Environments overview
A Harness environment represents where you are deploying your application. You categorize each environment as prod or non-prod.
Environments represent your deployment targets (QA, Prod, etc). Each environment contains one or more Infrastructure Definitions that list your target clusters, hosts, namespaces, etc.
Each infrastructure definition in an environment defines the specific VM, Kubernetes cluster, or target infrastructure where you plan to deploy your application. An environment can contain multiple infrastructure definitions. When you select an environment in a pipeline, you can pick which infrastructure definition to use.
The service configuration overrides allows you to override service properties when a service is deployed into a specific environment.
Environment variables are global variables for that environment. You can leverage those in their pipelines, manifests, etc.
For example, you might have an environment that is prod, and within prod you have 5 infrastructure definitions representing the 5 Kubernetes clusters associated with the production environment.
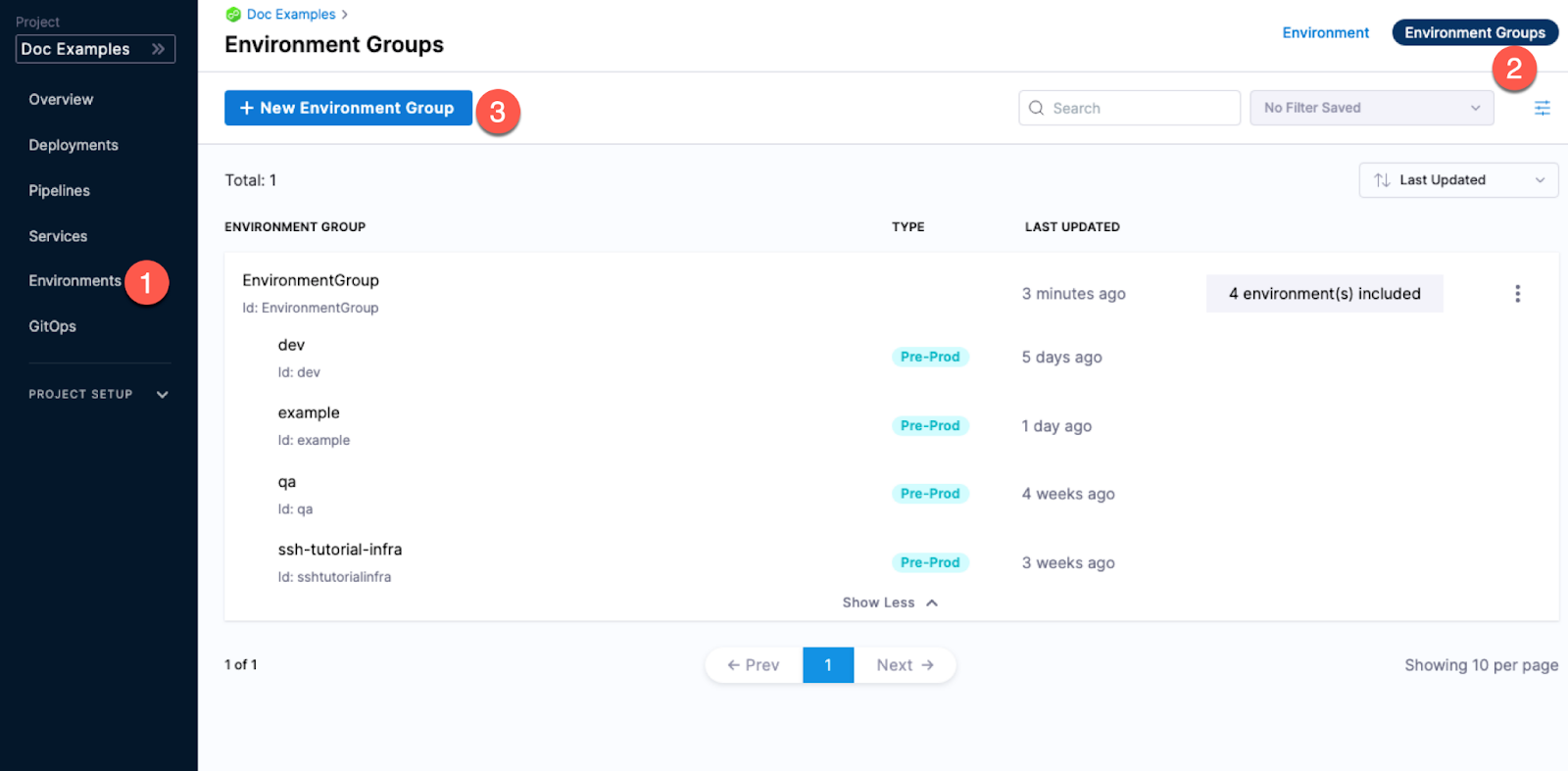
Creating environments
You can create environments from:
- An Account
- An Organization
- Within a pipeline
- Outside a pipeline
When you create an environment in a pipeline, it's automatically added to Environments. You can add the same environment to as many pipelines as you need.
For more information, go to create environments.
Creating environments at an account or organization level
You can create an environment and provide infrastructure definitions at an account or organization level from the Harness UI, using APIs or Terraform.
- Pipeline Studio
- API
- Terraform
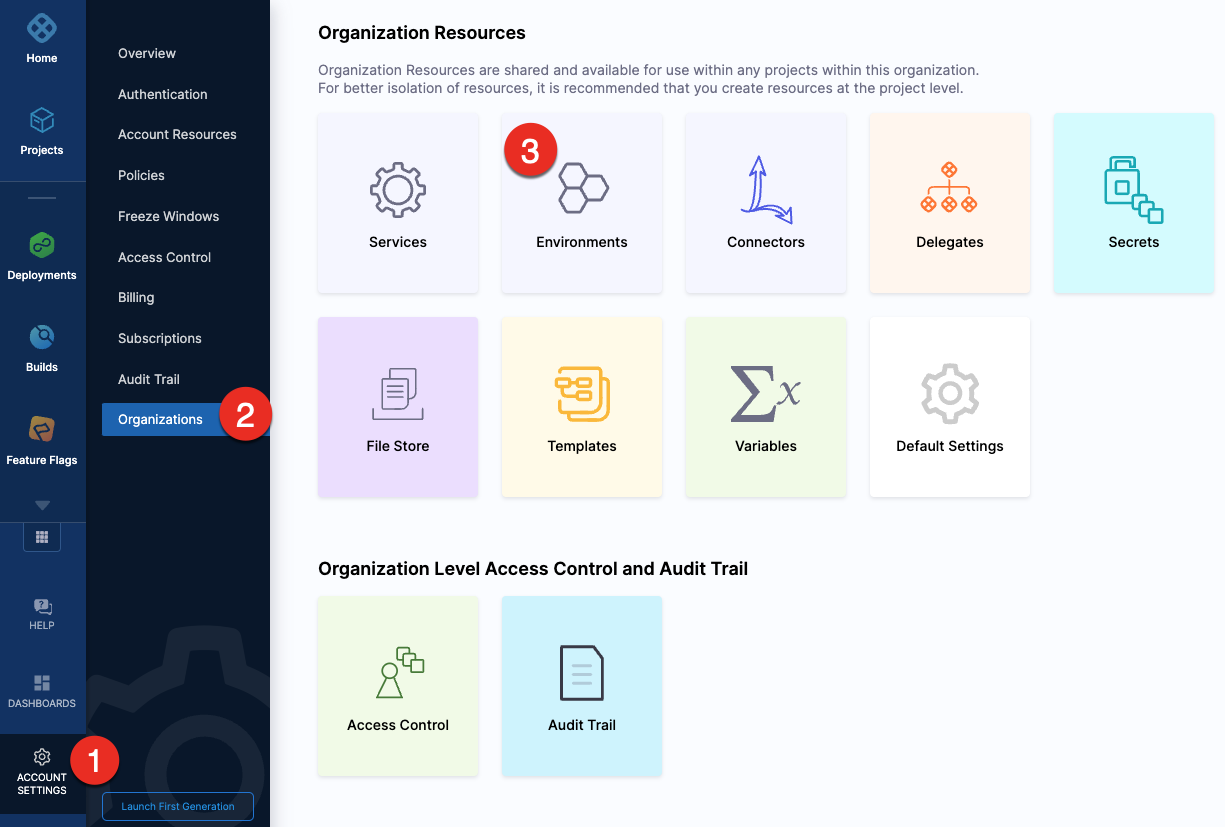
To create an environment at an account or organization level, go to Organization Resources >Environments.
