GameDay
This section describes what a GameDay is, why it is essential, how a typical GameDay is run, and its outcomes.
What is a GameDay?
GameDay is a methodology used by teams to practice chaos engineering. These teams execute chaos experiments on the application during a specific period. It is a template to schedule and execute one or more chaos experiments across your applications. It determines the incident response process, that is, how well your application responds/behaves during an outage, and how quickly and effectively it returns to normalcy.
Why is a GameDay important?
In general, GameDays helps apply a fatal scenario to your application in a safe environment, thereby determining the application's resilience and verifying the system at scale.
At every step in implementing a GameDay, you will either find a glitch in the system that you can address or gain confidence in your application.
Steps in a GameDay
A GameDay typically involves the following steps:
- Run chaos experiments on your application,
- Observe the impact of the failure,
- Discuss the technical outcomes.
This video provides a step-by-step walkthrough of GameDay execution.
GameDays help decide the type of failure the system would undergo based on the nature of the chaos experiments present within GameDay. Hence, HCE strongly recommends you begin with easy use cases with minimal blast radius, such as breaking one container, degrading one instance, and making one availability zone unavailable. Later, you can delve into more complex failures, such as failing an entire service or affecting a large percentage of requests.
How to execute a GameDay?
Running a GameDay using HCE's GameDay feature involves the following steps:
- Plan your GameDay
- Create a GameDay and specify the details
- Add experiments to the GameDay and save it
- Schedule or run the GameDay
- Record the conclusion and action items
Once you create a GameDay in HCE, you can run it multiple times. HCE saves information about every run, which includes the date, summary, and any notes you add.
Prerequisites to execute a GameDay
- HCE account
- Access to a cluster
- Appropriate permissions to execute a GameDay
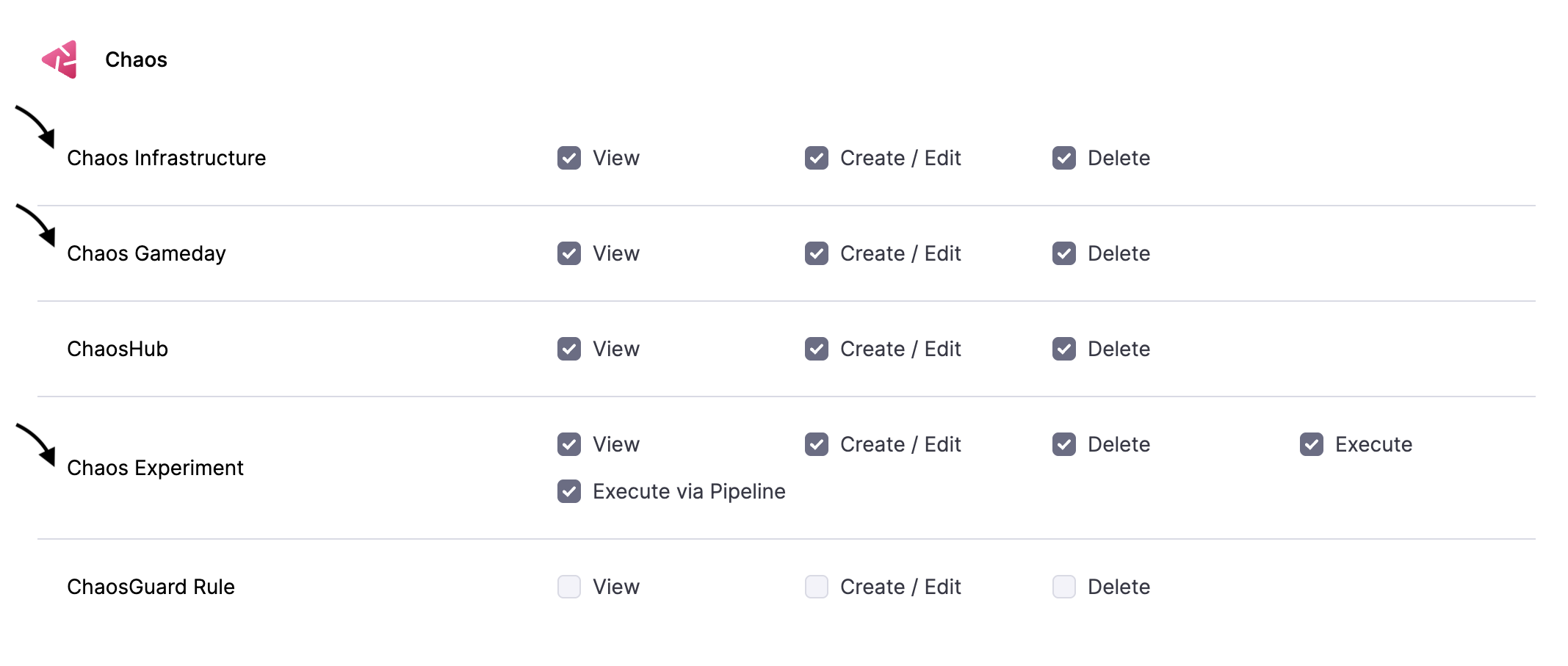
Permissions required
ChaosHubs are associated with chaos experiments, hence you need permissions to create new experiments and modify exisiting experiments. Chaos experiments, in turn, are executed in a chaos infrastructure, hence you need to have access to create/edit and view the chaos infrastructure. Go to Project Settings -> Access Control -> Roles and create a new role or ask your project admin to create an appropriate role.
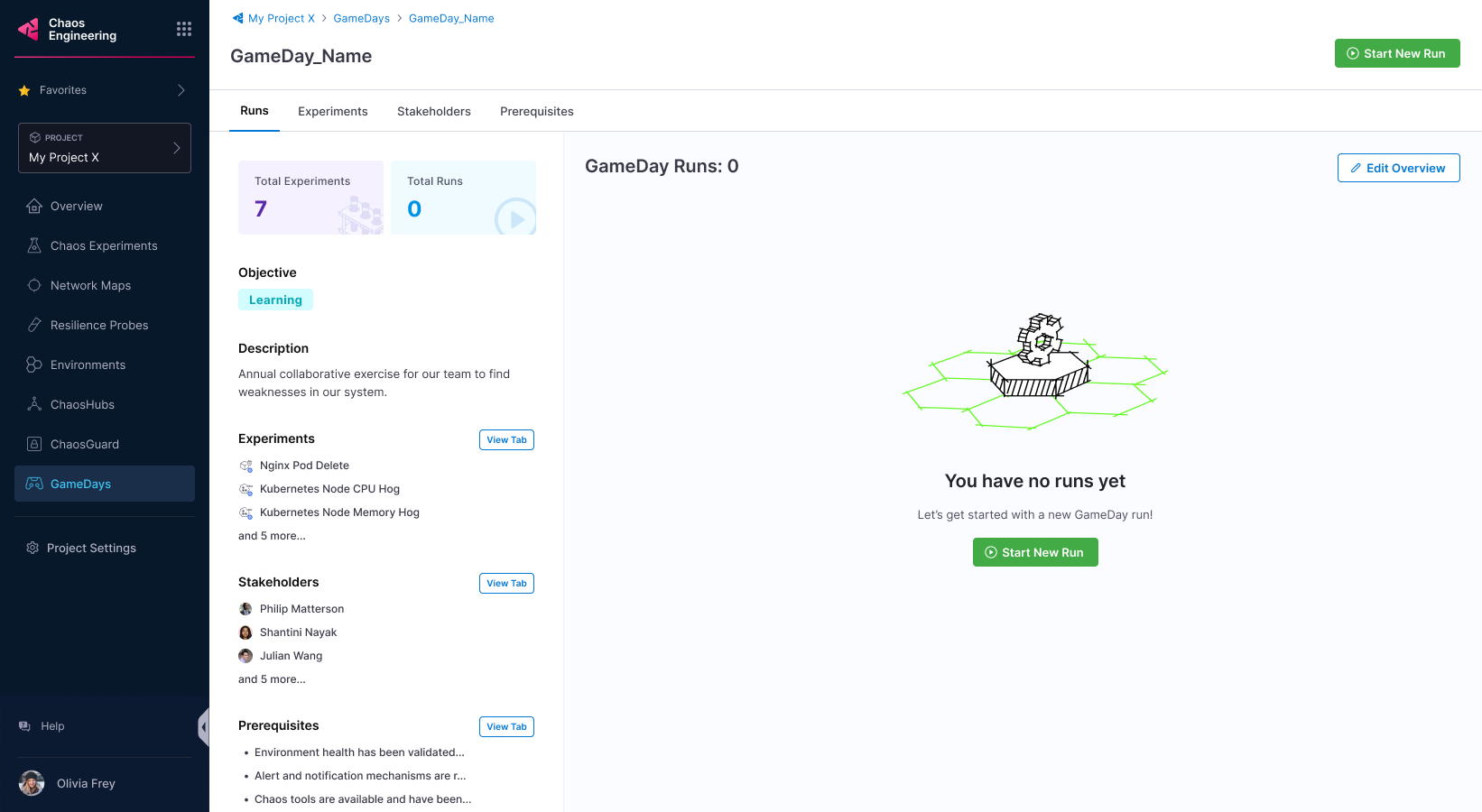
Plan your GameDay
Address the following questions before proceeding to run a GameDay:
- Which services should I test?
