Create a GitOps cluster with IAM role
This topic describes how to create a Harness GitOps cluster in Amazon EKS, and deploy applications to the cluster using an IAM role.
What is an IAM role?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles allow you to manage user access and permissions to various Amazon Web Services (AWS) services and resources. IAM roles are sets of permissions that you can assign to AWS services or resources, rather than individual users.
This tutorial covers how to handle Harness GitOps Agent setup in a multi-cluster AWS environment and deploy applications to those clusters by letting the Agent assume an IAM role.
GitOps clusters with IAM roles can be created only for a GitOps Agent installed in Amazon EKS.
Objectives
You'll learn how to create:
-
A management cluster that hosts the Harness GitOps Agent.
-
An IAM role,
role/ArgoCDthat the GitOps Agent assumes first. -
A testing cluster in which you can deploy a guestbook application.
-
An IAM role,
role/Deployerthat has permissions to deploy applications in your testing cluster.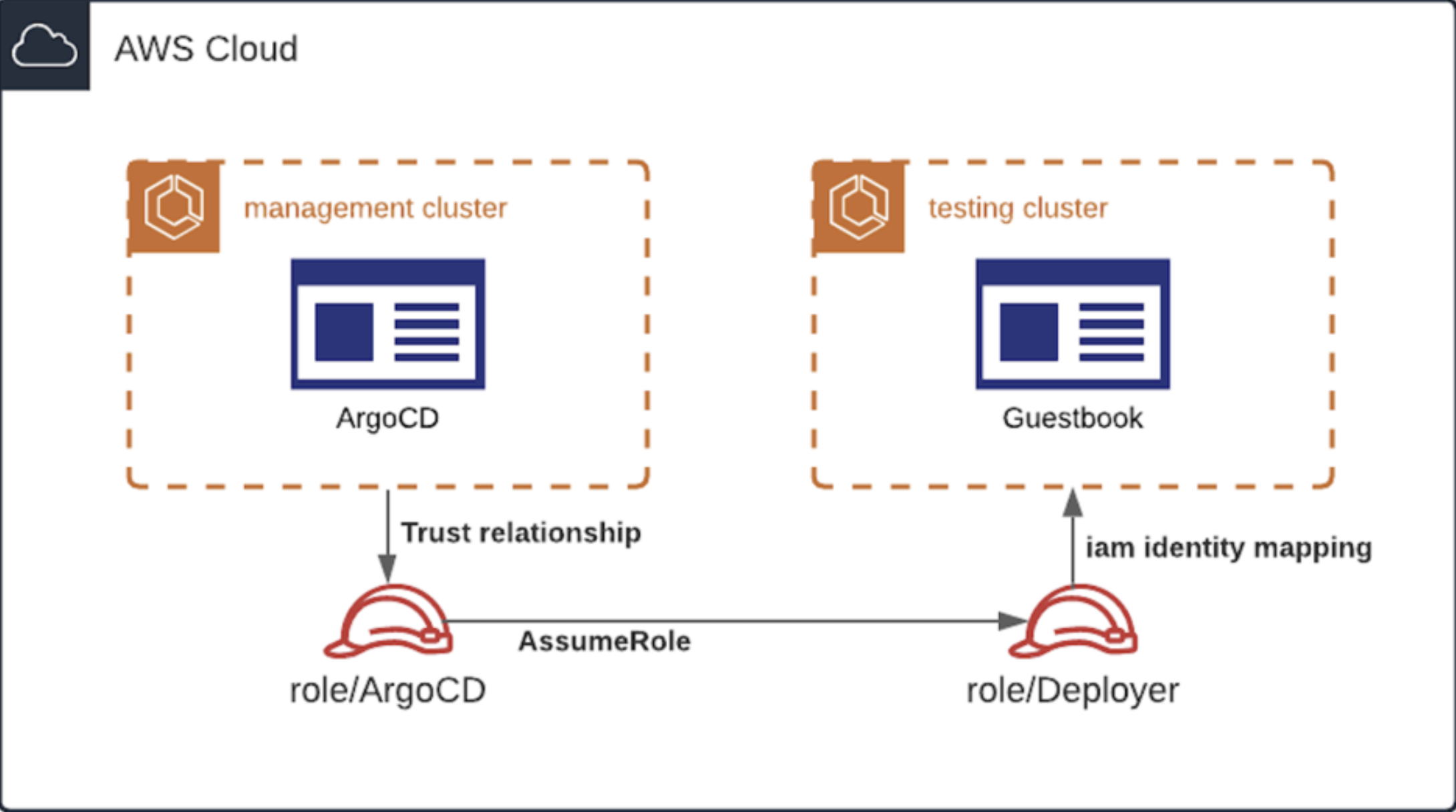
Requirements
Make sure that you have met the following requirements:
- You have an AWS account ready to receive a couple of new VPC's with EKS clusters.
- You have installed and configured awscli for your account.
- You have installed eksctl on your machine.
- You have installed kubectl on your machine.
Create a management cluster
Here, you will create two clusters in a single AWS account. The configuration works with cross-account and multi-cluster setups by setting the proper trust relations between the IAM roles.
