Key concepts
This section explains the key Harness Cloud Cost Management (CCM) concepts that you need to know before implementation.
Node Cost
If no cloud connector is configured, node cost is calculated based on the public pricing API of the cloud platform. If there is a cloud connector configured for either AWS or Azure, cost is trued up. GCP will always be based off of public pricing.
☆ NOTE — For ECS clusters, you can replace nodes with container instances and pods with tasks.
Here is an example of how node cost is calculated based on the following node specification:
| Operating system | Linux |
| Region | us-central1 |
| Instance family | n1-standard-4 |
| Instance Category | ON_DEMAND |
As per the cloud platform pricing, the per hour price of n1-standard-4 in us-central1 is $0.1900.
Here is the formula:
Cost for 24 hours = 24 * 0.1900 = $4.56.
☆ NOTE — Typically nodes are the same size. If they are running for a full day and are the same size, the cost will be the same.
Pod Cost
Pod cost is a ratio of the cost of the node it is running on. The price is equally distributed among CPU and memory. The following formula is used to calculate the pod cost:
Hourly pod cost = ((podCPU/nodeCPU) * nodeCPUPricePerHour) + ((podMemory/nodeMemory)) * nodeMemoryPricePerHour)
Here is an example of a pod cost calculation:
Pod Resources = (cpuUnits: 1024, memoryMB: 4096)
Node Resource = (cpuUnits: 4096, memoryMB: 15360) n1-standard-4
Node Resource = (cpuUnits: 4096, memoryMB: 15360) n1-standard-4
Pod cost = ((1024/4096) * 0.095 ) + ((4096/15360)) * 0.095) = 0.0490833333
System Cost
System cost is calculated by subtracting the total cost of the node from the allocatable resource cost.
Allocatable on a Kubernetes node is defined as the amount of compute resources that are available for pods. For more information, see Reserve Compute Resources for System Daemons in Kubernetes.

Here is the formula:
System cost = total cost of node - allocatable resource cost
System cost is used while calculating unallocated cost as described below.
Unallocated Cost
Unallocated cost is applicable to nodes only. There is no concept of unallocated costs for pods. Unallocated cost is the cost of unallocated node resources in a Kubernetes cluster or unallocated container instances in an ECS cluster.
Unallocated cost of node = node cost - the cumulative sum of pod costs running on that node - system cost of the node
Unallocated cost of cluster = sum of the node’s unallocated cost running in the cluster
Idle Cost
Idle cost is the cost of idle resources (CPU and memory) allocated to a Kubernetes pod or an Amazon ECS task but is not utilized.
Here is an example of pod idle cost calculation:
Instance cost = 75$, CPU cost = 25$, Memory cost = 50$
Avg cpu util = 75%, Avg memory util = 25%
CPU Idle cost = (25) * (1 - .75) = 6.25
Memory Idle cost = (50) * (1 - .25) = 37.50
Idle Cost= 6.25 + 37.50 = 43.75$
Node Idle cost = Cost of unutilized resources - unallocated resource
Here is an example of node idle cost calculation:
Instance cost = 75$, CPU cost = 25$, Memory cost = 50$
Avg cpu util = 75% , Avg memory util = 75%
CPU Idle cost = (25) * (1 - .75) = 6.25
Memory Idle cost = (50) * (1 - .75) = 12.5
Unallocated cost of cpu = 2.5$, Memory = 10$
Idle Cost = 6.25 + 12.50 - 2.5 - 10 = 6.25$
Total Cost
For Kubernetes clusters, the total cost is the sum of all the node costs. For ECS clusters, the sum of all container instances.
Utilized Cost
Utilized cost is the cost estimate for the utilized node or pod resources.
Utilized cost = Total cost - node idle cost - unallocated cost
Forecasted Cost
Forecasted costs are predictions based on your historical cost data. The forecasted date is applicable only where historical data exists. If there is insufficient data to compute the forecast, the value is not displayed. The forecasted cost is predicted for the same future time period as your selected date range.
The following table lists some of the examples for forecasted cost calculation. In this example, the current date is considered as March 30, 2021.
| Selected Date Range | Forecasted Date Range |
|---|---|
| Predefined date range, for example, Last 7 days, Last 30 days, Last month, and so on | Calculated for the next 7 days, next 30 days, or next month based on the selected date range |
| Custom date range, for example, March 25 - 30 (6 days) | March 31 - April 5 (next 6 days) |
| Future date range, for example, March 25 - April 3 (invalid date range) | Not applicable |
| Past date range, for example, March 1 -15 | Not applicable |
K8s Storage cost
To access information about persistent volumes, we retrieve data related to their specifications. These specifications include details such as the type of persistent volume being used. Currently, within our system, we support various types of persistent volumes, each serving different purposes. The supported types, known as PVTypes, include
enum PVType {
PV_TYPE_UNSPECIFIED = 0;
PV_TYPE_GCE_PERSISTENT_DISK = 1;
PV_TYPE_AWS_EBS = 2;
PV_TYPE_AZURE_DISK = 3;
PV_TYPE_NFS = 4;
}
For GCP Kubernetes persistent volumes (`PV_TYPE_GCE_PERSISTENT_DISK``), the exact price rate is calculated by calling the GCP Kubernetes APIs. For all other cloud providers, a hardcoded price value is used for cost calculation.
| PVType | Default Hardcoded price (perGBPerMonth) |
|---|---|
PV_TYPE_UNSPECIFIED | 0.040 |
PV_TYPE_AWS_EBS | 0.040 |
PV_TYPE_AZURE_DISK | 0.040 |
PV_TYPE_NFS | 0.001018 |
Later, the storage cost is added in the total cluster cost.
