Create and manage ApplicationSets
Harness provides two ways to work with GitOps ApplicationSets:
- First-Class Support (Recommended) - Enhanced UI wizard with Service/Environment integration, full CRUD operations, improved RBAC, and Terraform support
- Standard Flow - Create ApplicationSets as GitOps Applications with manual YAML configuration
The first-class ApplicationSet support is enabled by the feature flag GITOPS_APPLICATIONSET_FIRST_CLASS_SUPPORT.
If you have the feature flag enabled: Use the First-Class Support tab in the Create and Manage ApplicationSets section below.
If you don't have the feature flag: Use the Standard Flow tab. Contact Harness Support to enable first-class support for an enhanced experience.
What you'll learn
With First-Class Support:
- Create ApplicationSets using the Harness UI wizard
- Configure generators to dynamically create applications
- Define templates with Service and Environment labels
- Validate and preview ApplicationSet manifests
- Monitor ApplicationSet sync status and generated applications
With Standard Flow:
- Create ApplicationSets as GitOps Applications
- Configure ApplicationSet manifests in Git
- Sync ApplicationSets to generate child applications
- Monitor generated applications
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A Harness GitOps Agent installed and running
- At least one GitOps Cluster configured
- A GitOps Repository connected
- Appropriate RBAC permissions to create ApplicationSets
Additional for First-Class Support:
- Harness Services and Environments created in your project
Additional for Standard Flow:
- At least two target clusters (e.g., dev and prod)
- GitHub account with access to clone and modify repositories
ApplicationSets are project-scoped entities. All applications generated by an ApplicationSet belong to the same Harness project as the ApplicationSet itself.
ApplicationSet overview
An ApplicationSet is a Kubernetes custom resource that enables you to automatically generate and manage multiple Argo CD applications from a single manifest. It consists of two main components:
- Generator: Defines the source of parameters used to create applications (e.g., Git repositories, clusters, lists)
- Template: Defines the application structure with parameterized fields that get substituted with values from the generator
For more information about ApplicationSet concepts, see ApplicationSet basics.
Create and Manage ApplicationSets
Choose the appropriate tab below:
- First-Class Support: If you have access to the enhanced UI wizard (recommended)
- Standard Flow: If you're using the standard ApplicationSet creation method
- First-Class Support (Recommended)
- Standard Flow
This flow requires the feature flag GITOPS_APPLICATIONSET_FIRST_CLASS_SUPPORT to be enabled. If you don't have access to the ApplicationSet wizard, use the Standard Flow tab or contact Harness Support to enable this feature.
Navigate to ApplicationSets
- In your Harness project, go to Deployments > GitOps.
- Select Applications from the left navigation.
- Switch to the Application Set tab.
You'll see a list of all ApplicationSets in your project.
Create an ApplicationSet
Step 1: Start the ApplicationSet wizard
- On the Application Set tab, select + New Application Set.
- The ApplicationSet creation wizard opens with four tabs: Overview, Sync Policy, Configuration, and Preview.
Step 2: Configure Overview settings
On the Overview tab, provide the following details:
- App Set Name: Enter a unique name for your ApplicationSet.
- GitOps Operator: Select Argo (currently the only supported operator).
- GitOps Agent: Select the GitOps Agent that will manage this ApplicationSet.
- Service: Select the Harness Service associated with this ApplicationSet. This enables PR pipeline integration, service dashboard visibility, and RBAC policies.
- Environment: Select the Harness Environment associated with this ApplicationSet. This enables environment-based filtering and PR pipeline configuration.
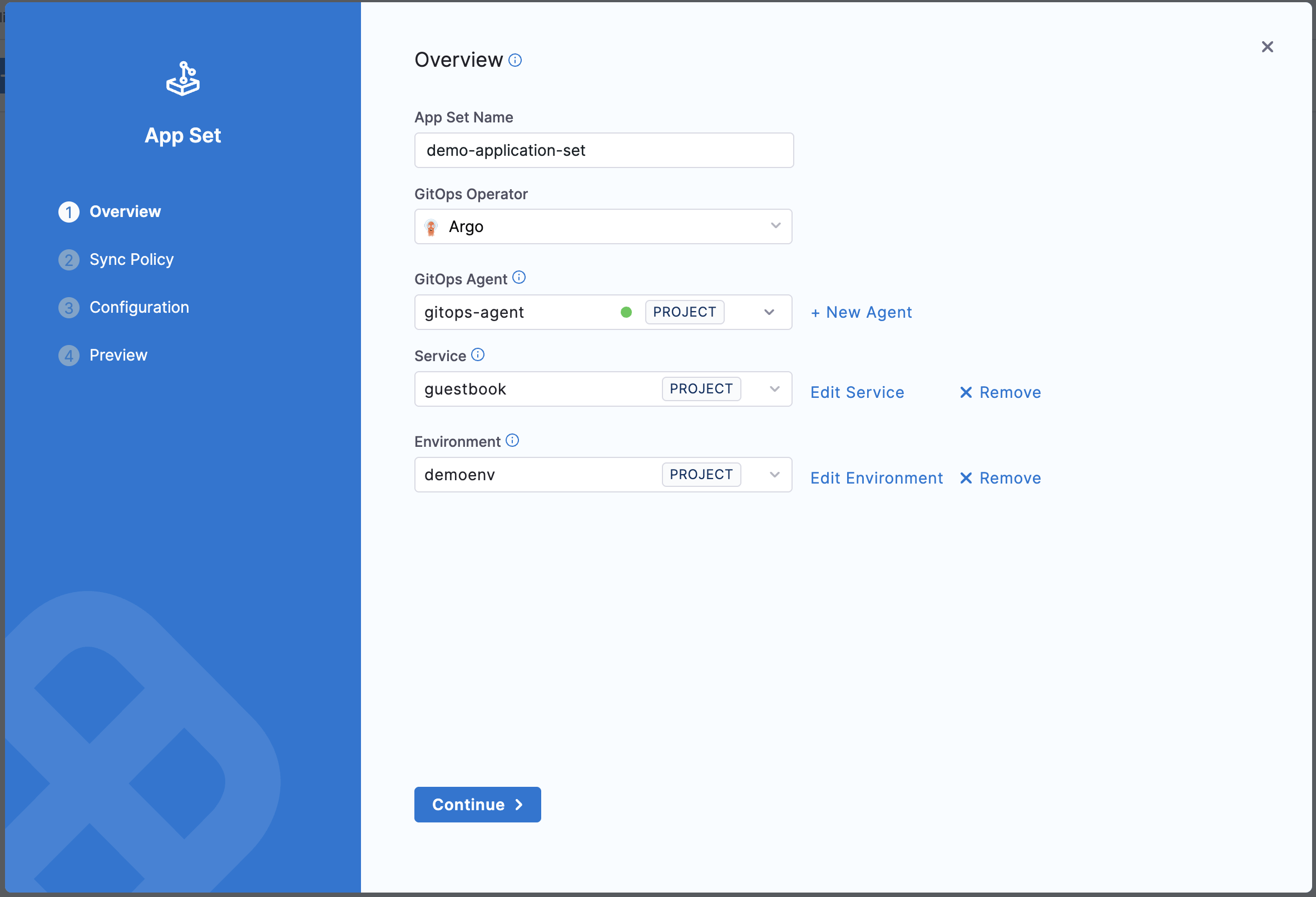
The Service and Environment selections automatically add harness.io/serviceRef and harness.io/envRef labels to the ApplicationSet template, enabling integration with Harness pipelines and RBAC policies.
Select Continue to proceed to the next step.
