Features of Cluster Orchestrator
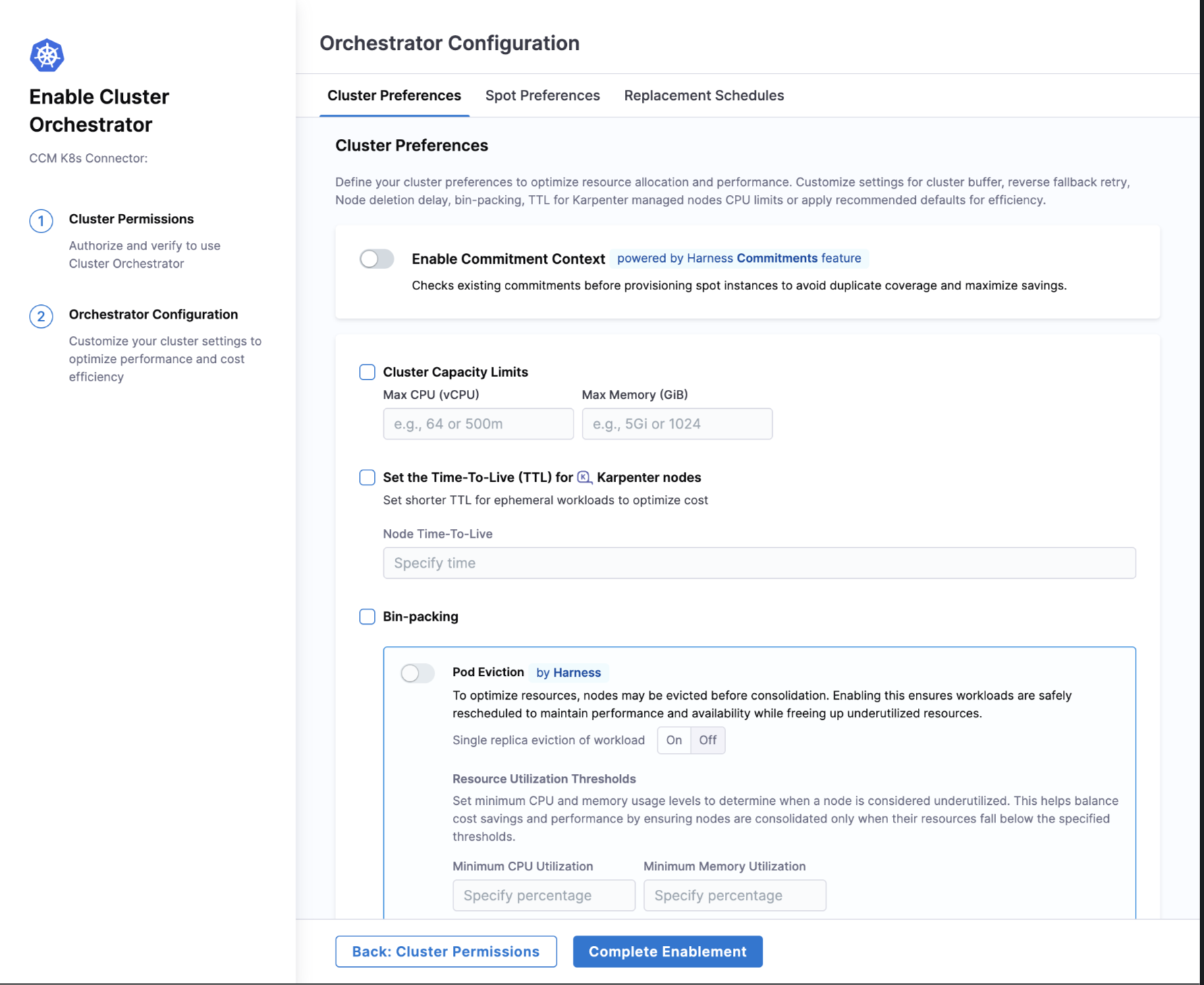
Enable Commitment Context (Integration with Commitment Orchestrator)
This feature allows you to maximize the value of your existing cloud commitments by selecting the Master Account from your connector dropdown. When enabled, Cluster Orchestrator first checks for any unused commitment capacity before provisioning spot instances. This intelligent prioritization prevents duplicate resource coverage and optimizes your cloud investment by ensuring pre-purchased compute capacity is fully utilized before additional resources are provisioned.
