Manage an Argo CD configuration in Git with Harness GitOps
You can define Argo CD applications, projects, and settings declaratively by using Kubernetes manifests, and you can manage these manifests in Harness GitOps just as you would a Harness GitOps application.
This topic walks you through setting up Harness GitOps to manage Argo CD configurations stored in your Git repository.
Create the GitOps application
A Harness GitOps application consists of a GitOps repository, cluster, and application settings.
To add the GitOps application for your Argo CD configuration, do the following:
-
Install a Harness GitOps agent on the destination cluster.
-
In Harness GitOps, add a GitOps repository for the repository where your Argo CD configurations are stored. For steps on how to do this, go to Add a Harness GitOps repository.
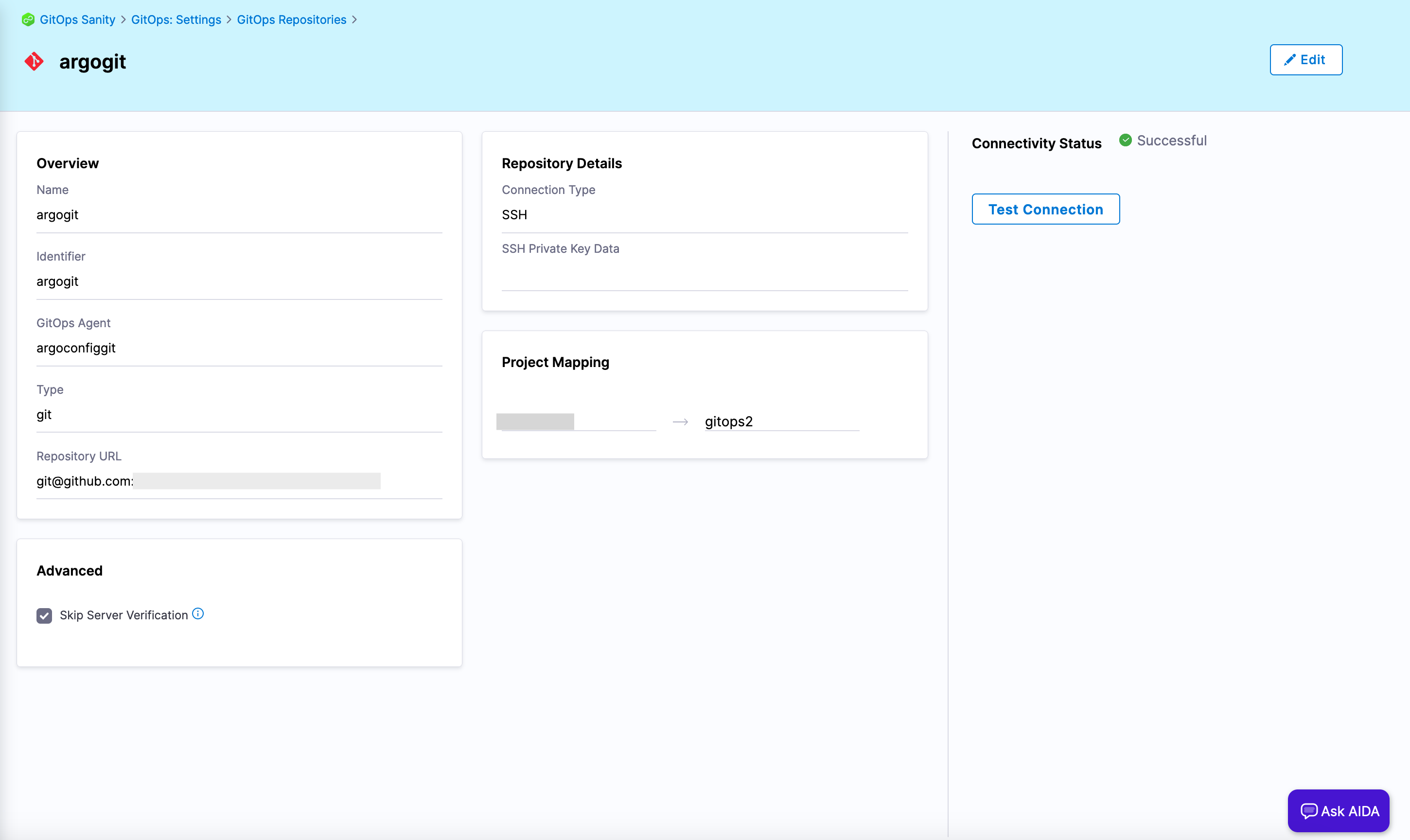
Figure 1: GitOps repository. -
Add a Harness GitOps cluster for the destination cluster where you installed the Harness GitOps agent.
