Getting Started with Deployments
This guide walks you through creating your first deployment pipeline in Harness Continuous Delivery (CD). You'll build a complete pipeline from scratch, step by step.
New to Harness CD?
Start with the CD Overview to understand key concepts, including Services, Environments, Pipelines, and Deployment Strategies.
What you'll accomplish:
- Create a deployment pipeline
- Configure a service (what to deploy)
- Set up an environment (where to deploy)
- Choose an execution strategy
- Run your first deployment
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A Harness account - Sign up for free
- Access to a Harness project - Use the Default Project or create your own
Platform-Specific Prerequisites
Select your deployment platform to see all requirements and set up connectors:
- Kubernetes
- SSH / Traditional
- Google Cloud Run
- Azure
- AWS Lambda
Infrastructure Requirements:
- A Kubernetes cluster (local like K3D, or cloud-managed like GKE, EKS, AKS)
kubectlaccess to your cluster- Application deployed to a container registry (Docker Hub, ECR, GCR, etc.)
- A Harness Delegate installed - Required to connect to your cluster. Follow the delegate installation guide
Quick Verification:
# Verify kubectl access
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
Required Connectors:
-
Kubernetes Cluster Connector - Connects Harness to your cluster
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → Kubernetes Cluster
- Choose connection method (Delegate, Service Account, etc.)
- Follow: Create a Kubernetes connector
-
Git Connector - For storing Kubernetes manifests
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket
- Provide repository URL and authentication (Personal Access Token recommended)
- Follow: Git connector setup
-
Docker Registry Connector - For pulling container images
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → Docker Registry
- For Docker Hub: Use
https://registry.hub.docker.com/v2/ - For ECR/GCR/ACR: Use respective registry URLs
- Follow: Docker Registry connector
Infrastructure Requirements:
- Target VMs or servers (on-premises or cloud)
- SSH key-based authentication configured
- Application artifacts in a repository (Artifactory, Nexus, S3, etc.)
- A Harness Delegate installed - Required to execute deployment commands on your servers. Follow the delegate installation guide
SSH Key Setup:
# Generate SSH key if needed
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f ~/.ssh/harness_deploy
# Copy public key to target servers
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/harness_deploy.pub user@server-ip
Required Connectors:
-
SSH Key Secret - Store your private SSH key
- Go to Project Setup → Secrets → New Secret → File
- Upload your private SSH key file
- Follow: SSH secret setup
-
SSH Connector - Connects to your servers
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → SSH
- Provide host details and select SSH key secret
- Follow: Add and reference SSH secrets
-
Artifact Repository Connector - For application packages
- For Artifactory: Go to Connectors → New Connector → Artifactory
- For Nexus: Go to Connectors → New Connector → Nexus
- For S3: Go to Connectors → New Connector → AWS → Configure S3 access
- Follow: Artifactory connector settings
Infrastructure Requirements:
- A GCP project with billing enabled
- For Cloud Run: Cloud Run API enabled
- For GKE: A GKE cluster
- Container image in GCR or Artifact Registry
Enable Required APIs:
# Enable Cloud Run API
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com
# Enable Artifact Registry
gcloud services enable artifactregistry.googleapis.com
# Enable Container Registry (if using GCR)
gcloud services enable containerregistry.googleapis.com
Required Connectors:
-
GCP Connector - Connects Harness to Google Cloud
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GCP
- Choose authentication: Service Account Key or GCE VM
- Provide service account key (JSON) with required permissions
- Follow: GCP connector setup
Required GCP Permissions:
- Cloud Run:
roles/run.admin - Artifact Registry:
roles/artifactregistry.reader - GKE:
roles/container.developer
-
Git Connector (if using Git for manifests)
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GitHub/GitLab
- Provide repository URL and authentication
- Follow: Git connector setup
-
GCR/Artifact Registry Connector - For container images
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GCR/GAR
- Select your GCP connector
- Specify registry hostname
- Follow: GCR connector setup
Infrastructure Requirements:
- An Azure subscription with appropriate permissions
- For Functions: Function App created in Azure Portal
- For Web Apps: App Service plan configured
- Application package or container image ready
Azure CLI Verification:
# Login to Azure
az login
# Verify subscription
az account show
# List resource groups
az group list
Required Connectors:
-
Azure Connector - Connects Harness to Azure
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → Azure
- Choose authentication: Service Principal or Managed Identity
- Provide:
- Application (Client) ID
- Tenant ID
- Client Secret (create as Harness Secret first)
- Follow: Azure connector setup
Required Azure Permissions:
- Contributor role on resource group
- Or specific:
Microsoft.Web/sites/*for Web Apps/Functions
-
Git Connector (for configuration files)
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GitHub/GitLab
- Provide repository URL and authentication
- Follow: Git connector setup
-
Azure Container Registry Connector (for containerized apps)
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → Docker Registry
- Use ACR login server URL (e.g.,
myregistry.azurecr.io) - Authenticate using Azure credentials or ACR admin credentials
- Follow: ACR connector setup
Infrastructure Requirements:
- An AWS account with appropriate IAM permissions
- Lambda execution role with required policies
- S3 bucket for deployment packages (or ECR for container images)
- Deployment package (ZIP file) uploaded to S3
AWS CLI Verification:
# Verify AWS credentials
aws sts get-caller-identity
# List S3 buckets
aws s3 ls
# Verify Lambda access
aws lambda list-functions --region us-east-1
Required Connectors:
-
AWS Connector - Connects Harness to AWS
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → AWS
- Choose authentication method:
- Access Key (recommended for getting started)
- IAM Role (recommended for production)
- IRSA (for EKS)
- For Access Key method:
- Create a secret for Access Key ID
- Create a secret for Secret Access Key
- Follow: AWS connector setup
Required IAM Policies:
AWSLambda_FullAccessorAWSLambdaFullAccessIAMReadOnlyAccess(for role verification)AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess(for artifact retrieval)
-
Git Connector - For Lambda function definitions
- Go to Project Setup → Connectors → New Connector → GitHub/GitLab
- Provide repository URL and authentication
- Example repo:
https://github.com/harness-community/harnesscd-example-apps - Follow: Git connector setup
-
AWS Secrets - Store AWS credentials
- Go to Project Setup → Secrets → New Secret → Text
- Create two secrets:
aws_access_key_id: Your AWS Access Key IDaws_secret_access_key: Your AWS Secret Access Key
- These will be used in the AWS connector
Pre-Deployment Setup:
- Upload your Lambda deployment package (ZIP) to S3 bucket
- Note the bucket name and file path - you'll need these in Step 3
- Ensure Lambda execution role ARN is ready - you'll need it in the function definition
Important Notes:
- Complete all connector setups before proceeding - You'll select these connectors in the following steps
- Test each connector - Use the "Test Connection" button to verify connectivity
- Save connector identifiers - You'll reference these by name when configuring services and environments
Step 1: Create Your Pipeline
Follow these steps to create your first deployment pipeline.
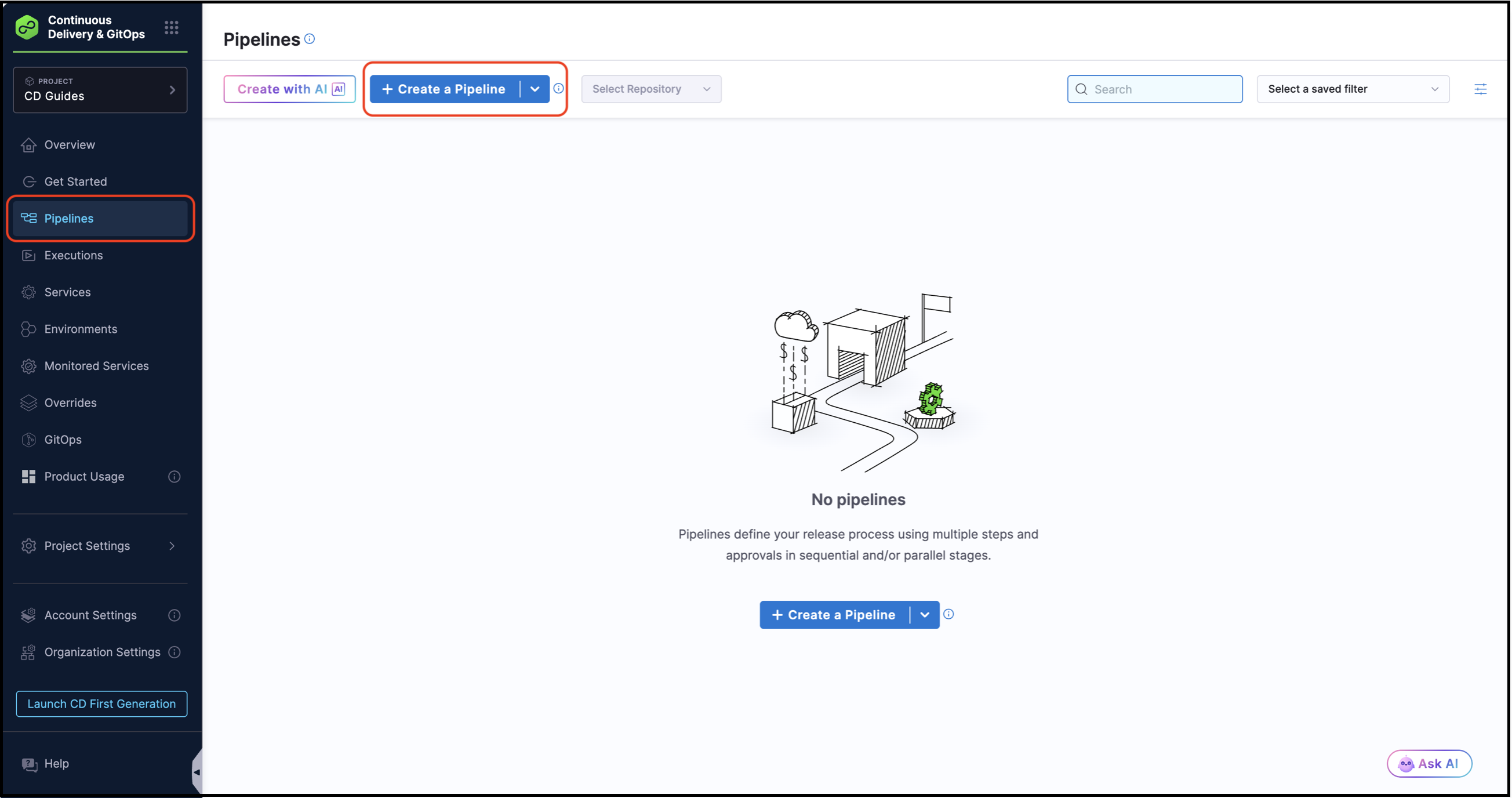
1. Navigate to Pipelines
- From your Harness project, select Pipelines from the left navigation menu.