Set the Time-To-Live (TTL) for Karpenter nodes
This feature allows you to define an automatic expiration time for Karpenter nodes. By setting a TTL value, nodes will be gracefully terminated after the specified period of inactivity, preventing idle resources from accumulating costs. This automated cleanup helps maintain optimal cluster efficiency and reduces unnecessary cloud spending.
Cluster Capacity Limits
This feature restricts the maximum resources a cluster per nodepool can scale up to. This prevents scenarios where configuration errors or unexpected behavior could result in uncontrolled node provisioning. When configured, Cluster Capacity Limits enforce limits on:
-
Maximum vCPUs (cores) – defines the total CPU capacity the cluster Nodepool can scale up to.
-
Maximum Memory (GiB) – defines the total memory capacity the cluster Nodepool can scale up to.
If, Karpenter Nodepools Already have limits configured, when new nodepools (spot/ondemand) are created out of the existing karpenter nodepools, the limits configuration will be copied over. If the limits are configured on the cluster level, then the limits will be copied over to all nodepools which does not have a limit set explicitly in the default nodepool. If limits are not set on Cluster Config/Default Nodepool, then a default limit will be calculated by cluster orchestrator with the following equation and will be applied on all the nodepools managed by Harness:
cpu = total cpu available in the cluster * 2
memory = total memory available in the cluster * 2
Bin-Packing
This feature uses an advanced resource optimization technique to efficiently distribute workloads across your Kubernetes cluster. Cluster Orchestrator intelligently consolidates workloads onto fewer nodes to maximize resource utilization, allowing underutilized nodes to be safely identified and removed from the cluster. Under Bin Packing, Cluster Orchestrator offers:
-
Pod Eviction By Harness: This setting allows Cluster Orchestrator to safely move workloads from underutilized nodes before removing those nodes from the cluster. When Pod Eviction By Harness is enabled, pods are automatically relocated to more efficient nodes, ensuring your applications continue running smoothly while eliminating wasted resources.
-
Users can also configure Single replica eviction of workload which determines whether pods with only one replica can be moved during optimization. When set to "On", even single-instance applications can be relocated to optimize resources. When set to "Off", applications with only one running instance will remain untouched, providing additional stability for critical single-instance workloads.
-
Users can set Resource Utilization Thresholds which define the minimum CPU and memory usage levels that determine when a node is considered underutilized. For example, setting a CPU threshold of 30% means any node using less than 30% of its CPU capacity becomes a candidate for consolidation. These customizable thresholds help you balance cost savings with performance needs - lower thresholds increase cost savings by consolidating more aggressively, while higher thresholds prioritize performance by keeping more nodes active.