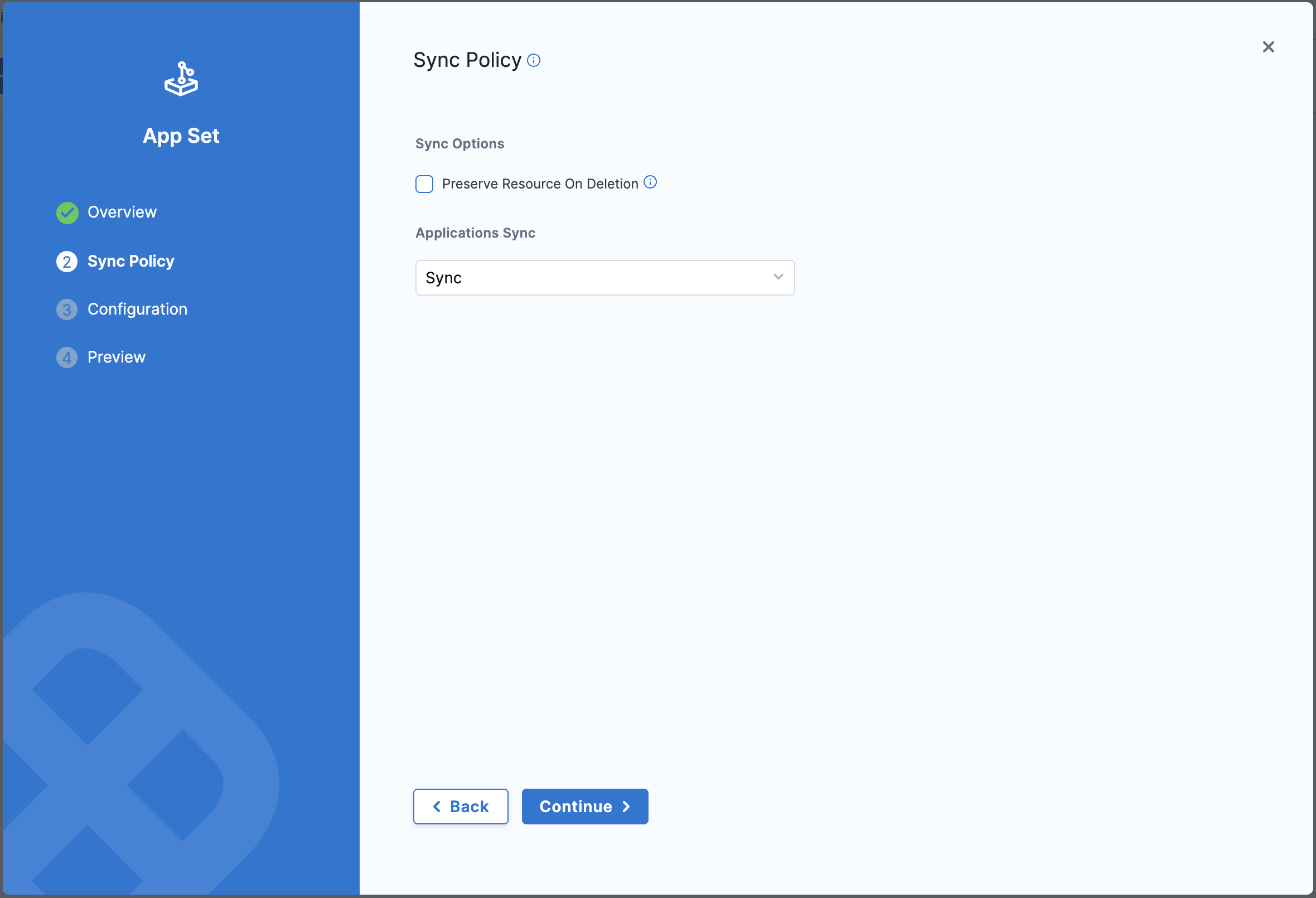
Step 3: Configure Sync Policy
On the Sync Policy tab, define the sync policy that governs the relationship between the ApplicationSet and its child applications.
Sync Options
- Preserve Resource On Deletion: Check this option if you want to preserve Kubernetes resources when the application is deleted from Argo CD.
Applications Sync
Select the sync policy for applications created by this ApplicationSet.
Currently, only the Sync policy is supported. While other options may appear in the UI, they are not yet functional.
Sync (Recommended): Fully automated sync with create, update, and delete operations. This is the current default and only supported option.
Future Options (Coming Soon):
- Create-Only: Only create applications; don't update or delete them automatically.
- Create-Update: Create new applications and update existing ones.
- Create-Delete: Create new applications and delete removed ones.
Select Continue to proceed to configuration.
Step 4: Configure Generator and Template
The Configuration tab is where you define the generator and template for your ApplicationSet.
Select Generator Type
Choose the generator type from the dropdown. Harness supports all Argo CD generator types:
- Git: Generate applications from files or directories in a Git repository
- List: Generate applications from a static list of parameters
- Cluster: Generate applications for each cluster registered in Argo CD
- Matrix: Combine multiple generators
- Pull Request: Generate applications from pull requests
- SCM Provider: Generate applications from repositories in an SCM provider
- Cluster Decision Resource: Generate applications based on custom Kubernetes resources
- Plugin: Use custom generator plugins
For more information on supported generator types, see Argo CD Generator Types.
When you select a generator type, Harness automatically generates a template skeleton for that generator.
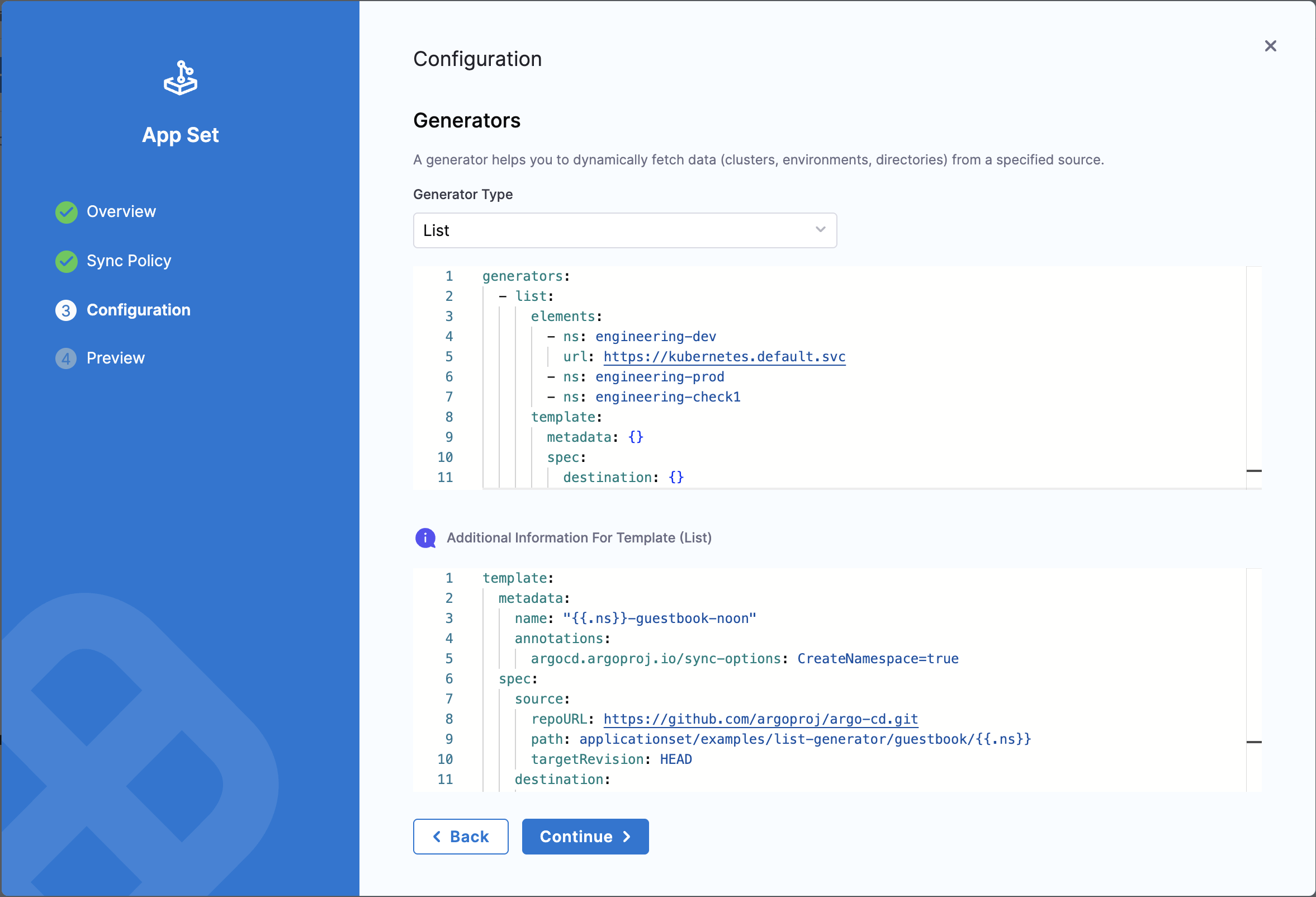
Configure Generator
The generator configuration appears in a YAML editor. Modify the template according to your needs.
Example: List Generator
generators:
- list:
elements:
- ns: engineering-dev
url: https://kubernetes.default.svc
- ns: engineering-prod
url: https://kubernetes.default.svc
- ns: engineering-check1
url: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Configure Template
Below the generator configuration, you'll see the template section with automatically added labels for Harness integration:
template:
metadata:
name: "{{.ns}}-guestbook"
labels:
harness.io/serviceRef: guestbook
harness.io/envRef: dev
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-options: CreateNamespace=true
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd.git
path: applicationset/examples/list-generator/guestbook/{{.ns}}
targetRevision: HEAD
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: "{{.ns}}"
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
The template includes:
- harness.io/serviceRef: References the Service you selected in the Overview step. This label is added to the ApplicationSet template metadata and will be inherited by all child applications generated from this ApplicationSet.