Expand the section below to see a sample account level environment YAML.Account level environment YAML
environment:
name: dev
identifier: dev
description: account wide dev environment
tags:
status: non-regulated
type: PreProduction
variables:
- name: port
type: String
value: "8080"
description: ""
- name: namespace
type: String
value: <+service.name>-dev
description: "namespace environment variable"
Expand the section below to see a sample account level infrastructure definition YAML.Account level infrastructure definition YAML
infrastructureDefinition:
name: dev-k8s
identifier: dev
description: development Kubernetes cluster
tags: {}
environmentRef: dev
deploymentType: Kubernetes
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: account.Harness_Kubernetes_Cluster
namespace: <+service.name>-dev
releaseName: release-<+INFRA_KEY_SHORT_ID>
allowSimultaneousDeployments: false
Expand the section below to see a sample organization level environment YAML.Organization level environment YAML
environment:
name: prod
identifier: prod
description: production environment for the organization
tags:
status: regulated
type: Production
orgIdentifier: default
variables:
- name: namespace
type: String
value: <+service.name>-prod
description: "namespace for prod environment"
- name: port
type: String
value: "8080"
description: "port for prod environment"
Expand the section below to see a sample organization level infrastructure definition YAML.Organization level infrastructure definition YAML
infrastructureDefinition:
name: prod-k8s
identifier: prodk8s
description: production kubernetes cluster
tags: {}
orgIdentifier: default
environmentRef: prod
deploymentType: Kubernetes
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: account.Harness_Kubernetes_Cluster
namespace: production
releaseName: release-<+INFRA_KEY_SHORT_ID>
allowSimultaneousDeployments: false
For information about creating an environment API, go to create an environment.
For information about creating infrastructure definition API, go to create an infrastructure in an environment.
The orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier field definitions are optional, and depend on where you want to create the environment. For example, if you create an environment at an account level, you will not need org or project identifiers in the post API call payload.
For information about creating a Harness platform environment, go to harness_platform_environment (Resource).
Expand the section below to see a sample platform environment in Terraform.Harness platform environment
resource "harness_platform_environment" "example" {
identifier = "identifier"
name = "name"
org_id = "org_id"
project_id = "project_id"
tags = ["foo:bar", "baz"]
type = "PreProduction"
## ENVIRONMENT V2 Update
## The YAML is needed if you want to define the Environment Variables and Overrides for the environment
## Not Mandatory for Environment Creation nor Pipeline Usage
yaml = <<-EOT
environment:
name: name
identifier: identifier
orgIdentifier: org_id
projectIdentifier: project_id
type: PreProduction
tags:
foo: bar
baz: ""
variables:
- name: envVar1
type: String
value: v1
description: ""
- name: envVar2
type: String
value: v2
description: ""
overrides:
manifests:
- manifest:
identifier: manifestEnv
type: Values
spec:
store:
type: Git
spec:
connectorRef: <+input>
gitFetchType: Branch
paths:
- file1
repoName: <+input>
branch: master
configFiles:
- configFile:
identifier: configFileEnv
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
files:
- account:/Add-ons/svcOverrideTest
secretFiles: []
EOT
}
For information about creating a Harness platform infrastructure definition, go to harness_platform_infrastructure (Resource).
Expand the section below to see a sample platform infrastructure definition in Terraform.Harness platform infrastructure definition
resource "harness_platform_infrastructure" "example" {
identifier = "identifier"
name = "name"
org_id = "orgIdentifer"
project_id = "projectIdentifier"
env_id = "environmentIdentifier"
type = "KubernetesDirect"
deployment_type = "Kubernetes"
yaml = <<-EOT
infrastructureDefinition:
name: name
identifier: identifier
description: ""
tags:
asda: ""
orgIdentifier: orgIdentifer
projectIdentifier: projectIdentifier
environmentRef: environmentIdentifier
deploymentType: Kubernetes
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: account.gfgf
namespace: asdasdsa
releaseName: release-<+INFRA_KEY_SHORT_ID>
allowSimultaneousDeployments: false
EOT
}
The org_id and project_id field definitions are optional, and depend on where you want to create the environment. For example, if you create an environment at an account level, you will not need org or project identifiers.
