Custom Health Source
This topic covers how to add and configure Custom Health as a Health Source for the Verify step.
Harness offers support for all major APM vendors and log providers, but there are cases where a customized APM or log provider is needed. The Custom Health Source lets you customize APMs and log providers of your choice.
Before you begin
This page assumes you have followed the rest of the steps to set up CV. To learn more, go to Configure CV
Add a custom health source
This option is available only if you have configured the service and environment as fixed values.
A Health Source is basically a mapping of a Harness Service to the service in a deployment environment monitored by an APM or logging tool.
In Health Sources, click Add. The Add New Health Source settings appear.
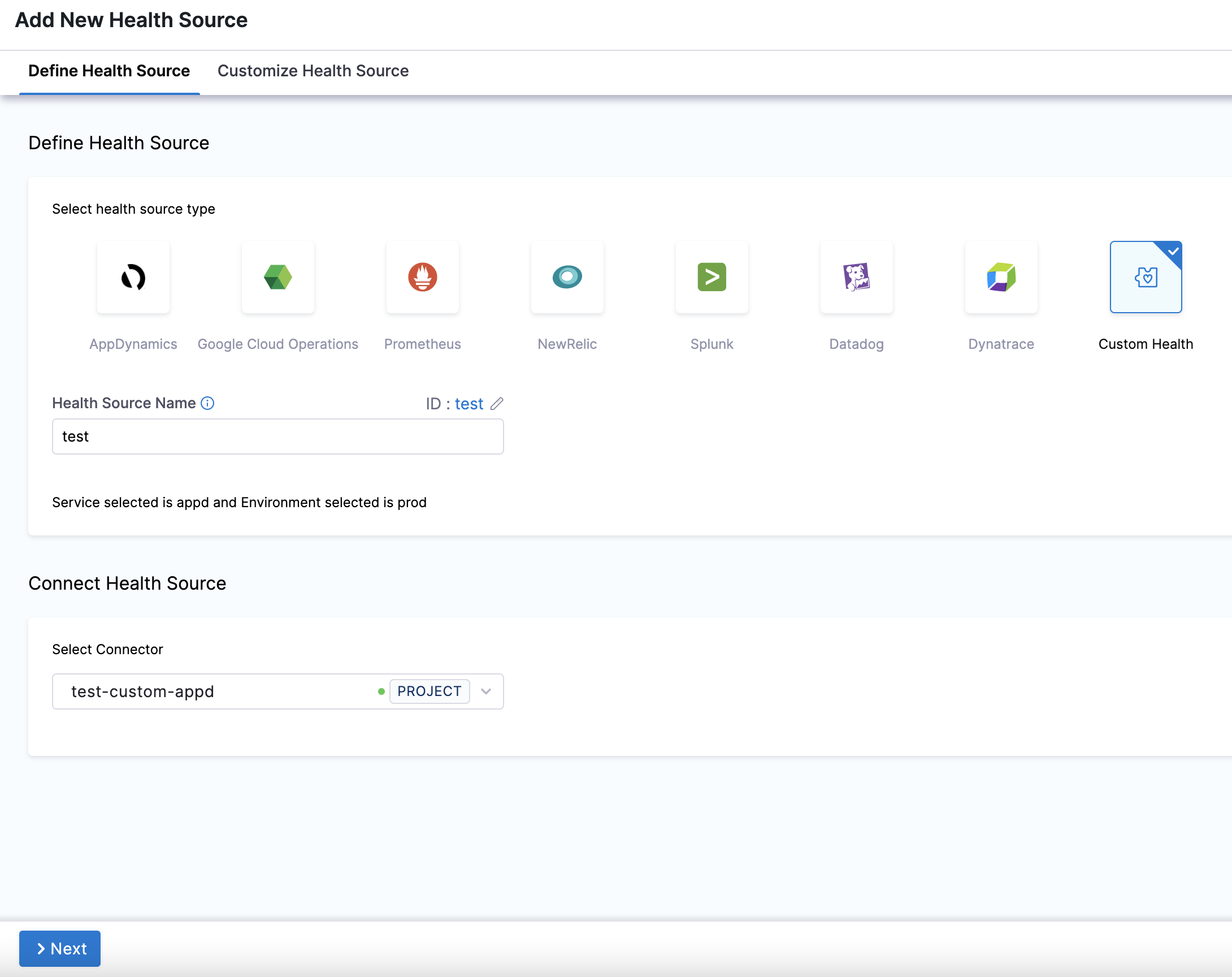
- In Select health source type, select Custom Health.