- harness.io/envRef: References the Environment you selected in the Overview step. This label is added to the ApplicationSet template metadata and will be inherited by all child applications generated from this ApplicationSet.
- project: The Argo CD project where the ApplicationSet is created. This is usually auto-populated based on the project where the ApplicationSet is created. You can also get this value from the agent details under Mapped Harness Project → Argo Projects.
The sample generator and template refer to the sample Argo CD guestbook ApplicationSet provided in the Argo CD GitHub repository.
How these labels are used:
The harness.io/serviceRef and harness.io/envRef labels are applied to all child applications generated by the ApplicationSet. These labels enable:
- Service Dashboard Tracking: Applications appear in the Harness Service dashboard for the referenced service
- PR Pipeline Configuration: The Fetch Linked Apps step in PR pipelines uses these labels to identify applications associated with a service
- Environment-based Filtering: Filter and organize applications by service and environment in the Harness UI
You can use variables in the format {{.variableName}} throughout the template. These variables will be substituted with values from the generator.
Step 5: Preview and Validate
On the Preview tab, you can review the complete ApplicationSet manifest before creating it.
Validate the Manifest
-
Review the generated YAML manifest.
-
Click Validate to check the manifest for:
- Syntax errors
- Template variable substitution issues
- Service and Environment references
- Repository and cluster access permissions
-
If validation succeeds, you'll see a success message.
-
If validation fails, review the error messages and go back to fix the configuration.
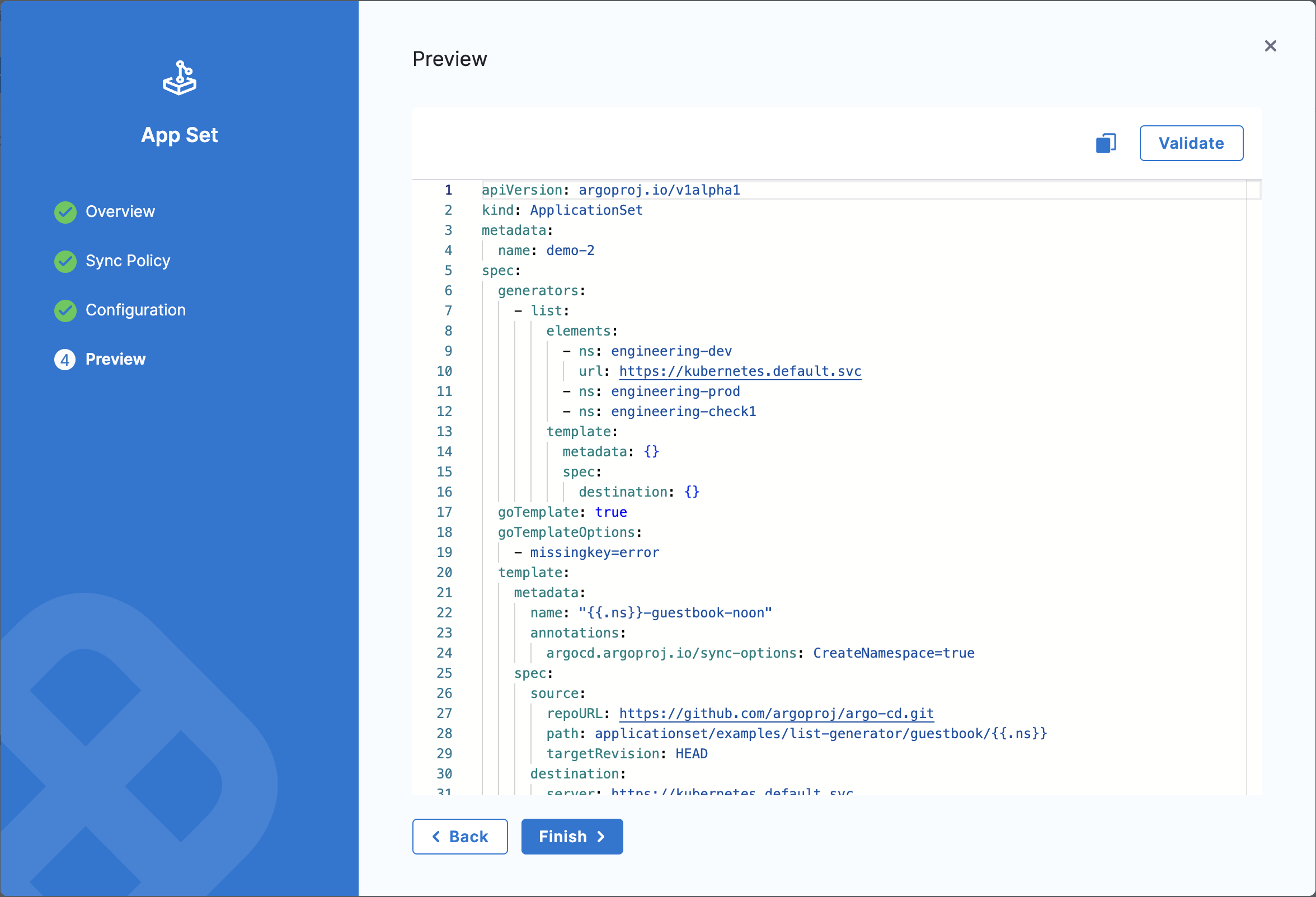
Create the ApplicationSet
Once validation passes, select Finish to create the ApplicationSet.
View ApplicationSet Details
After creating the ApplicationSet, you can view its details and monitor the applications it generates.
ApplicationSet Dashboard
- The ApplicationSet dashboard displays all ApplicationSets in the project, along with basic information such as:
- Applications within each ApplicationSet
- Labels
- The agent used to create the ApplicationSet
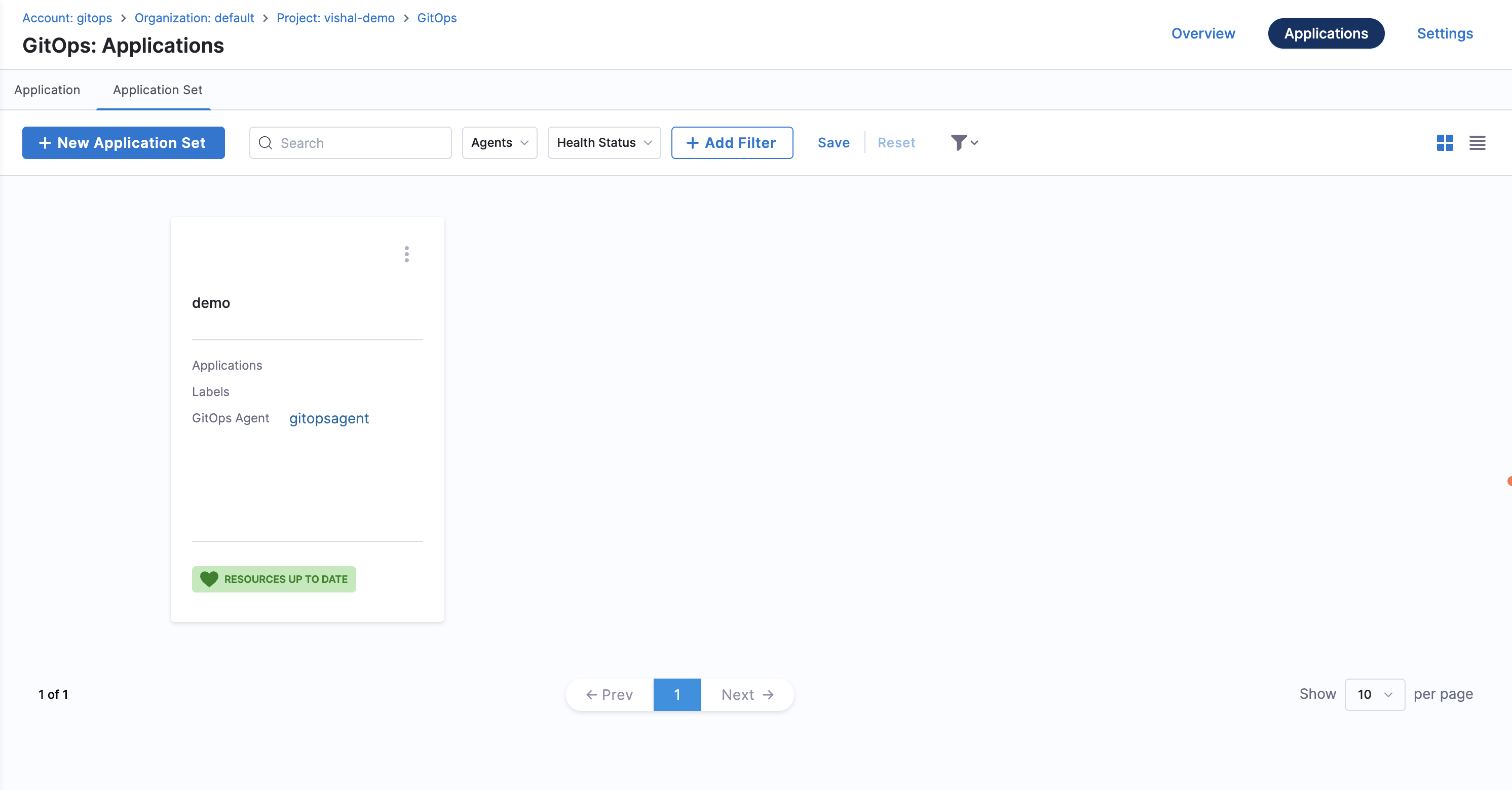
- Click on the ApplicationSet you created to view its details.
