Google Cloud Run Deployments
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag CDS_GOOGLE_CLOUD_RUN. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
This guide explains how to deploy artifacts to Google Cloud Run using Harness.
Overview
Harness supports deploying both Google Cloud Run Services and Google Cloud Run Jobs.
- A Google Cloud Run Service is a stateless containerized application that scales automatically based on traffic. It is ideal for APIs, websites, and event-driven backends.
- A Google Cloud Run Job is designed for task-based execution and runs to completion, making it ideal for batch processing, scheduled tasks, or background workloads.
Follow these steps to set up a Google Cloud Run Service in Harness:
Interactive guide
- Interactive guide
Here is an interactive guide to setup your Cloud Run Service pipeline.
Create a CD Pipeline
- In the Harness UI, create a new CD pipeline.
- Add a Deploy stage and select Google Cloud Run as the deployment type.
- Click Set Up Stage.
Configure the Service
Only Google Artifact Repository and Docker Registry are supported as artifact repositories.
- Select Add Service and add the Google Cloud Run Service Manifest Definition. This defines the containerized application compatible with Google Cloud Run.
- Save the new service.
Configure the Environment and Infrastructure
-
Select New Environment, provide a name for the environment, and click Save.
-
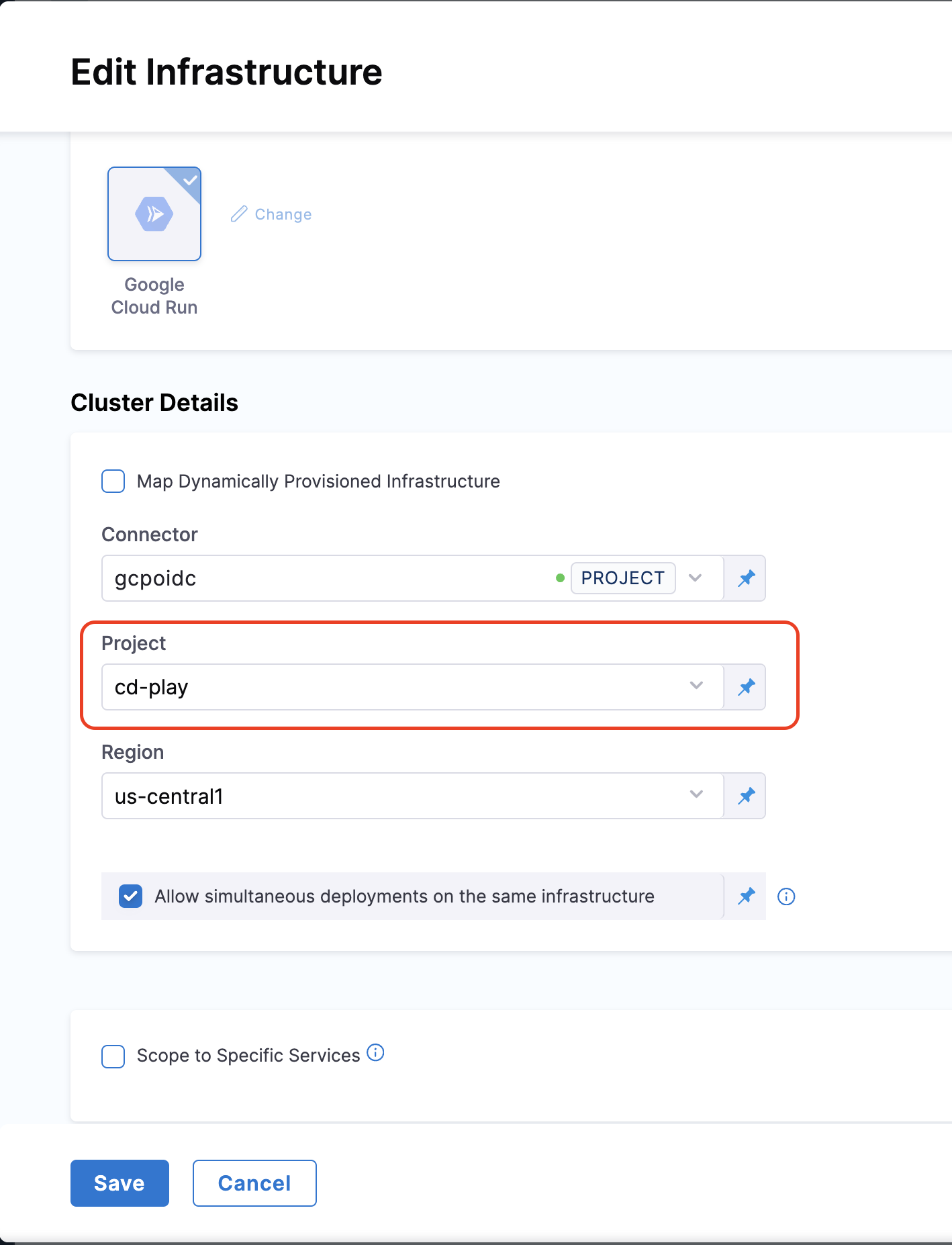
In the Infrastructure Definition section, click New Infrastructure and configure the following details:
- Harness GCP Connector: Create or select a Harness GCP connector to authenticate with your Google Account.
