Dedicated Delegate on Target Cluster
This topic describes the permissions required to deploy Delegate for each target cluster to execute chaos experiments.
Before you begin, review the following:
Why service accounts matter
A service account is required in the Delegate YAML when Delegate is installed in the target cluster to execute chaos experiments, because Delegate has to assume a role to execute chaos experiments.
In case the Delegate is deployed in a centralized infrastructure (and connected to the target cluster), service account is not required in the Delegate YAML because the Kubernetes connectors already have the role permissions, and Delegate only orchestrates the tasks.
Limit Permissions for Delegate
By default, Delegate uses the cluster admin role. To limit the permissions for the Delegate, follow the steps below.
Step 1. Create a dedicated namespace
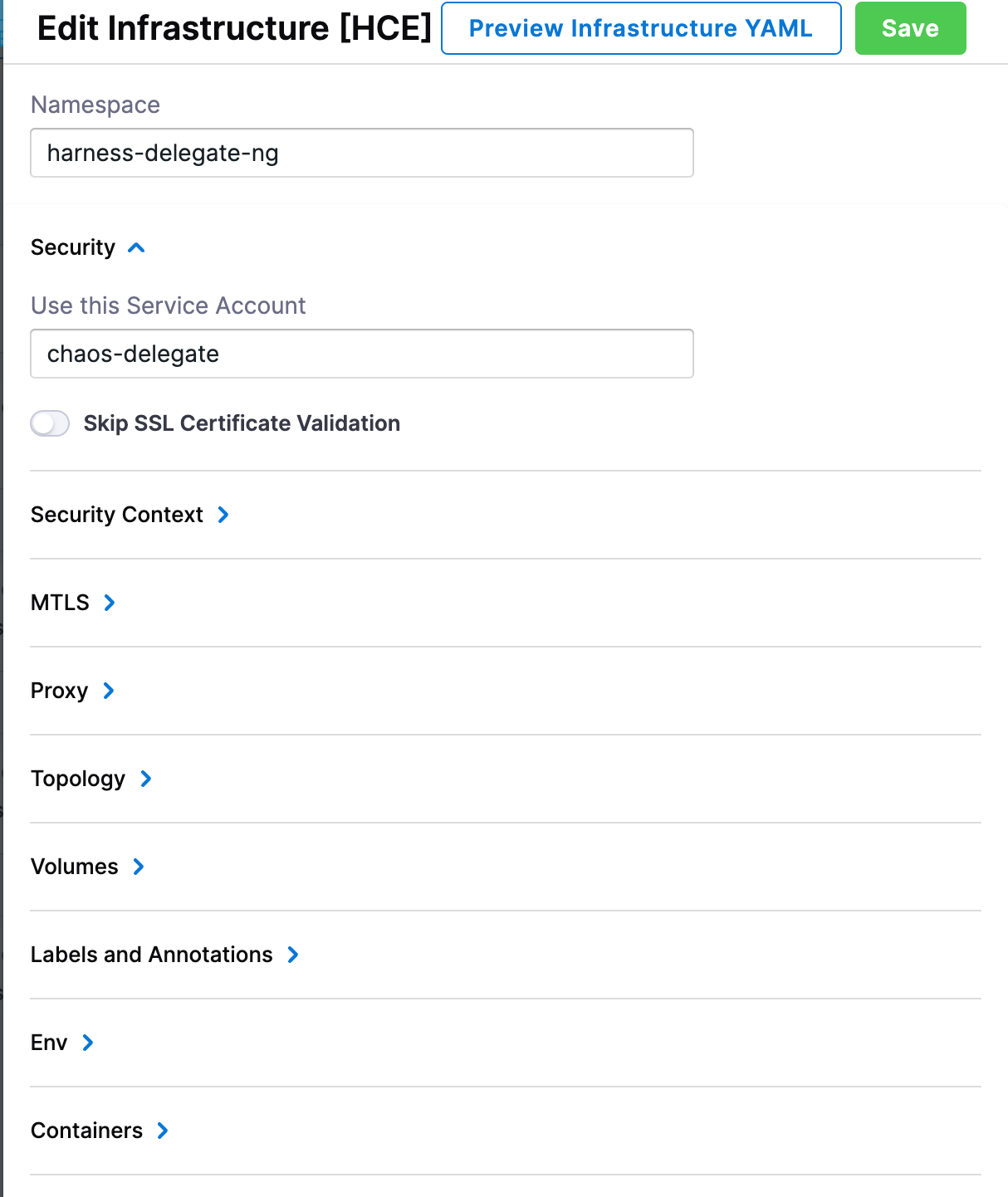
Create a dedicated namespace for Harness delegate during installation. For example harness-delegate-ng.
