Synchronize parallel stages and step groups using Barriers
This topic describes how to synchronize stages and step groups in your pipeline using barriers.
Harness provides multiple options for controlling resource usage and protecting capacity limits. Go to controlling resource usage with Barriers, Resource Constraints, and Queue steps for more information.
Barriers and synchronization
In complex pipelines that orchestrate interdependent services or components, you may need to coordinate the execution flow across different stages or step groups. For example, you might want to verify a group of services only after all of them are deployed successfully.
Harness provides Barriers to help with this kind of synchronization. Barriers allow you to pause execution at defined points and ensure that multiple parallel entities—such as stages or step groups—only proceed once all required parts reach the same barrier.
Barrier steps are only supported inside Deploy and Custom stage types.
How Barriers Work
- Barriers take effect only when two or more stages or step groups use the same barrier name (configured via the Barrier Reference field in the Barrier step) and are executed in parallel.
- All stages or step groups referencing the same barrier must reach the barrier point. Only then do they all proceed simultaneously past that point.
- If any one of the stages or step groups fails before reaching the barrier, the remaining ones are signaled to fail as well.
- Each stage or step group will then follow its configured failure strategy.
Barriers are also supported across child pipelines. A parent pipeline can define and use a barrier, and any child pipeline can reference and synchronize using the same barrier.
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag PIPE_BARRIERS_FOR_CHAINED_PIPELINES. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
Barriers can also be used with looping strategies. However, additional constraints apply when using barriers in looped parallel executions. For details, refer to the Important notes.
Example
Here’s a visualization of how barriers synchronize parallel stages:
- Stage A and Stage B both wait at Barrier X and proceed only when both reach it.
- Stage B and Stage C both wait at Barrier Y and proceed together once both are ready.
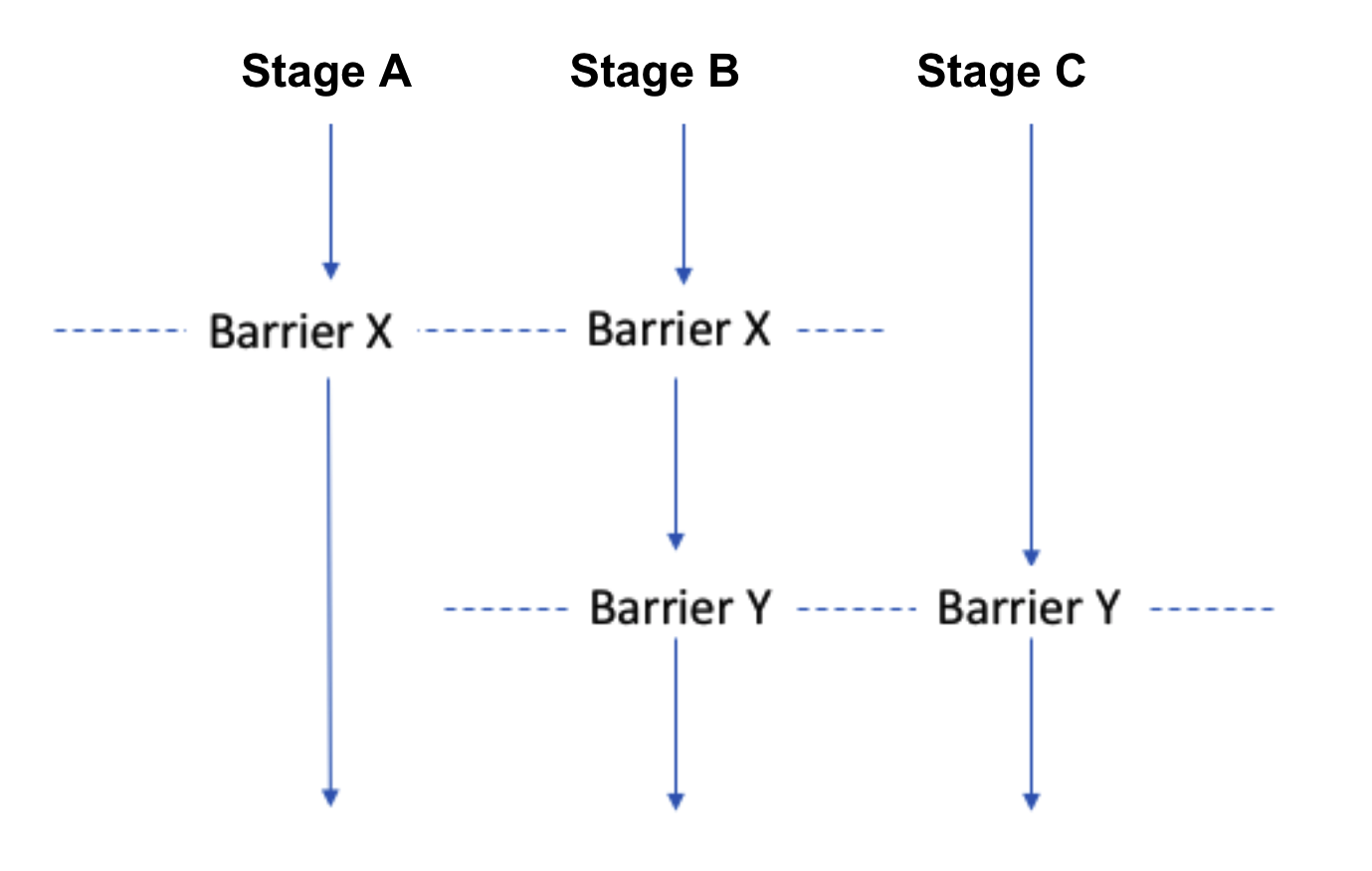
This allows you to control complex coordination logic within a pipeline without resorting to manual delays or checks.
