GitOps Agent Disaster Recovery
This document outlines the disaster recovery (DR) strategy for GitOps agents. It provides instructions for setting up DR agents, creating backups, and performing failover operations between primary and secondary agent clusters.
Introduction
Disaster recovery for GitOps agents ensures your GitOps operations can continue even if your primary agent cluster becomes unavailable. The DR strategy involves setting up primary and secondary GitOps agents across different Kubernetes clusters and coordinating between them.
GitOps Agent Architecture
GitOps agents store all information on the Kubernetes cluster, which serves as the source of truth at all times.
Important Agent Behaviors
- Multiple Agents: If two identical agents run in separate clusters, tasks go to either agent. Entities will only exist on one agent, and the other agent's reconciler will remove them if they don't exist in its state.
- Same Behavior in Different Namespaces: The same behavior occurs if an agent is installed in a different namespace on the same cluster.
- HA Agent Support: Harness supports high availability (HA) agents. Multiple replicas of the agent in the same namespace will work together, with one pod handling requests if another goes down.
Setting Up DR Agents
Prerequisites
- Two separate Kubernetes clusters (primary and secondary)
- Same namespace must be used on both clusters
- Primary and secondary agents must be of the same type (HA or non-HA, BYOA or non-BYOA)
Current Behavior Without DR Configuration
If your primary cluster loses connectivity and you switch to a secondary cluster by increasing the replica count for the same agent, all entities on Harness will be deleted. This happens because:
- The cluster is the source of truth at all times
- The secondary cluster is new and doesn't have any CRDs or data from the primary cluster
- The agent on the secondary cluster would clean up entities that don't exist in its state
Creating a Primary DR Agent
- Navigate to your Harness project and select GitOps > Settings > Agents
- Click New Agent
- Provide the agent name, namespace, and cluster
- Under the Advanced section, toggle the Disaster Recovery button
- Select Primary radio button and provide a primary identifier
- Complete the agent creation process
Creating a Secondary DR Agent
- Navigate to your Harness project and select GitOps > Settings > Agents
- Click New Agent
- Scroll down to the Advanced section
- Toggle the Disaster Recovery button
- Select Secondary radio button and provide a secondary identifier
- Select the primary agent from the list of agents
- Complete the agent creation process
Important: When the primary agent is selected, it will override the name (identifier) for the current agent. This is because primary and secondary agents share the same agent identifier but differ in disaster recovery identifier.
Make sure the secondary agent is setup in a different cluster. The two agents cannot be deployed to the same cluster.
To view your primary and secondary agents, you can expand on the primary agent in the agents dashboard.
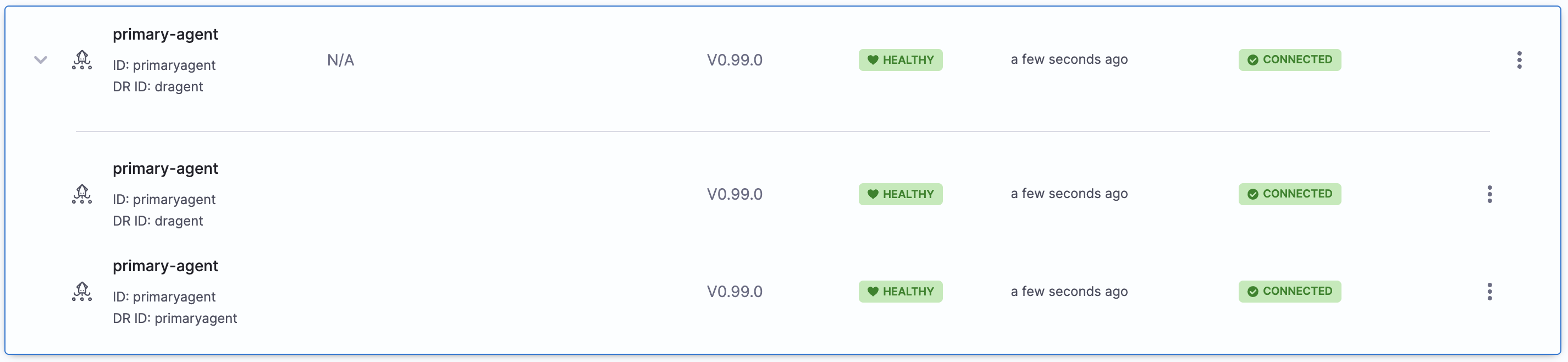
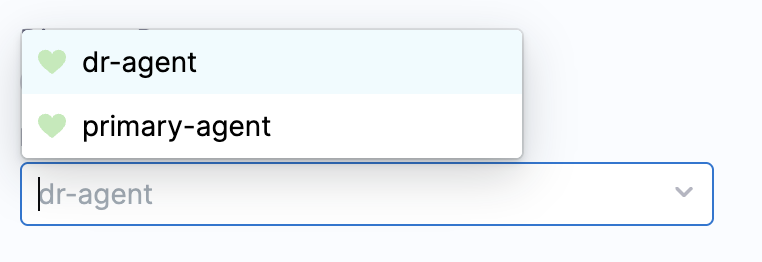
Switching Between Agents
To switch between primary and secondary agents:
- Navigate to the primary agent details page
- Find the list box that displays disaster recovery IDs
- The currently selected ID indicates which agent is active
- Change the disaster recovery identifier and save to change the currently active agent
Backup and Restore
Creating a Backup
To back up entities from the GitOps agent namespace (including applications, applicationsets, repositories, clusters, configmaps, and secrets), use the Argo CD binary from containers like application-controller, applicationset controller, or gitops-agent.