-
Bin Packing Supports Robust Distribution Mode from
0.5.1: Robust Distribution Mode is an enhancement to the default Cluster Orchestrator scheduling flow which gets automatically enabled when bin packing is enabled. With Bin Packing enabled, the orchestrator enforces the configured spot/on-demand distribution more effectively. It identifies pods that violate distribution rules due to configuration changes or missing tolerations. Using the Kubernetes Descheduler's policyRemovePodsViolatingNodeTaints, it automatically evicts pods from incompatible nodes and reschedules them to nodes that match your configured distribution.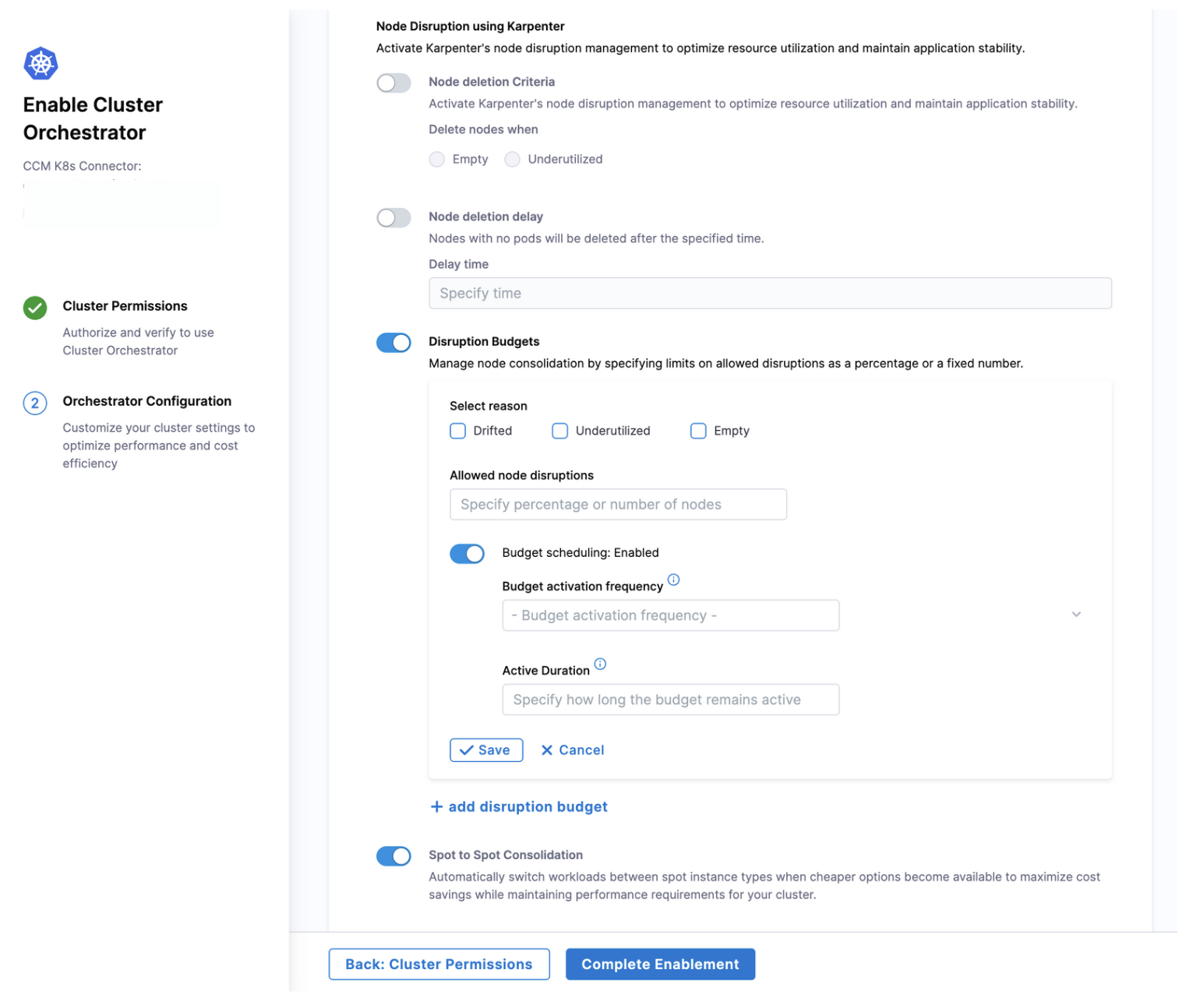
-
-
Node Disruption Using Karpenter: This feature leverages Karpenter's node management capabilities to intelligently remove unnecessary nodes while maintaining application stability. With configurable options, you can fine-tune how and when nodes are removed from your cluster:
-
Node Deletion Criteria: Define which nodes should be targeted for removal:
- Empty: When selected, only nodes with no running pods will be removed, ensuring zero workload disruption
- Underutilized: When selected, nodes that fall below your defined CPU and memory thresholds will be consolidated, maximizing resource efficiency
-
Node Deletion Delay: This setting defines a grace period before removing empty nodes. For example, setting a 10-minute delay means nodes will remain in the cluster for 10 minutes after becoming empty before deletion. This prevents rapid scale up/down cycles when workloads are temporarily removed and then quickly redeployed.