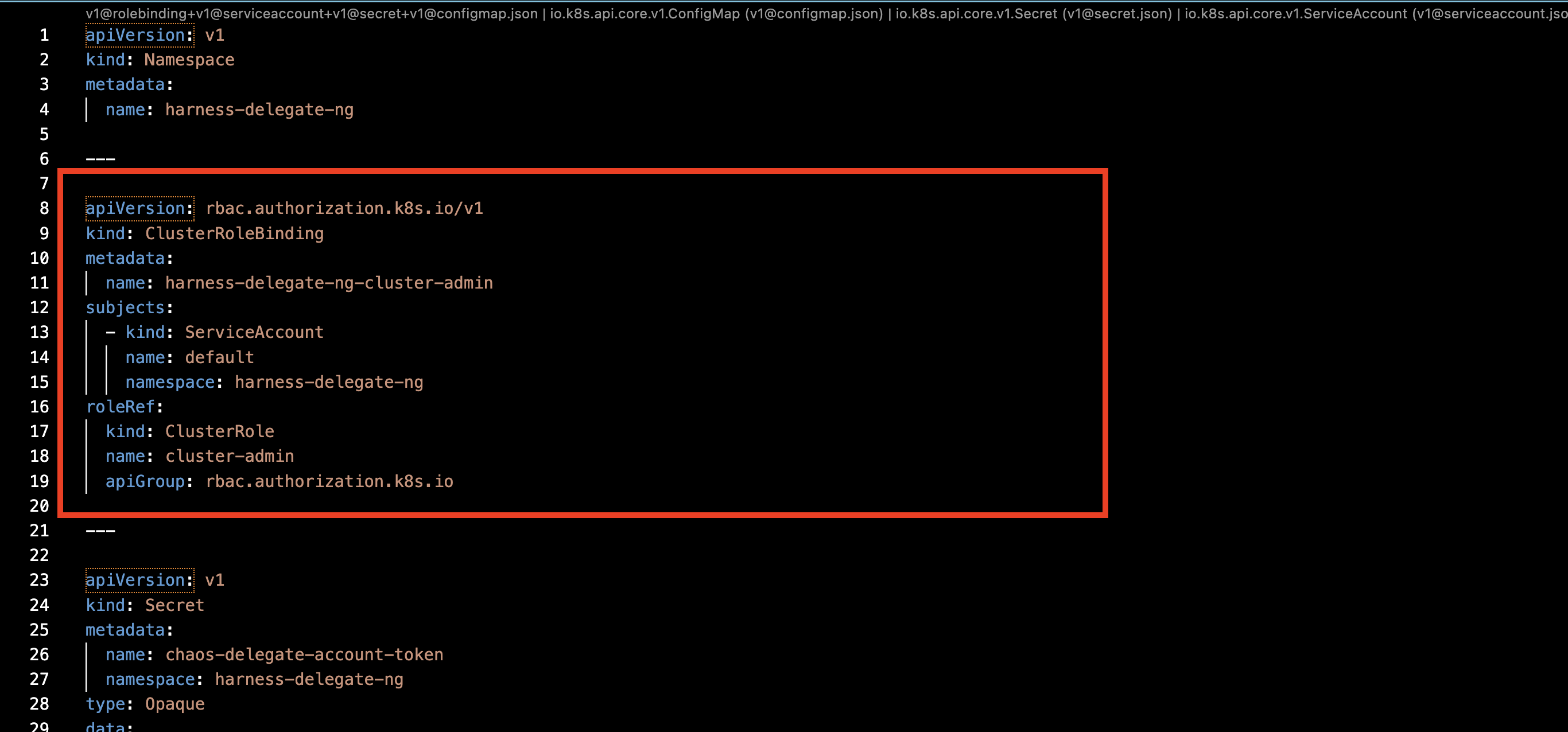
Step 2. Remove Cluster Role Binding
Remove the cluster role binding from the Delegate manifest, as shown in the diagram.