- What is the goal of the GameDay?
- What should I verify or determine by the end of the GameDay?
Once these questions have a viable answer, you can proceed to create a GameDay.
Creating a GameDay involves two steps:
- Specifying details about the GameDay,
- Adding chaos experiments to the GameDay.
Start a GameDay run
If you have created your GameDay earlier, select Start New Run to run the GameDay; otherwise, create a GameDay.
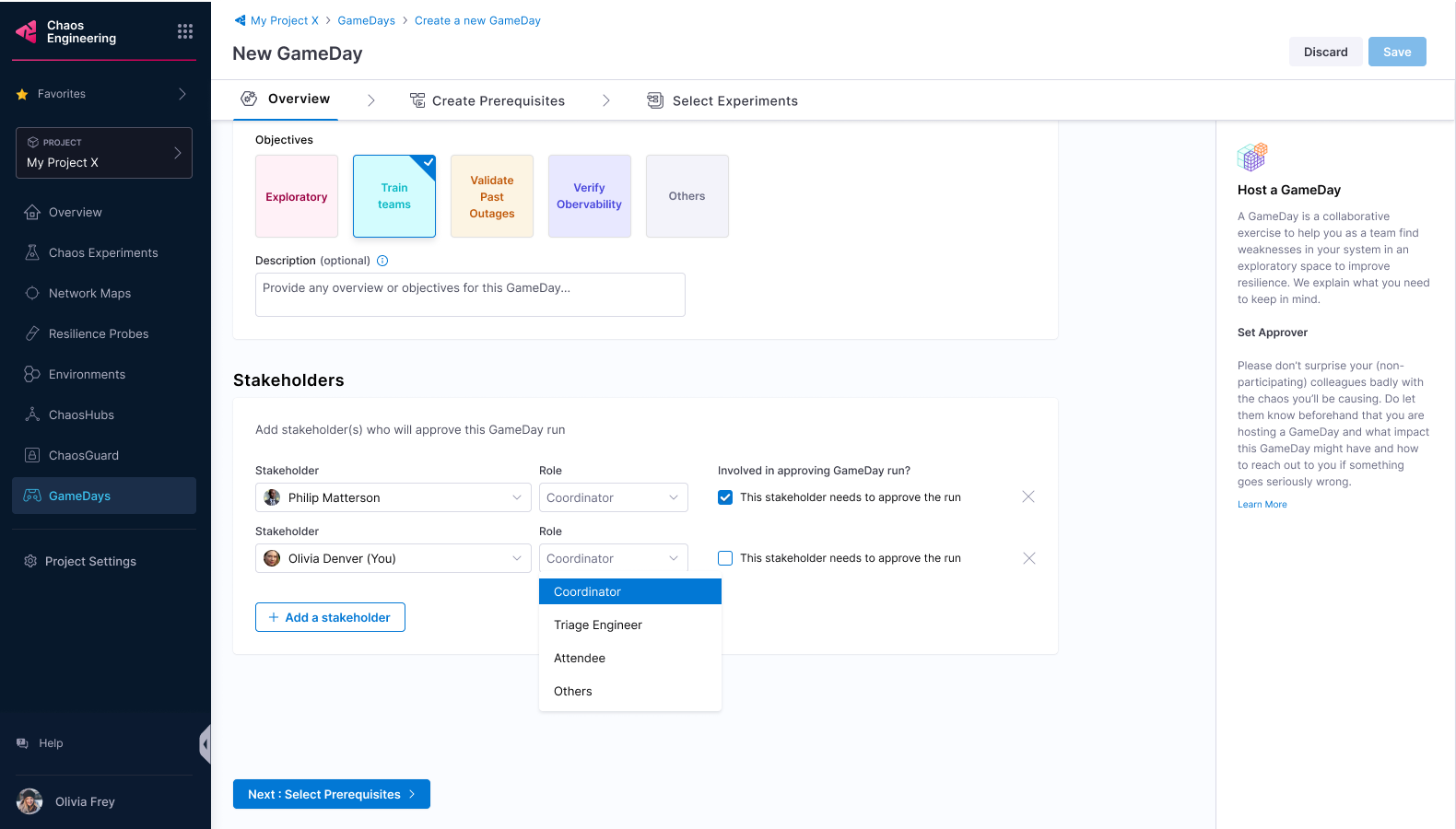
Create a GameDay
-
Go to Chaos module, select GameDay and click +New GameDay.
-
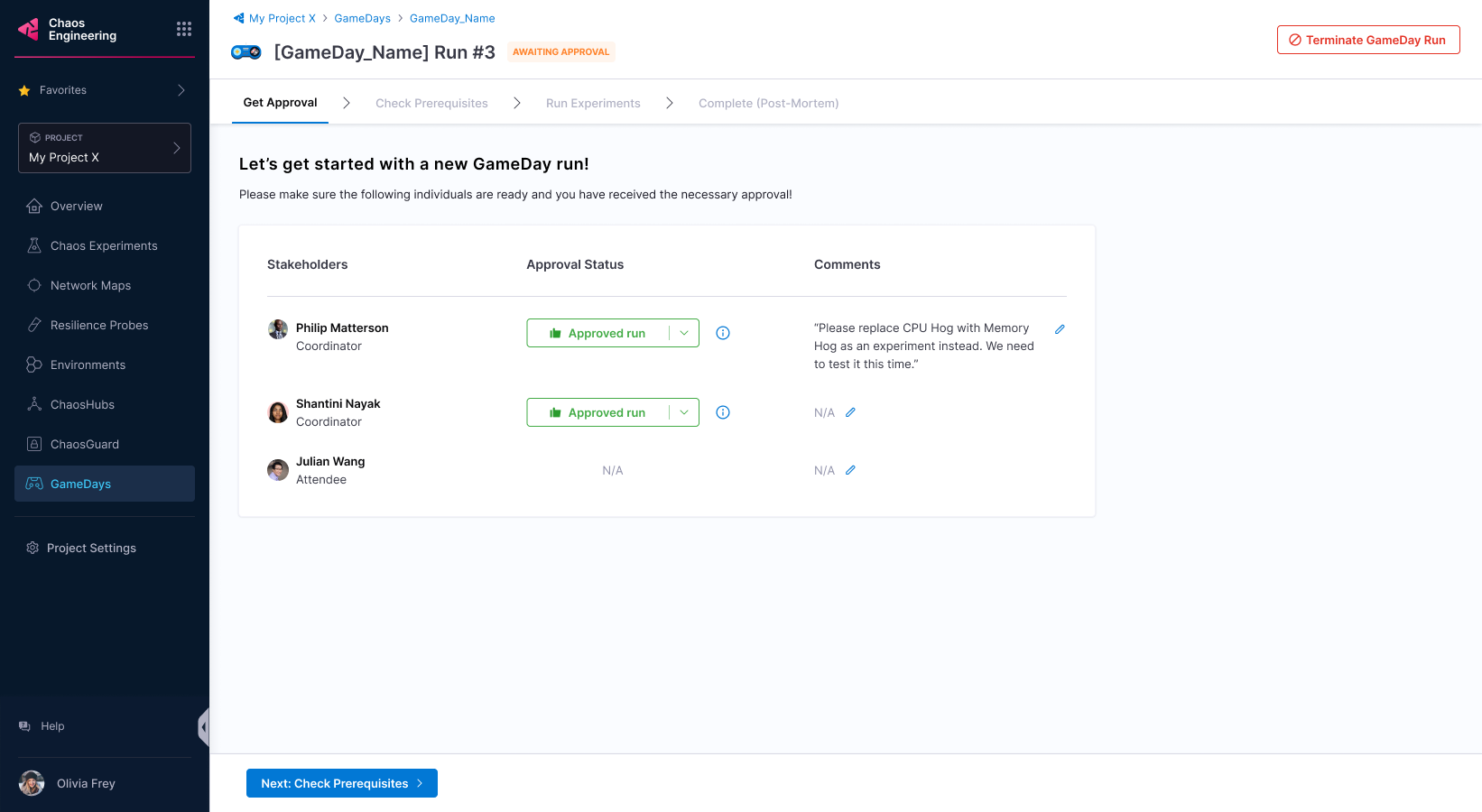
Add stakeholder names, their roles, and whether they are required to approve a GameDay run. Anyone can approve or reject a GameDay run. Select Next: Select Prerequisites.