-
Disruption Budgets: These safety limits prevent excessive node terminations that could impact application availability. For each budget, you can configure:
- Select reason: Choose which node conditions trigger the budget (Drifted, Underutilized, or Empty)
- Allowed node disruptions: Set limits as either a percentage or fixed number of nodes that can be removed at once
- Budget scheduling: Define when the budget is active (hourly, midnight, daily, weekly, monthly, or annually) and for how long, allowing for scheduled maintenance windows
-
Spot to Spot Consolidation
This feature intelligently migrates workloads between different spot instance types to optimize costs without compromising performance. When more cost-effective spot instance options become available, Cluster Orchestrator automatically identifies opportunities to relocate workloads to these cheaper instances. This continuous optimization ensures you're always running on the most cost-efficient infrastructure while maintaining your application's performance requirements and availability standards.
- If Node Deletion Delay or Bin Packing is not set, the cluster won't scale down.
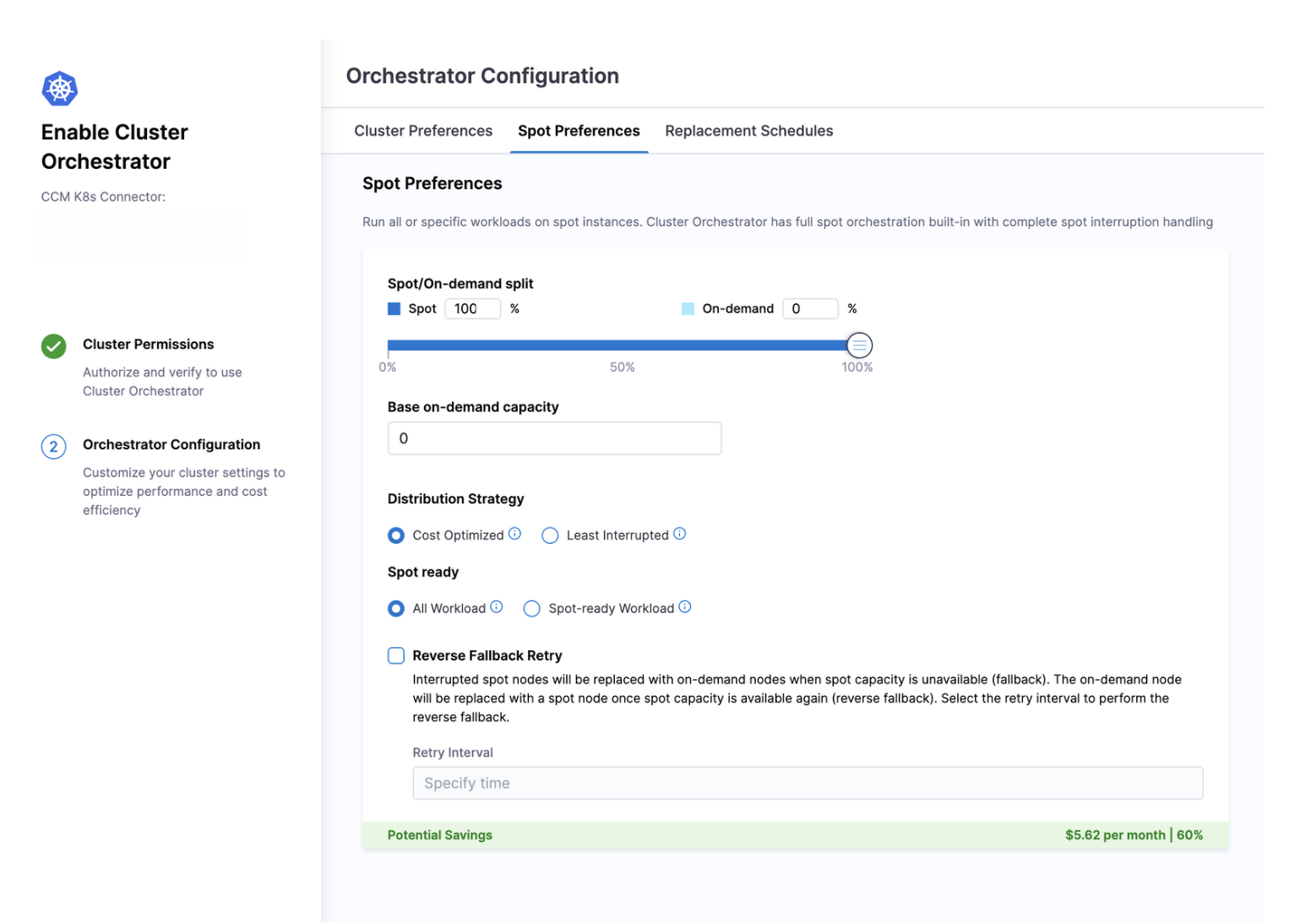
Spot Instance Management
This feature enables you to strategically deploy workloads on cost-effective spot instances, potentially reducing cloud compute costs by up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing. Cluster Orchestrator's intelligent spot management includes sophisticated interruption handling that automatically redistributes workloads when spot instances are reclaimed by cloud providers. This ensures your applications remain available and performant even during spot instance transitions, allowing you to maximize cost savings without sacrificing reliability.
Key Configuration Options
-
Spot/On-demand Split: Users can define the percentage distribution between spot and on-demand instances (out of 100). Higher spot percentages increase cost savings but may introduce more volatility.
-