Step 3. Create New Service Account
Create a new service account for the Delegate (to which you can assign a role further) in the dedicated namespace where the Delegate is installed.
Here, chaos-delegate refers to the name of the service account in the Delegate.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
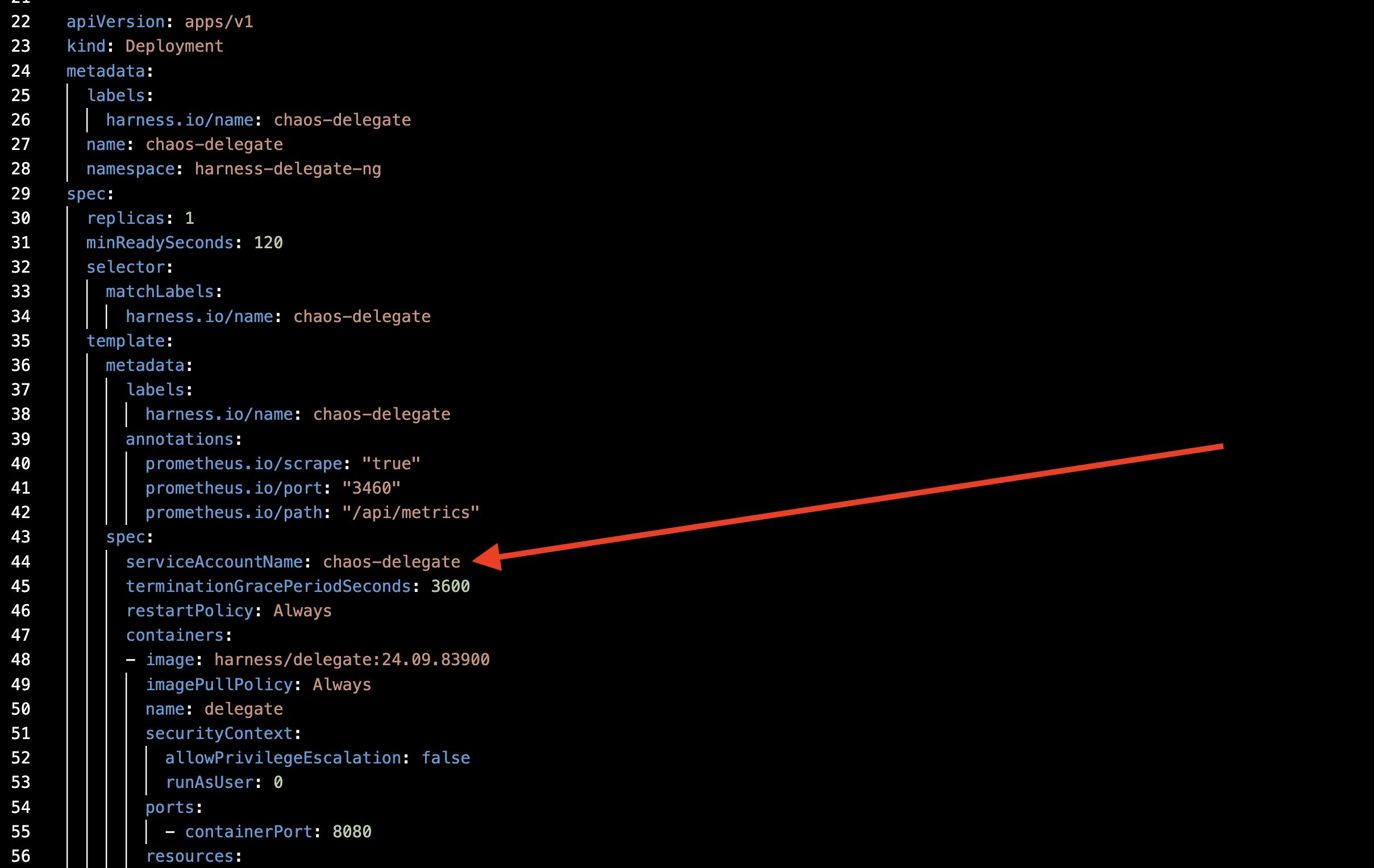
Step 4. Attach the Service Account
Attach the service account you created earlier to the Delegate YAML, as shown in the diagram.