Since the application-controller has higher memory resources assigned than the gitops-agent, it's recommended to use that container:
kubectl exec -it sts/argocd-application-controller -n <NAMESPACE> -- argocd admin export > backup.yaml
This command exports all GitOps resources, including:
- Applications
- ApplicationSets
- Repositories
- Clusters
- ConfigMaps
- Secrets (including Argo CD CM but excluding gitops-agent and gitops-agent-upgrader CM)
The backup file will contain a full export of your configuration in YAML format, including application definitions, repositories, clusters, and other Argo CD resources.
Sample YAML
apiVersion: v1
data:
admin.enabled: "true"
application.instanceLabelKey: argocd.argoproj.io/instance
url: https://your-argocd-url.example.com
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
annotations:
meta.helm.sh/release-name: argocd
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: your-namespace
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: server
app.kubernetes.io/instance: argocd
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-cm
name: argocd-cm
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
policy.csv: ""
policy.default: ""
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-rbac-cm
name: argocd-rbac-cm
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
ssh_known_hosts: |
# Standard SSH known hosts entries
github.com ssh-ed25519 EXAMPLE_SSH_KEY_CONTENT
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
admin.password: your_hashed_password
admin.passwordMtime: your_password_modified_time
server.secretkey: your_server_secret_key
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: server
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-secret
name: argocd-secret
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
config: your_cluster_config
name: your_cluster_name
server: your_cluster_server_url
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
name: cluster-example-123456789
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
name: your_repository_name
password: your_repository_password
project: your_project_id
type: git
url: https://github.com/your-org/your-repository
username: your_username
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
name: repo-example
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: AppProject
metadata:
name: example-project
spec:
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: '*'
kind: '*'
destinations:
- namespace: '*'
server: '*'
sourceRepos:
- '*'
status: {}
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: example-app
spec:
destination:
namespace: your-app-namespace
server: https://your-cluster-api-url
project: example-project
source:
path: your-app-path
repoURL: https://github.com/your-org/your-repository
targetRevision: main
syncPolicy:
automated: {}
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Restoring a Backup
To import a backup:
kubectl exec -it sts/argocd-application-controller -n <NAMESPACE> -- argocd admin import - < backup.yaml
The output will show all resources being created or configured in the namespace, such as:
/ConfigMap argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm in namespace <NAMESPACE> created
/Secret cluster-35.233.139.33-2495201771 in namespace <NAMESPACE> created
/Secret repo-3993363181 in namespace <NAMESPACE> created
argoproj.io/Application app in namespace <NAMESPACE> created
argoproj.io/Application app2 in namespace <NAMESPACE> created
Sync Windows
Sync windows can be used as a means of coordinating sync timing between multiple Argo CD instances (primary and secondary agents). This is particularly useful for controlling which Argo CD instance is performing syncs at any given time.
Conclusion
GitOps agent DR mode provides a robust solution for ensuring business continuity in case of cluster failures. By following the steps outlined in this document, you can set up DR agents, create backups, and perform failover operations when needed.
For additional assistance, contact Harness Support.