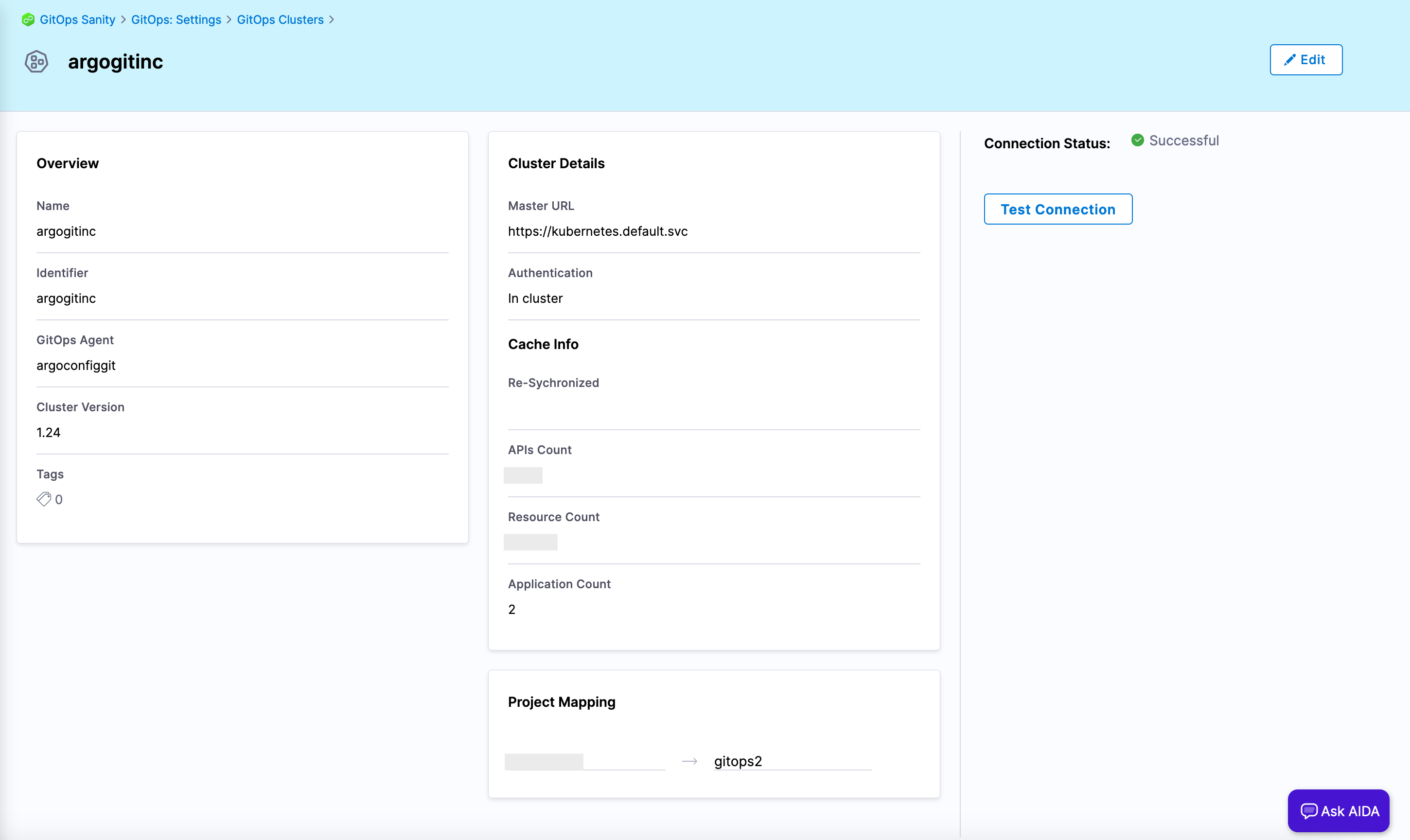
Figure 2: GitOps cluster. -
Add a Harness GitOps application for the Argo CD configuration.