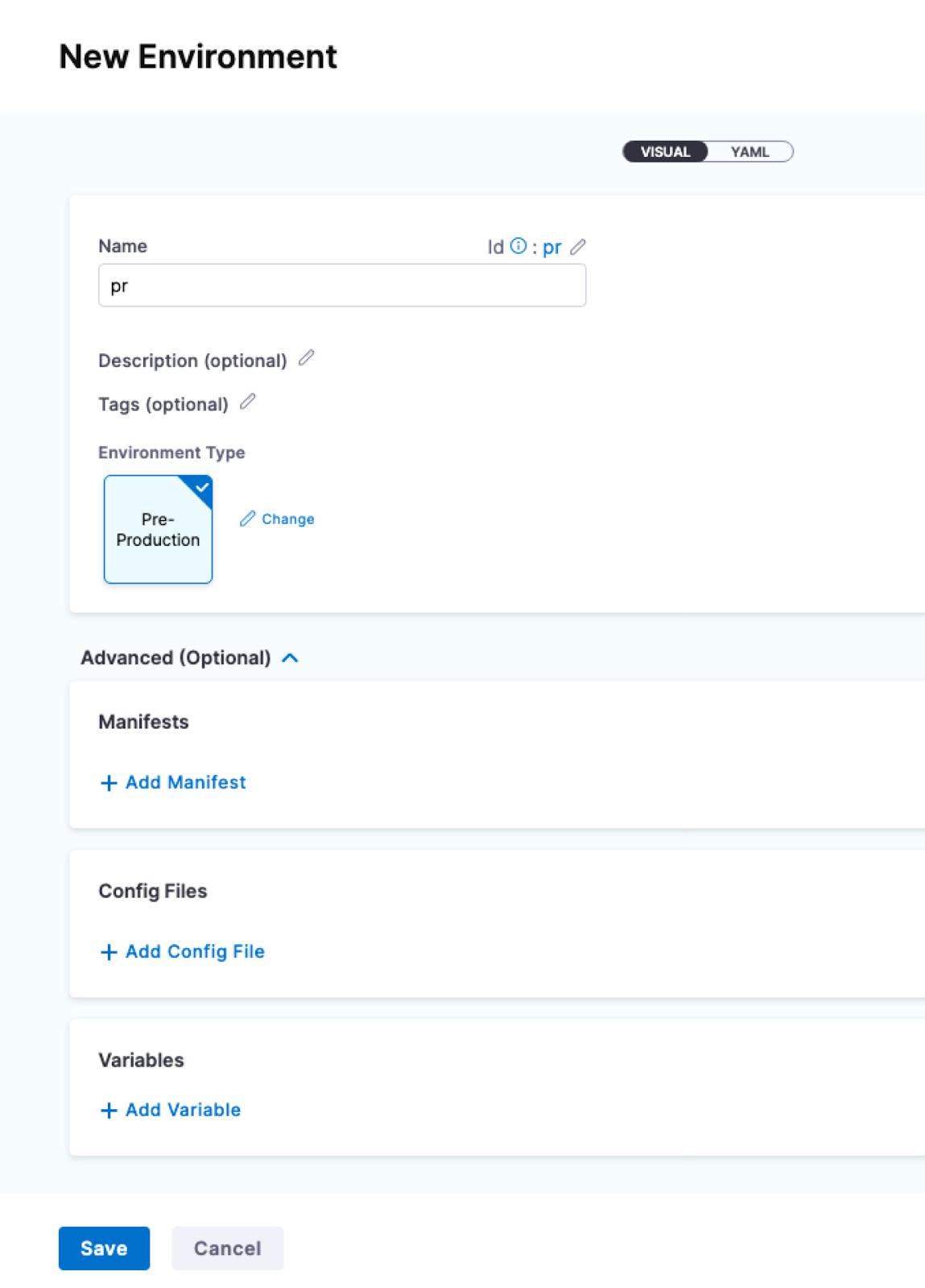
Creating environments inside a pipeline
To create an environment from inside of a pipeline, select New Environment in the Infrastructure tab of a new CD stage.
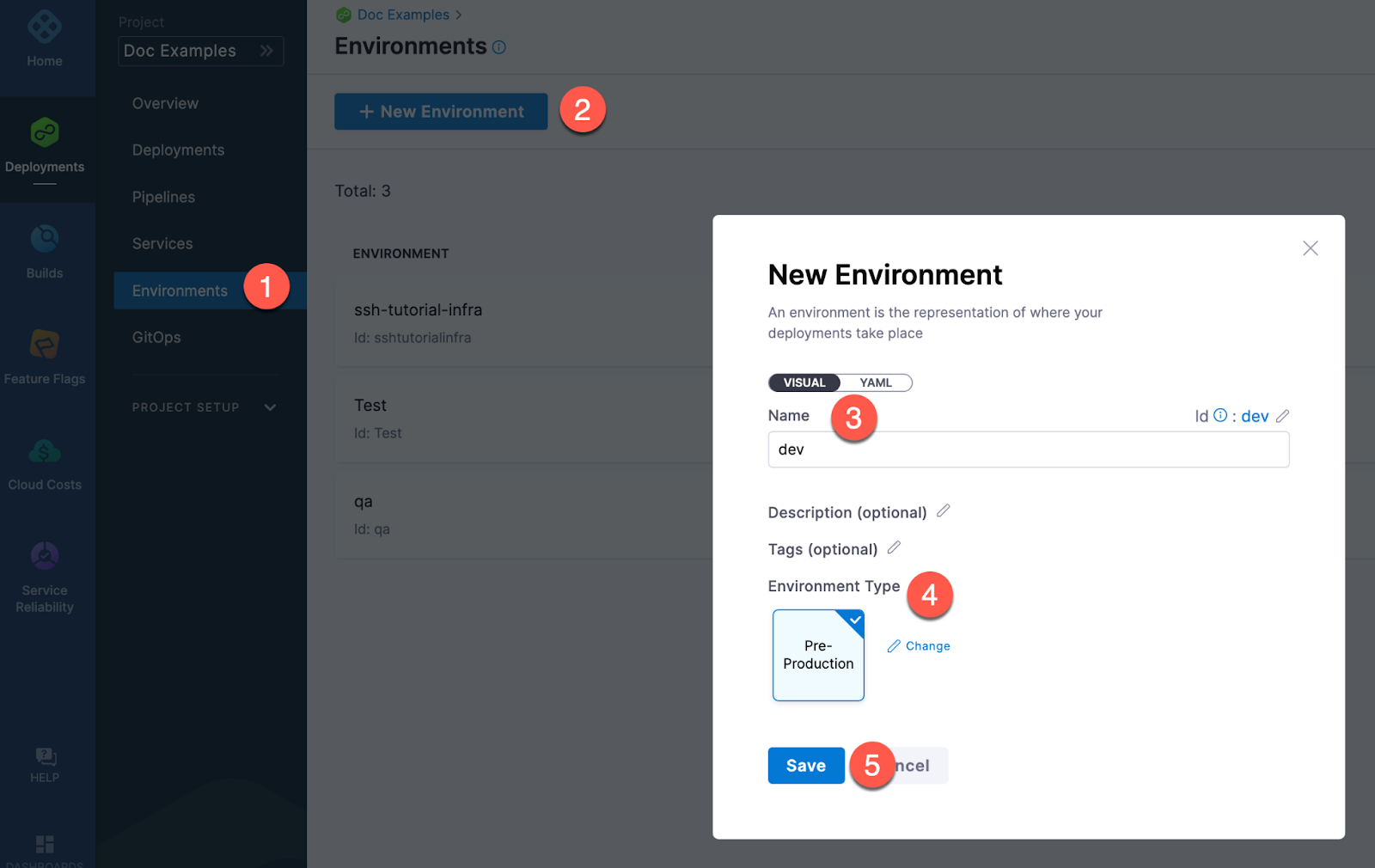
Creating environments outside a pipeline
To create an Environment from outside of a pipeline, you use Environments in the navigation pane.
Defining environment settings
After creating an environment, you can define all its settings:
- Configuration: the default environment configuration, including variables, manifests, specifications, and config files that will be used every time the environment is used in a stage.
