather information about your environment without being detected, gain backdoor access to your application, or escalate privileges to steal secrets.
You can allow your chaos experiments to run in specific namespaces, thereby limiting the exposure of all the services (including business-critical and potentially sensitive workflows) of your application.
If your application fails, the above-mentioned technique also helps pin-point the exact cluster, namespace, and services in your Kubernetes environment that failed.
Step 1. Install CE in cluster mode
- Install CE in cluster mode with the given installation manifest.
- Restrict
hceservice account to certain target namespaces.
Step 2. Delete hce ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding
- Once CE is up and running in cluster mode, delete the
hceClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding to restrict the chaos scope in all namespaces.
$> kubectl delete clusterrole hce
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "hce" deleted
$> kubectl delete clusterrolebinding hce
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "hce" deleted
Step 3. Create Role and RoleBinding in all target namespaces
This allows specific namespaces for chaos operations. Create Role and RoleBinding in these specific namespaces (say namespaceA and namespaceB).
The manifest for role-1.yaml in namespaceA will look as shown below.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: namespaceA-chaos
namespace: litmus
labels:
name: namespaceA-chaos
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: litmus
rules:
# Create and monitor the experiment & helper pods
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update", "deletecollection"]
# Performs CRUD operations on the events inside chaos engine and chaos result
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create","get","list","patch","update"]
# Fetch configmaps details and mount it to the experiment pod (if specified)
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get","list",]
# Track and get the runner, experiment, and helper pods log
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get","list","watch"]
# for creating and monitoring liveness services or monitoring target app services during chaos injection
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list"]
# for creating and managing to execute commands inside target container
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec", "pods/eviction", "replicationcontrollers"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "create"]
# for checking the app parent resources as deployments or sts and are eligible chaos candidates
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments", "statefulsets"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "patch", "update"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is deploymentConfig)
- apiGroups: ["apps.openshift.io"]
resources: ["deploymentconfigs"]
verbs: ["list","get"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is deploymentConfig)
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["replicationcontrollers"]
verbs: ["get","list"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is argo-rollouts)
- apiGroups: ["argoproj.io"]
resources: ["rollouts"]
verbs: ["list","get"]
# for configuring and monitor the experiment job by the chaos-runner pod
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create","list","get","delete","deletecollection"]
# for creation, status polling and deletion of litmus chaos resources used within a chaos workflow
- apiGroups: ["litmuschaos.io"]
resources: ["chaosengines","chaosexperiments","chaosresults"]
verbs: ["create","list","get","patch","update","delete"]
# for checking the app parent resources as replicasets and are eligible chaos candidates
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["replicasets"]
verbs: ["list", "get"]
# performs CRUD operations on the network policies
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["networkpolicies"]
verbs: ["create","delete","list","get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: namespaceA-chaos
namespace: litmus
labels:
name: namespaceA-chaos
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: litmus
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: namespaceA-chaos
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: litmus-admin
namespace: litmus
The manifest for role-2.yaml in namespaceB will look as shown below.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: namespaceB-chaos
namespace: namespaceB
labels:
name: namespaceB-chaos
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: litmus
rules:
# Create and monitor the experiment & helper pods
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create","delete","get","list","patch","update", "deletecollection"]
# Performs CRUD operations on the events inside chaos engine and chaos result
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create","get","list","patch","update"]
# Fetch configmaps details and mount it to the experiment pod (if specified)
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["get","list",]
# Track and get the runner, experiment, and helper pods log
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get","list","watch"]
# for creating and monitoring liveness services or monitoring target app services during chaos injection
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list"]
# for creating and managing to execute commands inside target container
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec", "pods/eviction", "replicationcontrollers"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "create"]
# for checking the app parent resources as deployments or sts and are eligible chaos candidates
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments", "statefulsets"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "patch", "update"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is deploymentConfig)
- apiGroups: ["apps.openshift.io"]
resources: ["deploymentconfigs"]
verbs: ["list","get"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is deploymentConfig)
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["replicationcontrollers"]
verbs: ["get","list"]
# deriving the parent/owner details of the pod(if parent is argo-rollouts)
- apiGroups: ["argoproj.io"]
resources: ["rollouts"]
verbs: ["list","get"]
# for configuring and monitor the experiment job by the chaos-runner pod
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create","list","get","delete","deletecollection"]
# for creation, status polling and deletion of litmus chaos resources used within a chaos workflow
- apiGroups: ["litmuschaos.io"]
resources: ["chaosengines","chaosexperiments","chaosresults"]
verbs: ["create","list","get","patch","update","delete"]
# for checking the app parent resources as replicasets and are eligible chaos candidates
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["replicasets"]
verbs: ["list", "get"]
# performs CRUD operations on the network policies
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["networkpolicies"]
verbs: ["create","delete","list","get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: namespaceB-chaos
namespace: namespaceB
labels:
name: namespaceB-chaos
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: litmus
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: namespaceB-chaos
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: litmus-admin
namespace: litmus
The rolebinding subjects point to the hce service account only (in HCE namespace).