- Use the Harness GitOps repository added earlier.
- In Path, select or add the path to the Argo CD configurations.
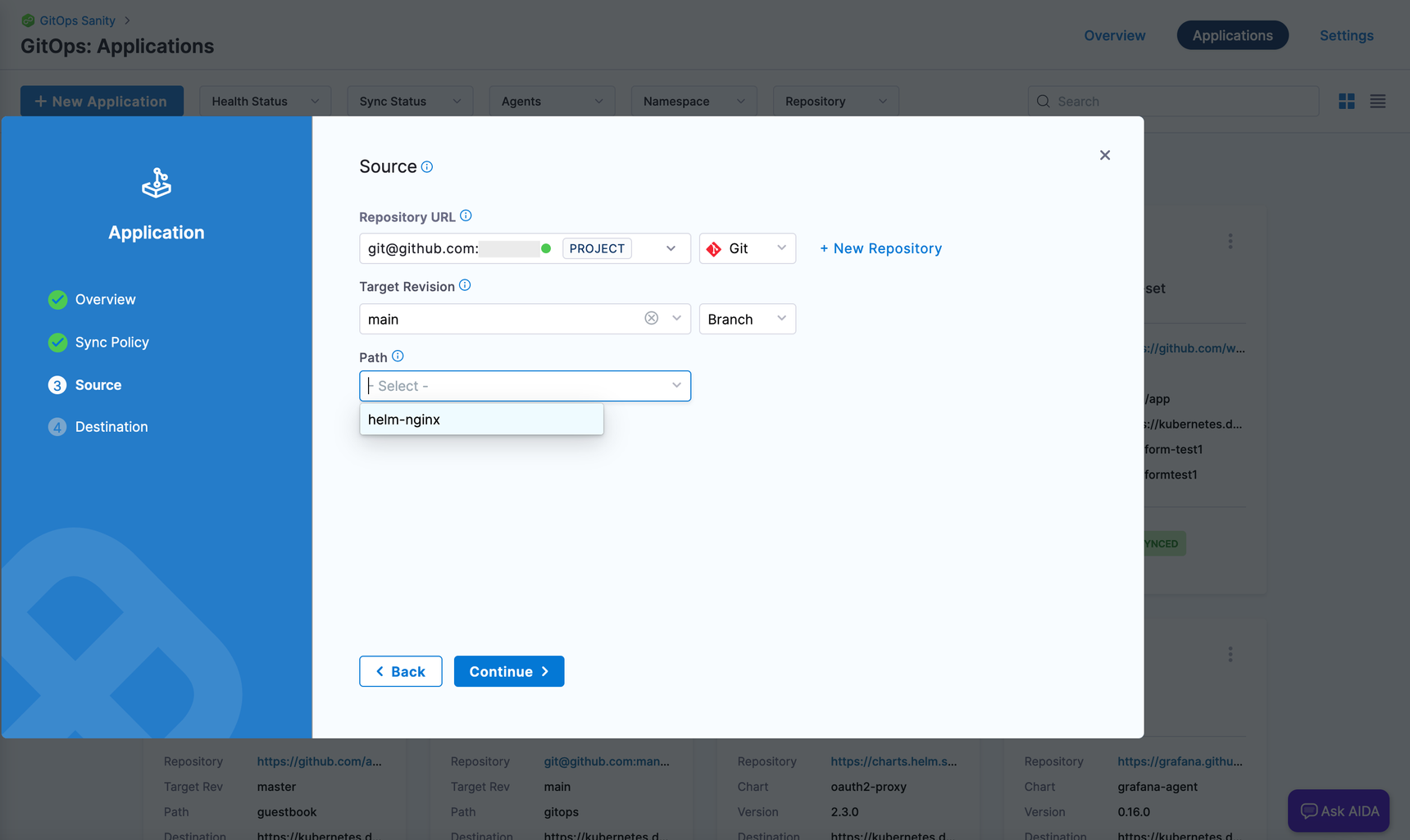
Figure 3: Path to Argo CD configs in GitOps application. noteIf the repository directory has subordinate directories, select Directory Recurse.