- In Health Source Name, enter a name for the health source. For example,
Quickstart. - In Connect Health Source, click Select Connector.
- In Connector settings, you can either choose an existing connector or click New Connector.
- Click Apply Selected. The Connector is added to the Health Source.
- In Select Feature, select the feature to be monitored. You can either select Custom Health Metrics or Custom Health Logs.
- Click Next.
Option: Custom Health Metrics
-
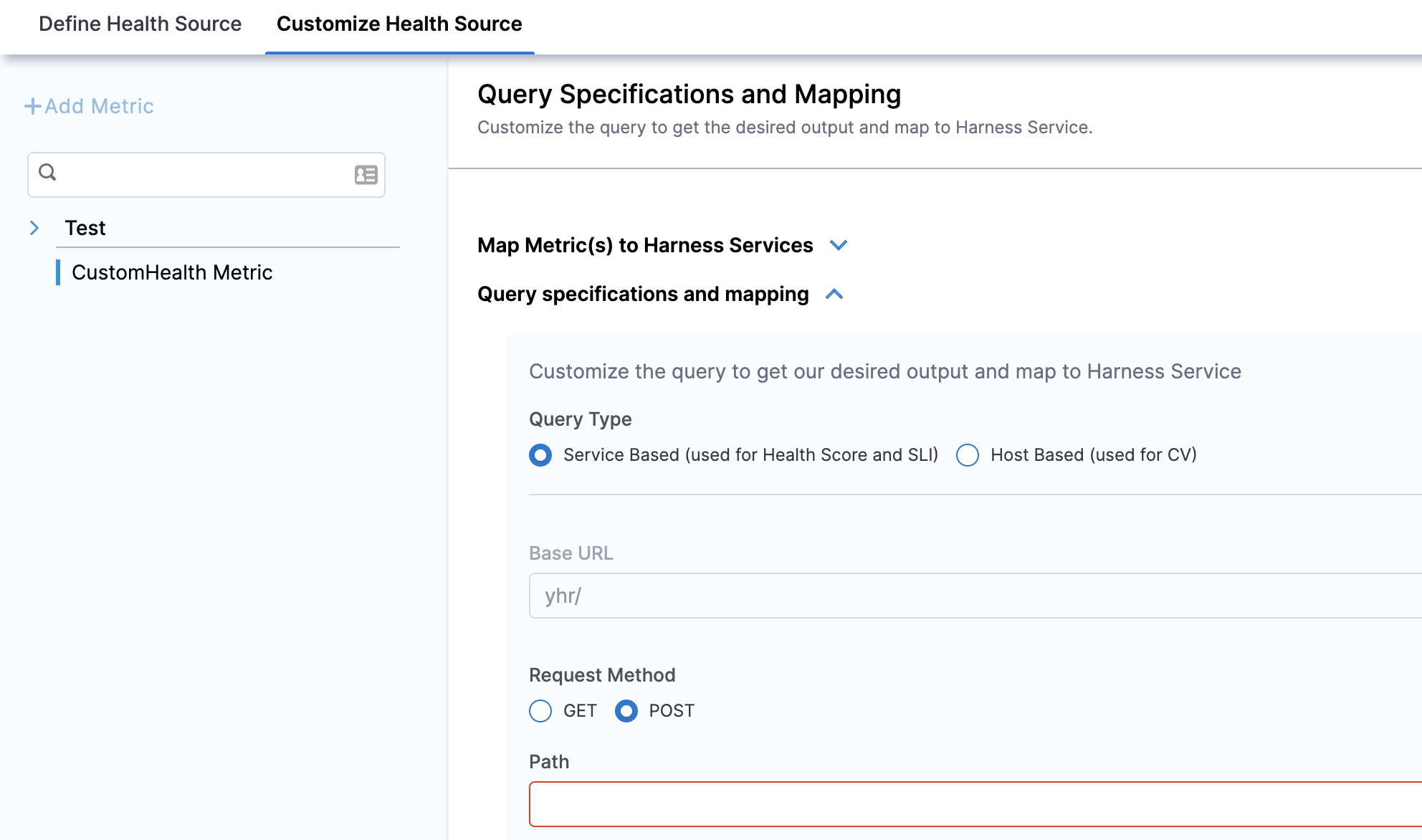
If you select Custom Health Metrics, the Customize Health Source settings appear as:
-
Click Map Metric(s) to Harness Services.
