Perform a Kubernetes dry run
This topic discusses how to set up the Dry Run step for a Kubernetes deployment.
The Dry Run step fetches the Kubernetes manifests or Helm charts in a stage and performs a dry run of those resources. This is the same as running a kubectl apply --filename=manifests.yaml --dry-run.
You can use the Dry Run step to check your manifests before deployment. You can follow the step with an Approval step to ensure the manifests are valid before deployment.
You can reference the resolved manifest from the Dry Run step in subsequent steps using a Harness variable expression.
<+pipeline.stages.[Stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[Step_Id].k8s.manifestDryRun>
When Harness performs a deployment, it compiles all values YAML files and manifests in the stage as a single manifest and applies it. The Dry Run step performs the dry run using this compiled manifest.
Limitations
The Dry Run step's resolved manifests are stored in the Harness cloud. There is a storage limit of 5MB per Dry Run step execution.
Add the Dry Run step
You add the Dry Run step before the deployment step(s) in your stage (such as the Apply, Rolling, Canary, Blue Green deployment steps).
You can add an Approval step after the Dry Run step to have a Harness user(s) validate the manifest output before deployment.
For example, here is a stage with a Dry Run step followed by an Approval step and subsequent Rolling Deployment step.
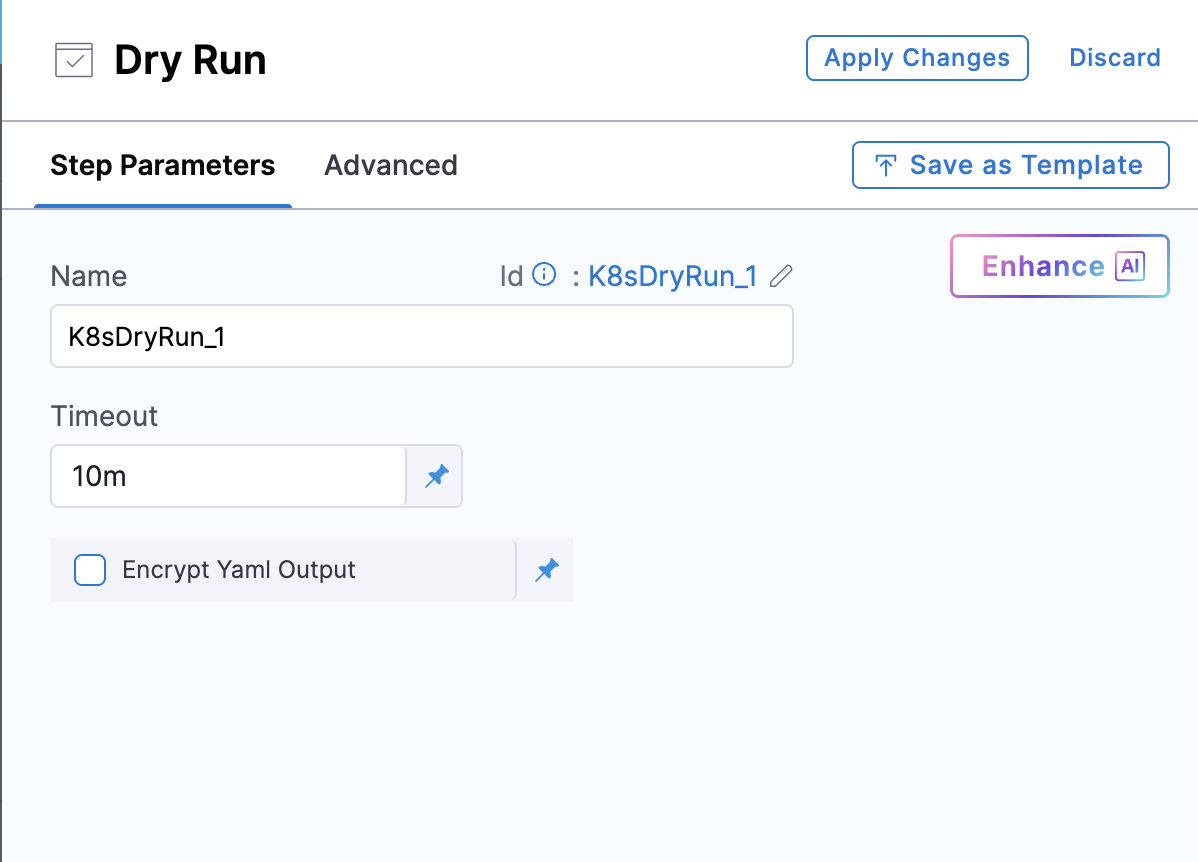
To add the Dry Run step, do the following:
- Visual
- YAML
-
In the CD stage Execution, select Add Step.
-
Select the Dry Run step.
-
Enter a name for the step.
-
(Optional) Enable Encrypt Yaml Output if you want the entire step output to be treated as a Harness secret. For more details on how this affects secret masking, go to Secret masking in Dry Run output.
-
In Timeout, enter how long this step should run before failing and initiating the step or stage failure strategy.
You can use:
wfor weeks.dfor days.hfor hours.mfor minutes.sfor seconds.msfor milliseconds.
The maximum is
53w.Timeouts can be set at the pipeline-level also, in the pipeline Advanced Options.