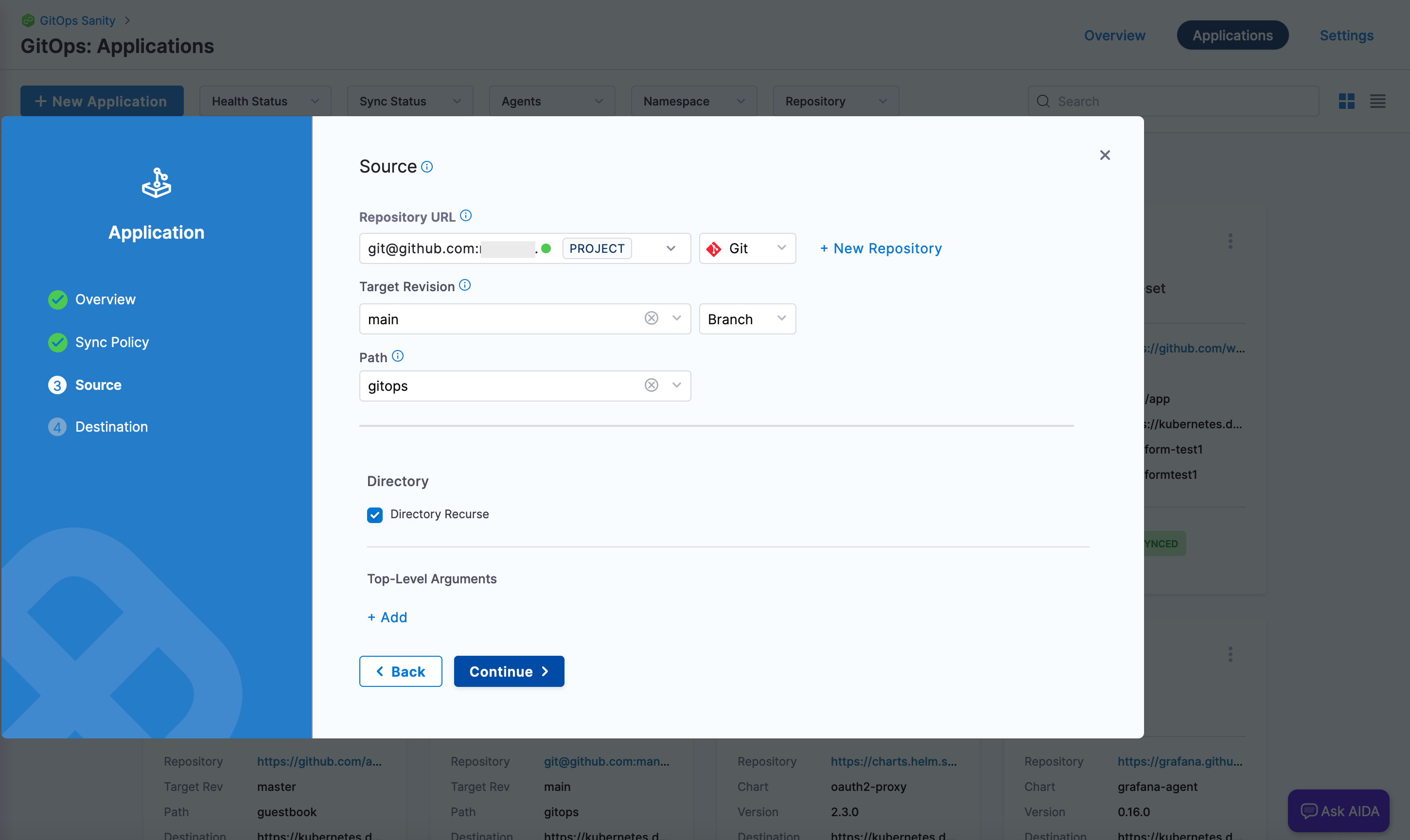
Figure 4: Directory Recurse option. - Use the Harness GitOps cluster added earlier. In Namespace, provide the namespace where the agent is installed.