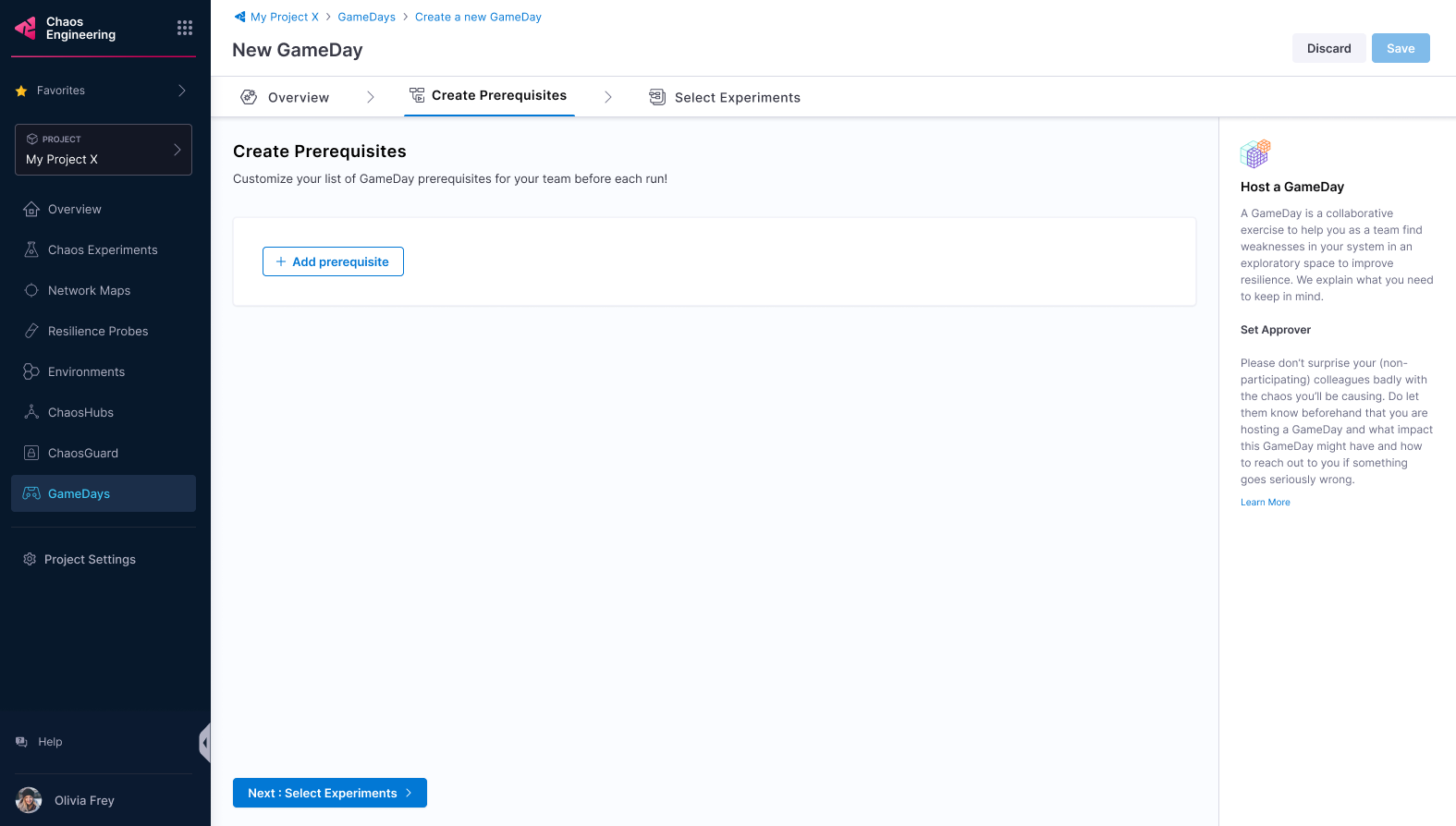
You can create prerequisites for your GameDay to:
- Validate environment health.
- Check the availability of relevant chaos tools.
- Check if the chaos tools are configured with the right chaos artefact sources.
- Check the availability of the team members.
-
Select + Add prerequisite. Enter a title and a description (optional). Select Save.
-
Select Next: Select Experiments to select chaos experiments to execute.

-
Select an environment, an infrastructure type, an infrastructure, and a ChaosHub. Select the chaos experiment and select Add Experiment to GameDay.
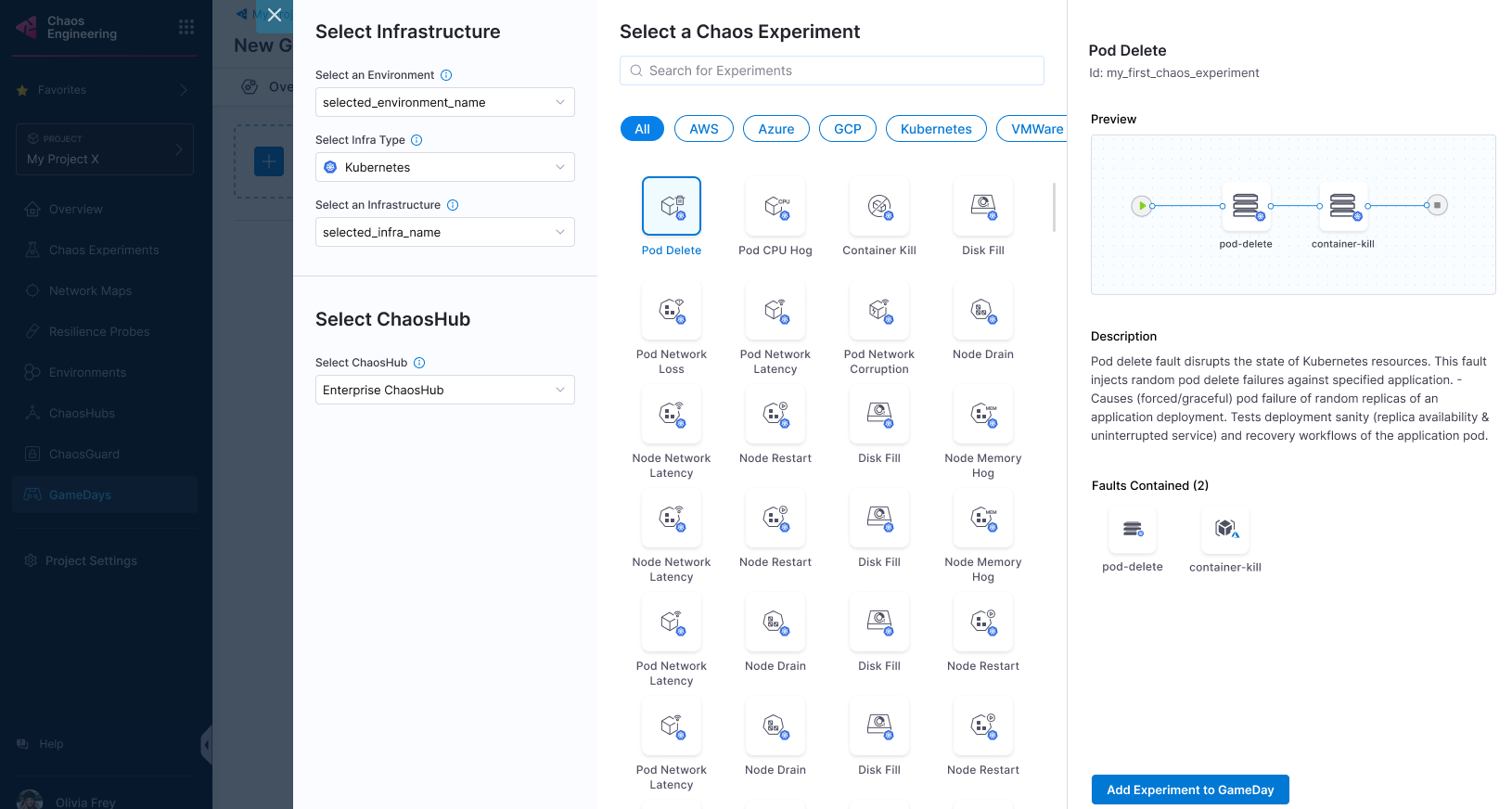
-
Select Save (or Discard if you don't want to proceed). You can add a new experiment, edit or delete existing experiments in this step.