- Click + Create a Pipeline.
2. Configure Pipeline Basics
- Provide a Name for your pipeline (e.g., "Deploy to Production")
- Choose Inline for Pipeline Storage (stores configuration in Harness)
- Click Start
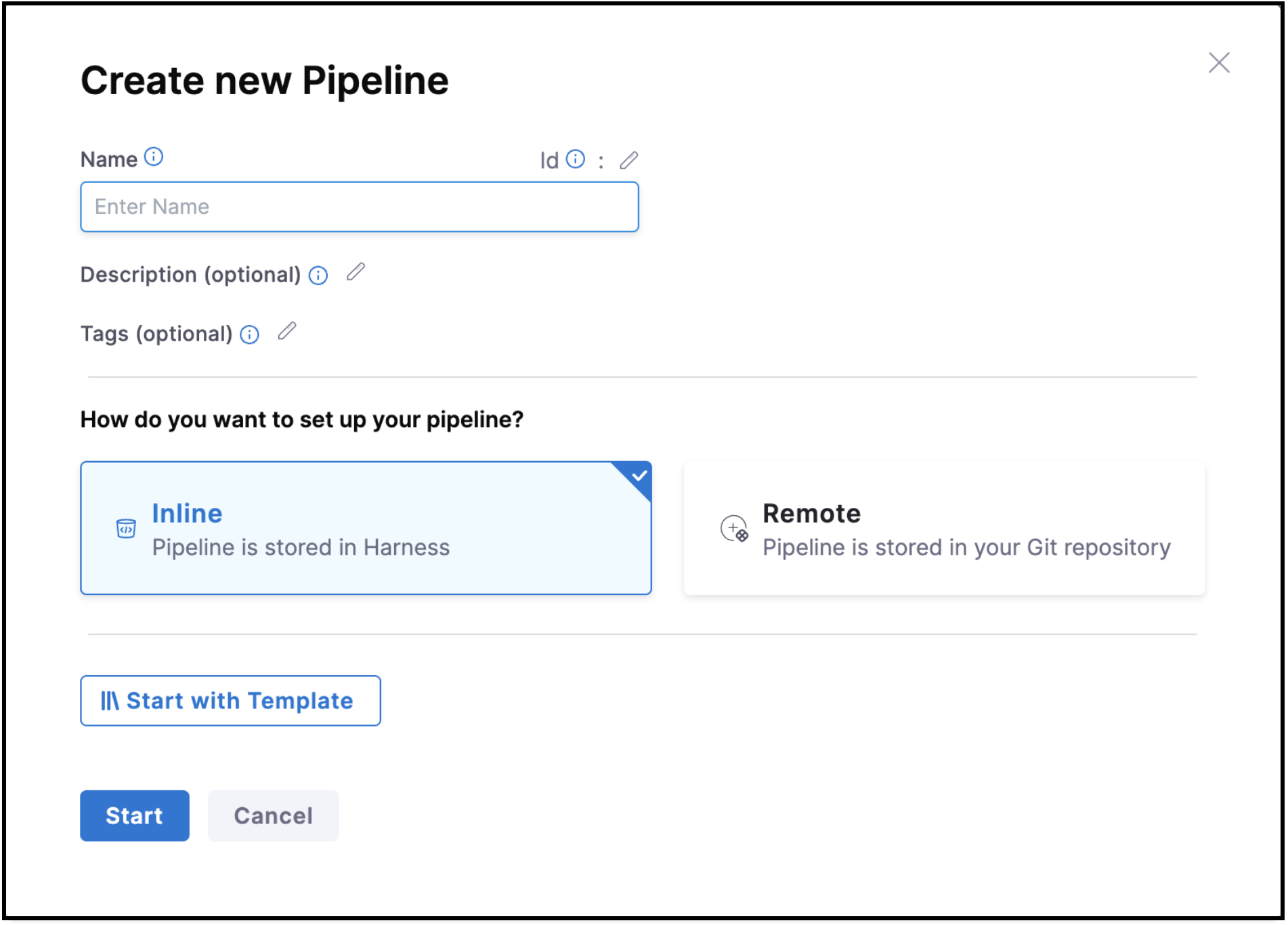
You can also store pipelines in Git using Remote storage. Learn more in the Pipelines documentation.