- Service Overrides: override specific services. You select a service and define what will be overridden whenever that Service is deployed to this environment.
- Infrastructure Definitions: represent one or more environment infrastructures.
- Infrastructure definitions are the actual clusters, hosts, etc., where Harness deploys a service. For example, you might have a QA environment with separate Kubernetes clusters (infrastructure definitions) for each service you want to test.
- You can add multiple infrastructure definitions to a single environment and select an infrastructure definition when you add the environment to a stage.
- GitOps Clusters: adding Harness GitOps clusters to an environment lets you select them as the deployment target in stages. For more information on Harness GitOps, go to Harness GitOps basics.
- Referenced by: displays the list of pipelines using the infrastructure definitions in the environment.
Configuration
In the environment Configuration, you can manage the Name, Description, Tags, and Environment Type of the environment.
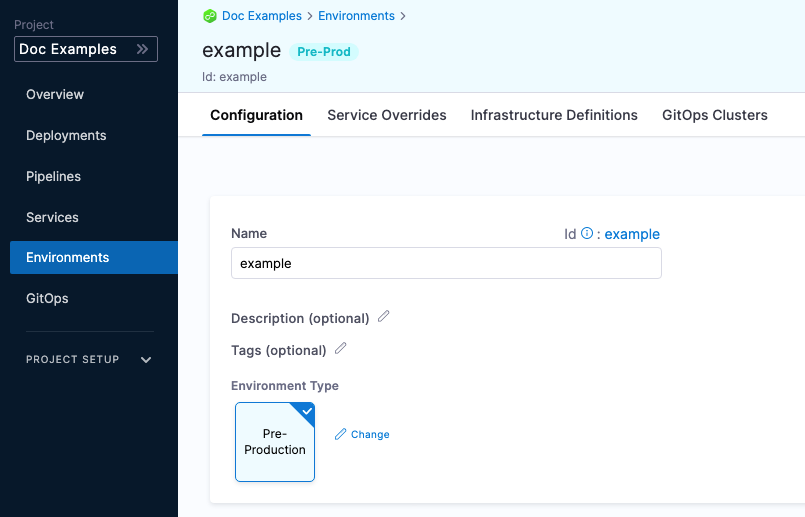
You can also set default manifests, specifications, config files, and variables to use whenever Harness deploys a service to this environment.
For example, a stage has a Kubernetes service with a manifest but whenever that service is deployed to the QA environment, the manifest in that environment's Configuration overwrites the namespace of the manifest in the service with QA.
Service overrides
Service overrides are different from Environment Configuration in the following ways:
- Environment Configuration: applies to every service that is used with the environment.
- Environment Service Overrides: applies to specific services you select. Whenever that service is used with that environment, the Service Override is applied.
Runtime inputs are not supported if you are trying to override services in multi-service and multi-environment set ups.
Override priority
When you are using environment configuration and service override to override service settings, it's important to understand the priority of the overrides.
The priority from top to bottom is:
- Environment service overrides
- Environment configuration
- Service settings
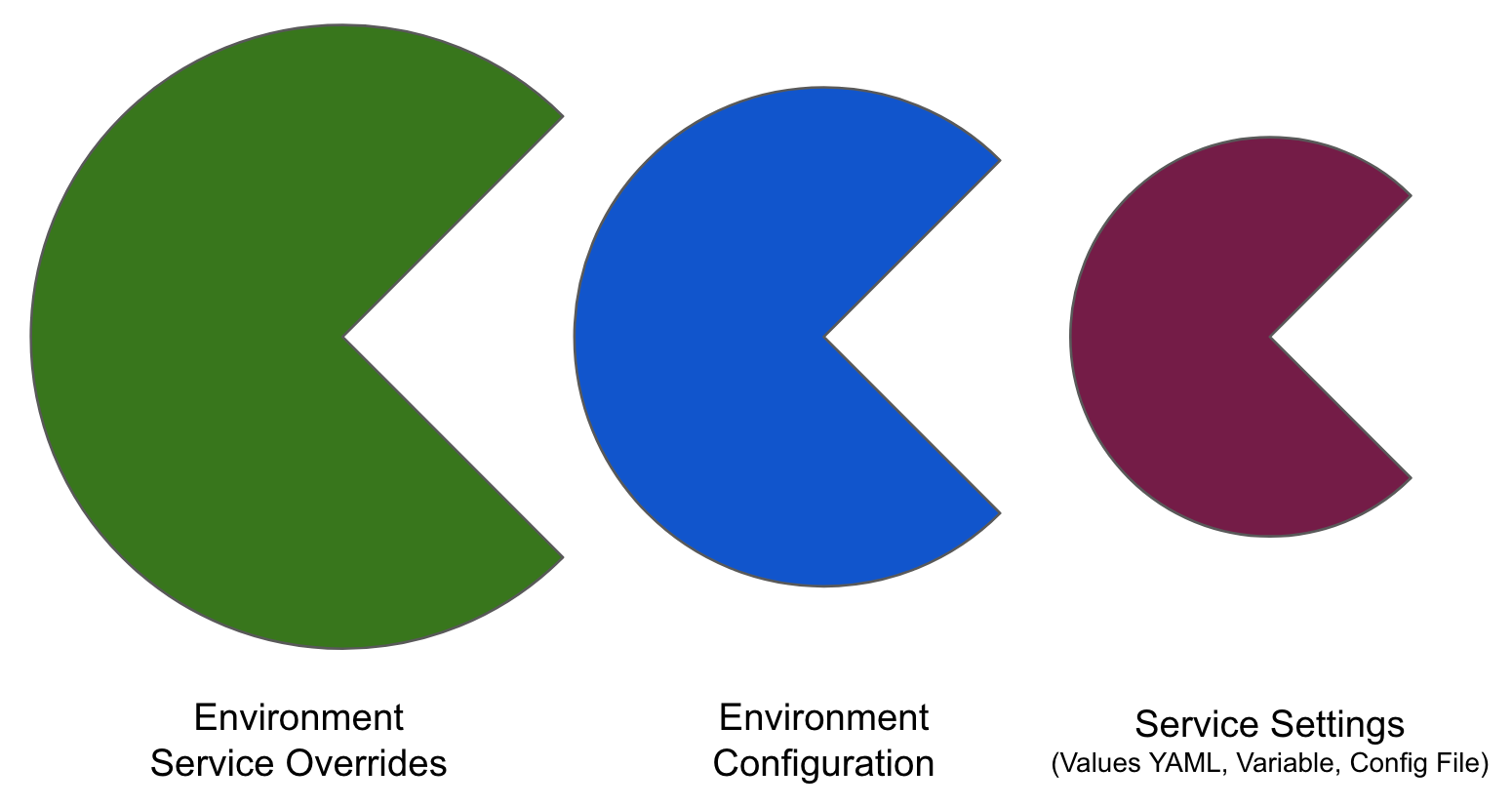
Override priority example
Suppose you have a pipeline that runs as follows:
- Deploys a service named
myService, which has a variablecpuset to 1. - Deploys
myServicetomyEnvironmentAlpha, and then overrides themyServicevariablecpuvalue to 2.
