Shell Script Provisioning
Harness has first-class support for Terraform, Terragrunt, AWS CloudFormation, Azure ARM and Blueprint provisioners, but to support different provisioners, or your existing shell script implementations, Harness includes Shell Script provisioning.
This topic provides steps on using Harness to provision a target environment or resources using shell scripts.
Important notes
- Harness Shell Script provisioning supports the following deployment types: Physical Data Centers, AWS ECS, AWS Lambda, and Kubernetes on Google Cloud Platform (GKE).
Permissions in your scripts
You need to give Harness permissions in your target environment so Harness can provision using you provisioner script.
You can add secret text and files to your script using Harness built-in secret manager or your own.
For details on using secret managers and secrets, go to:
Harness role permissions required
- Environments:
View/Create,Edit,Access,Delete.
Shell Script provisioning summary
Harness provisioning is categorized into the following use cases:
- Ad hoc provisioning: temporary and on-demand provisioning of resources for specific tasks or purposes.
- Dynamic infrastructure provisioning: provision the target deployment environment as part of the same deployment process. Typically, dynamic infrastructure provisioning is for temporary pre-production environments, such as dev, test, and qa. Production environments are usually pre-existing.
For details on Harness provisioning, go to Provisioning overview.
Dynamic provisioning steps for different deployment types
Each of the deployment types Harness supports (Kubernetes, AWS ECS, etc.) require that you map different script outputs to the Harness infrastructure settings in the pipeline stage.
To see how to set up dynamic provisioning for each deployment type, go to the following topics:
- Kubernetes infrastructure
- The Kubernetes infrastructure is also used for Helm, Native Helm, and Kustomize deployment types.
- Azure Web Apps
- AWS ASG
- AWS ECS
- AWS Lambda
- Spot Elastigroup
- Google Cloud Functions
- Serverless.com framework for AWS Lambda
- Tanzu Application Services
- VM deployments using SSH
- Windows VM deployments using WinRM
$PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH
To understand Harness Shell Script provisioning, it is important to understand the Harness $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH environment variable.
The Harness $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH variable can be used in the Shell Script provisioning script whenever you need to use the JSON output from your script.
For example, here is a shell script that pulls EC2 instance information from AWS:
apt-get -y install awscli
aws configure set aws_access_key_id $access_key
aws configure set aws_secret_access_key $secret_key
aws configure set region us-east-1
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters Name=tag:Name,Values=harness-provisioner > "$PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH"
This script returns a JSON array describing the instances.
The Harness environment variable $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH is initialized by Harness and stores the JSON collection returned by your script.
Now, in subsequent steps in your stage, you can use Harness expressions to reference labels in the JSON collection.
Put quotes around $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH as a best practice. The quotes are only required if the value of the variable will have spaces in it, but they cause no problem in any case.
Here is the YAML for a pipeline that simulates Shell Script provisioning so you can experiment with using the $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH output variable.
Shell Script provisioning simulation
In the stage's Shell Script Provision step, you will see a JSON array echoed and stored in $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH.
In subsequent Shell Script steps, you will see the JSON output referenced using the output expressions for the Shell Script Provision step.
Copy and paste the following YAML into a Harness pipeline, replacing the projectIdentifier and orgIdentifier with your own settings and replacing the secret in the secretvar stage variable with your own text secret.
pipeline:
name: Shell Script ad hoc
identifier: Shell_Script_ad_hoc
projectIdentifier: CD_Docs
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: shellscriptprovision
identifier: shellscriptprovision
description: ""
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: ShellScriptProvision
name: shell1
identifier: shell1
spec:
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo start
echo "{\"Instances\":[{\"Hostname\": \"host1\",\"value\": \"<+stage.variables.testinstance>\"},{\"Hostname\": \"<+stage.variables.secretvar>\",\"value\": \"$test\"}]}" >> "$PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH"
echo finish
environmentVariables:
- name: test
type: String
value: testvar
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: test output
identifier: test_output
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo <+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances>
if [ "<+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances[0].Hostname>" == "host1" ]; then
echo "first host match"
exit 0
else
echo "first host doesnt match"
exit 1
fi;
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
isNestedGroup: false
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: test expression
identifier: test_expression
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo <+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances>
if [ "<+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances[0].value>" == "testhostnamevalue" ]; then
echo "value match"
exit 0
else
echo "value doesnt match"
exit 1
fi;
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: test secret expression
identifier: test_secret_expression
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo <+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances>
if [ "<+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances[1].Hostname>" == "secretHost" ]; then
echo "second host match"
exit 0
else
echo "second host doesnt match"
exit 1
fi;
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: test env var
identifier: test_env_var
spec:
shell: Bash
onDelegate: true
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |-
echo <+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances>
if [ "<+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances[1].value>" == "testvar" ]; then
echo "env var value match"
exit 0
else
echo "env var value doesnt match"
exit 1
fi;
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
tags: {}
variables:
- name: testinstance
type: String
description: ""
value: testhostnamevalue
- name: secretvar
type: Secret
description: ""
value: shellScriptProvisionSecretHost
When you run this pipeline, the Shell Script Provision step show that the $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH environment variable has been initialized on the Harness Delegate.
"PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH" has been initialized to "/opt/harness-delegate/shellScriptProvisioner/F__QtYt1QdOyAc3QKUFIIA-zTte04H7SsG6iU9VIRxOAA-shell1/output.json"
When you select the Output tab of the executed Shell Script Provision step, you can see all of the outputs from the JSON. To reference an output, you simply copy its Output Name:
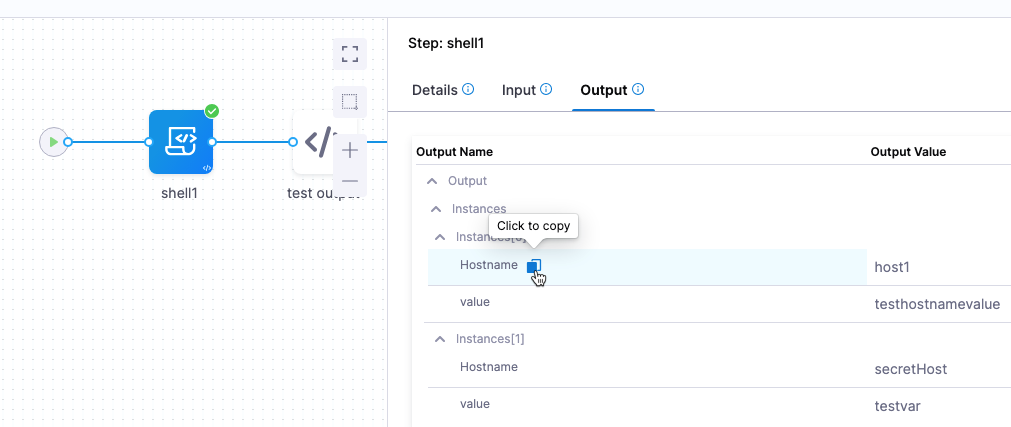
For example:
<+pipeline.stages.shellscriptprovision.spec.execution.steps.shell1.output.Instances[0].Hostname>
Using the expression in ad hoc and dynamic provisioning
The Harness $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH variable can be used in the Shell Script Provision step when it is used for ad hoc or dynamic provisioning, but it is mandatory for dynamic provisioning and anytime you want to produce some output from the Shell Script Provision step script.
Create Shell Script Provision step
The Shell Script Provision step runs the an inline or remote Bash script to provision your resources.
Script location
You can add your provisioning script inline in the Shell Script Provision step or store it in the Harness File Store.
Script
Your provisioning script can be used for ad hoc or dynamic provisioning.
For details on Harness provisioning, go to Provisioning overview.
If you want to use the outputs from your script, you need to use the Harness $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH environment variable.
For details on $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH, go to $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH in the current topic.
Script Input Variables
While you can simply declare a variable in your script using a Harness expression or string for its value, using Input Variables provides some additional benefits:
You can more easily identify and manage the Harness expressions used in your script. You can template your script.
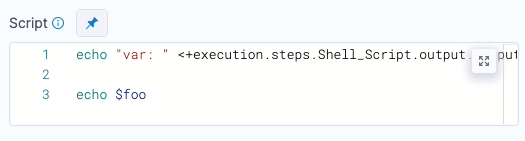
You can declare the variable using Name and Value in Script Input Variables and then reference the variable in the script just as you would any other variable: $var_name.
You can also use expressions in Value. For example, if you have an output variable from a previous Shell Script step, you can copy it from the executed step Outputs tab and use it in Value.
To use an expression, in Script Input Variables, select Expression and paste the expression in Value:
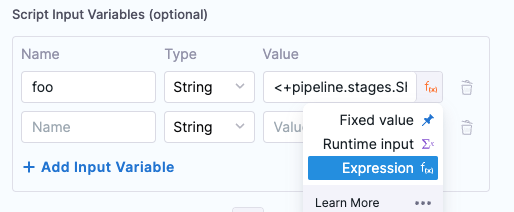
In the Script, you declare the variable using the Name from Script Input Variables (in this example, foo).
Rollback
Shell Script provisioning in Harness does not include rollback steps like the Harness provisioning support using Terraform, etc.
For rollback, you must add your own scripts to the Rollback section of the stage Environment (dynamic provisioning) or Execution (ad hoc provisioning).
Ad hoc provisioning
You can add the Shell Script Provision step to the Execution section of a CD Deploy stage. In the step, you add a script that provisions resources in your environment.
If you want to use the outputs from your script, you need to use the Harness $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH environment variable.
For details on $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH, go to $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH in the current topic.
Dynamic infrastructure provisioning
For dynamically provisioning the target deployment environment, you add the Shell Script Provision step to the Environment section of the CD Deploy stage.
Next, you map specific outputs from your script to the required settings in the Infrastructure Definition for the stage.
Adding dynamic provisioning to the stage
-
In the CD Deploy stage, enable the Provision your target infrastructure dynamically during the execution of your Pipeline option.
-
In What type of provisioner do you want to use?, select Script.
The Shell Script Provision step is added.
-
Configure the Shell Script Provision step with your provisioning script.
-
For dynamic provisioning, you must map the outputs from your script to the Harness Infrastructure Definition for the stage. You must use the Harness
$PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATHenvironment variable to capture the JSON output of your script.For details on
$PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH, go to $PROVISIONER_OUTPUT_PATH in the current topic.
Mapping script outputs to the Infrastructure Definition
Once you have added dynamic provisioning to the Environment section of the stage, you must map specific script outputs to the required Harness Infrastructure Definition used by the stage.
The following table shows the Infrastructure Definition settings that are mapped to Shell Script provisioner outputs.
| Infra type | Infra settings that require mapping |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes GCP | Namespace, Cluster, Release Name (optional) |
| Physical Data Center | Host Array Path, Host Attributes |
| SSH and WinRM on AWS | Region, Tags |
| SSH and WinRM on Azure | Subscription Id, Resource Group, Tags |
| AWS Lambda | Region |
| AWS ECS | Region, Cluster |
Steps on mapping outputs for each deployment type are covered in their topics:
- Kubernetes infrastructure
- This includes Kubernetes, Helm, Kustomize, and Native Helm.
- VM deployments using SSH
- Also covers Physical Data Center.
- Windows VM deployments using WinRM
- Also covers Physical Data Center.
- Azure Web Apps
- AWS ECS
- AWS Lambda