- GCP Project: Specify the project ID to define the target GCP project.
- GCP Region: Select the region where the Cloud Run service will be deployed.
-
Save the infrastructure configuration.
GCP Authentication Support
Harness supports the following methods for GCP authentication:
-
Google OIDC Support:
Create an OIDC connector to connect to the GCP account. For more details, refer to Use OpenID Connect (OIDC) Connector. -
Service Account:
Create a GCP connector by providing a Service Account. For more details, refer to Create a GCP connector.
Enable Cross-Project Access
You can have one connector scoped to multiple GCP projects, eliminating the need to create separate connectors for each project. With this feature, the connector will allow access to multiple GCP projects.
Prerequisite : For OIDC-based connectors, the associated service account (SA) must have cross-project access.
- Project (required): It can refer to a different project than the one configured in the connector, or the same project
- Region (required): It refers to the region where the container will be deployed.
Configure the Execution
In the Execution tab, select the deployment strategy. Currently, Harness supports the Basic and Canary deployment strategies for Google Cloud Run Service.
Harness automatically adds the Deploy Cloud Run Step Group based on the strategy you select.
The Basic Strategy includes the following steps:
-
Download Manifest
-
Google Cloud Run Prepare Rollback
-
Google Cloud Run Deploy Step
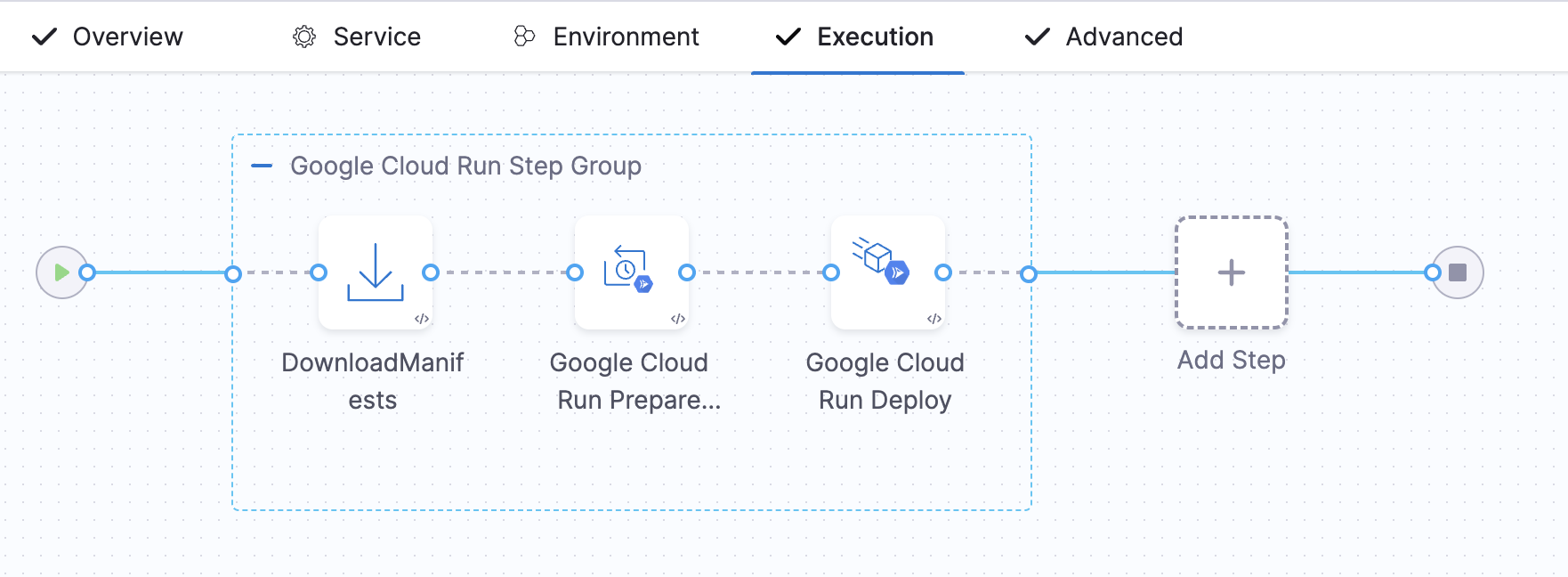
Optionally, you can add a Google Cloud Run Traffic Shift Step.
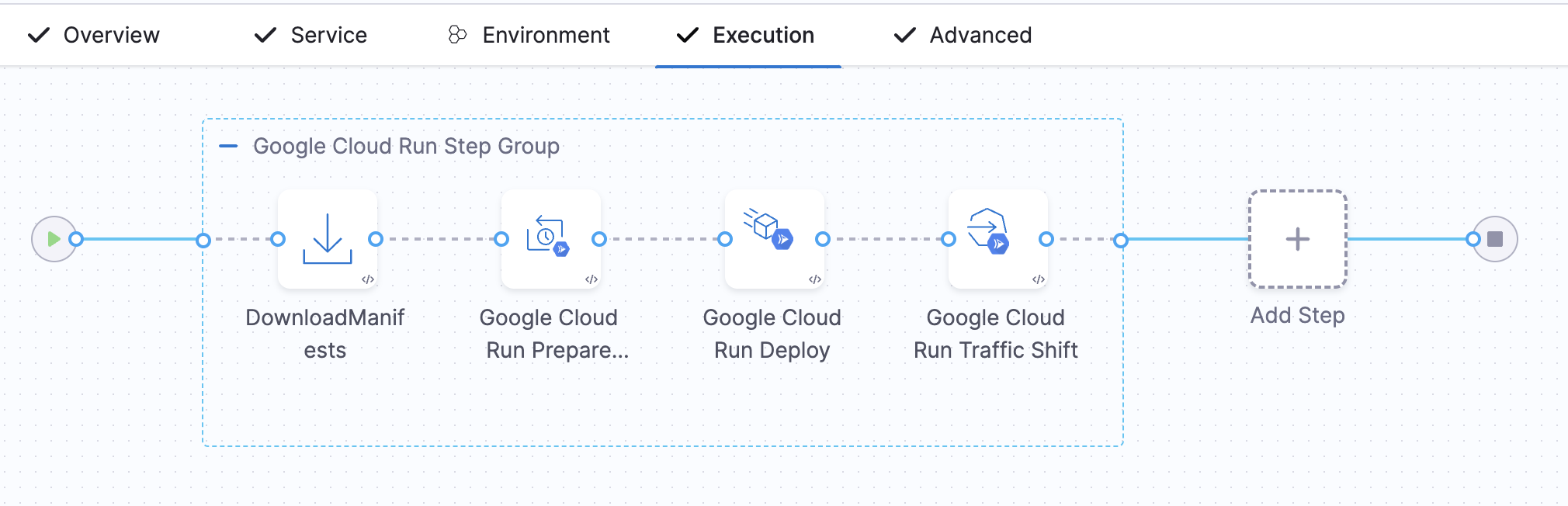
The Canary Strategy includes the following steps:
- Download Manifest
- Google Cloud Run Prepare Rollback
- Google Cloud Run Deploy Step
- Google Cloud Run Traffic Shift Step
Download Manifest
- Purpose: Downloads the manifest specified in the service.