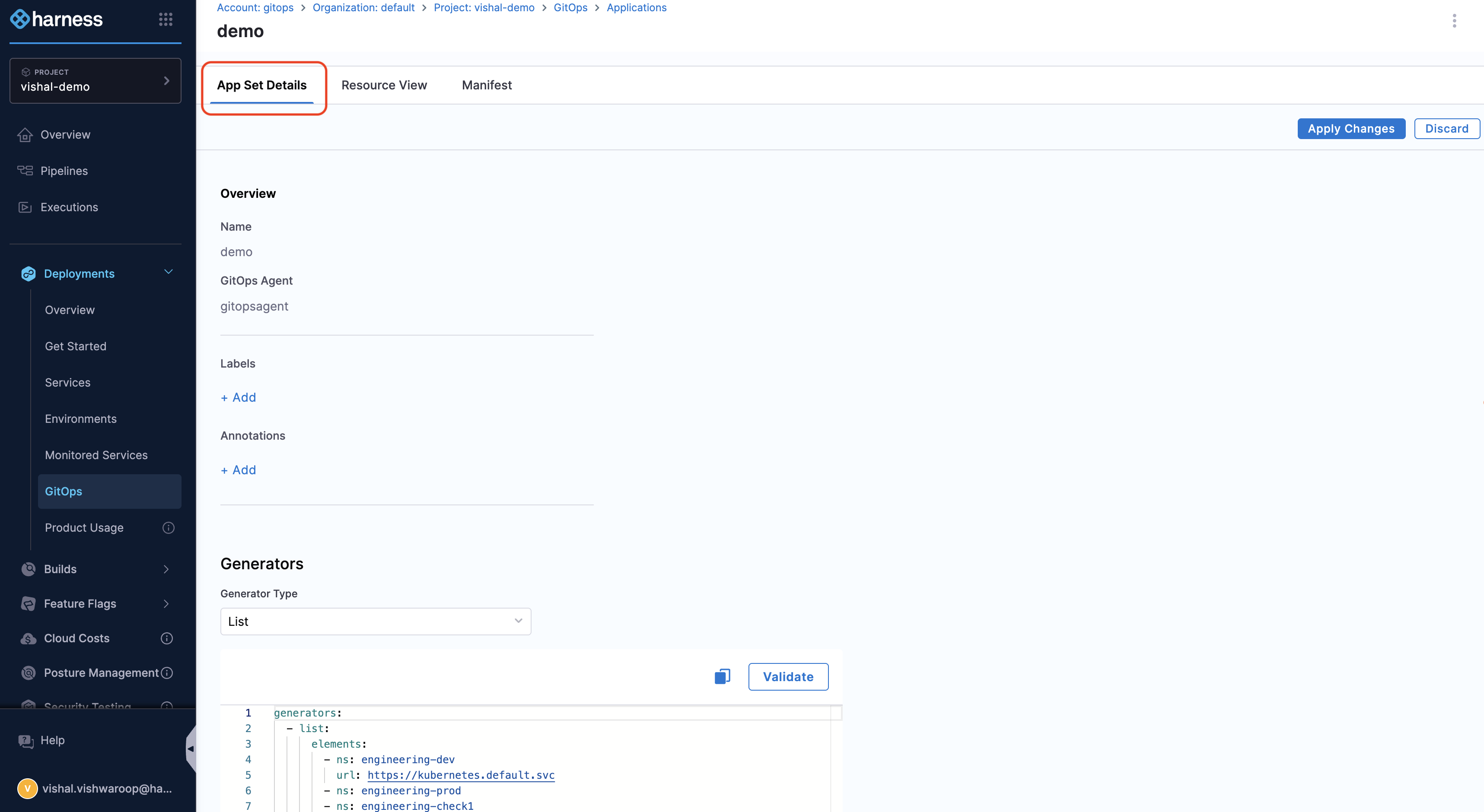
On the App Set Details page, you can see:
- ApplicationSet name
- GitOps agent used
- Labels and annotations
- Generator details
- Template generated based on the generator
- Sync options and policies
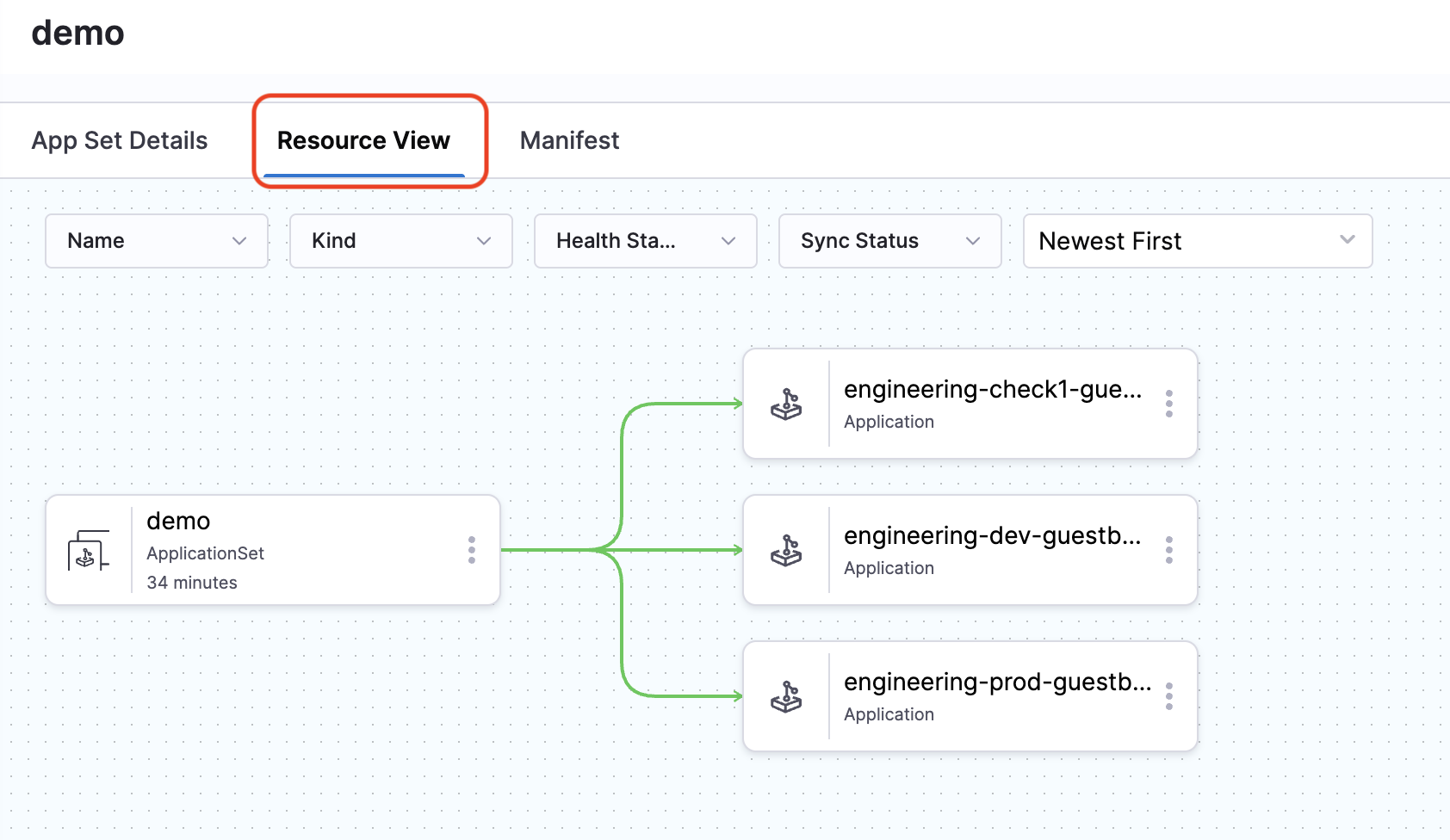
- Click on the Resource View tab to view the generated applications.