Step 2: Add a Deploy Stage and Configure Deployment
Add a Deploy stage and configure your deployment based on your target platform.
- Select the Deploy stage type.
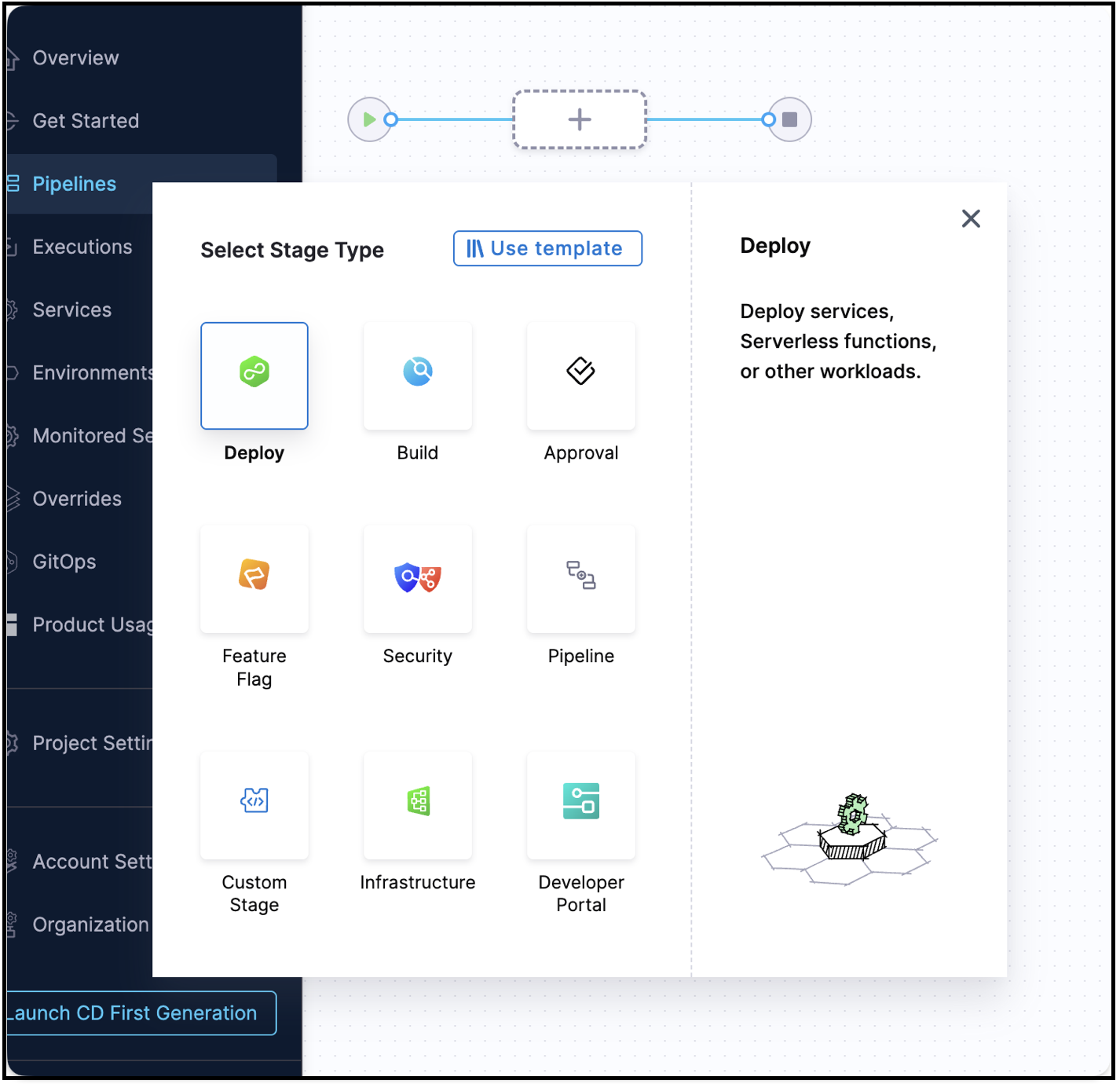
- In the "About your Stage" section:
- Enter a Stage Name (e.g., "Deploy to Dev")
- Select your Deployment Type
Select Your Deployment Type
This guide covers the most common deployment types. Select the one that matches your infrastructure:
- Kubernetes - Deploy to any Kubernetes cluster
- AWS Lambda - Serverless functions on AWS
- Google Cloud Run - Fully managed containers on GCP
- Azure Web Apps - PaaS web applications on Azure
- Azure Functions - Serverless compute on Azure
- SSH - Deploy to Linux/Windows servers
Harness supports 20+ deployment types including ECS, Helm, SAM, Google Cloud Functions, Spot, Tanzu, and more. For a complete list, see What's Supported in CD.
- Click Set Up Stage to continue.