-
In Metric Name, enter the name of the metric.
-
In Group Name, click Add New and enter a name for the metric group.
-
Click Query specifications and mapping.
-
In Query Type you can choose either Service Based (used for Health Score and SLI) or Host Based (used for CV). If you select the query type as Host Based (Continuous Verification), the verification won't happen for SLI and Health Score (Service Based), and vice versa.
-
In Request Method, you can select GET or POST. If you select POST, you need to define the body format.
-
In Path, enter the complete path of the metric.
-
In Start and End Time Placeholders, enter the following:
- In Start time placeholder, enter the start time placeholder in the metric path.
- In Unit, select the preferred unit of measurement.
- In End time placeholder, enter the end time placeholder in the metric path.
- In Unit, select the preferred unit of measurement.
-
Click Fetch Records to retrieve records from the provided URL.
-
Click Metric values and charts. For each path, click the + icon to select the appropriate path from the data source.
- For Metric Value Json Path, it expects at least 2
*in the json path. - For Timestamp Value Json Path, it expects at least 2
*in the json path. - For Service Instance Identifier Json Path, it expects at least 1
*in the json path. - In Timestamp Format, enter a static value in dd/mm/yy format.
- For Metric Value Json Path, it expects at least 2
-
Click Assign. Select the services for which you want to apply the metric. You can select Health Score or SLI or both options. The subsequent steps depend on the service you select in this step.1. In Risk Category, select a risk type. Available options for risk types are:
- Errors
- Infrastructure
- Performance/Throughput
- Performance/Other
- Performance/Response Time
-
In Deviation compared to Baseline, select one of the options based on the selected risk type. Available options are:
- Higher value is higher risk - Select this option if a high value of the selected risk type is a risk.
- Lower value is higher risk - Select this option if lower value of the selected risk type is a risk.
-
Click Submit.
Option: Custom Health Logs
-
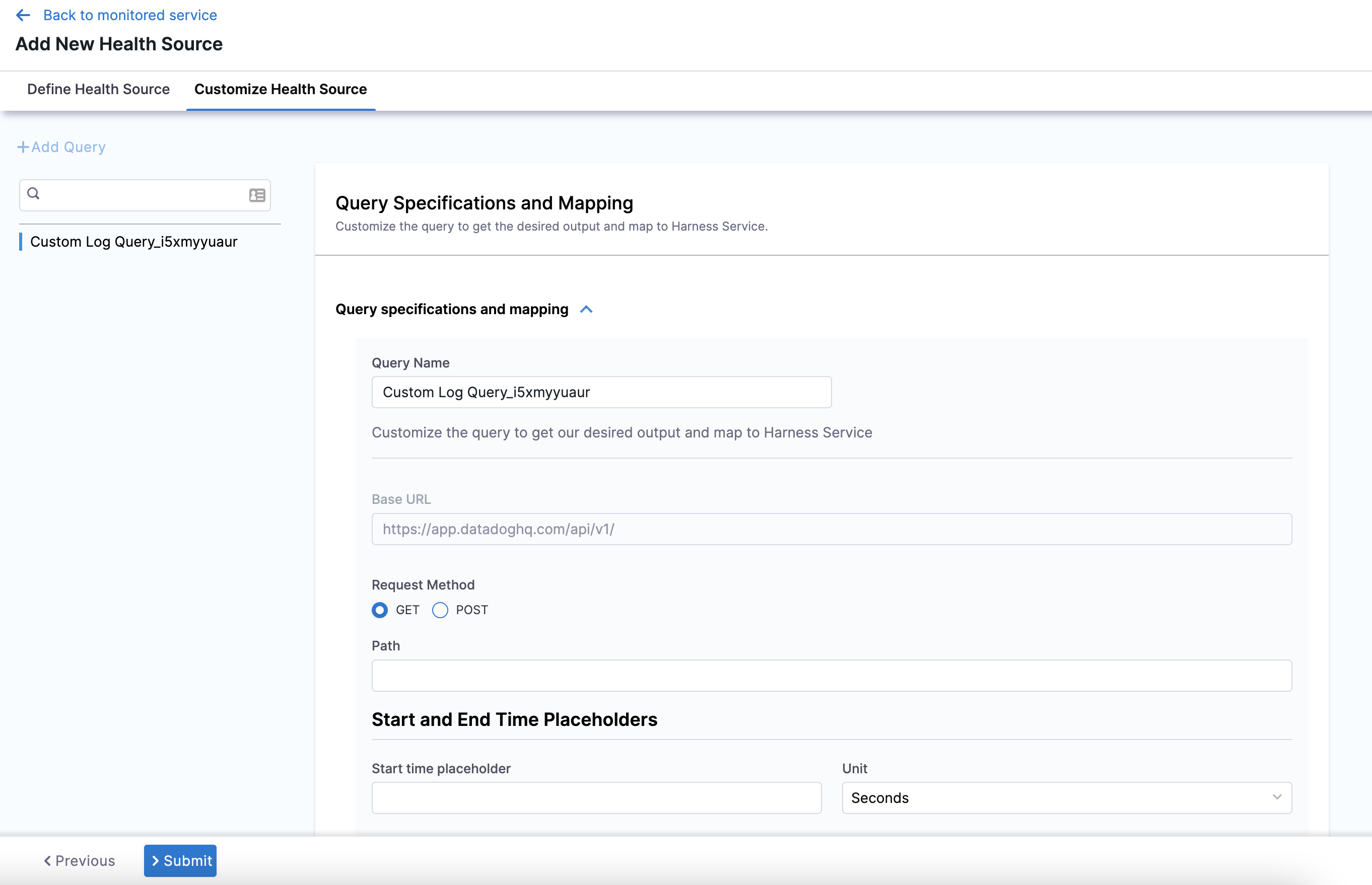
If you select Custom Health Logs, the Customize Health Source settings appear as:
-
Click Query specifications and mapping.
-
In Query Name, enter a name for the query. For example,
Custom Log Query. -
In Request Method, you can select GET or POST. If you select POST, you need to define the body format.
-
In Path, enter the complete path of the metric. For example,
v2/logs/events/search. -
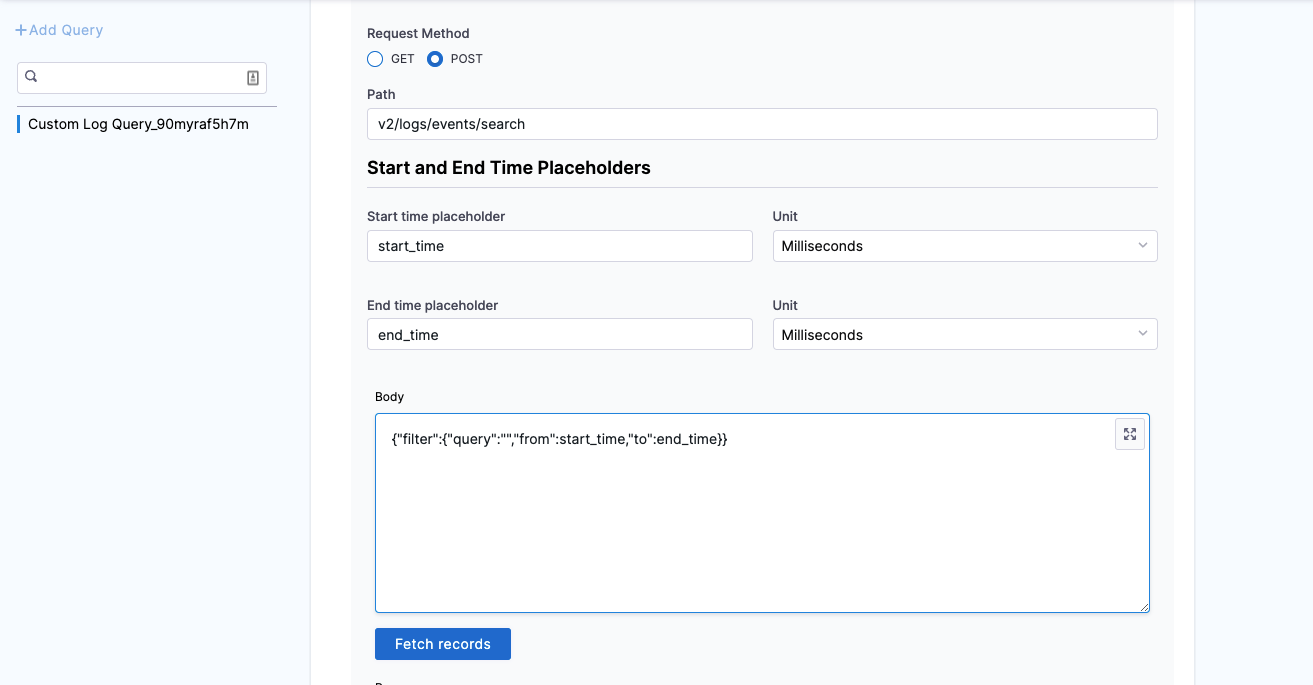