Base On-demand Capacity: Users can define a fixed number of on-demand replicas, with additional capacity split between On-Demand and Spot nodes according to their preferences. By defining on-demand base capacity, it ensures that a minimum number of nodes are always running as on-demand instances, providing a stable foundation for critical workloads that require guaranteed availability.
-
Distribution Strategy: Cluster Orchestrator allows users to choose between two distribution strategies:
- Cost Optimized: All Spot replicas run on the minimum number of nodes, maximizing cost savings but increasing risk. The Spot Instances come from the lowest-priced pool that has available capacity. If the lowest-priced pool doesn't have available capacity, the Spot Instances come from the next-lowest-priced pool that has available capacity. Read More
- Least Interrupted: Cluster Orchestrator identifies the pools with the highest capacity availability for the number of instances that are launching. This means that it will request Spot Instances from the pools that have the lowest chance of interruption in the near term. It also splits the replicas to multiple Spot nodes to minimize disruption. Read More
-
Spot Ready: Determine which workloads can run on spot instances:
- All Workloads: Apply spot/on-demand split to all workloads regardless of replica count (more aggressive savings)
- Spot-ready Workloads Only: Apply spot configuration only to workloads with multiple replicas (>1), ensuring single-replica critical services remain on reliable on-demand instances
-
Reverse Fallback Retry: This feature helps maintain cost efficiency during spot instance interruptions. When spot instances are reclaimed by cloud providers, Cluster Orchestrator automatically replaces them with on-demand instances to ensure workload continuity. The Reverse Fallback Retry setting then controls how aggressively the system attempts to transition these workloads back to spot instances when capacity becomes available again. By configuring this setting, you can balance between immediate cost optimization (more frequent retry attempts) and operational stability (less frequent retry attempts), ensuring your cluster returns to its optimal cost-efficient state without disrupting application performance.