The Resource View shows:
- The ApplicationSet as the parent resource
- All applications generated by the ApplicationSet
- The sync status and health of each application
You can:
- Click on any generated application to view its details
- Monitor the sync status and health of all applications
- See which applications are healthy, progressing, or degraded
When viewing the ApplicationSet resource tree, child application objects may appear out of sync even if the individual application page shows a synced status. This is because the ApplicationSet resource tree refreshes every 3 minutes by default. For the most up-to-date status of a specific application, click on the application to view its dedicated details page.
- Click on the Manifest tab to see the complete manifest generated for the ApplicationSet.
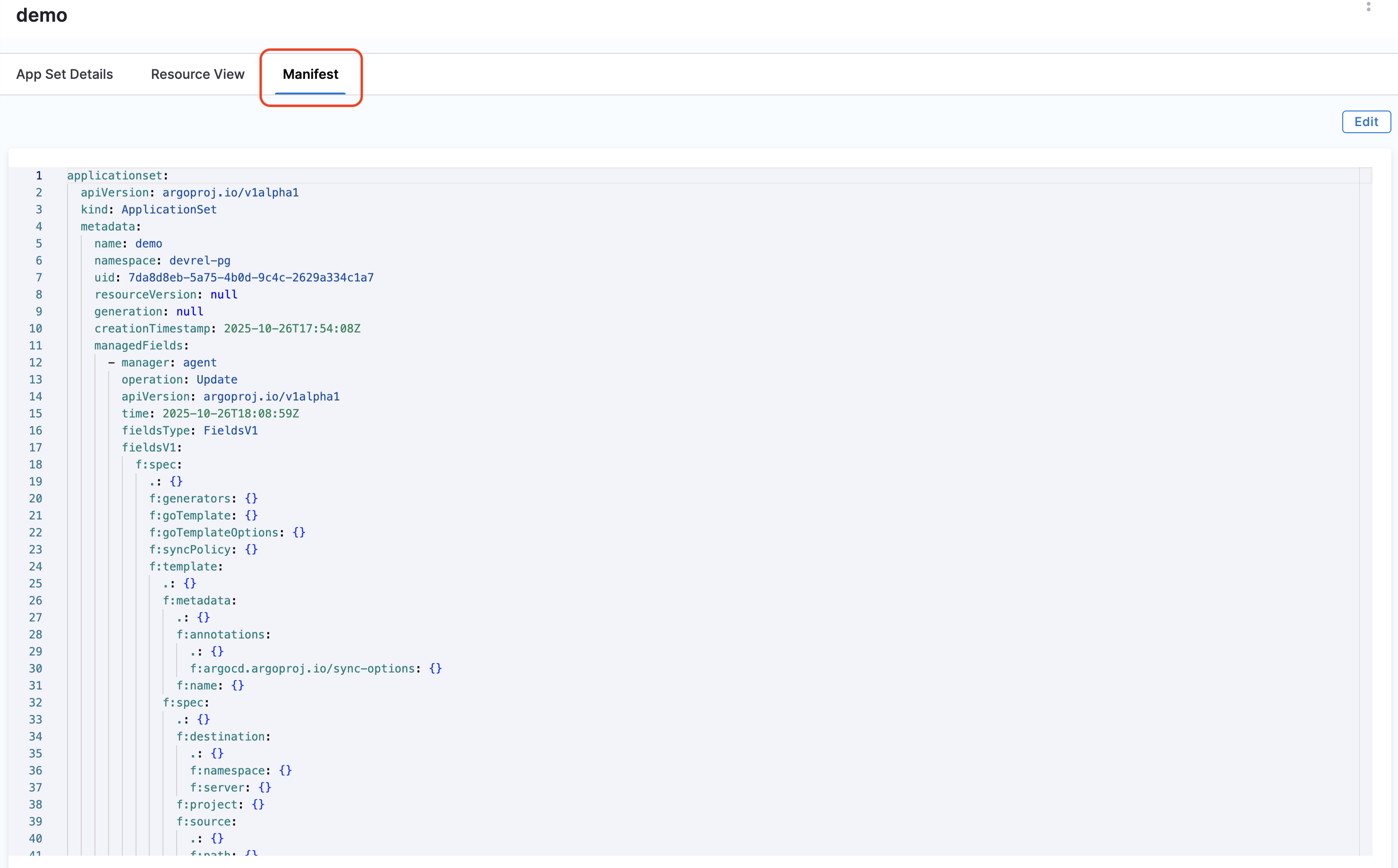
If you want more details about the applications created by the ApplicationSet, navigate to the Applications page. Filter by the agent and cluster to view the applications created by the ApplicationSet. Typically, all applications created by an ApplicationSet will use the same agent and cluster.
Auto-create services and environments
When importing Argo CD projects through a Bring Your Own Argo CD (BYOA) setup, Harness can automatically create services and environments in the target Harness project based on the harness.io/serviceRef and harness.io/envRef labels defined in your ApplicationSet template.
If a service or environment matching the label value already exists, the application is mapped to it. If it does not exist, Harness creates it automatically and maps it to the application.
To use this with ApplicationSets:
-
Define labels in your ApplicationSet template: Add
harness.io/serviceRefandharness.io/envReflabels to thetemplate.metadata.labelssection. You can templatize these values so each generated application gets its own service and environment reference. -
Enable the toggle on the Map Projects screen: When importing the Argo CD project during the BYOA agent setup, turn on the Enables automatic creation of service environments toggle.
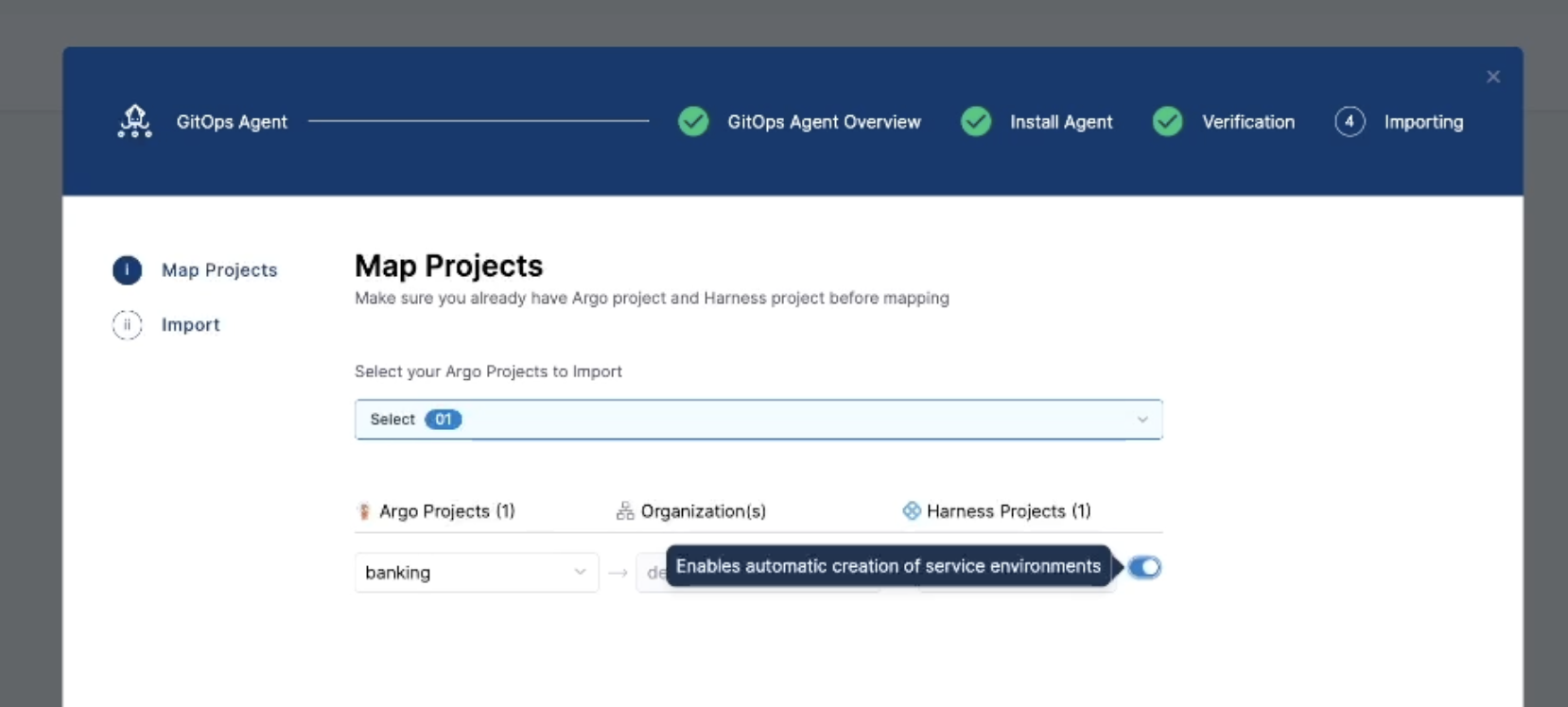
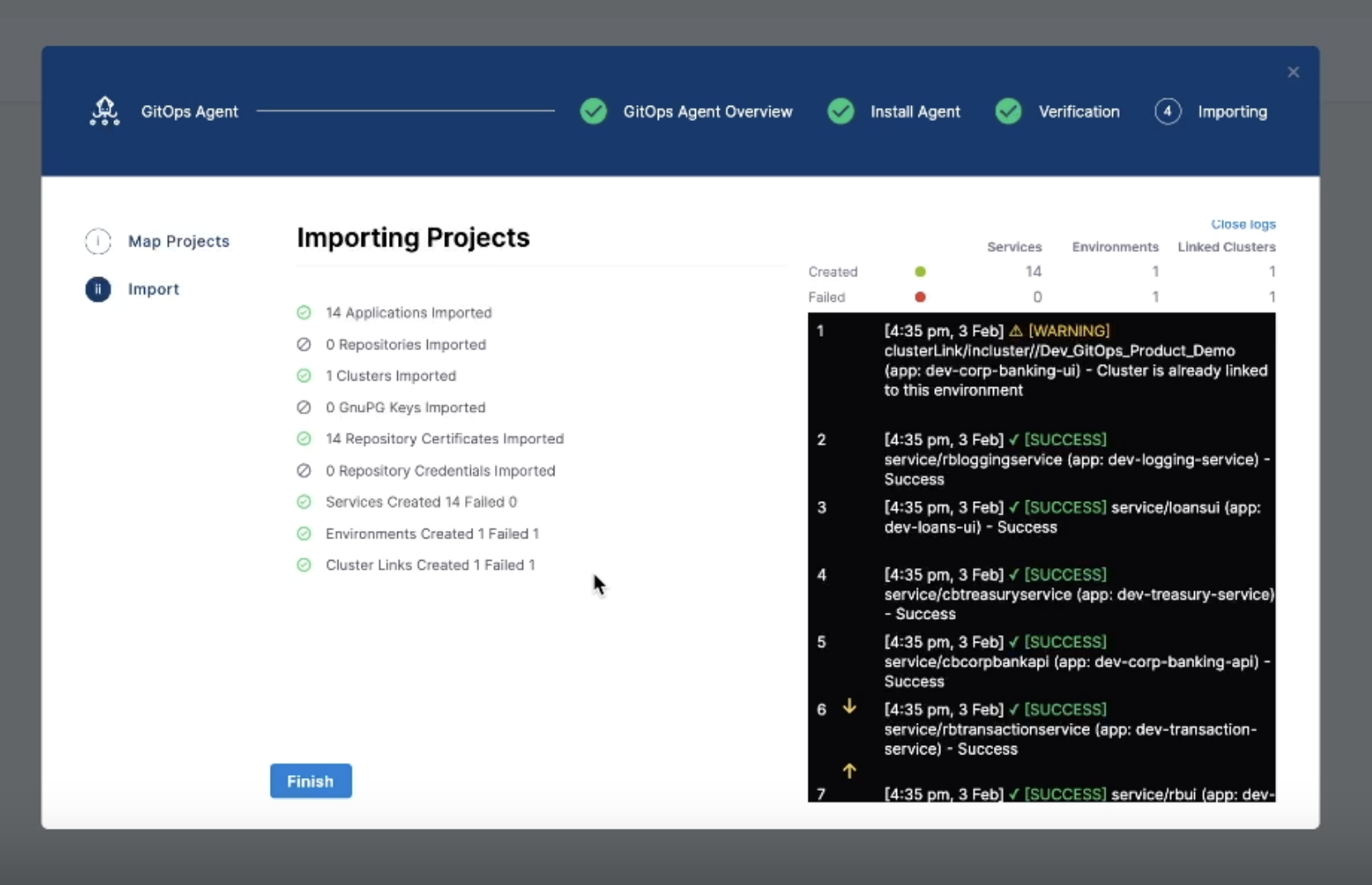
- Import the project: Select Import & Continue. Harness processes all applications generated by the ApplicationSet. The import summary shows the number of services, environments, and cluster links that were created or mapped.
Example ApplicationSet YAML with serviceRef and envRef labels
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: dev-microservices
namespace: argocd
spec:
goTemplate: true
goTemplateOptions:
- missingkey=error
generators:
- list:
elements:
- domain: corporate-banking
service: compliance-service
namespace: corporate-banking
serviceRef: cbcomplianceservice
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