Step 5. Apply RBAC
Apply the below RBAC to configure the permissions to create chaos runners (that is, transient pods).
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
name: chaos-runner-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- pods/log
- pods/exec
- secrets
- services
- configmaps
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-runner-rolebinding
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: chaos-runner-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Step 6. Create a Cluster Role
Create a cluster role that will be used later to onboard application namespaces.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: chaos-clusterrole
rules:
# Discovery permissions
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- services
- statefulsets
- nodes
- namespaces #(nodes and namespace permissions are required to autocreate network experiments)
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- batch
resources:
- jobs
- cronjobs
verbs:
- watch
- list
- get
# Chaos permissions
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- patch
- update
- watch
- deletecollection
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- networkpolicies
verbs:
- create
- delete
- get
- list
- apiGroups: #(Prerequisite: Metrics server should be installed on the cluster. This is required if your are running a custom script in command (CMD) source probe to get CPU and memory metrics for pods and nodes.)
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
- replicasets
- daemonsets
- statefulsets
verbs:
- list
- get
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- replicationcontrollers
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps.openshift.io
resources:
- deploymentconfigs
verbs:
- list
- get
- apiGroups:
- argoproj.io
resources:
- rollouts
verbs:
- list
- get
Step 7. Create Cluster Role Binding (Optional)
If you wish to provide access to all namespaces, create a cluster role binding.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-rolebinding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: chaos-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
-
Now, you can onboard a namespace by creating a role binding in the application namespace (For example, Onboarding app1, app2 and so on)
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: chaos-rolebinding
namespace: app1 #for app2, provide namespace as app2
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: chaos-clusterrole
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: chaos-delegate
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
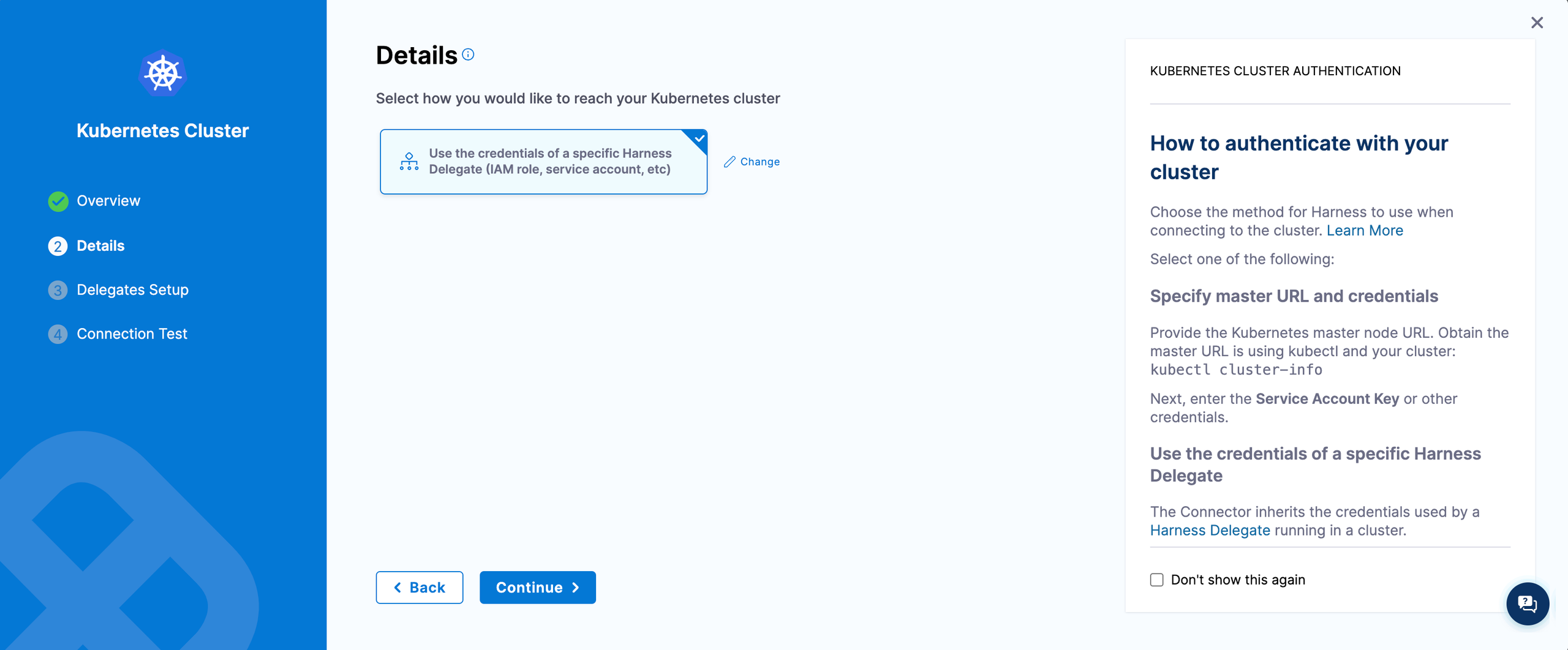
Step 8. Create a Kubernetes connector
Create a Kubernetes connector using Delegate permissions.