In this case, the environment variable takes precedence, and overrides the service variable. When the pipeline runs, it uses the cpu value of 2.
Now, suppose you have another pipeline that deploys myService to myEnvironmentKappa, which has a service override that sets cpu to 4. In this case, the environment service override takes precedence over the environment configuration and the service setting. When the pipeline runs, it uses the cpu value of 4.
Infrastructure definitions
Infrastructure definitions represent an environment's infrastructures physically. They are the actual clusters, hosts, namespaces, etc, where you are deploying a service.
An environment can have multiple Infrastructure Definitions.
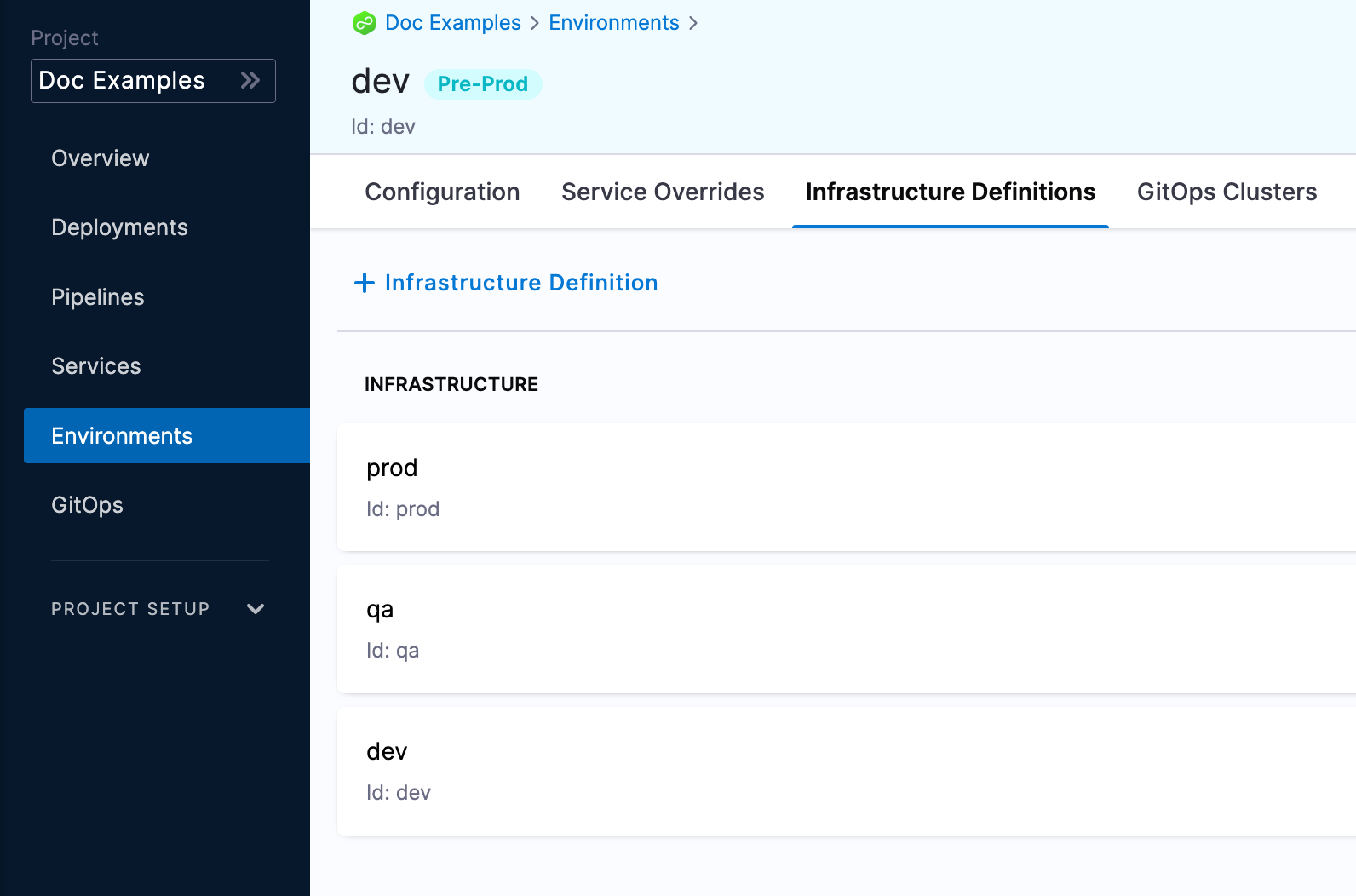
When you select an environment in a stage, you can select the Infrastructure Definition to use for that stage.
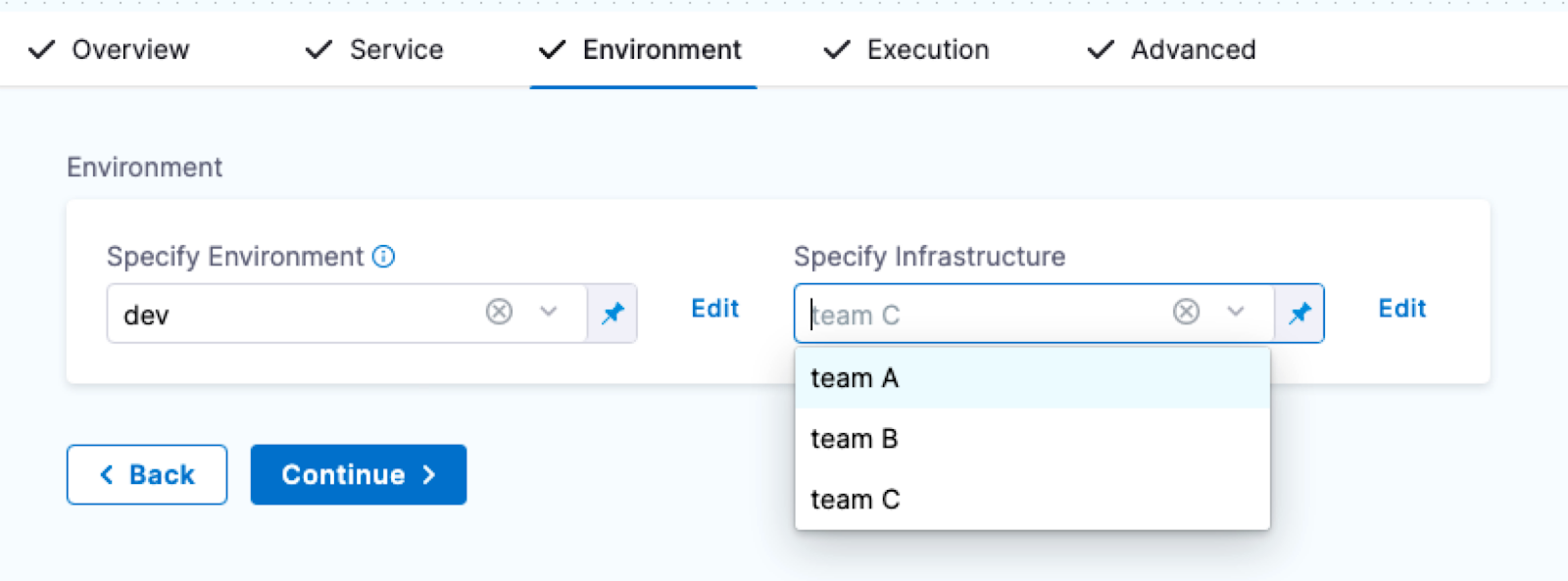
During pipeline execution, all infrastructure definitions are displayed, regardless of whether they are scoped to the selected service. Users are advised to manually ensure that only the appropriate infrastructure definitions are chosen for their services. This limitation is more prominent when services or environments are dynamically expressed, as scoping may not apply consistently.