- domain: corporate-banking
service: corp-banking-api
namespace: corporate-banking
serviceRef: cbcorpbankapi
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
- domain: corporate-banking
service: treasury-service
namespace: corporate-banking
serviceRef: cbtreasuryservice
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
- domain: retail-banking
service: account-service
namespace: retail-banking
serviceRef: rbaccountservice
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
- domain: retail-banking
service: transaction-service
namespace: retail-banking
serviceRef: rbtransactionservice
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
- domain: loans
service: loans-api
namespace: loans
serviceRef: loansapi
envRef: Dev_GitOps_Product_Demo
template:
metadata:
name: "dev-{{.service}}"
labels:
environment: "dev"
app: "{{.service}}"
harness.io/serviceRef: "{{.serviceRef}}"
harness.io/envRef: "{{.envRef}}"
spec:
project: banking
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/example-org/gitops-demo
targetRevision: main
path: "services/{{.domain}}/{{.service}}/overlays/dev"
destination:
server: "https://kubernetes.default.svc"
namespace: "{{.namespace}}"
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
In this example, each element in the list generator defines a serviceRef and envRef that are substituted into the template labels. When the BYOA import runs with auto-creation enabled, Harness creates a service and environment for each unique serviceRef/envRef value and maps the generated applications accordingly.
Filter ApplicationSets
You can filter ApplicationSets in the list view using:
- Search: Enter text to search by ApplicationSet name
- Agent: Filter by GitOps Agent
- Sync Status: Filter by sync status (Synced, OutOfSync, Unknown)
- Health Status: Filter by health status (Healthy, Progressing, Degraded, Suspended, Missing)
Edit ApplicationSets
To edit an existing ApplicationSet:
- Go to the Application Set tab.
- Select your ApplicationSet.
- Select the Manifest tab.
- Select Edit to modify the manifest.
- Make your changes and select Save.
Editing an ApplicationSet may cause applications to be created, updated, or deleted based on the changes you make to the generator or template.
Delete ApplicationSets
To delete an ApplicationSet:
-
Go to the Application Set tab.
-
Find your ApplicationSet in the list.
-
Select the three vertical dots (⋮) next to the ApplicationSet.
-
Select Delete.
-
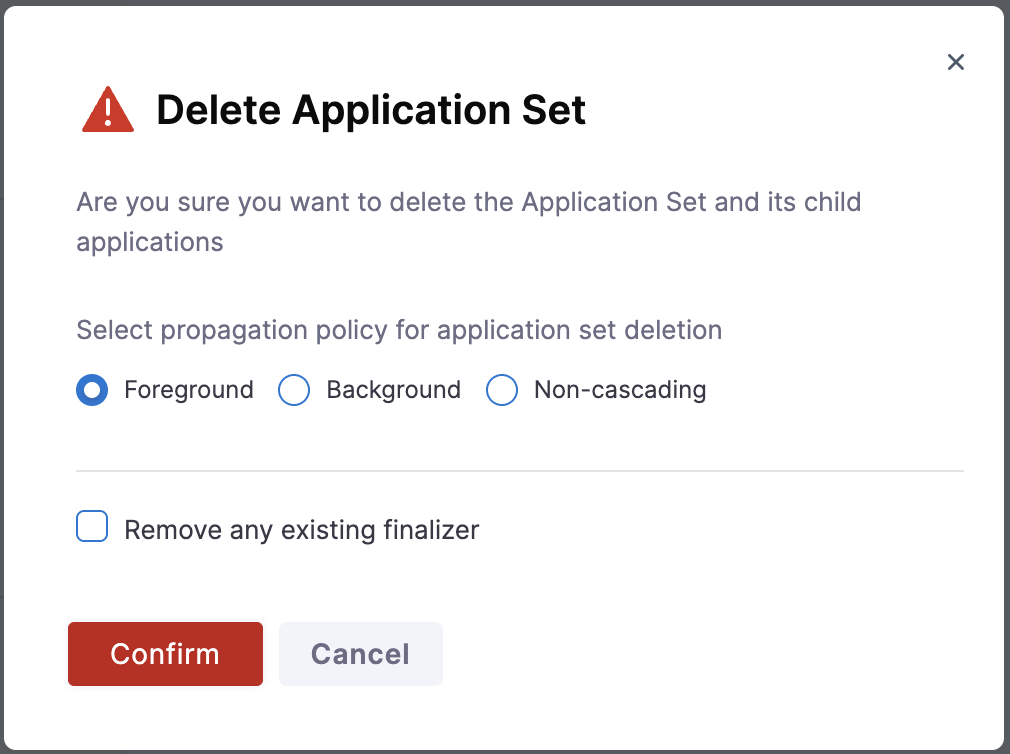
In the Delete Application Set dialog, configure the deletion options:
Propagation Policy: Select how the deletion should be handled:
- Foreground (recommended): Deletes the ApplicationSet first, then waits for all child applications and their resources to be deleted. This ensures a clean, ordered deletion process.