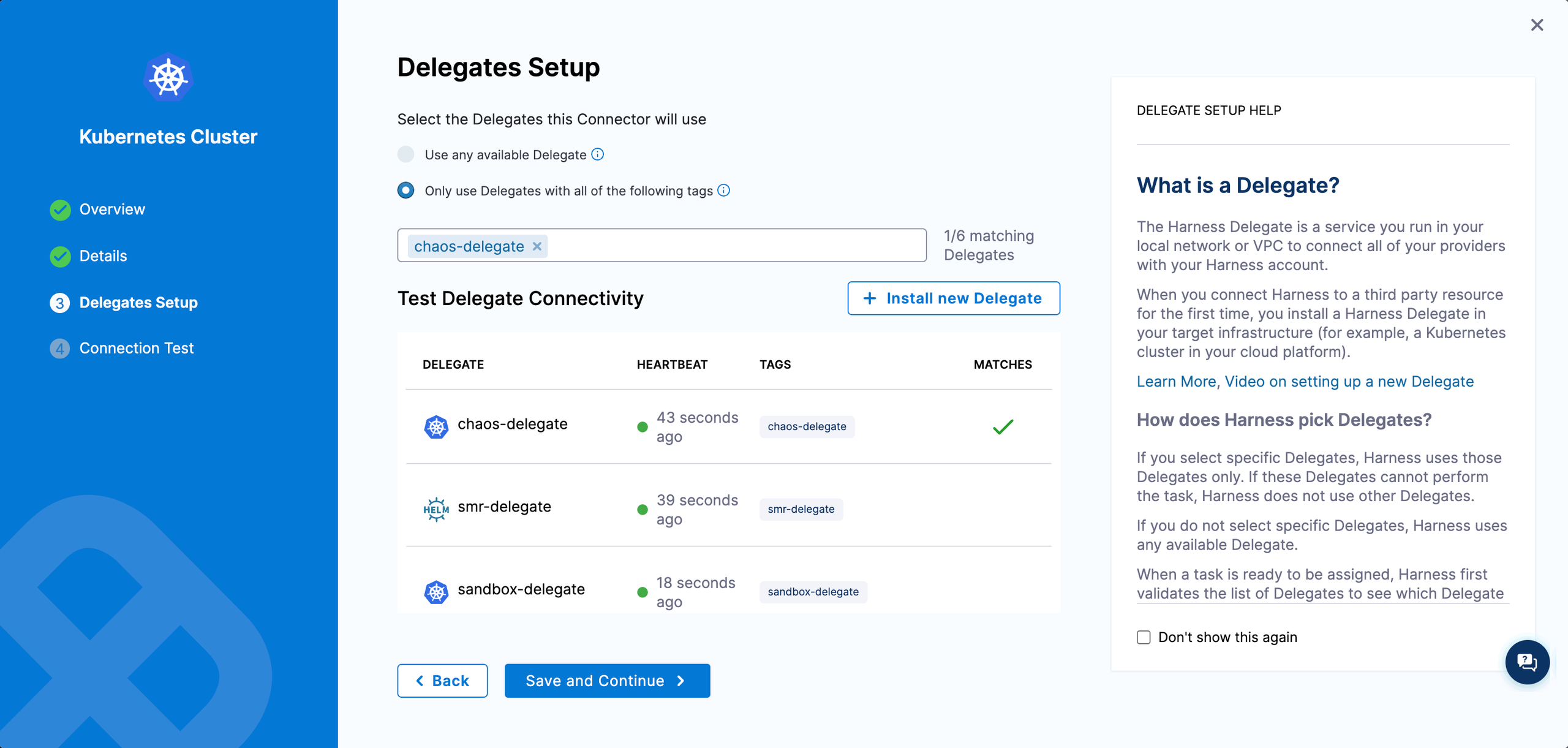
Step 9. Create Kubernetes Infrastructure
Finally create the Kubernetes infrastructure using the Kubernetes connectors created in the step 8.