The deployment type you select here determines the configuration needed in Service, Environment, and Infrastructure sections. Make sure to follow the same deployment type throughout all configuration steps.
Step 3: Configure Your Service
The Service defines what you're deploying (application, artifacts, manifests). Select your deployment platform below:
- Kubernetes
- SSH / Traditional
- Google Cloud Run
- Azure
- AWS Lambda
Kubernetes Service Configuration
- In the Service tab, click + Add Service
- Provide a Name (e.g.,
nginx-service) and click Save
Add Kubernetes Manifest
- Click Add Manifest → Select K8s Manifest
- Configure:
- Manifest Identifier:
k8s-manifest - Git Connector: Select the Git connector you created in Prerequisites
- Repository: Use
https://github.com/harness-community/harnesscd-example-apps - Branch:
master - File Path:
guestbook/manifest.yaml
- Manifest Identifier:
Sample Manifest:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: guestbook-ui
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: guestbook-ui
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: guestbook-ui
spec:
containers:
- name: guestbook-ui
image: <+artifact.image>
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: guestbook-ui
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: guestbook-ui
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
Add Container Image
-
Click Add Primary Artifact → Select Docker Registry
-
Configure:
- Artifact Source Name:
nginx - Docker Registry Connector: Select the Docker Registry connector you created in Prerequisites
- Image Path:
library/nginx - Tag: Select
stableor use<+input>for runtime input
- Artifact Source Name:
-
Click Continue to proceed to Environment configuration.
You can also use Helm charts or Kustomize for Kubernetes deployments.
SSH Deployment Service Configuration
- In the Service tab, click + Add Service
- Provide a Name (e.g.,
tomcat-app) and click Save
Add Application Package
- Click Add Primary Artifact
- Select artifact source based on what you configured in Prerequisites:
- Artifactory: For JARs, WARs, etc.
- Nexus: For Maven artifacts
- Amazon S3: For packages
- Configure:
- Connector: Select the artifact repository connector you created in Prerequisites
- Artifact Path: Path to your application package
- Format: JAR, WAR, TAR, ZIP, etc.
Example: For a WAR file from Artifactory
- Repository:
libs-release-local - Artifact Path:
com/example/myapp/1.0/myapp-1.0.war
Add Deployment Scripts (Optional)
-
Click Add Config File to add installation/startup scripts
-
Add pre-deployment and post-deployment scripts as needed
-
Click Continue to proceed to Environment configuration.
Harness also supports WinRM deployments for Windows servers.
Google Cloud Run Service Configuration
Sample configuration files are available at the harnesscd-example-apps repository.
- In the Service tab, click + Add Service
- Provide a Name (e.g.,
cloud-run-service) and click Save
Add Cloud Run Service Definition
- Click Add Manifest → Select Google Cloud Run Service Definition
- Configure:
- Manifest Source: Git Repository
- Git Connector: Select the Git connector you created in Prerequisites
Sample Cloud Run Service Definition:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: <+service.name>
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- image: <+artifact.image>
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: ENV
value: "production"
Add Container Image
-
Click Add Primary Artifact → Select Google Artifact Registry or GCR
-
Configure:
- GCP Connector: Select the GCP connector you created in Prerequisites
- Project: Your GCP project ID
- Image Path: Path to your container image
- Tag: Select tag or use
<+input>
-
Click Continue to proceed to Environment configuration.
Harness also supports Google Cloud Functions and GKE.
Azure Functions Service Configuration
Sample configuration files are available at the harnesscd-example-apps repository.
- In the Service tab, click + Add Service
- Provide a Name (e.g.,
azure-function) and click Save
Add Azure Function Configuration
- Click Add Manifest → Select Azure Function App Configuration
- Configure:
- Manifest Source: Git or Harness File Store
- Git Connector: Select the Git connector you created in Prerequisites (if using Git)
Sample Application Settings:
{
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "<storage-connection-string>",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "node",
"FUNCTIONS_EXTENSION_VERSION": "~4"
}
Add Function Artifact
-
Click Add Primary Artifact
-
Select artifact source:
- Azure Artifacts: For packages
- ACR: Select the ACR connector you created in Prerequisites
-
Configure connector and artifact details
-
Click Continue to proceed to Environment configuration.
Harness also supports Azure Web Apps and AKS.
AWS Lambda Service Configuration
Sample configuration files are available at the harnesscd-example-apps repository.
- In the Service tab, click + Add Service
- Provide a Name (e.g.,
lambda-function) and click Save
Add Lambda Function Definition
- Click Add Manifest → Select AWS Lambda Function Definition
- Configure:
- Manifest Source: Git or Harness File Store
- Git Connector: Select the Git connector you created in Prerequisites (if using Git)
- File Path: Path to your function definition JSON
Sample Lambda Function Definition (view full example):
{
"FunctionName": "hello-world-lambda",
"Runtime": "python3.9",
"Role": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/lambda-execution-role",
"Handler": "lambda_function.lambda_handler",
"Code": {
"S3Bucket": "<+artifact.bucketName>",
"S3Key": "<+artifact.key>"
},
"Description": "Hello World Lambda function",
"Timeout": 30,
"MemorySize": 128,
"Publish": true
}
Replace the Role ARN with your actual Lambda execution role ARN.
