Use custom service account with DDCR
This topic describes how to:
- Install the Harness Delegate with limited permissions.
- Use the infrastructure to run chaos experiments in single or multiple namespaces in a Kubernetes cluster.
Before you begin, review the following:
Why service accounts matter
A service account is required in the Delegate YAML when Delegate is installed in the target cluster to execute chaos experiments, because Delegate has to assume a role to execute chaos experiments.
In case the Delegate is deployed in a centralized infrastructure (and connected to the target cluster), service account is not required in the Delegate YAML because the Kubernetes connectors already have the role permissions, and Delegate only orchestrates the tasks.
Attach a service account to the Delegate
By default, Delegate uses the cluster admin role. To limit the permissions for the Delegate, follow the steps below.
- Remove the cluster role binding from the Delegate manifest, as shown in the diagram.
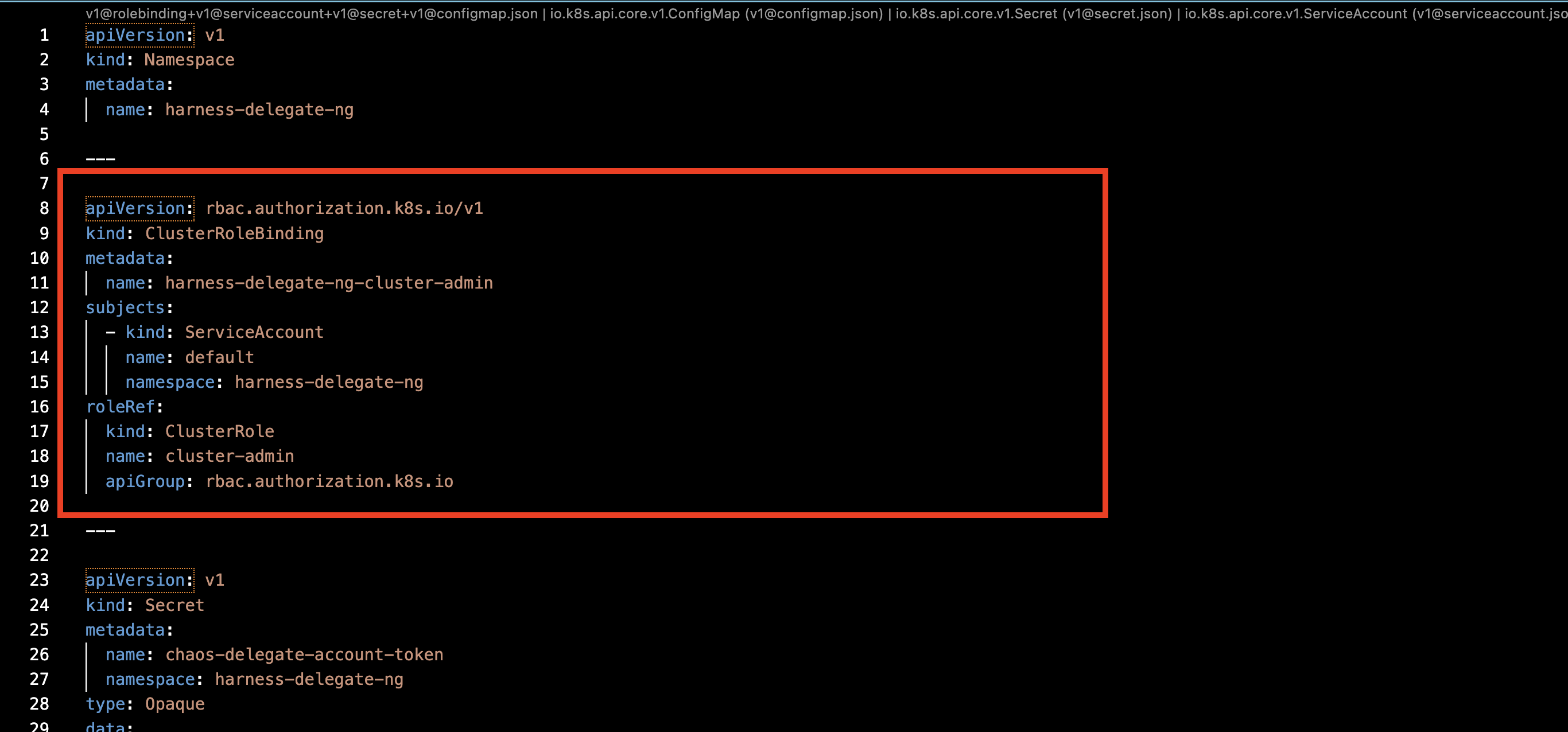
- Create a new service account for the Delegate (to which you can assign a role further).