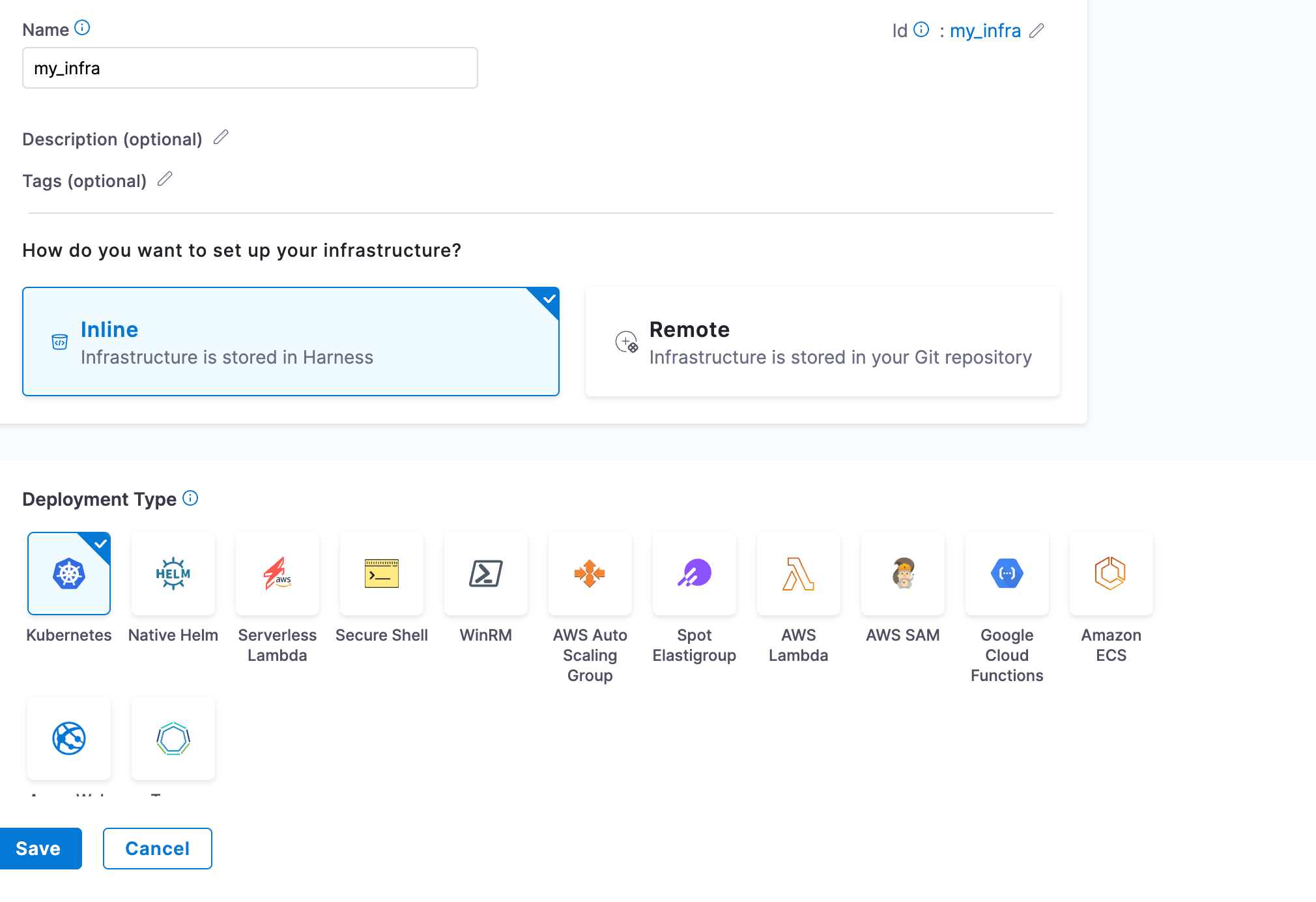
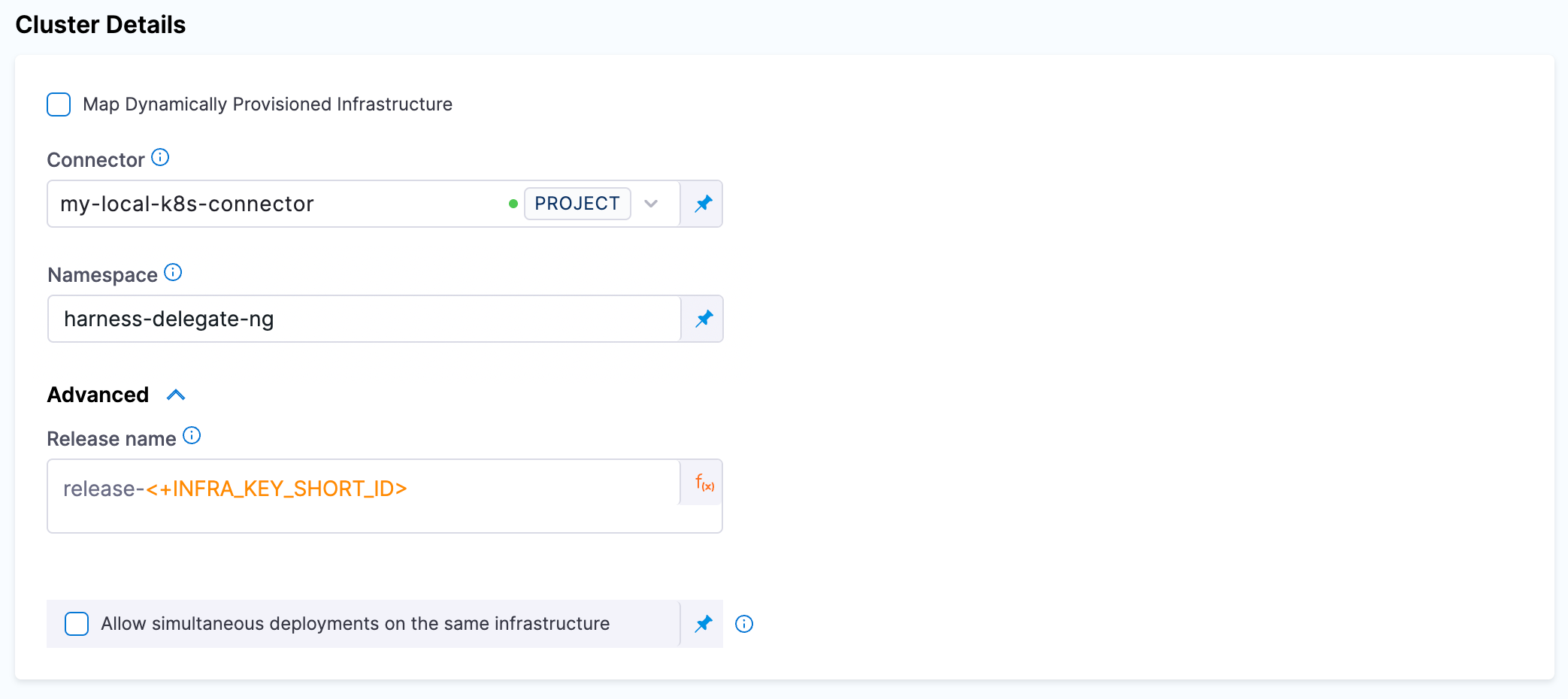
Step 10. Edit Infrastructure
Edit the infrastructure you created in step 9 to provide the details of dedicated namespace that was created earlier. This is the namespaace where the chaos runner will be launched along with the Service Account to ensure that experiments run with relevant permissions.