Infrastructure Tags
Tags can be attached to infrastructure definitions representing their characteristics. These tags can be key value pairs.
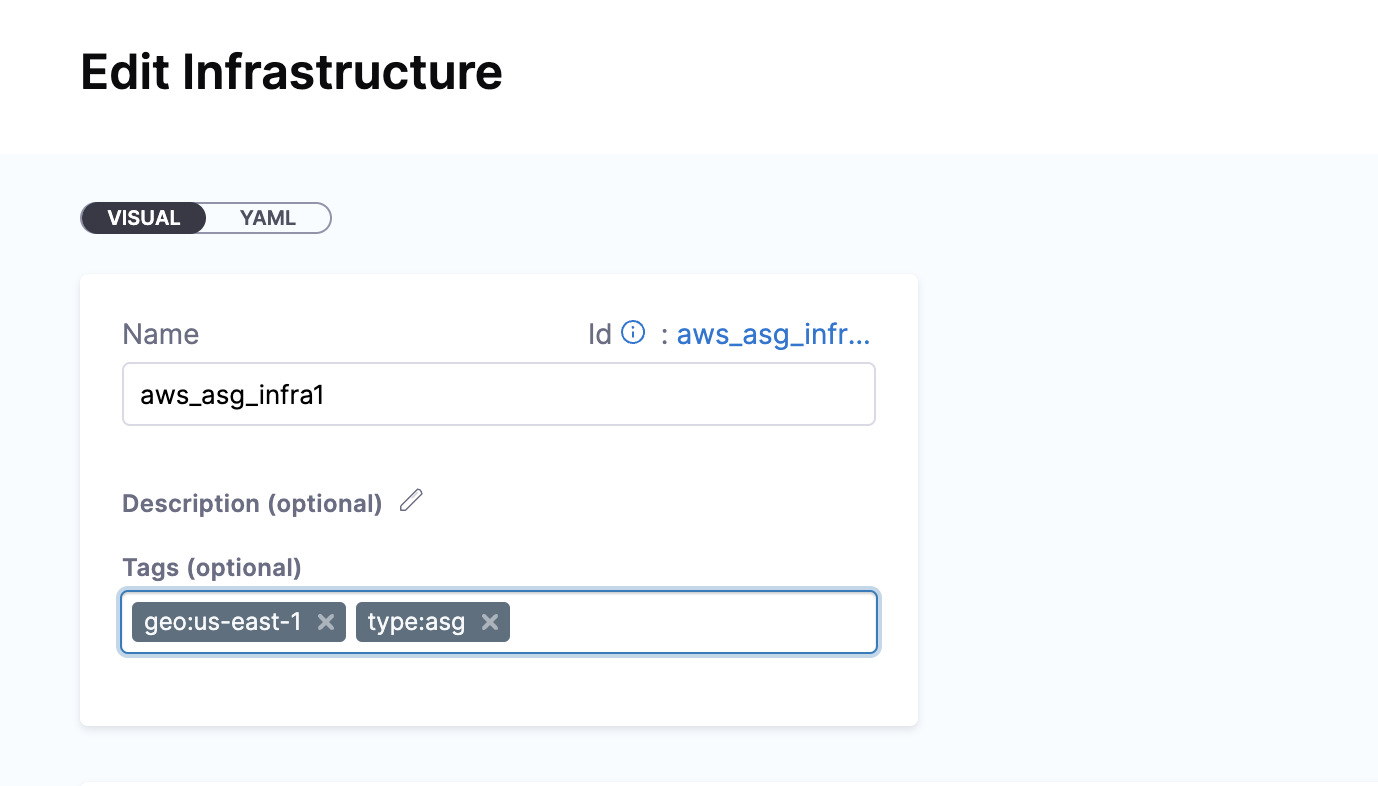
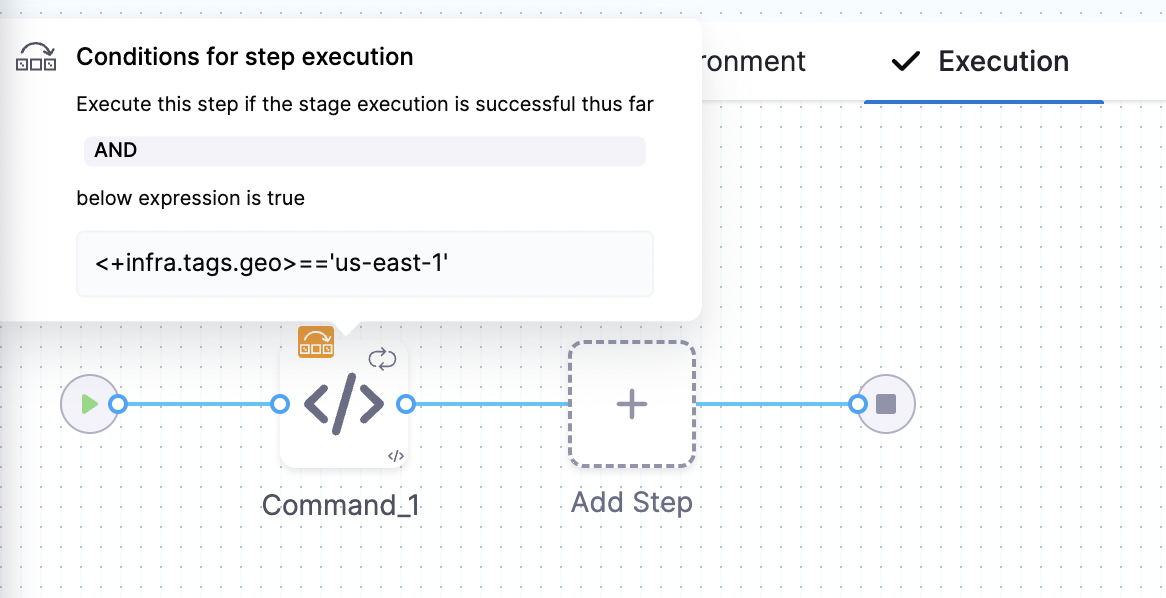
When you select the Infrastructure Definition for a stage, the attached tags can be accessed using their keys with the expression, <+infra.tags.tag_key>. This expression is available for use throughout the stage.