- Details: The manifest contains all the configuration details necessary for deploying the service.
Google Cloud Run Prepare Rollback
- Purpose: Fetches and saves the current deployment configurations for potential rollback scenarios.
- Details:
- Uses the
gcloud run services describecommand to retrieve service details. - Saves configuration details for use during rollback if required.
- For more information, see the Google Cloud Run Documentation.
- Uses the
Google Cloud Run Deploy Step
- Purpose: Applies the YAML manifest to create a new service or revision.
- Details:
- Executes the
gcloud run services replacecommand to deploy the service. - Updates the container image in the YAML manifest to match the specified artifact.
- Harness fetches and logs instance details using the Google Cloud Monitoring SDK.
- Additional configuration options can be specified under Google Cloud Run Services Replace Command Options.
- For more information, see the Google Cloud Run Documentation.
- Executes the
We do not use the Google Run Deploy command here as this command takes every field as a command flag. Instead, we use the replace command and replace all the configurations provided in the YAML file.
Skip Traffic Shift
The Deploy step includes a Skip Traffic Shift option that allows you to create a new revision without immediately shifting traffic to it.
Configuration:
- step:
type: GoogleCloudRunDeploy
name: Google Cloud Run Deploy
identifier: Google_Cloud_Run_Deploy
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: harness/google-cloud-run-plugin:1.0.0-linux-amd64
imagePullPolicy: Always
skipTrafficShift: true
timeout: 10m
When skipTrafficShift: true:
- The Deploy step only creates a new revision without shifting traffic to it
- Traffic shifting will be performed explicitly in the Google Cloud Run Traffic Shift step
- When disabled (default), traffic shifts to the new revision immediately upon deployment
For the first deployment, traffic is always shifted to the new revision regardless of this setting. This applies to subsequent deployments only.
Google Cloud Run Traffic Shift Step
- Purpose: Manages traffic distribution across different revisions of the service.
- Details:
- Uses the
gcloud run services update-trafficcommand. - Allows users to specify the percentage of traffic each revision should handle.
- For more information, see the Google Cloud Run Documentation.
- Uses the
Tags
The Traffic Shift step supports assigning tags to revisions. Tags provide named aliases for revisions (e.g., 'stable', 'canary', 'latest') and create named URLs for accessing specific revisions.
Configuration:
- step:
type: GoogleCloudRunTrafficShift
name: Google Cloud Run Traffic Shift
identifier: Google_Cloud_Run_Traffic_Shift
spec:
revisionTrafficDetails:
- revisionName: latest
trafficValue: 100
tag: canary, latest
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: harness/google-cloud-run-plugin:1.0.0-linux-amd64
imagePullPolicy: Always
Field Details:
revisionName- The name of the Cloud Run revisiontrafficValue- The percentage of traffic to route to this revision (0-100)tag(optional) - Comma-separated list of tags to assign to this revision
If any tags are provided, all existing tags in the service will be removed and replaced with the new ones. If no tags are specified, existing tags will remain unchanged.
Container Configuration
For Container Registry, create or select a Docker connector to access the container registry. Use the following public Docker images:
- Docker Hub:
harness/google-cloud-run-plugin:1.0.4-linux-amd64 - GAR:
- Europe region: GAR Image Repository for Google Cloud Run Plugin (Europe)
This image is required to perform deployments to Google Cloud Run
Optional Configurations
Harness allows for several optional configurations to customize deployment behavior:
- Pre-Execution Command: Run commands before deployment.
- Image Pull Policy: Specifies when to pull the container image from the registry.
- Run as User: Configures the user identity for security and access control.
- Limit Memory: Defines the maximum memory for the container or function.
- Limit CPU: Sets a limit on CPU usage for the container or function.