Here,
chaos-delegaterefers to the name of the service account in the Delegate.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
- Attach the service account to the Delegate YAML, as shown in the diagram.
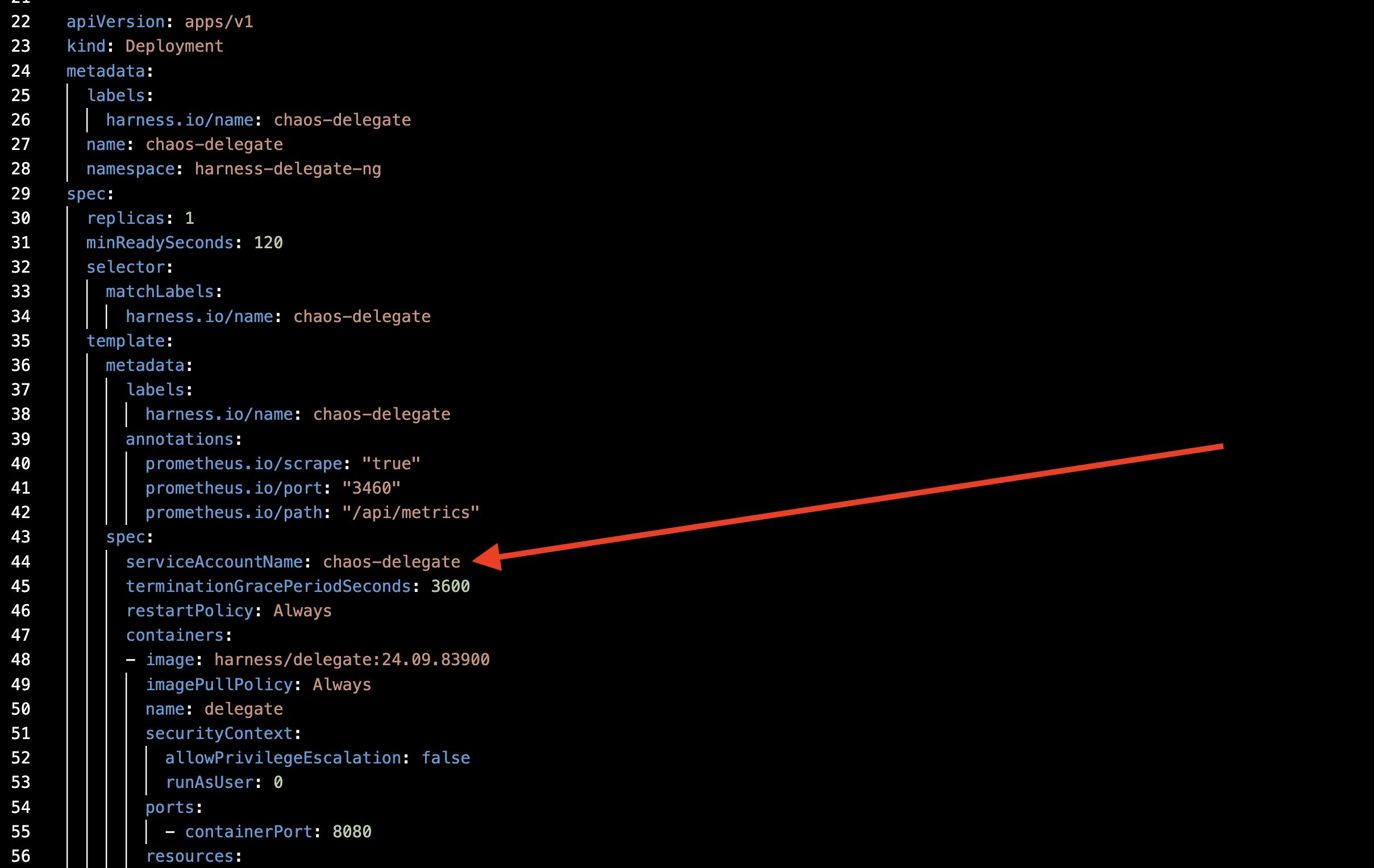
Permissions to manage Delegate resources
While using Harness Delegate, transient pods are created. Harness recommends you provide dedicated namespace for the transient resources. Delegte manages the resources, that require specific permissions in the dedicated namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
name: chaos-delegate
rules:
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- secrets
- services
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: chaos-delegate
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
- events
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- namespaces
verbs:
- patch
resourceNames:
- harness-delegate-ng
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: chaos-delegate
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
Enable Chaos in Namespaces
Case 1: One Infrastructure, Multiple Namespaces
One of the use cases of enabling chaos in selected namespaces is to use one infrastructure to execute chaos experiments in these selected (multiple) namespaces.