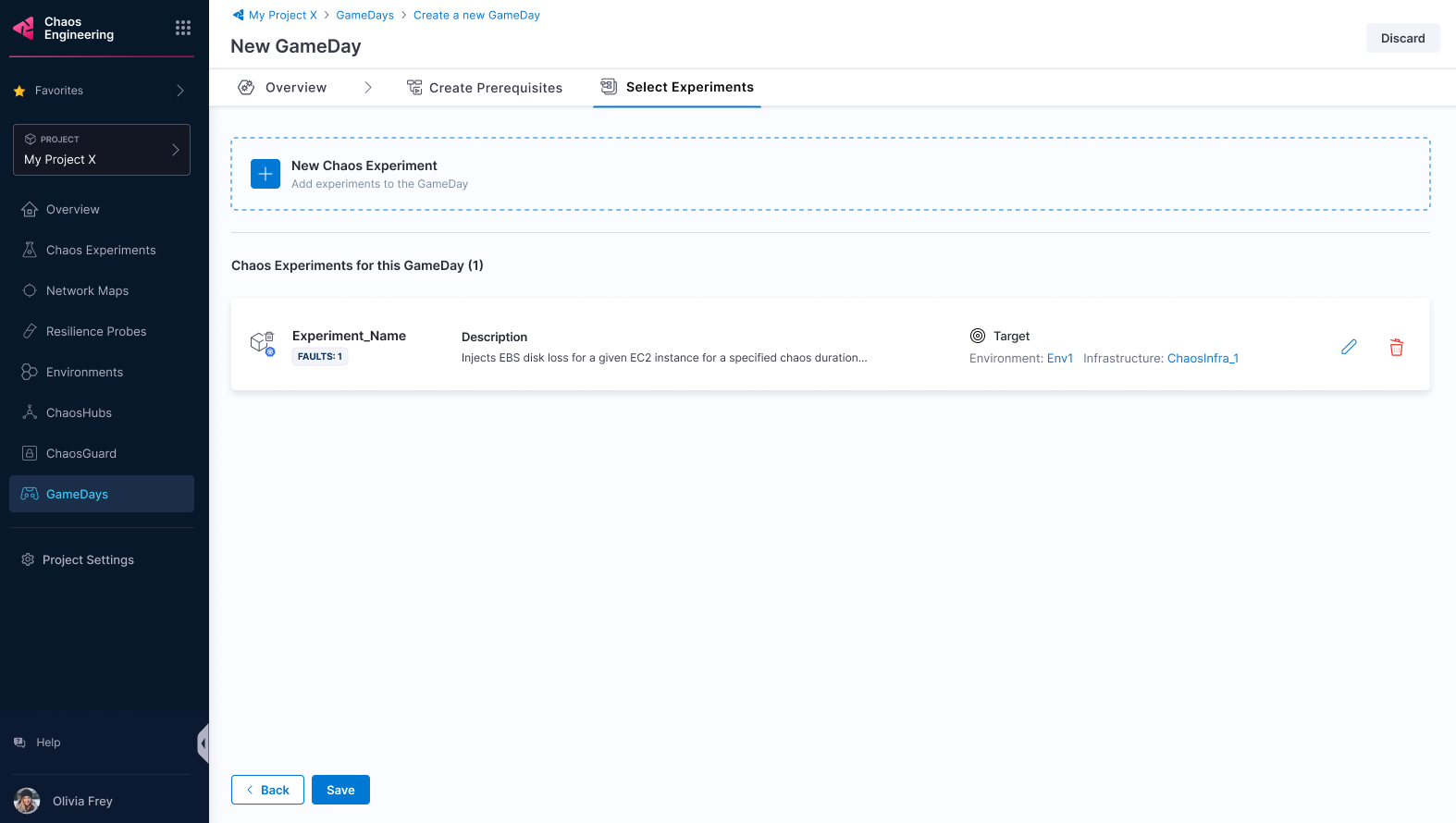
-
Once the stakeholders approve the GameDay run, you can proceed.
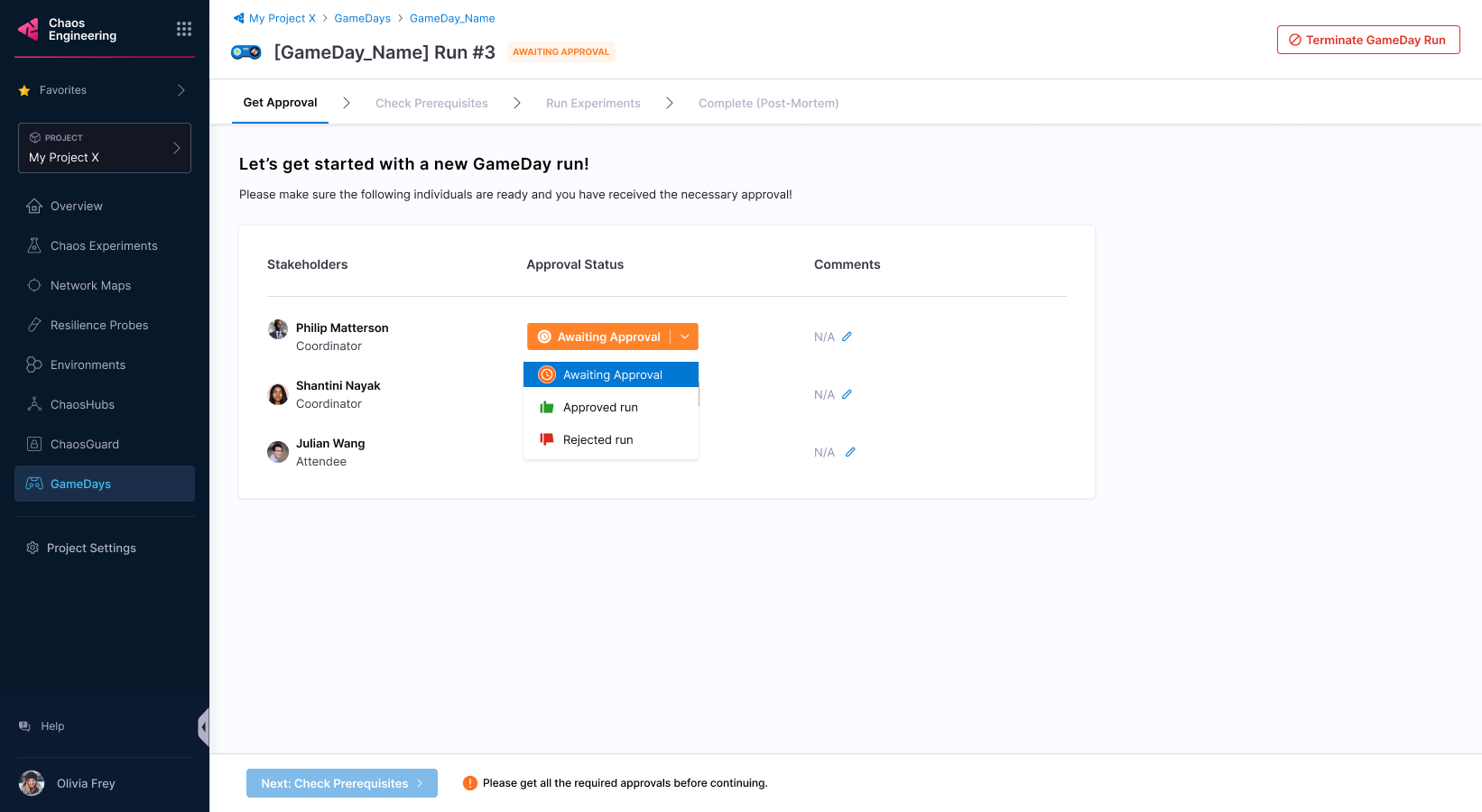
-
A stakeholder can reject the run and state reasons in the comments.