- Environment Variables: Additional environment variables can be configured.
Rollback Steps
Harness provides rollback functionality to revert to previous configurations or states:
- First Deployment: Deletes the service using the
gcloud run services deletecommand. - Subsequent Deployments: Redirects traffic to older revisions using the
gcloud run services update-trafficcommand.
Google Cloud Run does not allow deletion of the new revision; only traffic can be diverted to previous revisions.
Google Cloud Run Job Step
You can add a Google Cloud Run Job step in the Execution tab.
- Interactive guide
Here is an interactive guide to setup your Cloud Run Job Stage.
Container Configuration
For Container Registry, create or select a Docker connector to access the container registry. Use the following public Docker image:
This image is required to perform deployments to Google Cloud Run.
You can define your job using either Job Name or Job Manifest.
Job Name: Select Job Name when you already have a job defined in your Google Cloud Platform and you only want to execute it.
- Under Job Name, specify the name of the job you want to run.
- You can also make it a Runtime Input or an Expression.
Job Manifest: Select Job Manifest when you want to deploy a new job or update an existing job using a manifest file.
- Click + Google Cloud Run Job Manifest.
- In the Specify Google Cloud Run Job Manifest Store, select the source where the manifest file is stored.
- In Manifest Details, specify the path where the manifest file is stored.
If you are deploying a container-based Google Cloud Run Job, ensure that you:
- Create a Step Group by clicking on Add Step Group in the execution tab.
- Provide the Name of the Step Group. Enable the Enable Container-Based Execution toggle.
- Provide Kubernetes Cluster details.
- Add the Google Cloud Run Job Step to the Step Group.
These steps are necessary for successful execution.
Deploy Step
The deploy step uses the deploy gcloud run jobs replace command and execute gcloud run jobs execute command in sequence.
For more information on gcloud run jobs replace command, refer to the Google Documentation.
For more information on gcloud run jobs execute command, refer to the Google Documentation.
Optional Configurations
You can provide additional command options (flags) in the Optional Configuration section:
- Google Cloud Run Jobs Replace Command Options: Used for the replace function.
- Google Cloud Run Jobs Execute Command Options: Used for the execute function.
Additionally, you can configure the following options:
- Pre-Execution Command: Run commands before deployment.
- Image Pull Policy: Specifies when the container image should be pulled from the registry.
- Run as User: Configures the user identity under which the function or container should run, useful for security and access control.
- Limit Memory: Defines the maximum memory that can be allocated to the container or function during execution.
- Limit CPU: Sets a limit on the CPU usage for the function or container, ensuring the function does not consume excessive resources.
- Environment Variables: Additional environment variables can be configured.
Cloud Run Permission Requirements
Cloud Run Minimum Permissions
The following are the minimum set of permissions required for deploying Google Cloud Run services:
-
List, Get, and Describe Services:
run.services.listrun.services.get
-
Create or Deploy Services:
run.services.createrun.services.update
-
Delete Services:
run.services.delete
-
Manage Cloud Run Jobs:
run.jobs.createrun.jobs.updaterun.jobs.getrun.jobs.run
-
Invoke Cloud Run Services (if needed for execution):
run.routes.invoke
-
Get Service Monitoring Data for Instance Sync:
monitoring.timeSeries.list
-
View Configuration and Permissions:
run.configurations.listrun.configurations.get
-
Manage IAM Policies for Services:
resourcemanager.projects.getIamPolicyresourcemanager.projects.setIamPolicy
-
Authentication Using OIDC:
iam.workloadIdentityPools.createCredentialConfig
-
Authentication Using Service Account Key:
iam.serviceAccounts.getiam.serviceAccounts.signBlob
- Service Account Impersonation:
iam.serviceAccounts.actAs- Required on the service identity used for Cloud Run (the
serviceAccountNameconfigured for the Cloud Run service). - This permission is needed even if the deployer service account and Cloud Run service identity are the same account.
- If no custom service account is configured, this permission is required on the Compute Engine default service account.