In Start and End Time Placeholders, enter the following:
- In Start time placeholder, enter the start time placeholder in the metric path. For example, start_time.
- In Unit, select the preferred unit of measurement. For example, Milliseconds.
- In End time placeholder, enter the end time placeholder in the metric path. For example, end_time.
- In Unit, select the preferred unit of measurement. For example, Milliseconds.
-
In Body, enter the request body. For example,
{"filter":{"query":","from":start_time,"to":end_time}}. -
Click Fetch Records to retrieve records from the provided URL.
-
Once the response is retrieved, click JSON path selection.
- In Log Message JSON path, click the plus icon to select the path to the log message from the data source. For example,
$.data.[*].attributes.message. - In Timestamp Field/Locator JSON Path, click the plus icon to select the path to the log message from the data source. For example,
$.data.[*].attributes.timestamp. - In Provide Service Instance to map to Harness Service Instance, click the plus icon to select the Service instance from the data source. For example,
$.data.[*].attributes.tags.[4].
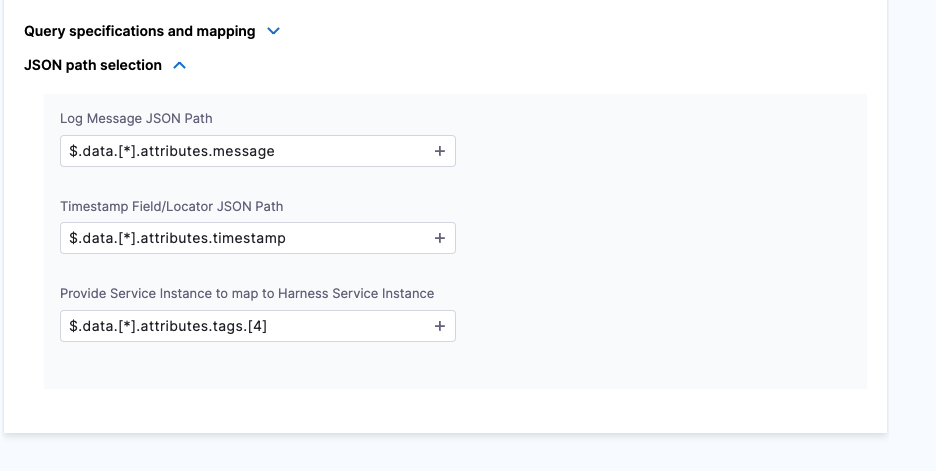
- In Log Message JSON path, click the plus icon to select the path to the log message from the data source. For example,
-
Click Submit.