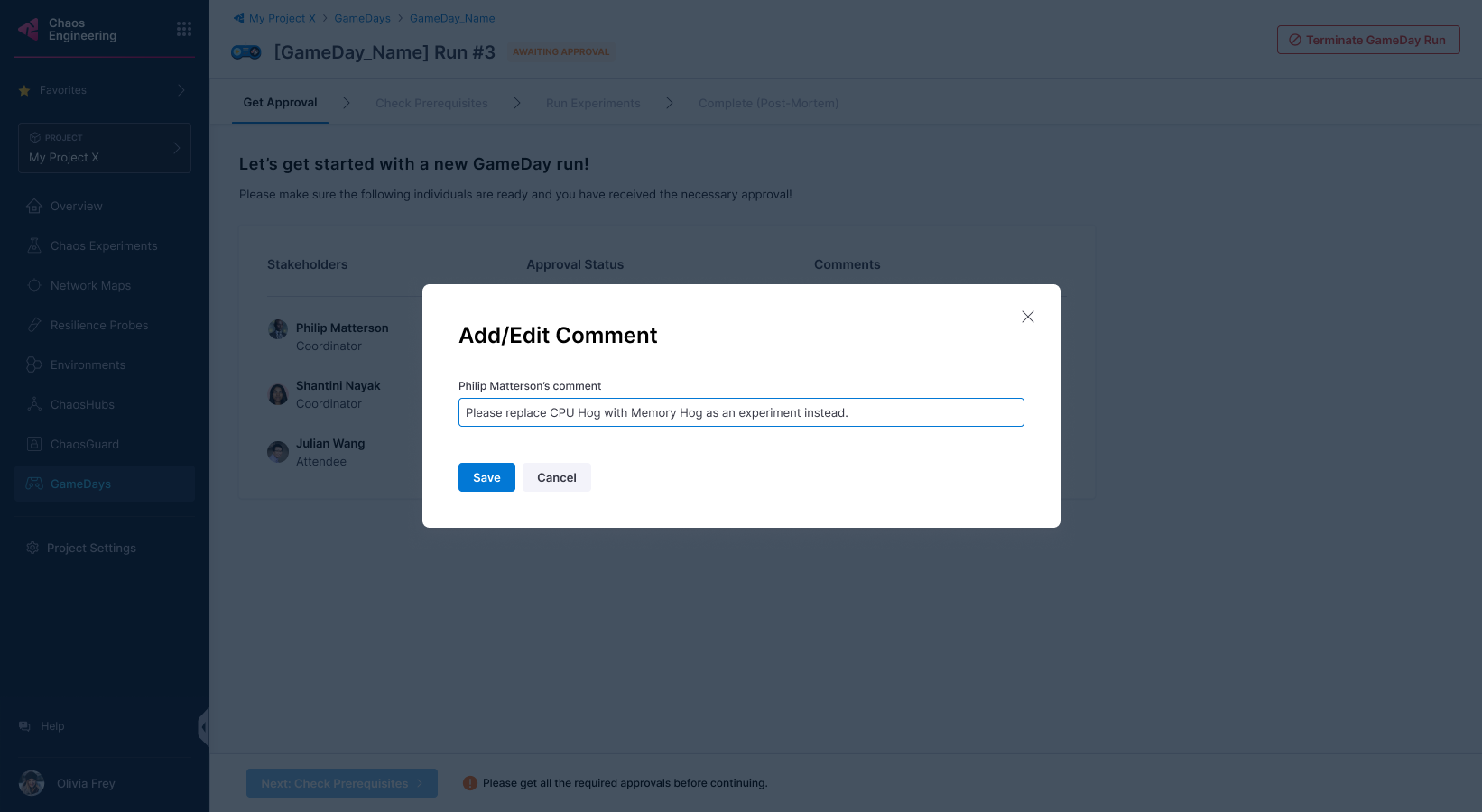
-
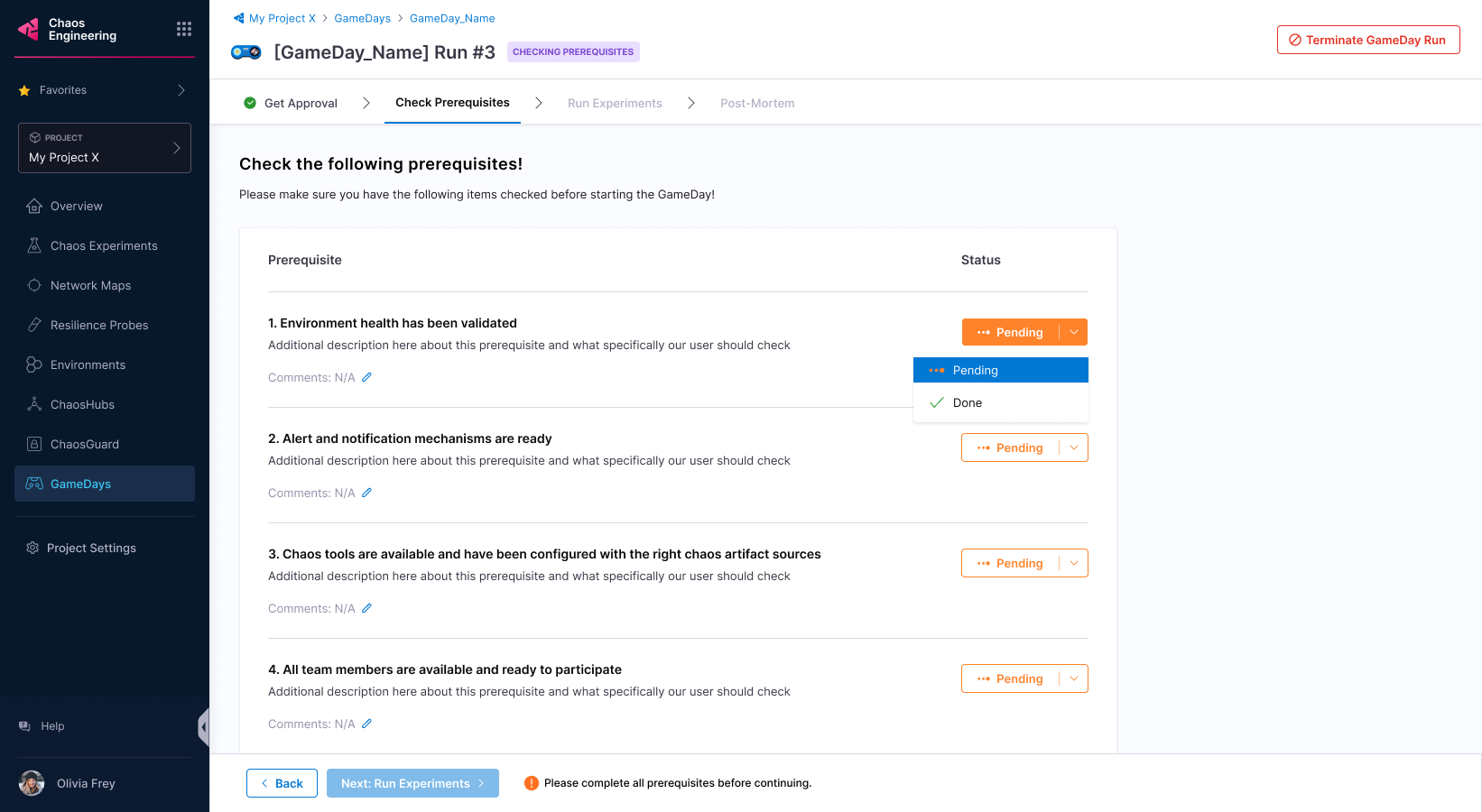
Select Next: Check prerequisites to validate whether the prerequisites you mentioned earlier have been fulfilled.
-
You can verify if the prerequisites are fulfilled, and check them. If one of them is not fulfilled, you will not be able to execute the experiments.