Add Lambda Artifact
- Click Add Primary Artifact → Select Amazon S3
- Configure:
- AWS Connector: Select the AWS connector you created in Prerequisites
- Region:
us-east-1(or your region) - Bucket: Your S3 bucket name (where you uploaded the ZIP in Prerequisites)
- File Path:
hello-world.zip(the file you uploaded)
Sample artifact: hello-world.zip
- Click Continue to proceed to Environment configuration.
Harness also supports ECS, SAM, and other AWS services.
Step 4: Configure Environment and Infrastructure
Define where you're deploying (Environment) and the specific infrastructure details. Select your deployment platform:
- Kubernetes
- SSH / Traditional
- Google Cloud Run
- Azure
- AWS Lambda
Kubernetes Environment & Infrastructure
Create Environment
- Click + New Environment
- Configure:
- Name:
dev-environment - Environment Type: Pre-Production
- Name:
- Click Save
Define Infrastructure
-
Click + Select Infrastructure
-
Provide Name:
k8s-dev-cluster -
Configure connection:
- Connector: Select the Kubernetes cluster connector you created in Prerequisites
- Namespace: Enter target namespace (e.g.,
default,dev,production) - Release Name:
release-<+INFRA_KEY>(for deployment tracking)
-
Click Continue to proceed to Execution.
See Kubernetes infrastructure for advanced configuration options.
SSH Deployment Environment & Infrastructure
Create Environment
- Click + New Environment
- Configure:
- Name:
production-servers - Environment Type: Production
- Name:
- Click Save
Define Infrastructure
- Click + Select Infrastructure
- Provide Name:
prod-vms - Configure SSH connection:
For Static Host List:
- Connector: Select the SSH connector you created in Prerequisites
- Hosts: Add target host IPs or hostnames (e.g.,
192.168.1.10,server1.example.com) - Host Attributes: Add tags for organization (optional)
For Dynamic Infrastructure:
- Cloud Provider: Select AWS/Azure/GCP connector from Prerequisites
- Region: Select region
- Tags: Define filters to dynamically select instances
- Click Continue to proceed to Execution.
See SSH infrastructure for configuration details.
Google Cloud Run Environment & Infrastructure
Create Environment
- Click + New Environment
- Configure:
- Name:
gcp-production - Environment Type: Production
- Name:
- Click Save
Define Infrastructure
-
Click + Select Infrastructure
-
Provide Name:
cloud-run-infra -
Configure:
- GCP Connector: Select the GCP connector you created in Prerequisites
- Project: Your GCP project ID (e.g.,
my-project-123456) - Region: Select region (e.g.,
us-central1,us-east1)
-
Click Continue to proceed to Execution.
See Cloud Run infrastructure for configuration details.
Azure Functions Environment & Infrastructure
Create Environment
- Click + New Environment
- Configure:
- Name:
azure-prod - Environment Type: Production
- Name:
- Click Save
Define Infrastructure
-
Click + Select Infrastructure
-
Provide Name:
azure-func-infra -
Configure:
- Azure Connector: Select the Azure connector you created in Prerequisites
- Subscription: Select your Azure subscription ID
- Resource Group: Your resource group name (e.g.,
my-function-rg) - Function App Name: Your function app name (the one you created in Azure Portal)
-
Click Continue to proceed to Execution.
See Azure Functions infrastructure for configuration details.
AWS Lambda Environment & Infrastructure
Create Environment
- Click + New Environment
- Configure:
- Name:
aws-lambda-prod - Environment Type: Production
- Name:
- Click Save
Define Infrastructure
-
Click + Select Infrastructure
-
Provide Name:
lambda-infra -
Configure:
- AWS Connector: Select the AWS connector you created in Prerequisites
- Region: Select your AWS region (e.g.,
us-east-1,us-west-2)
-
Click Continue to proceed to Execution.
See Lambda infrastructure for configuration details.
