Environment Variables
This guide walks you through the steps required to set environment variables for your containers without altering the container images. This feature allows you to manage application configurations and customize development environments to suit your specific requirements.
You can define environment variables in your container using the containerEnv property in the devcontainer.json specification. (Read more about the devcontainer.json configuration here.)
What is "containerEnv"?
containerEnv is a set of name-value pairs where each pair defines an environment variable and its corresponding value. This property sets these variables directly on the Docker container itself, meaning their scope is limited to all processes running inside the container.
Adding containerEnv to devcontainer.json
Here’s how you can include the containerEnv property in your devcontainer.json configuration:
"containerEnv": {
"MY_CONTAINER_VAR": "some-value-here"
}
This property is static for the container’s lifecycle.
Here’s an example of a complete devcontainer.json file with the containerEnv property:
{
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/devcontainers/javascript-node:1-18-bullseye",
"containerEnv": {
"VAR1": "value1",
"VAR2": "value2"
}
}
Verifying Environment Variables
Once you’ve added the containerEnv property, you can verify the environment variable setup by checking the container logs while creating a Gitspace through the Harness UI.
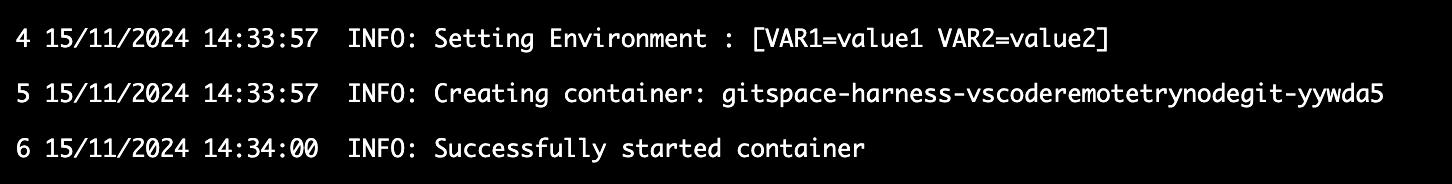
Using Environment Variables
You can start using your environment variables directly within your Gitspaces. To verify, open your Gitspace and launch the Terminal.
Run the following command:
env
This will display the environment variables you’ve configured, as shown in the output below.