-
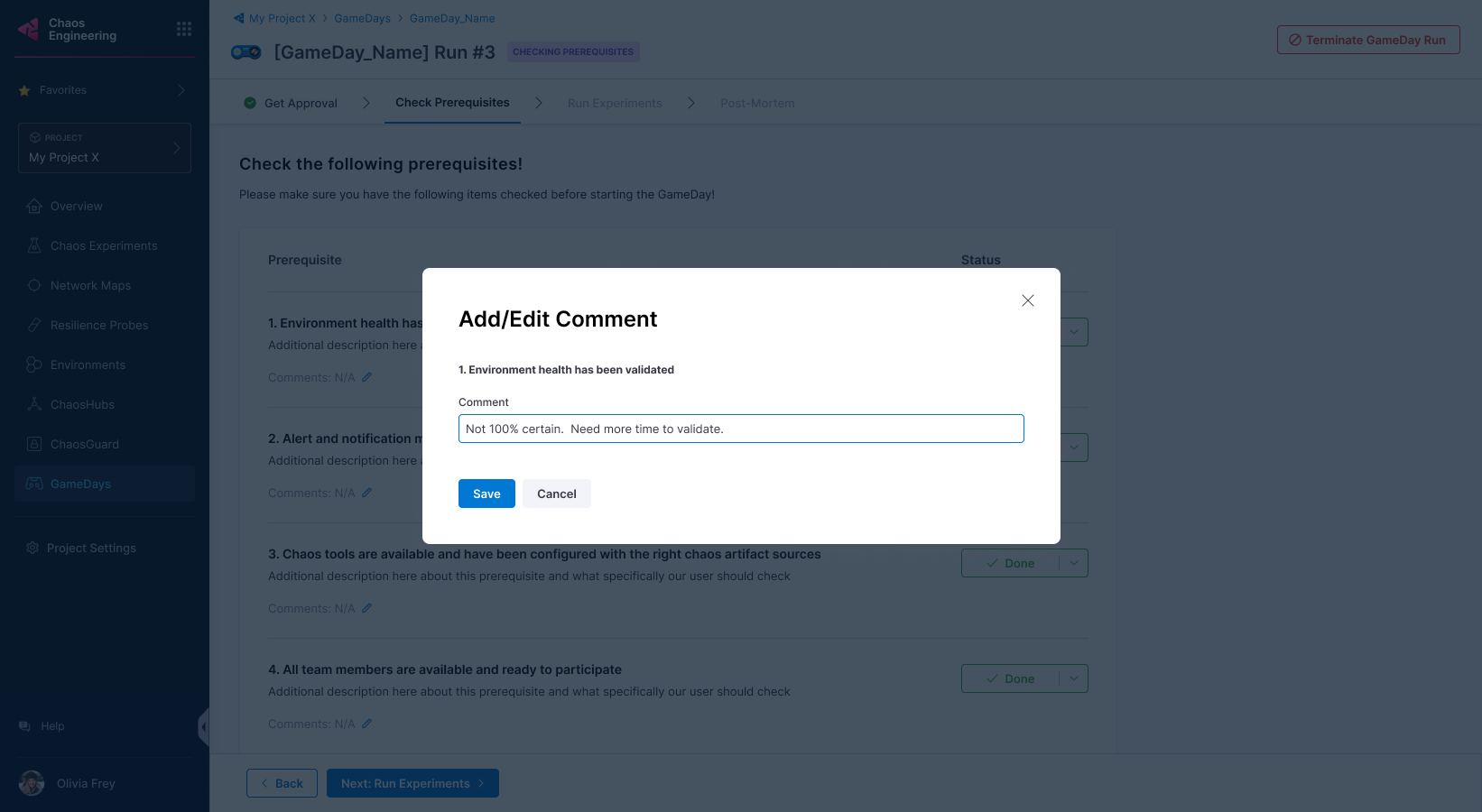
You can add comments about the prerequisite validation.
-
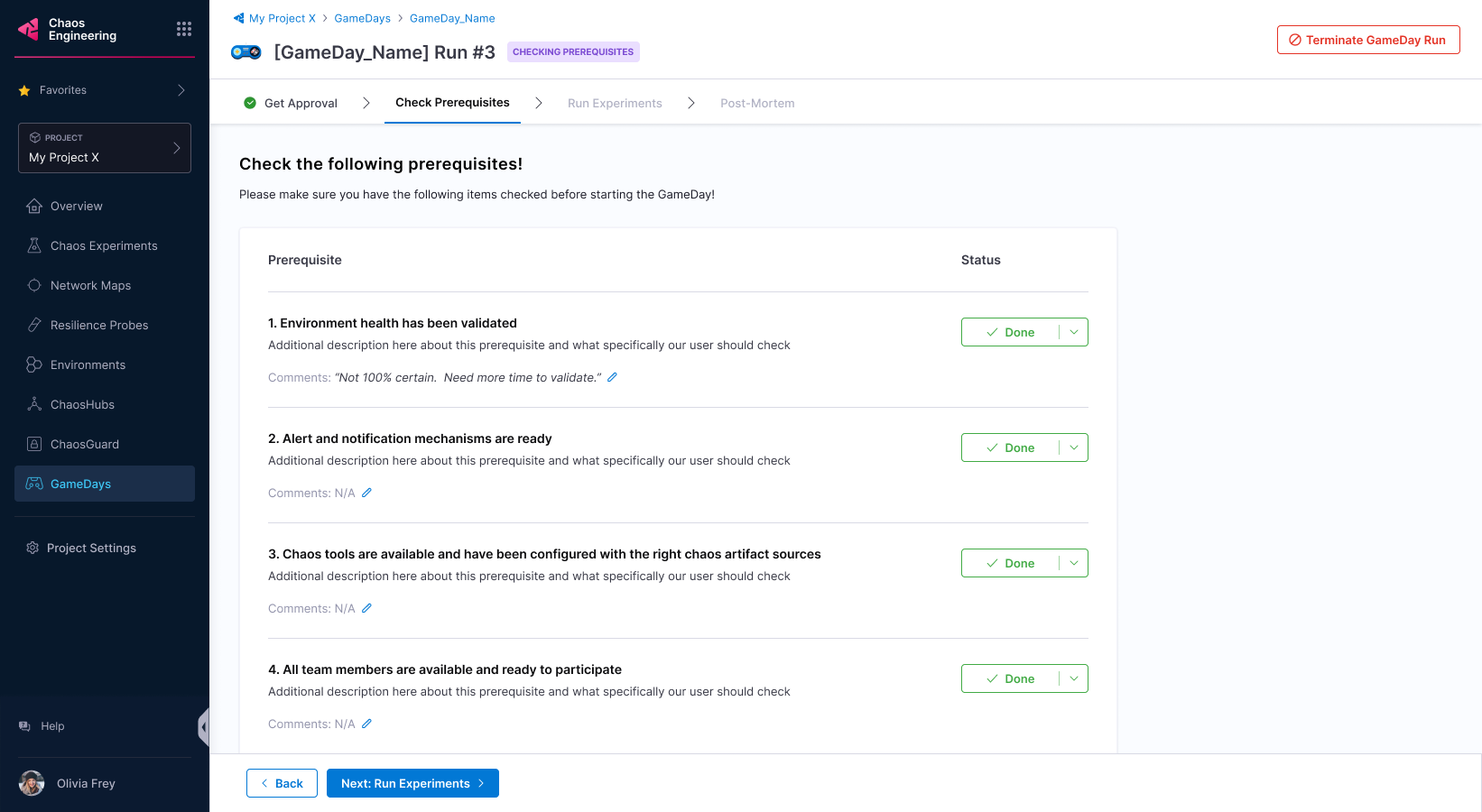
Once all the prerequisites are fulfilled, select Next: Run experiments.
-
Once all the experiments complete execution, select Done Running Experiments.

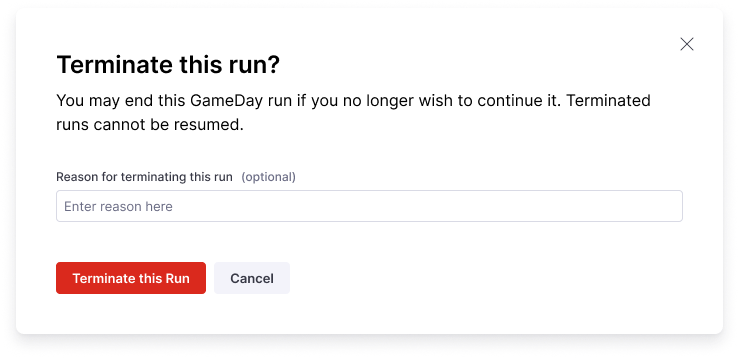
- Select Terminate GameDay Run to stop GameDay execution. Select Terminate this run to confirm.
- Select Add/View Notes to note your findings about experiments in the GameDay.