Execute the below one-time steps.
- Create a Kubernetes cluster connector: A connector describes how the delegate communicates with the target cluster.
Two cases arise when a Delegate communicates with target cluster: a. When the target application and the delegate are running in the same cluster.
b. When the target application and the delegate are running on different clusters.
Target application and delegate running in same cluster
After creating a Kubernetes cluster, follow the steps below:
- Add permissions to manage the discovery and transient chaos pods in the delegate namespace (
harness-delegate-ngin the example below). Harness recommends you keep the delegate and chaos infrastructure in the delegate namespace.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
name: chaos-delegate
rules:
- apiGroups:
- "*"
resources:
- "*"
verbs:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: chaos-delegate
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- Create a Kubernetes cluster connector using the delegate permissions you added in the previous step.
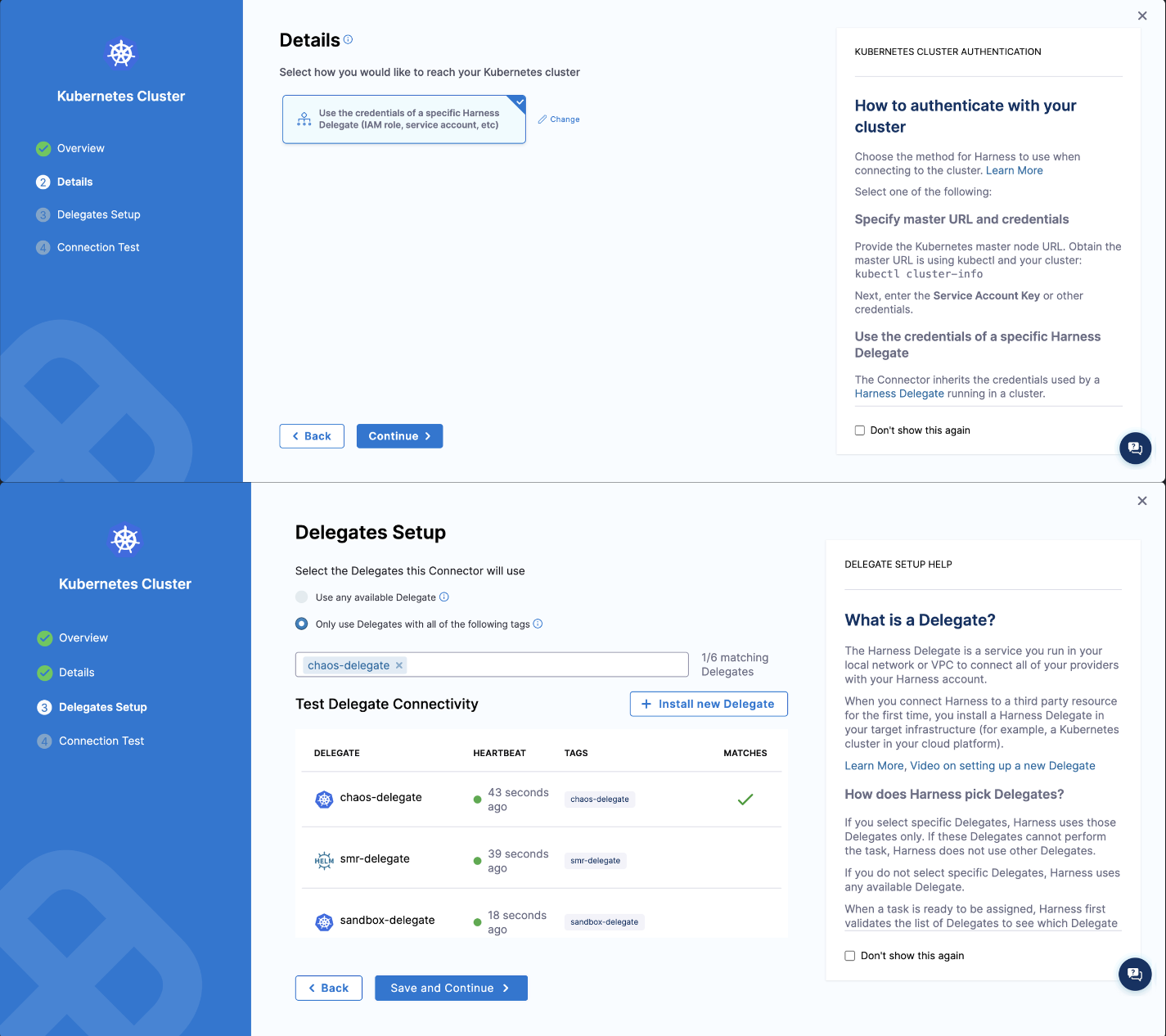
Target application and delegate running on different clusters
- Create a service account in the target cluster with the permissions mentioned below. These permissions allow the Harness chaos transient pods to be present in a dedicated namespace. Harness recommends you keep the delegate and chaos infrastructure in the delegate namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: targetclustersa
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: targetclustersa-secret
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: targetclustersa
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
name: transient-pod-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- "*"
resources:
- "*"
verbs:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: tranisent-pod-rolebinding
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: targetclustersa
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: transient-pod-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- Create a Kubernetes cluster connector using service account based authentication. Obtain the master URL by executing the command