Total cluster cost = CPU + Memory + Storage
Cost Trend
The cost trend is calculated based on the previous spending. It can be calculated only if the previous data is available.
Cost Efficiency Score
A measure of how cost-optimized your resource usage is across your clusters. It is derived from the total and idle (and or unallocated) spend of your resources.
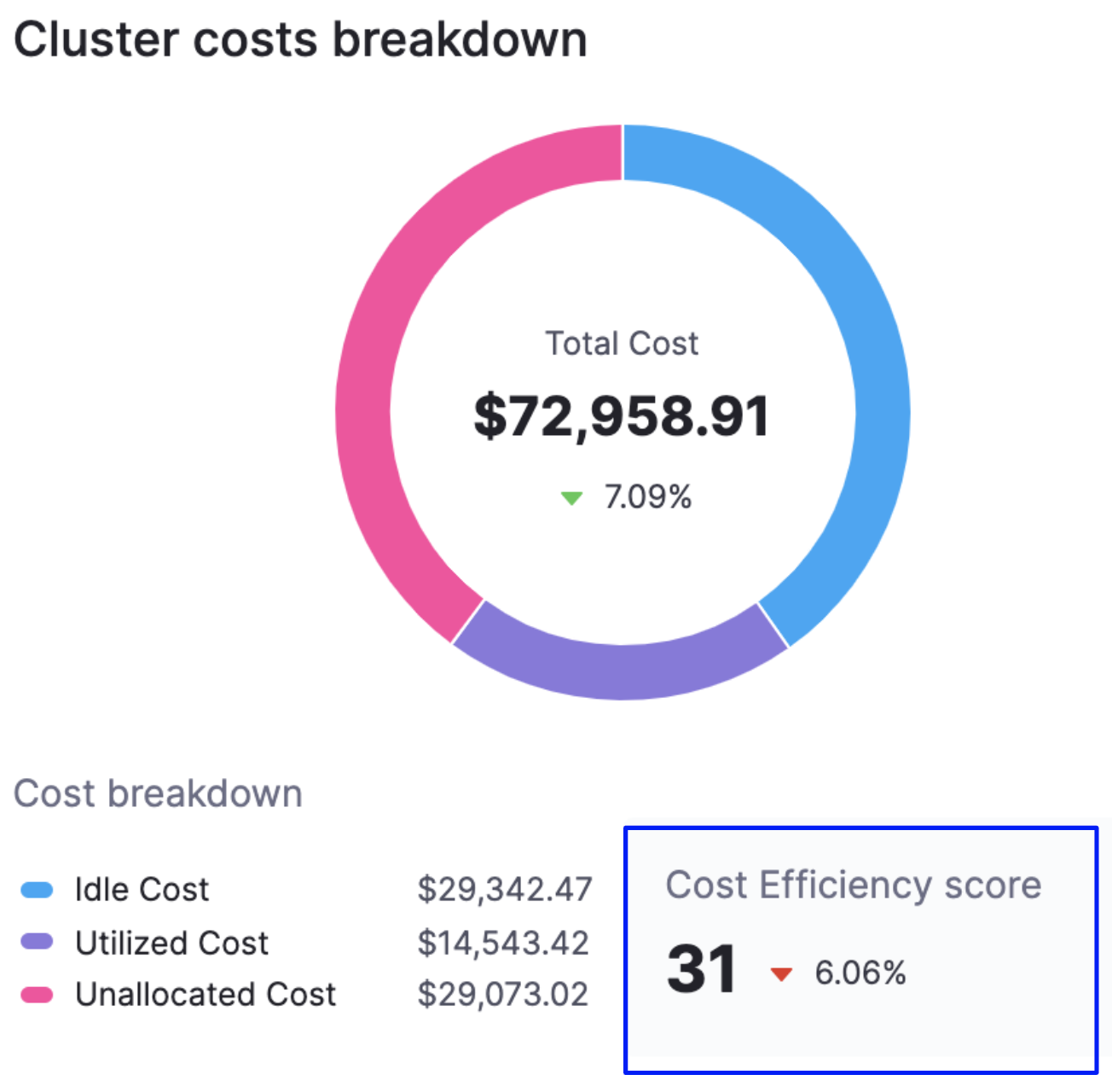 The efficiency score is the deviation of actual utilization from the expected utilization baseline.
The efficiency score is the deviation of actual utilization from the expected utilization baseline.
Expected utilization baseline = utilized resources (100 - x - y)%,
where x% is allowed unallocated cost and y% is allowed idle cost
Here is an example:
Allowed unallocated resources = 5% of the total cost
Allowed idle resources = 30% of the total cost
Utilized resources baseline defined = 65%
If the utilization is 58% of total cost, then the efficiency score =
[1 - [(65-58)/65]] * 100 ~ [89 efficiency score]