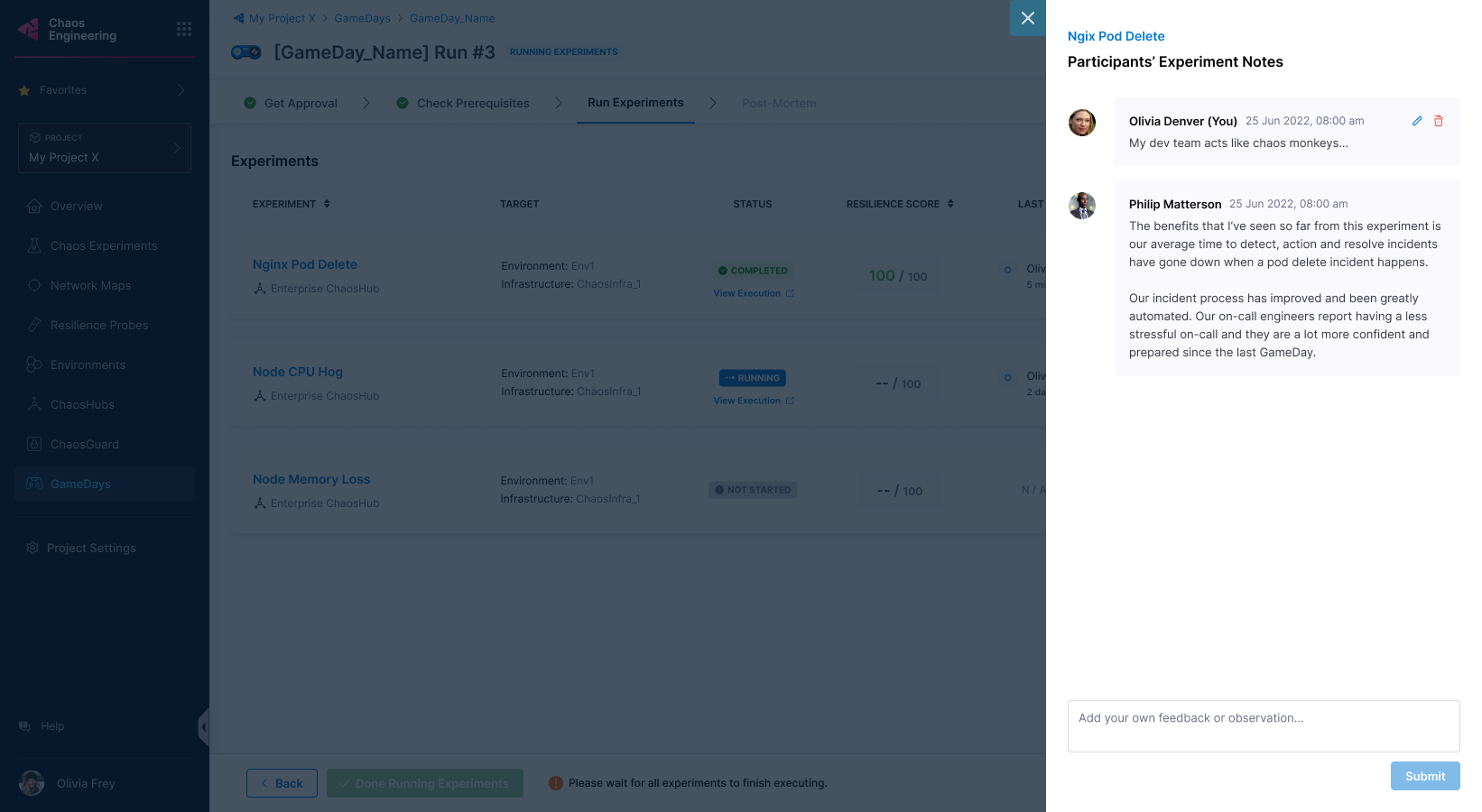
-
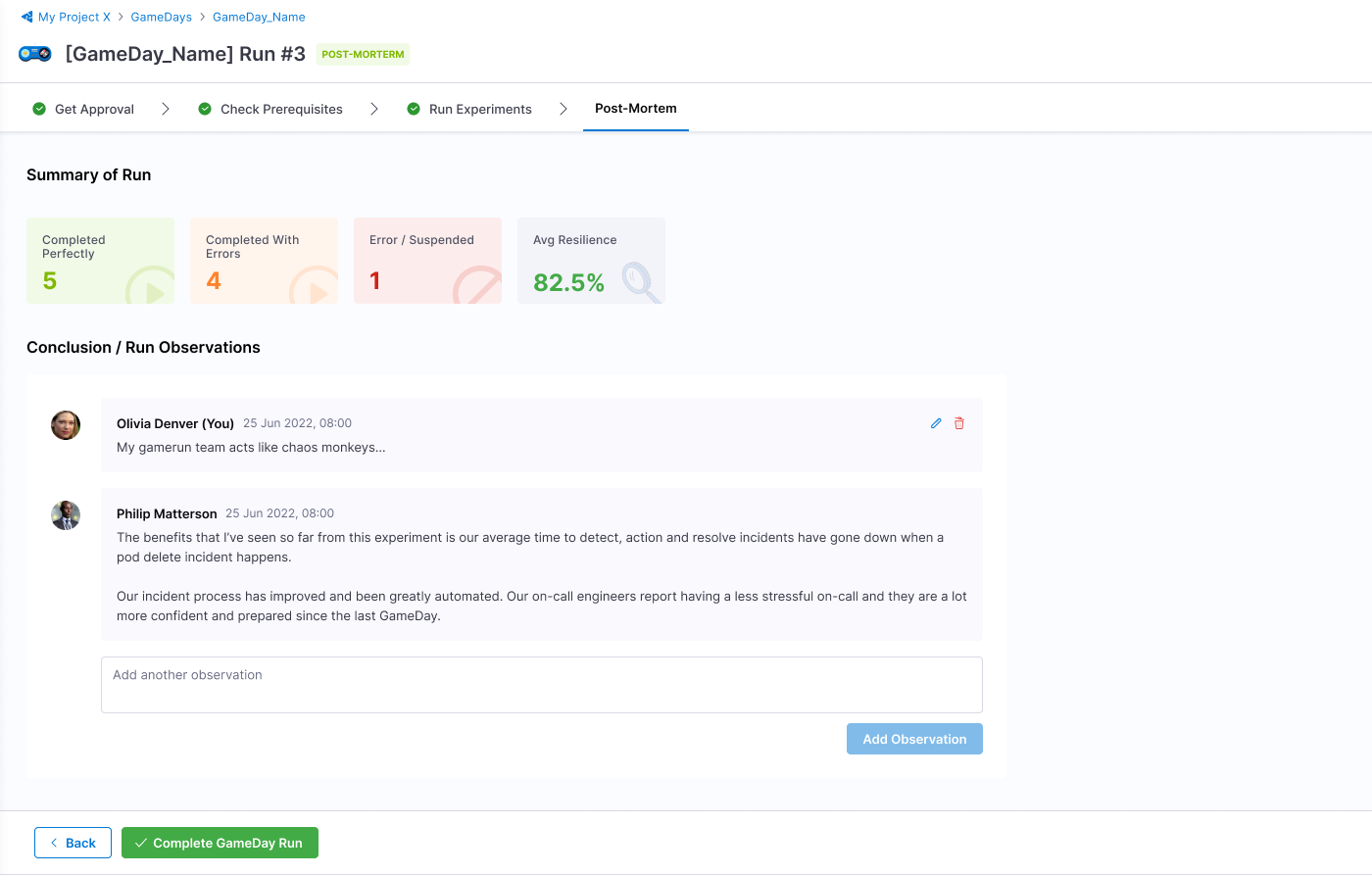
Once the experiments complete execution, select Complete GameDay Run. You can view the summary of the runs and the run observations.
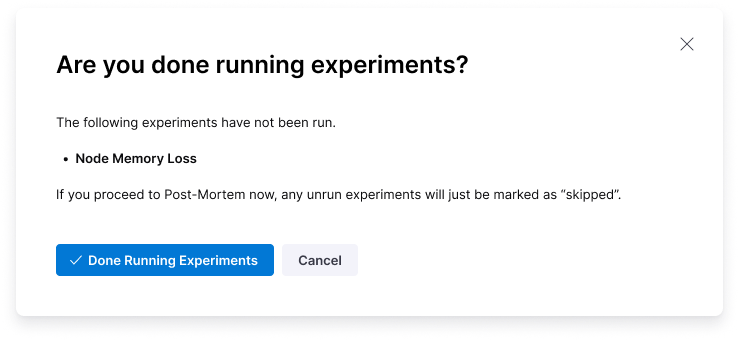
- Select Done Running Experiments to complete the run. If your chaos experiments have faults that have not run, they will be marked Skipped.