Create the roles
$> kubectl apply -f role-1.yaml
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/namespaceA-chaos created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/namespaceA-chaos created
$> kubectl apply -f role-2.yaml
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/namespaceB-chaos created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/namespaceB-chaos created
Step 4. Create Role and RoleBinding in all target namespaces
Create a Role and RoleBinding in the chaos namespace as well. This will be used by chaos runner pod to launch experiment.
Step 5. Verify the chaos execution on different namespaces
Run an experiment, say pod-delete in both the namespaces to verify if these namespaces have the permission to run experiments.
For namespaceA:
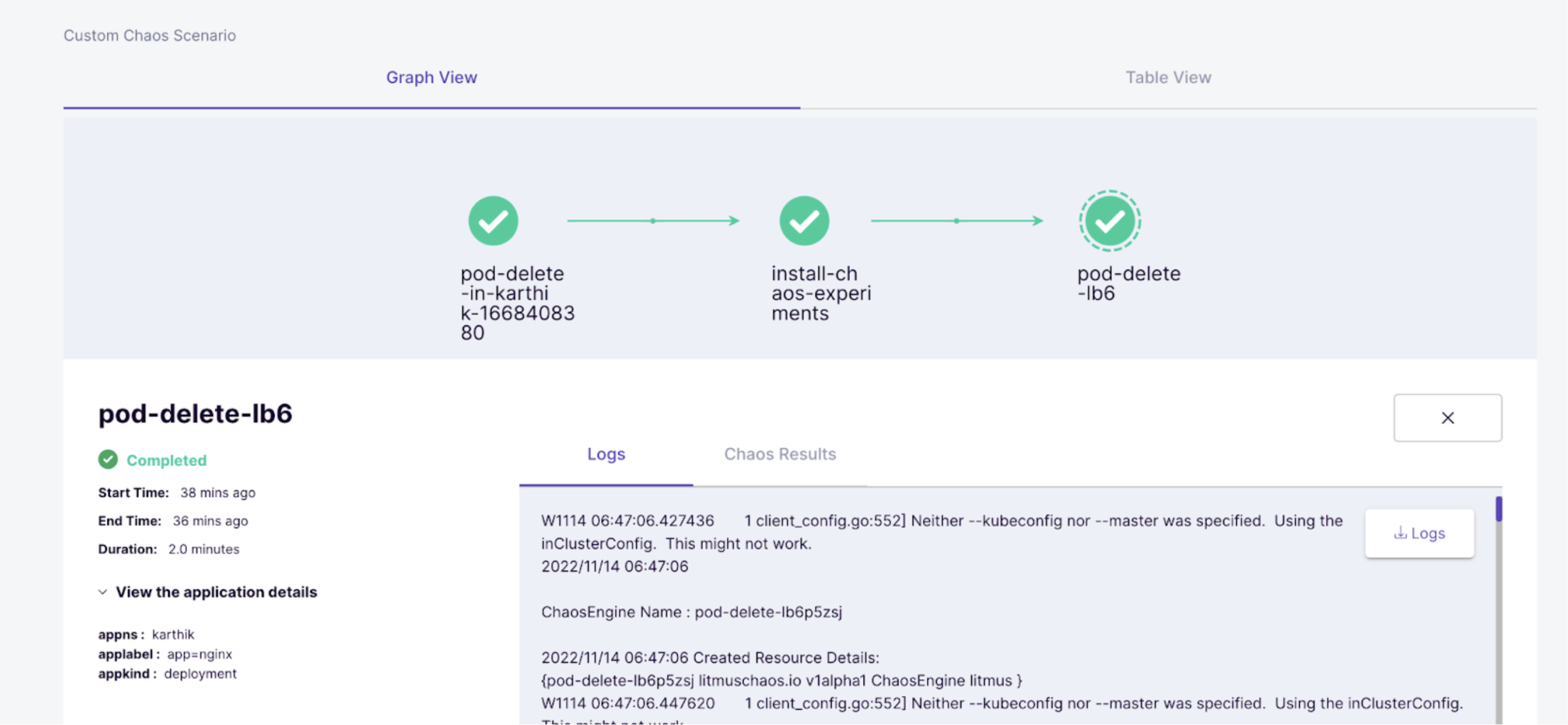
For namespaceA:
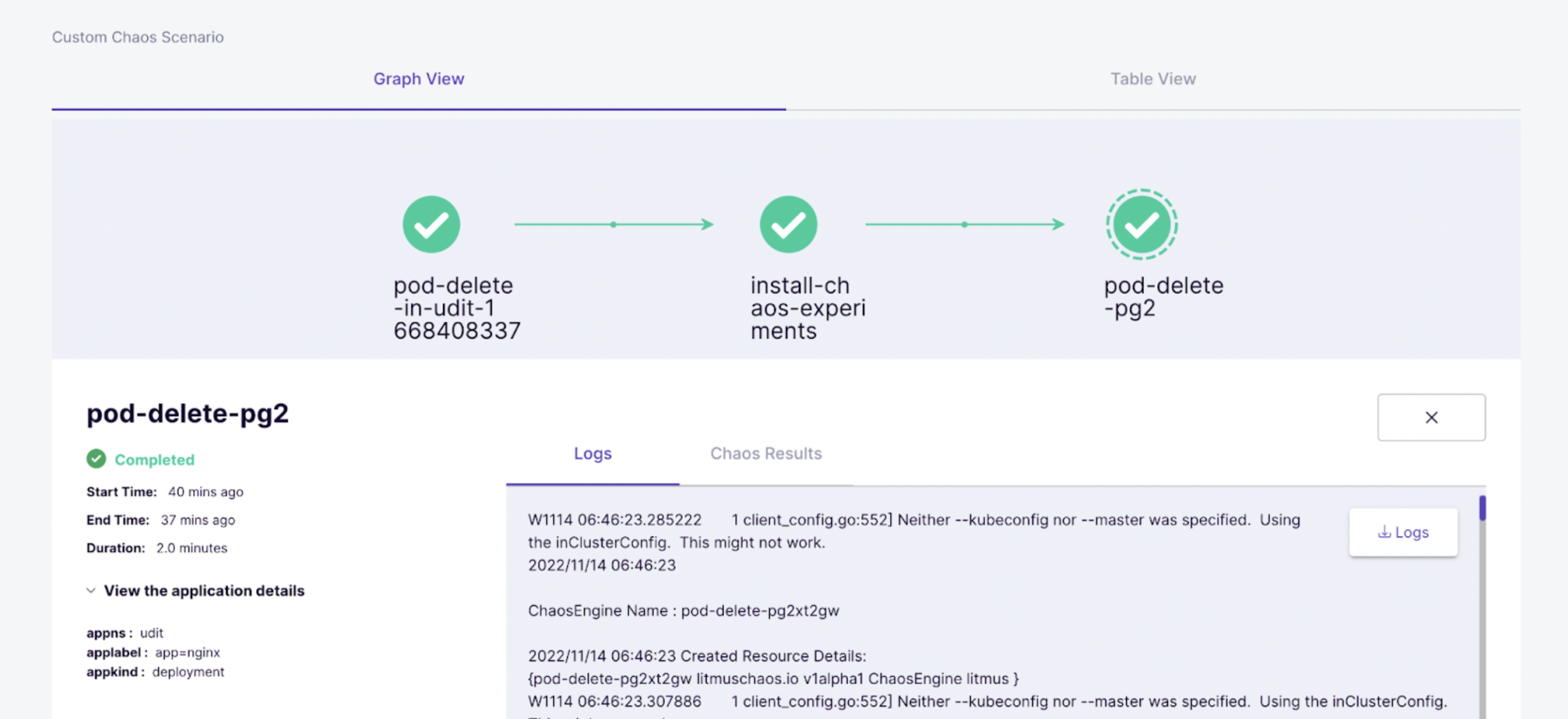
You are able to run chaos on the target namespaces (namespaceA and namespaceB). Now, you can check to see if namespace test can be used to run chaos experiments.
For test namespace:
The experiment fails to run and experiment pod logs.
time="2022-11-14T06:47:47Z" level=info msg="Experiment Name: pod-delete"
time="2022-11-14T06:47:47Z" level=info msg="[PreReq]: Getting the ENV for the pod-delete experiment"
time="2022-11-14T06:47:49Z" level=info msg="[PreReq]: Updating the chaos result of pod-delete experiment (SOT)"
time="2022-11-14T06:47:51Z" level=info msg="The application information is as follows" Namespace=test Label="app=nginx" Chaos Duration=30
time="2022-11-14T06:47:51Z" level=info msg="[Status]: Verify that the AUT (Application Under Test) is running (pre-chaos)"
time="2022-11-14T06:47:51Z" level=info msg="[Status]: Checking whether application containers are in ready state"
time="2022-11-14T06:50:53Z" level=error msg="Application status check failed, err: Unable to find the pods with matching labels, err: pods is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:litmus:litmus-admin\" cannot list resource \"pods\" in API group \"\" in the namespace \"test\""
You have successfully restricted CE to run chaos on certain namespaces instead of all namespaces. kubectl delete clusterrole hce