Step 5: Configure Execution Strategy
Different deployment types support different execution strategies. Select your deployment platform to see available strategies:
- Kubernetes
- SSH / Traditional
- Google Cloud
- Azure
- AWS Lambda
Kubernetes Execution Strategies
Choose how your Kubernetes deployment will be executed:
- In the Execution tab, Harness automatically adds a Rollout Deployment step
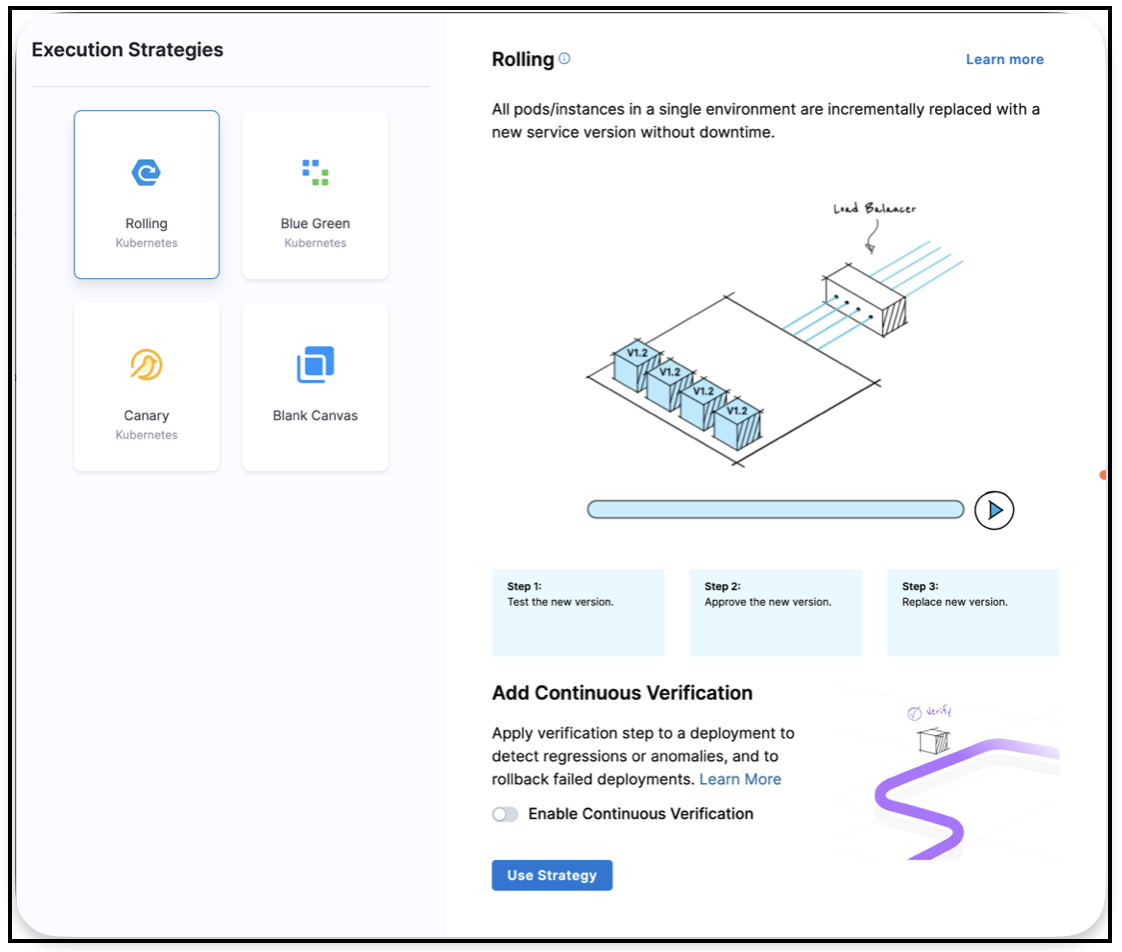
- Click on the step to choose your execution strategy:
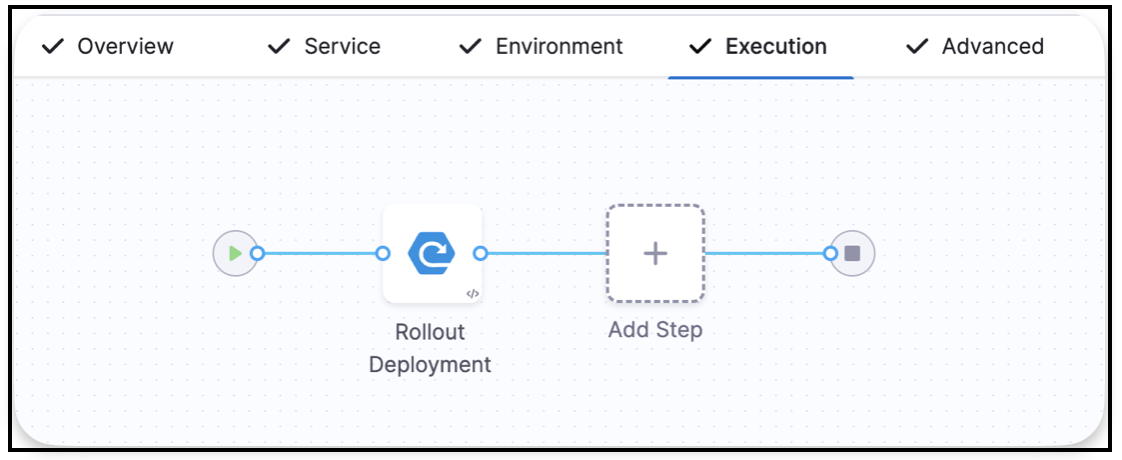
Available Strategies for Kubernetes:
- Rolling: Incrementally updates pods with zero downtime. Supports all Kubernetes workloads (Deployment, DaemonSet, etc.)
- Blue Green: Deploys new version alongside old, then switches traffic instantly. Supports Deployment workloads only
- Canary: Gradually routes traffic to new version in phases. Supports Deployment workloads only
- Blank Canvas: Start with empty execution for custom workflows
- Select your strategy and click Use Strategy
For more details on Kubernetes deployment strategies, see What Can I Deploy in Kubernetes?