Provision the management cluster
Use the following command to provision the management cluster using an OpenID Connect (OIDC) provider:
eksctl create cluster --name management --with-oidc
This command takes anytime between 10 to 20 minutes to execute. It creates a management cluster, and everything it needs to function such as VPC, security groups, EC2 nodegroup, and so on.
The AWS authenticator packaged with Harness GitOps Agent uses the OIDC provider to acquire a token. Using this token, the Agent can assume the IAM role, role/ArgoCD that you'll create in the next step.
Create an IAM role for your GitOps Agent
-
Set the management cluster
AWS_ACCOUNT_IDandOIDC_PROVIDERas environment variables using the following commands:AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query "Account" --output text)OIDC_PROVIDER=$(aws eks describe-cluster --name management --query "cluster.identity.oidc.issuer" --output text | sed -e "s/^https:\/\///") -
Create a
trust.jsonfile with the variables you set in the previous step.You must reference the namespace on which you will deploy your GitOps Agent so that all cluster roles can assume the IAM role you'll create in the next step.
read -r -d '' TRUST_RELATIONSHIP <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:oidc-provider/${OIDC_PROVIDER}"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"${OIDC_PROVIDER}:sub": "system:serviceaccount:iam:*"
}
}
}
]
}
EOF
echo "${TRUST_RELATIONSHIP}" > trust.json && cat trust.jsonMake sure that the
trust.jsonfile includes the properAWS_ACCOUNT_IDandOIDC_PROVIDER:
aws iam create-role --role-name ArgoCD --assume-role-policy-document file://trust.json --description "IAM Role to be used by Harness GitOps Agent to gain AWS access" -
Create an inline policy that gives the IAM role the ability to assume other roles so that GitOps Agent can assume the Deployer role that you'll create later.
You could also use the Argo CD role directly. However, having a separate role to deploy resources into the testing cluster is recommended as it is more flexible and secure.
read -r -d '' POLICY <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AssumeRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
EOF
echo "${POLICY}" > policy.json && cat policy.json
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name ArgoCD --policy-name AssumeRole --policy-document file://policy.jsonUse the AWS web console to check the role you just created. The Kubernetes service accounts that the Agent uses in the management cluster assumes the IAM role through the OIDC provider.
Set up Harness GitOps Agent
Create a namespace for Harness GitOps Agent in the management cluster using the following command:
kubectl create namespace iam
Go to Installing a GitOps Agent for a tutorial on how to create a Harness GitOps Agent.
Patch the GitOps Agent
-
Annotate the Kubernetes service accounts the Agent used with the ARN of the role to instruct the GitOps Agent to use the role you defined earlier.
kubectl -n iam patch serviceaccount argocd-application-controller --type=json \
-p="[{\"op\": \"add\", \"path\": \"/metadata/annotations/eks.amazonaws.com~1role-arn\", \"value\": \"arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/ArgoCD\"}]"
kubectl -n iam patch serviceaccount gitops-agent --type=json \
-p="[{\"op\": \"add\", \"path\": \"/metadata/annotations/eks.amazonaws.com~1role-arn\", \"value\": \"arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/ArgoCD\"}]"It is important that the annotations show the correct ARN of the ArgoCD role otherwise the Agent won't know which IAM role to assume.
-
Verify that the service accounts are changed correctly using the following commands:
kubectl -n iam describe serviceaccount gitops-agent
kubectl -n iam describe serviceaccount argocd-application-controller -
Patch the deployments to set the
securityContext/fsGroupto999so that the Docker image user can use the IAM authenticator.The IAM authenticator tries to mount a secret on
/var/run/secrets/eks.amazonaws.com/serviceaccount/token. If the correctfsGroup(999 corresponds to the Argo CD user) isn't set, it will fail.kubectl -n iam patch deployment gitops-agent --type=json \
-p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/template/spec/securityContext/fsGroup", "value": 999}]'
kubectl -n iam patch statefulset argocd-application-controller --type=json \
-p='[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/template/spec/securityContext/fsGroup", "value": 999}]'After patching Deployment and StatefulSet, the
application-controllerandgitops-agentpods restart.Ensure that the GitOps Agent is healthy and connected before proceeding any further.
Create a testing cluster
You have a working management cluster with GitOps Agent installed now. Next, you have to set up a testing cluster to which you can deploy the GitOps Agent.
Provision the testing cluster
Enter the following command to provision the testing cluster:
eksctl create cluster --name testing
You don't need an OIDC provider for the testing cluster. However, you need an IAM role to deploy applications in this cluster.
Create an IAM Role to deploy applications
-
Create a trust relationship for the Argo CD role so that it can assume the Deployer role.
infoIn a multi account setup, you can change the trust relationship to reference the Argo CD role in the account that holds the management cluster, and place the Deployer role in the same account as the testing cluster.
read -r -d '' TRUST_TESTING <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/ArgoCD"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {}
}
]
}
EOF
echo "${TRUST_TESTING}" > trust-testing.json && cat trust-testing.json -
Verify that the
AWS_ACCOUNT_IDfor the ArgoCD role is correct:aws iam create-role --role-name Deployer --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-testing.json --description "IAM Role to be used by AWS to Deploy in the testing cluster"
eksctl create iamidentitymapping --cluster testing --arn arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/Deployer --group system:masters --username deployer
Register the testing cluster with Harness to create and deploy applications
-
In Harness, select Deployments > GitOps.