-
Select Apply Changes.
The Dry Run step is ready.
- In Pipeline Studio, select YAML.
- Paste the following YAML example and select Save:
- step:
type: K8sDryRun
name: Output Service Manifests
identifier: OutputService
spec:
encryptYamlOutput: false
timeout: 10m
Set encryptYamlOutput to true to treat the entire manifest output as a Harness secret. For more details on how this affects secret masking, go to Secret masking in Dry Run output.
Secret masking in Dry Run output
By default, the Dry Run step masks sensitive values in the rendered manifest output. When your service manifests include Kubernetes Secret resources, Harness replaces the values inside the data field with a masked placeholder. The masked value appears as Kioq, which is the Base64-encoded form of ***.
For example, if your Secret manifest contains a data field like password: cGFzc3dvcmQxMjM=, the Dry Run step output will instead show password: Kioq. Other resource types such as Deployments, ConfigMaps, and Services are rendered as-is without masking.
This default masking prevents accidental exposure of sensitive data in step logs and the Harness UI while still producing a structurally valid Kubernetes manifest.
Encrypt Yaml Output
The Dry Run step includes a Encrypt Yaml Output toggle that changes how the step handles secret masking. When this option is enabled, Harness does not mask individual secret values during manifest rendering. Instead, it marks the entire step output as a Harness secret.
With this toggle enabled:
- The rendered manifest retains the original secret values (no per-field masking).
- The entire
manifestDryRunstep output is marked as a secret, so it displays as***in the Harness UI and logs. - You can still reference the output using the Harness expression in subsequent steps, and the expression resolves to the full, unmasked manifest at runtime.
<+pipeline.stages.[Stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[Step_Id].k8s.manifestDryRun>
This is useful when downstream steps need access to the complete, unmasked manifest for processing, while still ensuring the raw output is not visible in the pipeline execution UI.
Step output example
When you run the pipeline, the output of the Dry Run step indicates that the manifest was applied as a dry run using (dry run):
Validating manifests with Dry Run
kubectl --kubeconfig=config apply --filename=manifests-dry-run.yaml --dry-run
namespace/dev created (dry run)
configmap/nginx-k8s-config created (dry run)
service/nginx-k8s-svc created (dry run)
deployment.apps/nginx-k8s-deployment created (dry run)
Done.
Using the Dry Run step output in other steps
You can reference the resolved dry run manifest from the Dry Run step using this Harness expression:
<+pipeline.stages.[Stage_Id].spec.execution.steps.[Step_Id].k8s.manifestDryRun>
For example, if the stage Id is Deploy and the Dry Run step Id is Dry_Run the expression would be:
<+pipeline.stages.Deploy.spec.execution.steps.Dry_Run.k8s.manifestDryRun>
Another example is to use a Harness Shell Script step to perform logic using kubectl diff:
cat << 'EOM' > manifest.yaml
<+pipeline.stages.Deploy.spec.execution.steps.Dry_Run.k8s.manifestDryRun>
EOM
cat manifest.yaml
echo "K8s client/server version:"
kubectl version --output yaml
echo "K8s manifest diff:"
# kubectl diff exist codes: 0 - no diff, 1 - there is a diff, 2 - something is wrong
# Since exit code 1 is failure, make will always fail if there is a diff, so code modification required
kubectl -n <+env.variables.DEPLOY_ENV> diff -f manifest.yaml || (st=$?; if [ $st = 1 ]; then exit 0; else echo $st; exit $st; fi)
If you do not quote the ('EOM'), any variables and commands within the block will be substituted.
You can enter the expression in subsequent steps such as the Shell Script step or Approval steps.
Dry Run steps and Skip Dry Run settings
The Apply, Rolling, Canary, and Blue Green deployment steps include a Skip Dry Run setting.
By default, Harness uses the --dry-run flag on the kubectl apply command for all these steps. If the Skip Dry Run setting is selected, Harness will not use the --dry-run flag.
The Skip Dry Run setting is different from the Dry Run step. The Dry Run step only performs a dry run. The Dry Run step does not impact whether or not a deployment step performs a dry run.
Using the Dry Run with a Native Helm Deployment
When using the Dry Run step with a native Helm deployment, Harness will run a Helm template and render the manifests. In the Dry Run step log you will see something like this:
KUBECONFIG=/opt/harness-delegate/repository/k8s/7d800125-18f7-3ad9-9db4-a32ec8876c3e/config /opt/harness-delegate/client-tools/helm/v3.12.0/helm template release-10b758 /opt/harness-delegate/repository/k8s/7d800125-18f7-3ad9-9db4-a32ec8876c3e/manifest-files/nginx-ingress-controller --namespace dev -f values-0.yaml
The above will run the Helm template against the manifests fetched. After running the Helm template, Harness will then perform the dry run on the templated and rendered manifest resources.
Validating manifests with Dry Run
kubectl --kubeconfig=config apply --filename=manifests-dry-run.yaml --dry-run=client
configmap/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller-default-backend created (dry run)
serviceaccount/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
service/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
service/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller-default-backend created (dry run)
deployment.apps/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller created (dry run)
deployment.apps/release-10b758-nginx-ingress-controller-default-backend created (dry run)
ingressclass.networking.k8s.io/nginx created (dry run)