kubectl cluster-infoand get the service account token and secret from the Kubernetes secret.
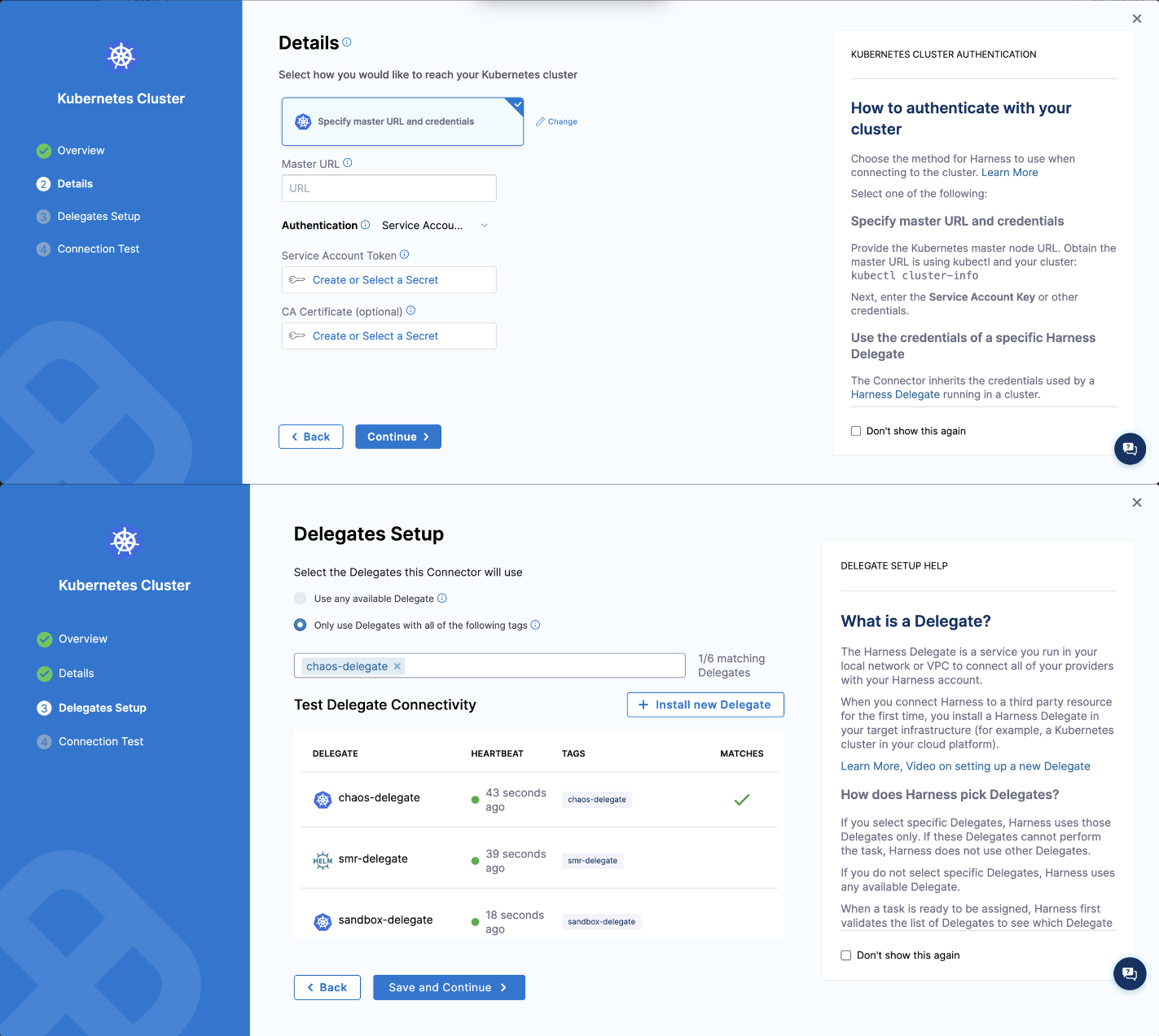
-
Create Harness infrastructure definition using the same Kubernetes cluster connector.
-
Create a cluster role and provide cluster-wide access or cluster role binding for selected namespaces using role binding, depending on your usage. You can use this configuration to onboard application namespaces. To discover the resources and run chaos, use the permissions (described below) in each namespace.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: agentless-model-clusterrole
rules:
# Discovery permissions
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- services
- statefulsets
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
# Chaos permissions
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- list
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- replicationcontrollers
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps.openshift.io
resources:
- deploymentconfigs
verbs:
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- rollouts
verbs:
- list
- get
- You can onboard a namespace by creating a role binding in the application namespace (Onboarding
app1namespace).
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: agentless-model-rolebinding-app1
namespace: app1
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: agentless-model-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: targetclustersa
namespace: harness-delegate-n
-
To onboard a new application namespace, create another role binding in the application namespace (Onboarding
app2namespace, replace thenamepsacefield in the above YAML spec withapp2.) -
To give access to all namespaces, use the following YAML configuration:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: CluesterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: agentless-model-rolebinding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: agentless-model-rolebinding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng -
For the above setting to work, ensure you update the namespace and the service account in the Harness portal service discovery agent setting and chaos infrastructure settings.
Case 2: One Infrastructure, One Namespace
To use one infrastructure to execute multiple experiments in one namespace, follow the steps below.
- Create a service account and role to execute chaos experiments, and ensure they are in the application namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: app3
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: app3
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: chaos-delegate
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: app3
rules:
# Discovery management permissions
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods/log
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
# Discovery process permissions
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- services
- statefulsets
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
# Chaos management permissions
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- secrets
- configmaps
- services
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods/log
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods/exec
verbs:
- get
- list
- create
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- deletecollection
# Chaos execution permissions
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- list
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- replicationcontrollers
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps.openshift.io
resources:
- deploymentconfigs
verbs:
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- rollouts
verbs:
- list
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: app3
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: chaos-delegate
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: app3
- Create a Kubernetes cluster connector with the service account credentials. Obtain the master URL by executing the command
kubectl cluster-infoand get the service account token and secret from the Kubernetes secret.
-
Create Harness infrastructure definition using the same Kubernetes cluster connector.
-
Ensure to use the application namespace as chaos infrastructure namespace and update the service account name accordingly.