SSH Deployment Execution Strategy
SSH deployments primarily use the Rolling deployment strategy:
- In the Execution tab, Harness automatically adds deployment steps
Available Strategy:
- Rolling: Deploys to target hosts incrementally, either all at once or in phases. You can specify:
- Number of instances to deploy simultaneously
- Percentage-based deployment phases
- Custom deployment patterns
The Rolling strategy is ideal for traditional deployments as it:
- Maintains service availability during deployment
- Allows for gradual rollout verification
- Supports easy rollback if issues are detected
- Click Save to save your pipeline
For more details on SSH deployments, see SSH deployments
Google Cloud Run Execution Strategies
Choose how your Cloud Run deployment will be executed:
- In the Execution tab, select your deployment strategy
Available Strategies for Cloud Run:
- Basic: Deploys new revision and routes 100% of traffic immediately
- Steps: Download Manifest → Prepare Rollback → Deploy
- Canary: Gradually shifts traffic from old to new revision
- Steps: Download Manifest → Prepare Rollback → Deploy → Traffic Shift
For Google Cloud Functions (2nd gen):
- Basic: Deploys new function version and routes 100% traffic
- Canary: Gradually routes traffic to new version
- Blue Green: Deploys new version and switches traffic at once
For Google Cloud Functions (1st gen):
- Basic only: Deploys new function and terminates the old one
-
Select your strategy and Harness will automatically add the required steps
-
Click Save to save your pipeline
For more details, see Google Cloud Functions and Google Cloud Run
Azure Web Apps & Functions Execution Strategies
Choose how your Azure deployment will be executed:
- In the Execution tab, select your deployment strategy
Available Strategies for Azure Web Apps:
- Basic: Deploys to target slot without traffic shifting
- Step: Slot Deployment
- Canary: Shifts traffic from production to deployment slot incrementally
- Steps: Slot Deployment → Traffic Shift (incremental) → Swap Slot
- Blue Green: Deploys to deployment slot, then swaps all traffic at once
- Steps: Slot Deployment → Swap Slot
For Azure Functions:
- Basic: Deploys new function version
- Custom: Define your own deployment workflow
Azure Web Apps use slots for staging and production environments. Rolling strategy is not supported as it doesn't suit the slot-based deployment model.
-
Select your strategy and Harness will automatically add the required steps
-
Click Save to save your pipeline
For more details, see Azure Web Apps and Azure Functions
AWS Lambda Execution Strategies
Choose how your Lambda deployment will be executed:
- In the Execution tab, select your deployment strategy
Available Strategies for Lambda:
- Basic: Deploys new function version and routes 100% traffic immediately
- Steps: AWS Lambda Deploy → AWS Lambda Rollback (for rollback)
- Canary: Gradually shifts traffic to new version using AWS Lambda's traffic shifting
- Steps: Lambda Canary Deploy → Traffic Shift (e.g., 10%) → Traffic Shift (100%) → Canary Rollback
Canary Deployment Details:
- Deploy new version without shifting traffic initially
- Incrementally route traffic (e.g., 10%, then 100%)
- Add approval steps between traffic shifts to validate deployment health
- Automatic rollback if failure detected
-
Select your strategy and Harness will automatically add the required steps
-
Click Save to save your pipeline
For more details, see AWS Lambda Deployments
Optional: Enable Continuous Verification
Add automated health monitoring to any deployment:
- Toggle Enable Continuous Verification
- Configure your monitoring tools (APM, logging, metrics)
Learn about verification in the Continuous Verification documentation.
Step 6: Run Your Pipeline
After completing all configuration steps, execute your deployment:
- Ensure your pipeline is saved (click Save if needed)
- Click Run in the top right corner
- Provide any required runtime inputs:
- Artifact versions or tags
- Environment variables
- Infrastructure parameters
- Click Run Pipeline to begin execution
Harness will execute your deployment and display real-time progress, logs, and status for each step.
For detailed information on monitoring execution, viewing logs, troubleshooting failures, and understanding deployment status, see the Pipeline Execution Walkthrough.
Next Steps
Explore More Tutorials
Now that you've completed your first deployment, dive deeper with platform-specific tutorials and sample applications:
- Browse all CD Tutorials - Step-by-step guides for every deployment type
- Harness CD Example Apps Repository - Ready-to-use sample applications for Kubernetes, Helm, AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Run, and more
The harnesscd-example-apps repository contains complete working examples with manifests, configurations, and artifacts that you can fork and use in your own pipelines.
What's Next
Congratulations on completing your first deployment! Continue your Harness CD journey:
- Learn about Variables - Use variables for dynamic pipeline configuration
- Set up Pipeline Triggers - Automate deployments based on events
- Explore Continuous Verification - Add automated deployment verification
- Configure Approval Steps - Add manual or automated approvals
For an interactive onboarding experience including advanced features like canary deployments, blue-green strategies, and automated rollbacks, check out Harness CD self-paced training.