Add a Barrier
A barrier is simply a name added in a pipeline's Flow Control settings.
-
In your pipeline, select Flow Control.
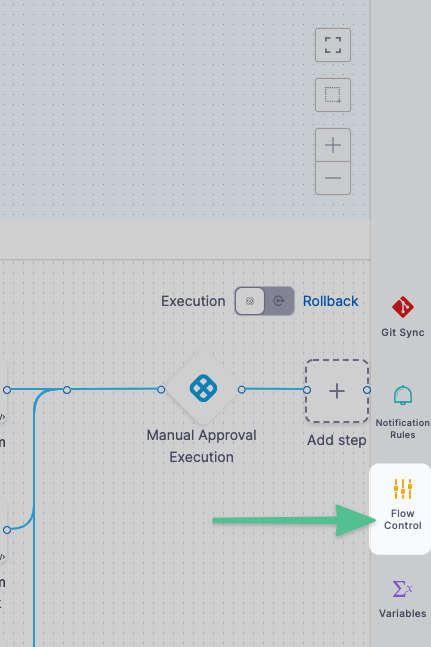
-
In Flow Control, select Add Barrier.

-
In Barrier Name, enter a unique name, and then click outside of the settings. The barrier is created.
Next, the name is selected using the Barrier step in the stages where you want to synchronize.
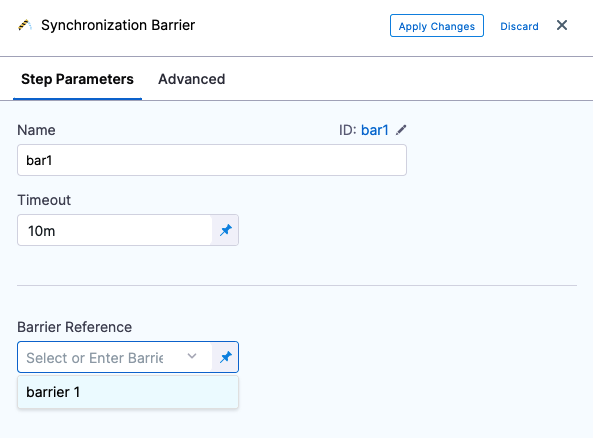
Use a Barrier in a Step
To apply a barrier, do the following:
-
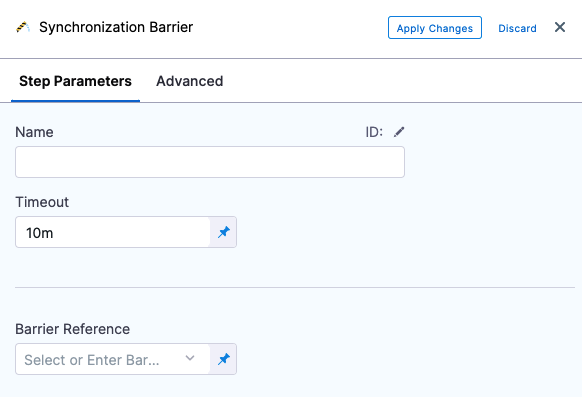
In your stage, under Execution, select Add Step, and then select Barrier.
-
Enter a name for the step.
-
In Timeout, enter the timeout period in milliseconds. For example,
600000milliseconds is 10 minutes. The timeout period determines how long each stage with a barrier must wait for the other stage(s) to reach the barrier point. When the timeout expires, it is considered a deployment failure. -
Barrier timeouts are not hard timeouts. A barrier can fail anytime between the timeout value and
timeout + 1 minute. -
In Barrier Reference, select the name of an existing barrier.
-
Select Apply Changes.
Using Barriers with Looping Strategies
You can also use barriers with looping strategies.
Using Barriers with Looping strategies
There are a few behaviors to note when using Barriers within a looping strategy (for example, when setting up a matrix that creates multiple stages that run in parallel, and the stages contain a Barrier step):
- In general, Barriers are supported in all the looping strategies. You can use them when repeating stages, looping, or in matrices, or when using multi-service or multi-environment stages in pipelines.
- When setting up the Barrier step, ensure that you are using the same Barrier Reference in all of the looped stages (this ensure that all the looped stages execute until the Barrier step, and then continue/fail together.
- You cannot use the
maxConcurrencyparameter in setting up looping. When this parameter is used, not all the stages start up in parallel, and some wait for the first few to end. Barriers will prevent the initial set of stages from ending, so the pipeline will get stuck. - When using barriers with a multi-service deployment, please select the Deploy Services in Parallel option, so that the pipeline does not wait for a stage to complete before beginning the next one.
- You can use barriers to coordinate between multiple sets of looped stages, or between a single stage and a group of looped stages. As mentioned before, the same Barrier Reference must be used across all the sets of stages. The stages will all execute up to the Barrier step and wait for the others. This applies even if one of the groups starts later than another.
- Barriers are also supported across child pipelines. A parent pipeline can define and use a barrier, and any child pipeline can reference and synchronize using the same barrier.
Important notes
-
You can have multiple Barrier steps in a stage/step group. Every Barrier step in the same stage/step group must use a unique Barrier Reference.
-
Ensure the Barrier Reference string for each related barrier across the different stages/step groups matches.
-
Please do not use the same Barrier Reference in sequential stages. This results in the first stage with the Barrier step never ending and the flow never reaches the next stage with the second Barrier step.
-
You can use the same Barrier only within a single pipeline. If you attempt to use a Barrier name from one pipeline in the Barrier step of another pipeline, it will not function.