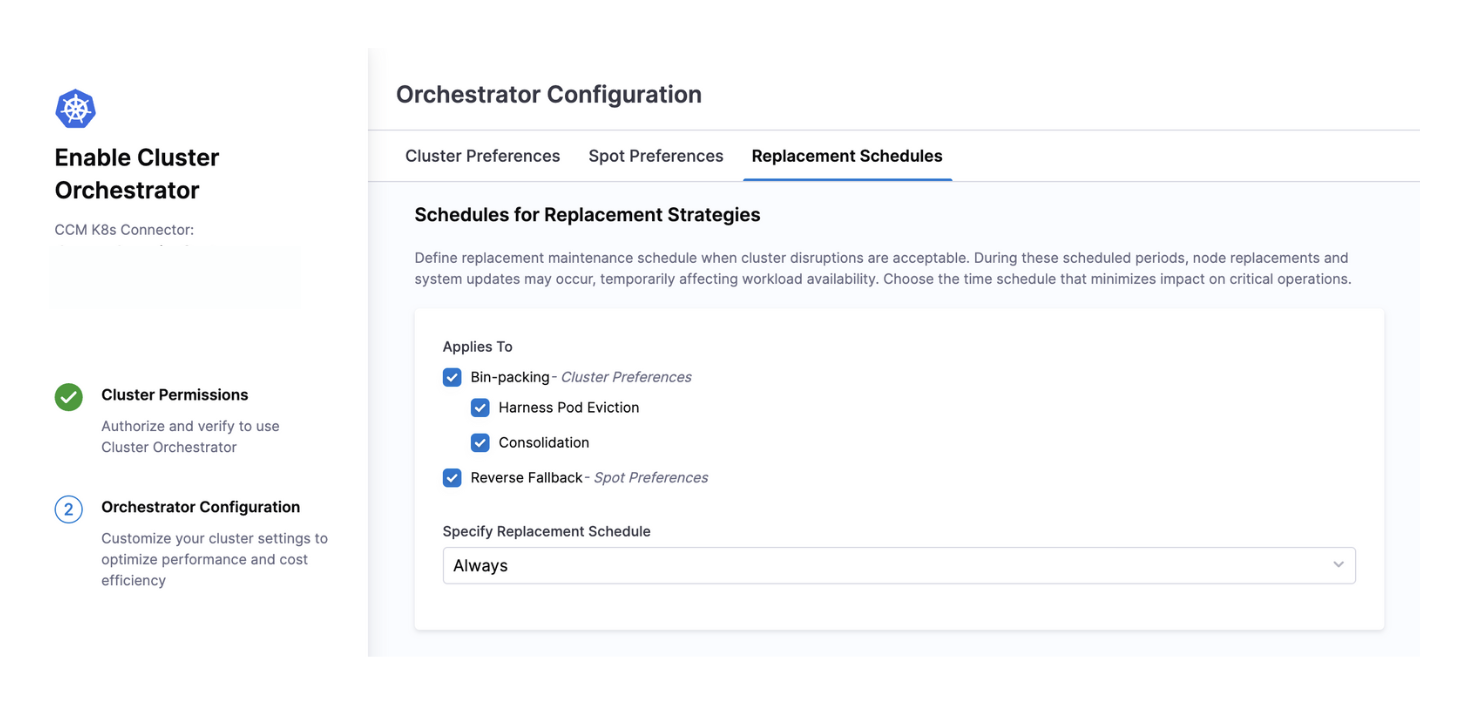
Define precise time windows when cluster disruptions are acceptable for maintenance operations. During these scheduled periods, Cluster Orchestrator performs node replacements, consolidations, and system updates that might temporarily affect workload availability.
Schedule Options
-
Custom: Define specific days and time windows when maintenance can occur (e.g., weekends, off-hours, or maintenance windows aligned with your business cycle). This gives you complete control over when potentially disruptive operations take place.
-
Always: Maintenance operations can occur at any time, prioritizing cost savings and efficiency over potential disruption. Best for non-production environments or systems with built-in resilience.
-
Never: Disables automatic maintenance operations completely. All changes require manual intervention. Use this for highly sensitive production workloads where any disruption is unacceptable.
Operations Governed by Schedules:
-
Bin-packing Operations:
- Harness Pod Eviction: Controls when pods can be evicted from nodes to facilitate consolidation
- Node Consolidation: Determines when underutilized nodes can be drained and removed
-
Spot Instance Management:
- Reverse Fallback: Schedules when on-demand instances can be replaced with spot instances after spot capacity becomes available again
VPA (Vertical Pod Autoscaler)
The Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA) is a Kubernetes component that automatically adjusts the CPU and memory resource requests and limits of containers in pods based on their historical usage. VPA helps optimize resource allocation by ensuring pods have the right amount of resources they need to run efficiently.