-
Save the Harness GitOps application.
-
If the sync policy is manual, sync the application manually.
Once these steps are complete, you should be able to see the newly created GitOps entities in the Harness project that you configured in Git.
Git Configuration Files
Most entities, such as ConfigMaps, repository credentials, and applications will work without requiring modifications. Some entities, namely clusters, repositories, and AppProject, need some Harness-specific values added to the existing Argo-provided templates.
Sample repository configuration
Here's a sample repository configuration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: my-https-anon-repo
namespace: argo-config-git
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
name: my-https-anon-repo
project: default
url: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps
type: git
Sample cluster configuration
Here's a sample cluster config:
apiVersion: v1
data:
config: eyJiZWFyZXJUb2tlbiI6InRlc3QiLCJ0bHNDbGllbnRDb25maWciOnsiaW5zZWN1cmUiOnRydWV9fQ==
server: aHR0cHM6Ly90ZXN0LmNvbQo=
stringData:
name: argogitcluster1
project: default
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
managed-by: argocd.argoproj.io
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
name: cluster-test1
namespace: argo-config-git
type: Opaque
Additional fields for clusters and repositories
Here are the additional fields required for clusters and repositories:
-
stringData.projectordata.project, whose value is the AppProject name. Provide this field only if you want the entity to reside within the scope of a Harness project or organization. -
stringData.nameordata.name, whose value is the name of the entity in Harness.
The remaining fields remain the same as in Argo CD.
Sample Argo AppProject configuration
Here's a sample configuration for the Argo CD AppProject:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: AppProject
metadata:
labels:
accountId: b.<harness-account-id>.e
orgId: <harness-organization>
projectId: <harness-project>
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
name: default
namespace: argo-config-git
spec:
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: '*'
kind: '*'
destinations:
- namespace: '*'
server: '*'
sourceRepos:
- '*'
# SourceNamespaces defines the namespaces application resources are allowed to be created in
sourceNamespaces:
- x
- y
- z
# PermitOnlyProjectScopedClusters determines whether destinations can only reference clusters which are project-scoped
permitOnlyProjectScopedClusters: true
A Harness account ID is a MongoDB document ID that could start with an underscore (_). This ID is not a valid Kubernetes label according to the syntax and character set documentation for Kubernetes labels. Therefore, Harness GitOps creates a hash of the account ID. The hash is of the form b.<harness-account-id>.e.
Additional fields required for the Argo CD AppProject
Following are the additional fields required for the AppProject:
-
metadata.labels.accountId, whose value is the Harness account identifier. -
metadata.labels.orgId, whose value is the Harness organization identifier. -
metadata.labels.projectId, whose value is the Harness project identifier.
The remaining fields remain the same as in Argo CD.
By default, Harness creates an AppProject for you when you create the repository and cluster at the beginning of this procedure. The name of this AppProject is available on the agent details page, under Mapped Harness Project. If you are creating a new AppProject, remember to add the mapping for the Argo project to the Harness project in the GitOps Agent, and then use the value of metadata.name in the project field of the entity configurations. The UI requires that information to show the entities.
You can use all other entity configurations without modifying them.