-
Select Settings on the top right corner, and then select Clusters > New Cluster.
-
Enter a name for the cluster.
-
Select the GitOps Agent, and then select Continue.
-
In Details:
- Master URL: Enter the HTTP endpoint of the Kubernetes API of the server.
- Authentication: Select IRSA. IRSA stands for IAM Roles for Service Accounts.
- Role ARN: Enter the role your GitOps Agent will have to assume to deploy to this cluster.
- Certificate Authority Data: Enter the corresponding public certificate of the Kubernetes API.
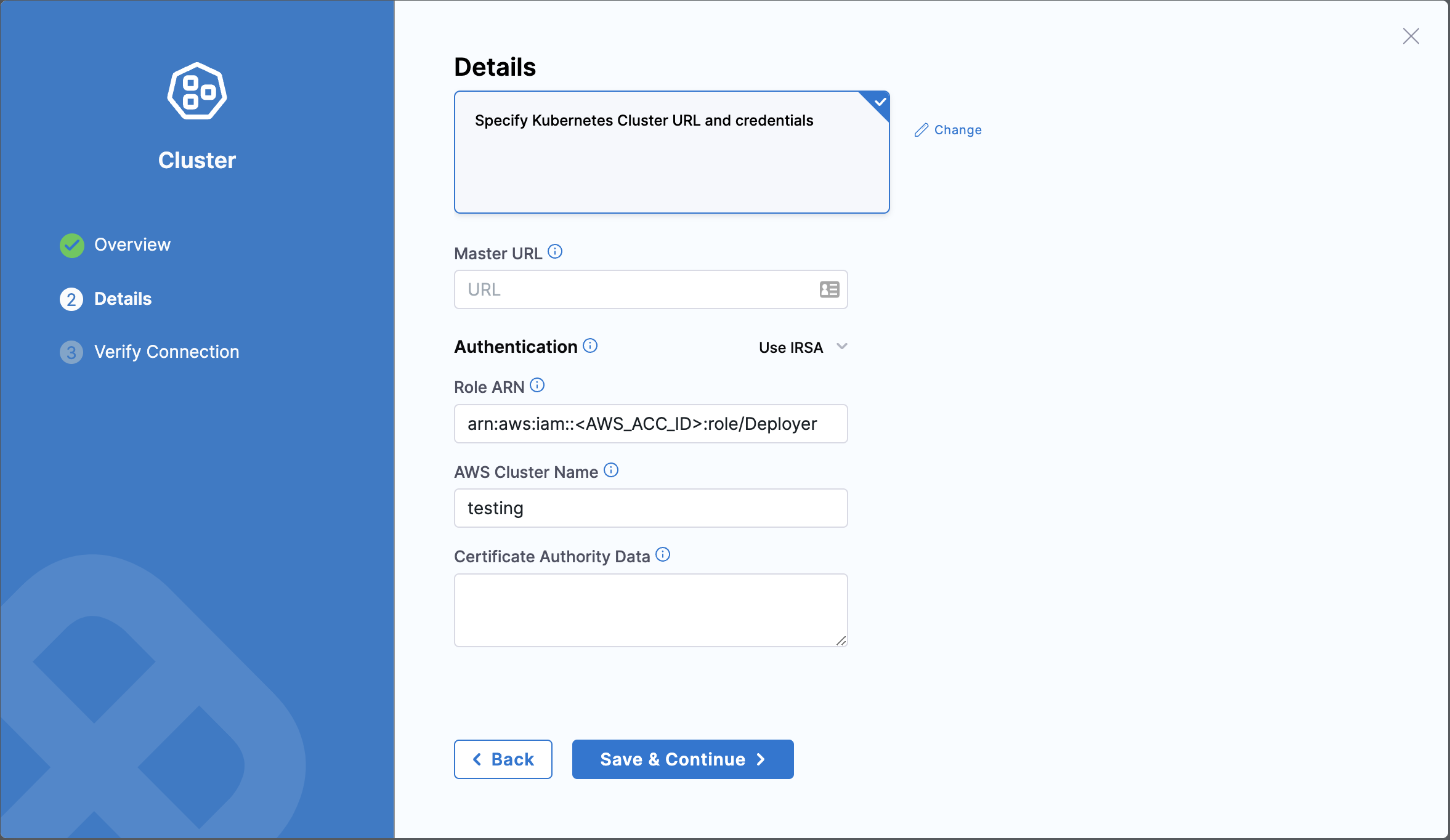
You have successfully created a cluster in Harness with the connection status, unknown.
Deploy applications to your cluster
You can now deploy applications to your cluster through Harness. Go to Add a Harness GitOps application for more details.