By enabling VPA in Harness Cluster Orchestrator, you gain the ability to automatically optimize resource allocation for your workloads, leading to better performance and cost efficiency across your Kubernetes clusters.
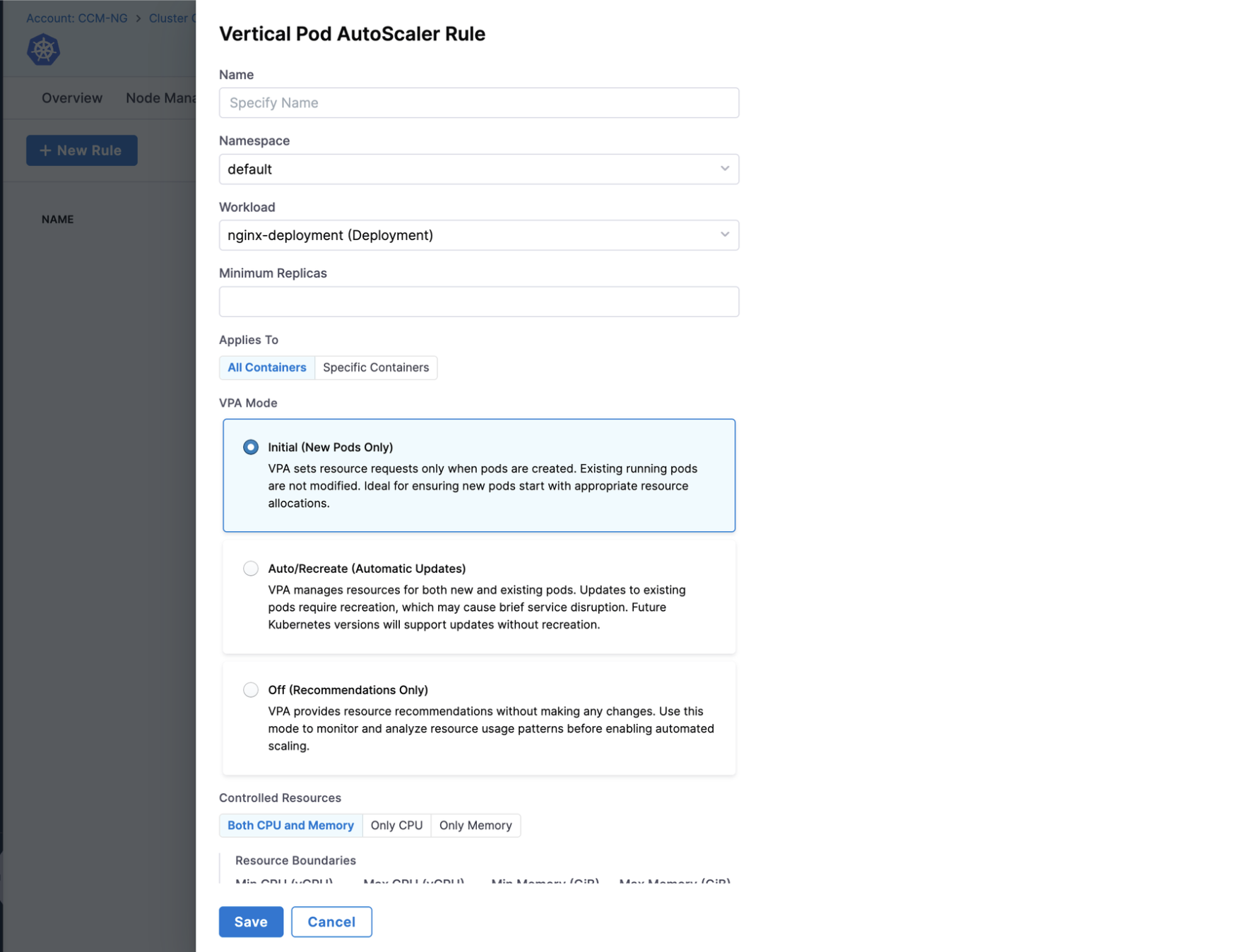
See how to create a VPA rule: Creating a New VPA Rule