Sample application
Here's a sample application:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: guestbook
# You'll usually want to add your resources to the argocd namespace.
namespace: argo-config-git
# Add this finalizer ONLY if you want these to cascade delete.
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
# Add labels to your application object.
labels:
name: guestbook
spec:
# The project the application belongs to.
project: default
# Source of the application manifests
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git # Can point to either a Helm chart repo or a git repo.
targetRevision: master # For Helm, this refers to the chart version.
path: guestbook # This has no meaning for Helm charts pulled directly from a Helm repo instead of git.
helm:
# Ignore locally missing valueFiles when installing Helm chart. Defaults to false
ignoreMissingValueFiles: true
# Skip custom resource definition installation if chart contains custom resource definitions. Defaults to false
skipCrds: true
# Skip schema validation if chart contains JSON schema validation. Defaults to false
skipSchemaValidation: true
# SkipTests skips test manifest installation step (Helm's --skip-tests).
skipTests: true
# Sources field specifies the list of sources for the application
sources:
- repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argocd-example-apps.git # Can point to either a Helm chart repo or a git repo.
targetRevision: HEAD # For Helm, this refers to the chart version.
path: guestbook # This has no meaning for Helm charts pulled directly from a Helm repo instead of git.
ref: my-repo # For Helm, acts as a reference to this source for fetching values files from this source. Has no meaning when under `source` field
# Destination cluster and namespace to deploy the application
destination:
# cluster API URL
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
# or cluster name
# name: in-cluster
# The namespace will only be set for namespace-scoped resources that have not set a value for .metadata.namespace
namespace: guestbook
# Extra information to show in the Argo CD Application details tab
info:
- name: 'Example:'
value: 'https://example.com'
# Sync policy
syncPolicy:
automated: # automated sync by default retries failed attempts 5 times with following delays between attempts ( 5s, 10s, 20s, 40s, 80s ); retry controlled using `retry` field.
prune: true # Specifies if resources should be pruned during auto-syncing ( false by default ).
selfHeal: true # Specifies if partial app sync should be executed when resources are changed only in target Kubernetes cluster and no git change detected ( false by default ).
allowEmpty: false # Allows deleting all application resources during automatic syncing ( false by default ).
syncOptions: # Sync options which modifies sync behavior
- Validate=false # disables resource validation (equivalent to 'kubectl apply --validate=false') ( true by default ).
- CreateNamespace=true # Namespace Auto-Creation ensures that namespace specified as the application destination exists in the destination cluster.
- PrunePropagationPolicy=foreground # Supported policies are background, foreground and orphan.
- PruneLast=true # Allow the ability for resource pruning to happen as a final, implicit wave of a sync operation
managedNamespaceMetadata: # Sets the metadata for the application namespace. Only valid if CreateNamespace=true (see above), otherwise it's a no-op.
labels: # The labels to set on the application namespace
any: label
you: like
annotations: # The annotations to set on the application namespace
the: same
applies: for
annotations: on-the-namespace
# The retry feature is available since v1.7
retry:
limit: 5 # number of failed sync attempt retries; unlimited number of attempts if less than 0
backoff:
duration: 5s # the amount to back off. Default unit is seconds, but could also be a duration (e.g. "2m", "1h")
factor: 2 # a factor to multiply the base duration after each failed retry
maxDuration: 3m # the maximum amount of time allowed for the backoff strategy
# Will ignore differences between live and desired states during the diff. Note that these configurations are not
# used during the sync process.
ignoreDifferences:
# for the specified json pointers
- group: apps
kind: Deployment
jsonPointers:
- /spec/replicas
# for the specified managedFields managers
- group: "*"
kind: "*"
managedFieldsManagers:
- kube-controller-manager
# RevisionHistoryLimit limits the number of items kept in the application's revision history, which is used for
# informational purposes as well as for rollbacks to previous versions. This should only be changed in exceptional
# circumstances. Setting to zero will store no history. This will reduce storage used. Increasing will increase the
# space used to store the history, so we do not recommend increasing it.
revisionHistoryLimit: 10