- Background: Deletes the ApplicationSet immediately and removes child applications asynchronously in the background. The ApplicationSet is removed from the UI before all resources are fully cleaned up.
- Non-cascading: Deletes only the ApplicationSet itself without deleting child applications. The applications become orphaned and continue running independently.
Remove any existing finalizer: Check this option to remove Kubernetes finalizers and force immediate deletion. Only use this if the ApplicationSet is stuck in a deleting state.
-
Click Confirm to proceed with the deletion.
Deleting an ApplicationSet with Foreground or Background propagation will also delete all applications generated by it and their deployed resources, unless you've configured the sync policy to preserve resources or you select Non-cascading.
Create ApplicationSet (Standard Flow)
If you don't have the GITOPS_APPLICATIONSET_FIRST_CLASS_SUPPORT feature flag enabled, follow this standard flow to create ApplicationSets.
We recommend requesting the first-class ApplicationSet support feature flag for a better experience with enhanced UI, Service/Environment integration, and improved management capabilities. Contact Harness Support to enable it.
Step 1: Update manifests in Git
The following example uses a Git generator from the Argo Project's public repository.
-
Clone the ApplicationSet repository and navigate to the example directory.
-
Update
git-generator-files.yamlwith the following YAML configuration:apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: guestbook
spec:
generators:
- git:
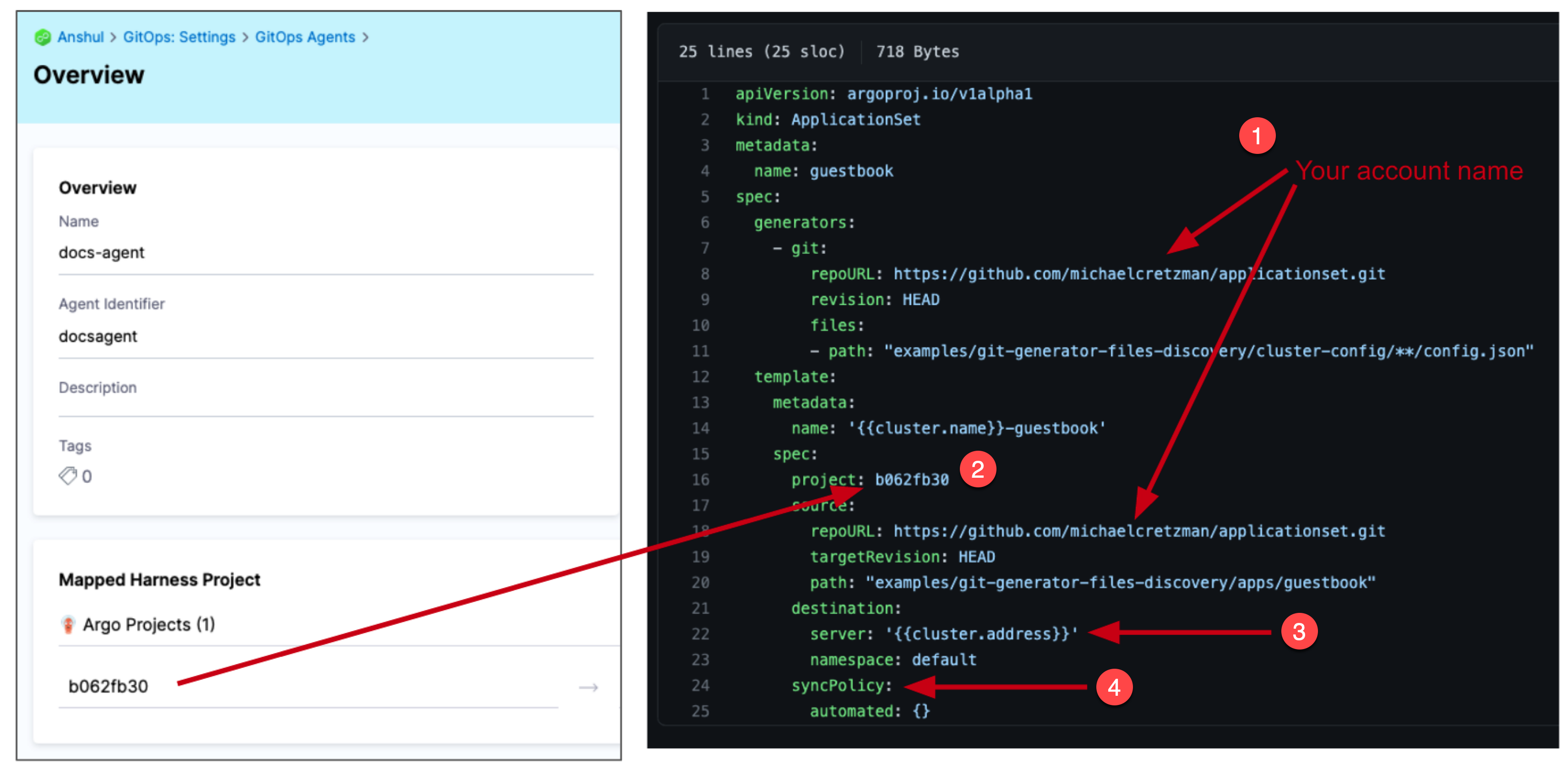
repoURL: https://github.com/<YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME>/applicationset.git
revision: HEAD
files:
- path: "examples/git-generator-files-discovery/cluster-config/**/config.json"
template:
metadata:
name: '{{cluster.name}}-guestbook'
labels:
harness.io/envRef: '{{envTag}}'
harness.io/serviceRef: '{{serviceTag}}'
harness.io/buildRef: '{{releaseTag}}'
spec:
project: <PROJECT_ID_IN_AGENT_PAGE>
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/<YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME>/applicationset.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: "examples/git-generator-files-discovery/apps/guestbook"
destination:
server: '{{cluster.address}}'
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated: {} -
To get the project ID:
- Go to Deployments > GitOps > Settings > GitOps Agents
- Find the Argo Project ID you want to use to create the ApplicationSet
-
Navigate to
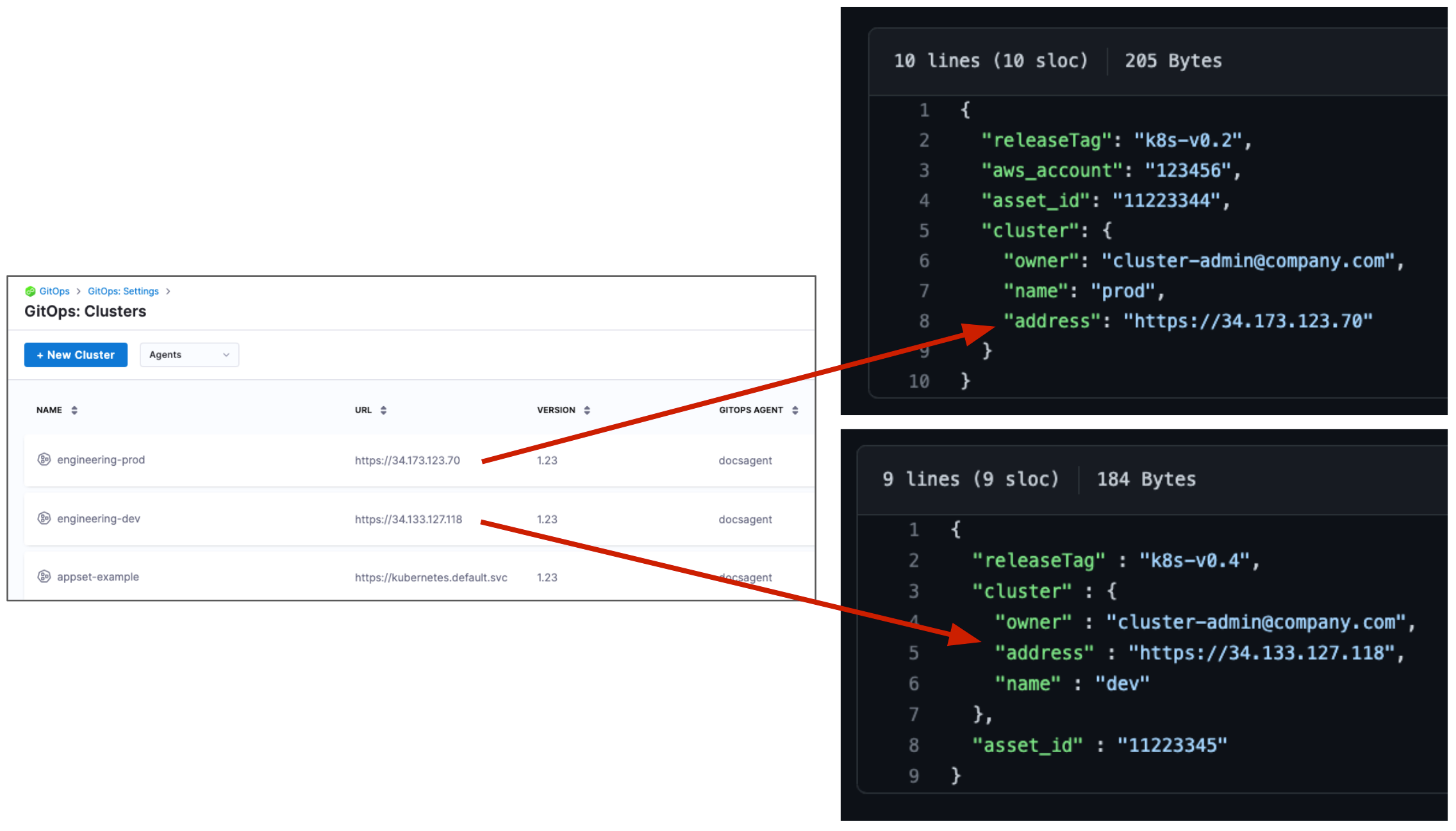
applicationset/examples/git-generator-files-discovery/cluster-config/engineering/dev/config.json -
Replace
"address": "https://1.2.3.4"with the Endpoint IP address for your dev target cluster. Ensure you use thehttps://scheme.noteThis cluster must be created in Harness beforehand.