View GameDay run report
To view the GameDay run report, navigate to your GameDay run and select View Report.
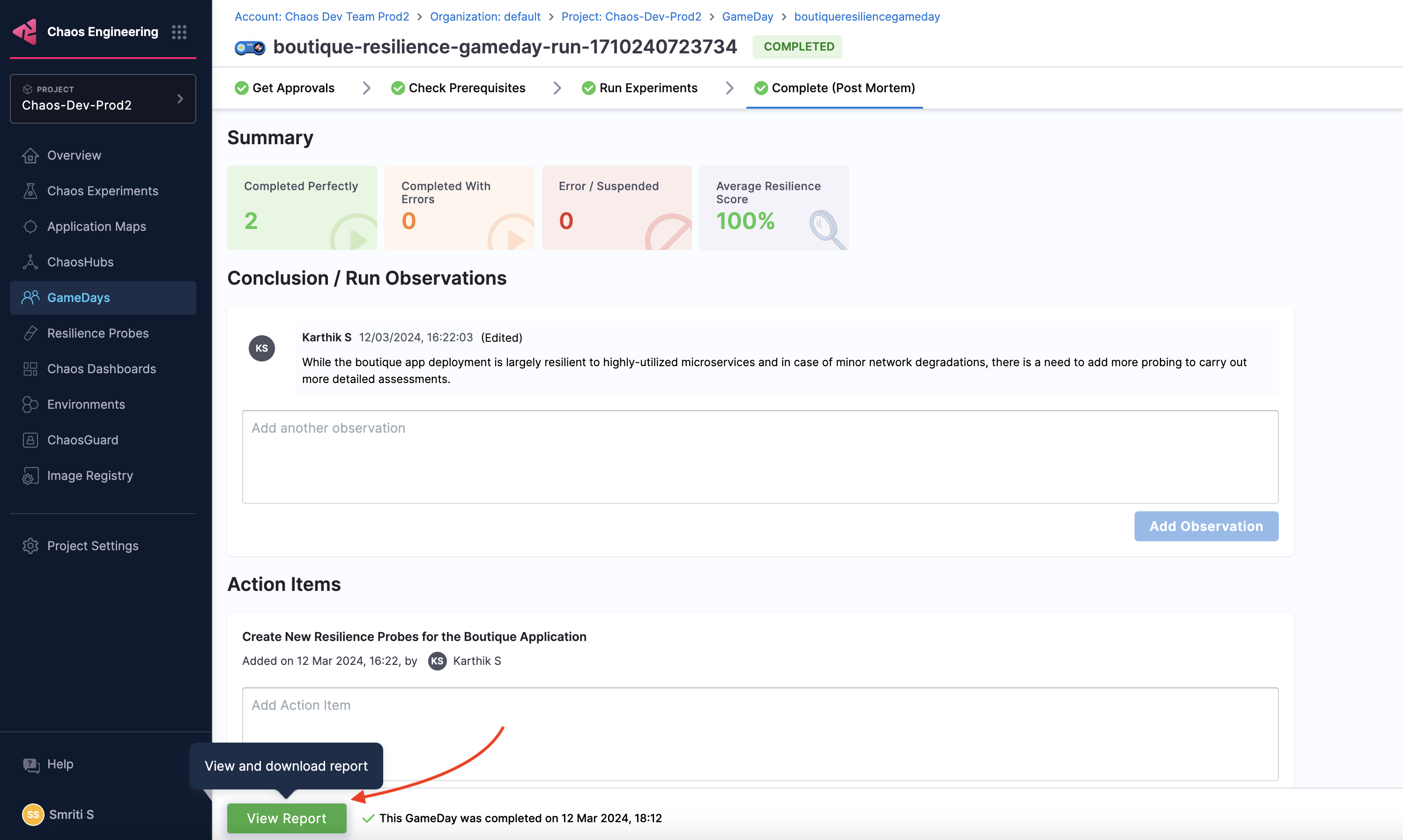
Download GameDay run report
-
To download the report, select Download Report on the page where you view the GameDay run report.

-
Select Save and specify a name for the file (or use the default name provided).
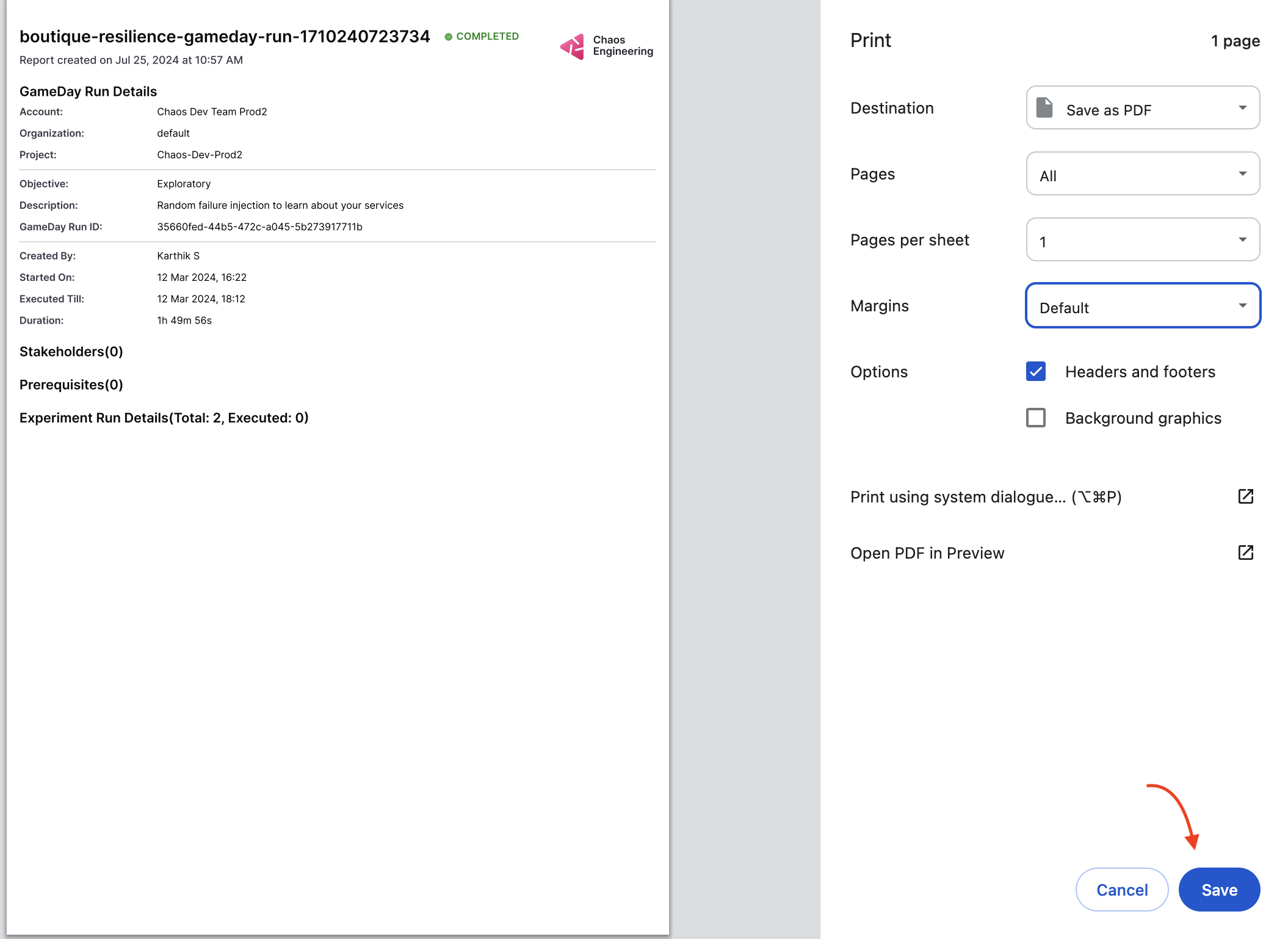
Conclusion
Congratulations on scheduling (or running) your GameDay! Based on the results, you can take steps to improve the resilience of your application.