Alternatively, the following roles can also be used:
-
Cloud Run Admin (
roles/run.admin):- Grants full administrative access to manage Cloud Run services, including creating, updating, and deleting services.
- Essential for deploying services to Cloud Run.
-
Service Account User (
roles/iam.serviceAccountUser):- Grants permission to use service accounts, which are required to run Cloud Run services.
- This role must be assigned on the service identity used for Cloud Run (the
serviceAccountNameconfigured for the Cloud Run service, or the Compute Engine default service account if not specified). - Required even when the deployer service account and Cloud Run service identity are the same account.
-
Logging Viewer (
roles/logging.viewer):- Access to logs for debugging Cloud Run services.
-
Monitoring Viewer (
roles/monitoring.viewer):- Permission to view service monitoring data.
-
IAM Workload Identity Pool Admin (
roles/iam.workloadIdentityPoolAdmin):- This role grants you the necessary permissions to create, update, and delete workload identity pools and providers.
Google Cloud Run Sample
To see an example of how to deploy Google CLoud Run Service using Harness, visit the Harness Community Repository.
This repository provides a ready-to-use sample application and the necessary configuration files to help you get started quickly.
Manifest Format and CLI Compatibility
Harness uses the gcloud run CLI commands in the background for Google Cloud Run deployments. This means we support all manifest formats that are compatible with gcloud run commands, providing full flexibility in how you define your Cloud Run services.
Harness executes gcloud run CLI commands in the background for Google Cloud Run steps. Therefore, we support all manifest formats that are compatible with these commands, including:
gcloud run services replacefor service deploymentsgcloud run jobs replaceandgcloud run jobs executefor job deployments- All standard Cloud Run YAML configurations and Knative serving specifications
This ensures full compatibility with Google Cloud Run's native deployment mechanisms.
For detailed YAML reference and manifest specifications, refer to the official Google Cloud Run YAML Reference documentation.
Limitations and Troubleshooting
Invalid Service Name Error
Google Cloud Run service names must use only lowercase alphanumeric characters and dashes. Underscores are not allowed. If you encounter Invalid resource name errors, replace underscores with dashes in your service name (e.g., my_service → my-service). For details, see Google Cloud Run naming conventions.
Authentication Error with "Inherit from Delegate" Mode
Issue: Pipeline fails when using a GCP connector configured with the Inherit from Delegate authentication mode, displaying the following error:
Executing command: /google-cloud-sdk/bin/gcloud auth list --filter="status:ACTIVE" --format="value(account)"
ERROR: (gcloud.auth.list) Name expected [ table[title='Credentialed Accounts'](
status.yesno(yes='*', no=''):label=ACTIVE,
account
) *HERE* "value(account)"].
Google Cloud Run plugin execution failed with error:
An error occurred while setting up google cloud credentials:
Error running gcloud auth list command: error executing command: exit status 1
Root Cause: This issue occurs when the Google Cloud SDK in the plugin container outputs additional messages (such as update notifications or survey prompts) along with the account information. These extra messages interfere with the expected output format of the gcloud auth list command, causing the authentication setup to fail.
Example of problematic output:
customer-success-244100.svc.id.goog
Updates are available for some Google Cloud CLI components. To install them,
please run:
$ gcloud components update
To take a quick anonymous survey, run:
$ gcloud survey
Solution: Use the updated Google Cloud Run plugin image that handles these additional messages correctly:
harness/google-cloud-run-plugin:1.0.4-linux-amd64
Steps to Update:
- Navigate to your pipeline's Execution tab.
- Locate the Google Cloud Run Deploy Step or Google Cloud Run Job Step.
- In the Container Configuration section, update the image reference to:
- Docker Hub:
harness/google-cloud-run-plugin:1.0.4-linux-amd64
- Docker Hub:
- Save and re-run your pipeline.
The updated plugin image (1.0.4) includes improved parsing logic that filters out extraneous messages from the gcloud CLI output, ensuring reliable authentication when using the "Inherit from Delegate" mode.
This issue specifically affects deployments using GCP connectors configured with Inherit from Delegate authentication. If you're using Service Account or OIDC authentication methods, you may not encounter this issue.