-
Repeat for the prod target cluster by modifying
applicationset/examples/git-generator-files-discovery/cluster-config/engineering/prod/config.json
Here's an example of the cluster configuration:
Both JSON and YAML formats are supported for ApplicationSet configuration files.
Step 2: Create the ApplicationSet application
-
In your Harness project, go to Deployments > GitOps.
-
Select Applications from the left navigation.
-
Click New Application.
-
Enter the following details:
- Application Name: Enter a name for your ApplicationSet
- GitOps Agent: Select the agent that will manage this ApplicationSet
- Sync Policy: Leave the default settings or configure as needed
-
Click Continue.
-
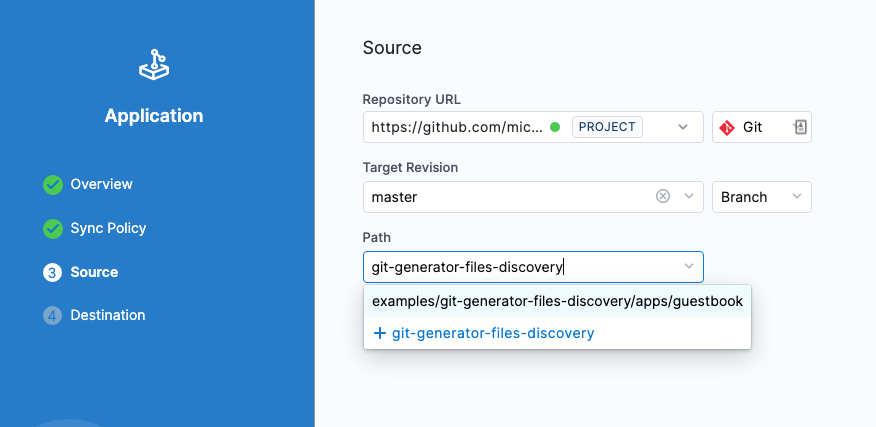
In the Source section, configure:
- Repository URL: Select the GitOps repository you added earlier
- Target Revision: Select master or your main branch
- Path: Enter
examples/git-generator-files-discovery
-
Click Continue.
-
In the Destination section:
- Cluster: Select the cluster where your GitOps agent is installed
- Namespace: Select the namespace where your GitOps agent is installed
-
Click Save to create the ApplicationSet application.
Step 3: Sync the ApplicationSet application
You can sync the ApplicationSet from two places: the Applications view or a PR pipeline.
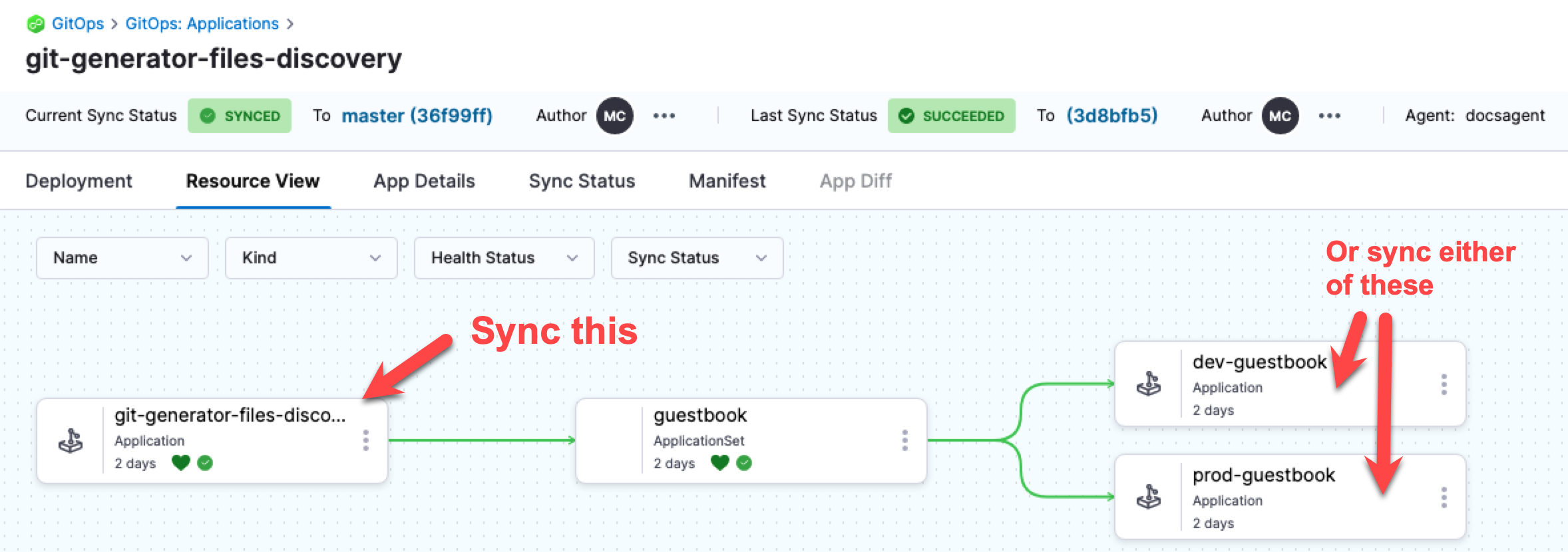
Sync from Applications View
From the Applications view, you can sync the Harness ApplicationSet application or the individual child applications independently.
Automatic Syncing
If you configure automatic syncing in the ApplicationSet template, the applications sync automatically. See syncPolicy.automated in the following example:
template:
metadata:
name: '{{cluster.name}}-guestbook'
spec:
project: 191b68fc
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/johndoe/applicationset.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: "examples/git-generator-files-discovery/apps/guestbook"
destination:
server: '{{cluster.address}}'
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated: {}
Sync via PR Pipeline
For syncing ApplicationSets through PR pipelines, refer to Sync GitOps applications.
Consider enabling the GITOPS_APPLICATIONSET_FIRST_CLASS_SUPPORT feature flag to access the enhanced ApplicationSet experience with a dedicated UI wizard, Service/Environment integration, and better management capabilities.
Next Steps
- Learn about ApplicationSet basics
- Explore PR Pipelines with ApplicationSets
- Understand GitOps Application management