For example, skipping certain steps in pipeline based on the tags attached to the infrastructure.
You can now define allowed values in the Select Hosts settings under infrastructure. In the runtime view, a multi-select dropdown will be displayed, allowing users to choose from the predefined allowed values.
Values YAML overrides and merges
You can specify values YAML files at the environment's Service Overrides and Configuration, and the service itself.
Here is an example of specifying it at the environment's Configuration:
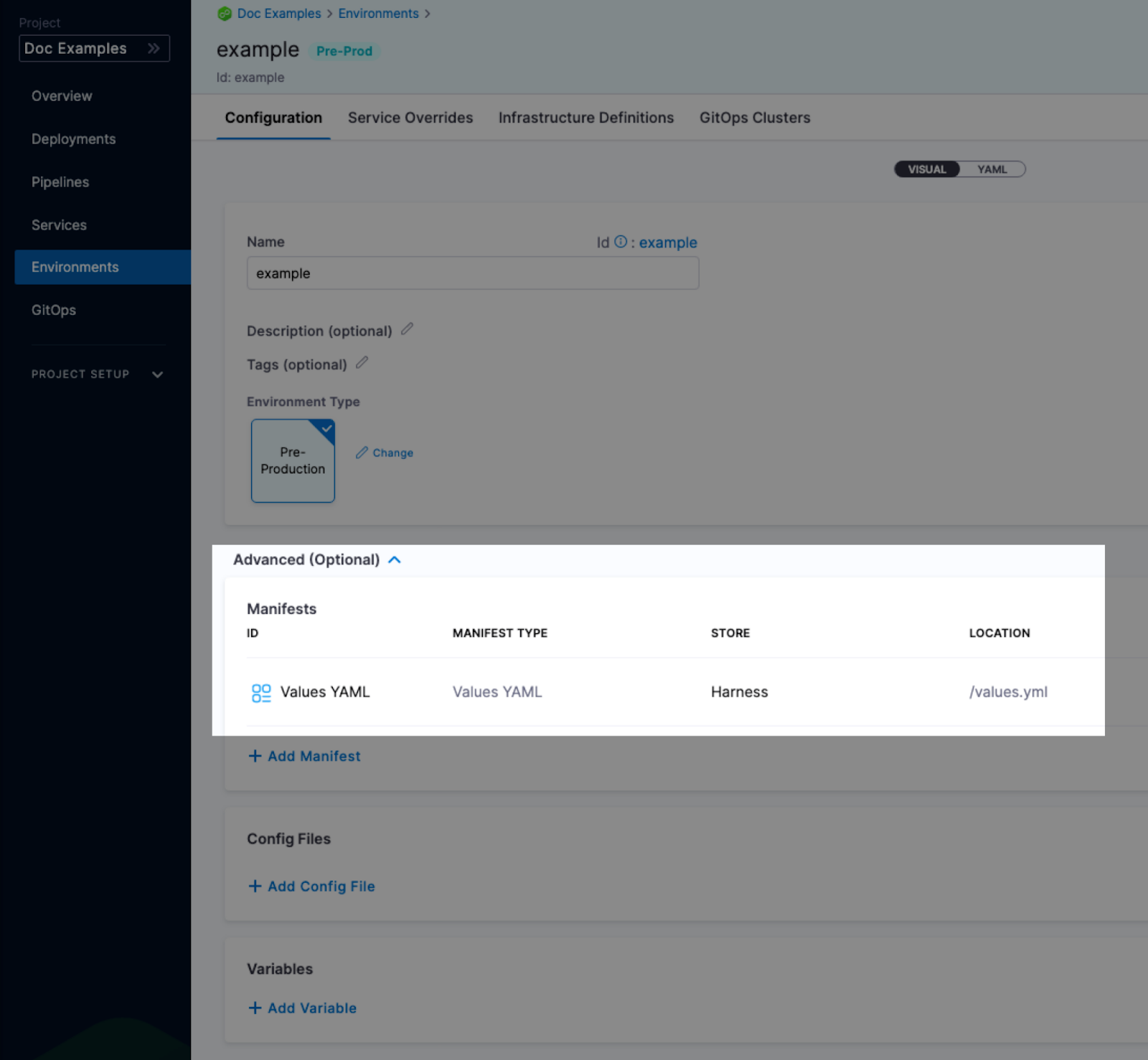
When you have a values yaml file at two or more of the environment Service Overrides, Environment Configuration, and the service itself, Harness merges the files into a single values YAML for deployment. This merging is performed at pipeline execution runtime.
Overriding occurs when the higher priority setting has the same name:value pair as a lower priority setting.
Let's look at two examples.
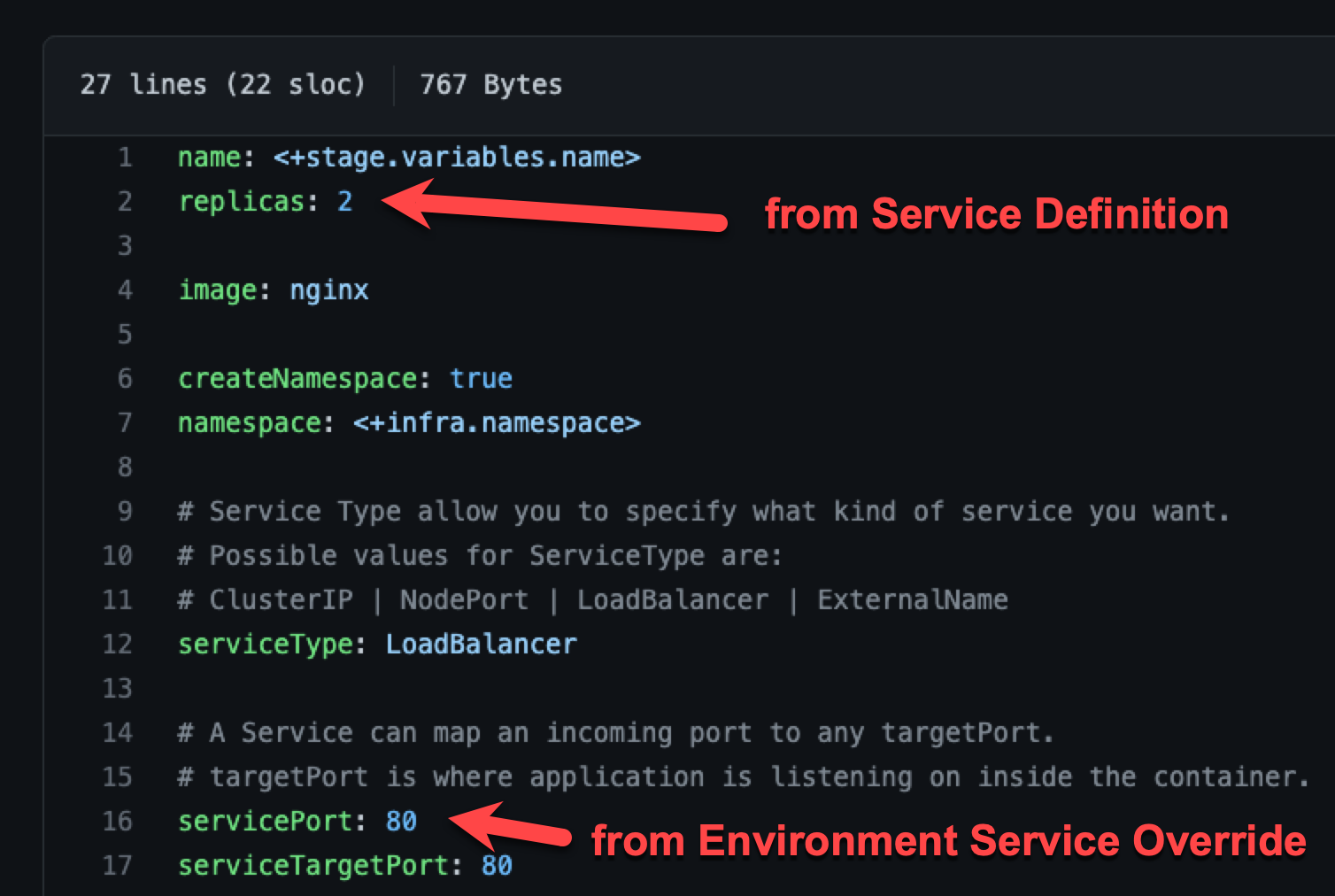
Merging values YAML name:value pairs
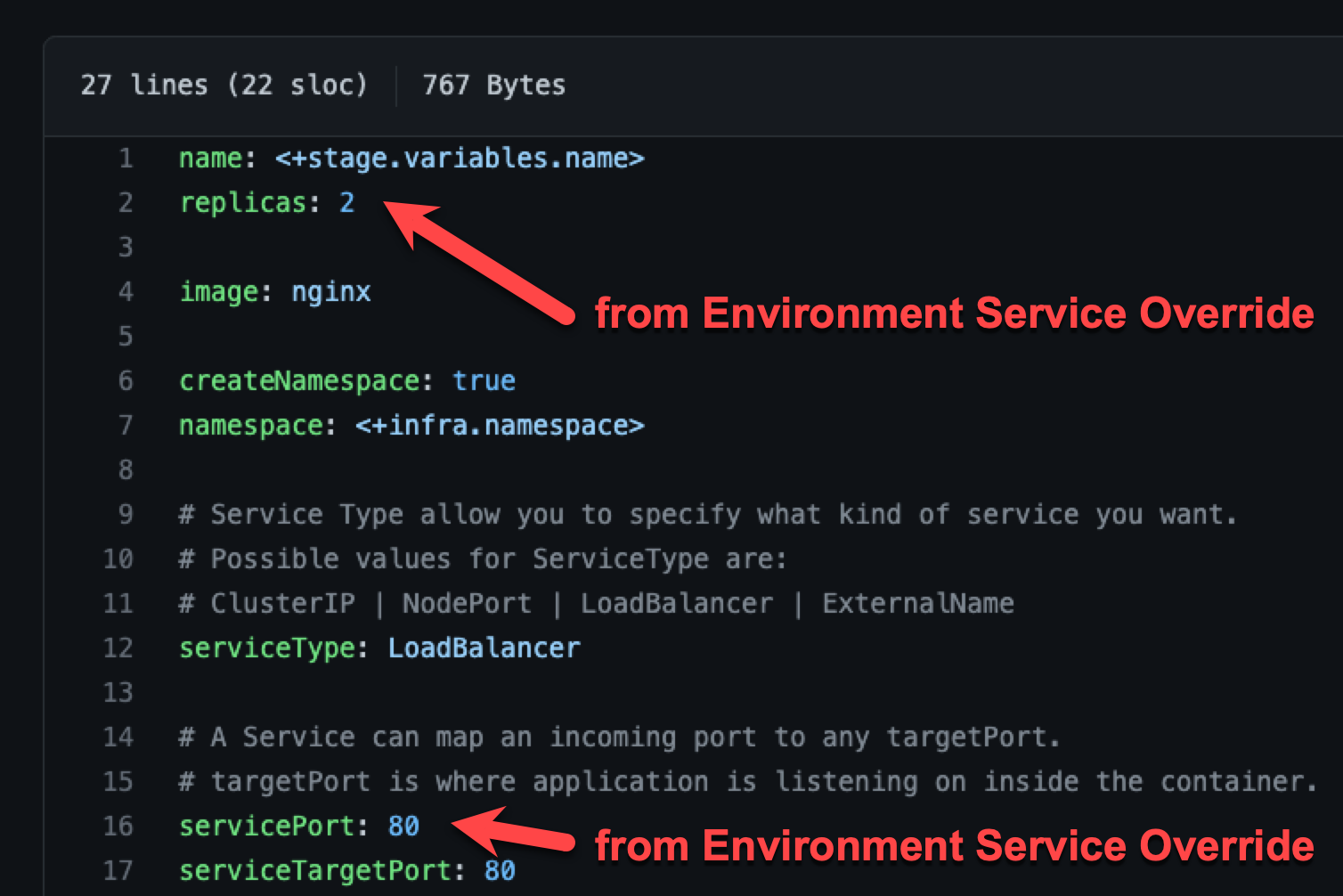
An environment's Service Overrides values YAML has the name:value pair servicePort: 80 but no replicas name:value.
A service's Service Definition has a values YAML with replicas: 2 but no servicePort name:value.
At runtime, the two values YAML files are merged into one.
The servicePort: 80 from the environment Service Overrides values YAML is merged with the Service Definition's replicas: 2 in the values YAML:
Fully overriding values YAML name:value pairs
An environment's Service Overrides values YAML has the name:value pairs replicas: 2 and servicePort: 80.
A service's Service Definition has a values YAML with replicas: 4 and servicePort: 8080.
At runtime, the name:value pairs from the environment Service Overrides values YAML fully override the service values YAML. The replicas: 2 and servicePort: 80 from the environment Service Overrides are used.
Config files and variables are completely overridden
Config files are a black box that can contain multiple formats and content, such as YAML, JSON, plain text, etc. Consequently, they cannot be overridden like Values YAML files.
Variables cannot be partially overridden either. They are completely replaced.
When you have Config files at two or more of the environment Service Overrides, Configuration, and the service itself, the standard override priority is applied.
When you have Variables with the same name at two or more of the environment Service Overrides, Configuration, and the service itself, the standard override priority is applied.
GitOps Clusters
When you use Harness GitOps you can add GitOps clusters to an environment.
To learn more about Harness GitOps, go to Harness GitOps Basics.
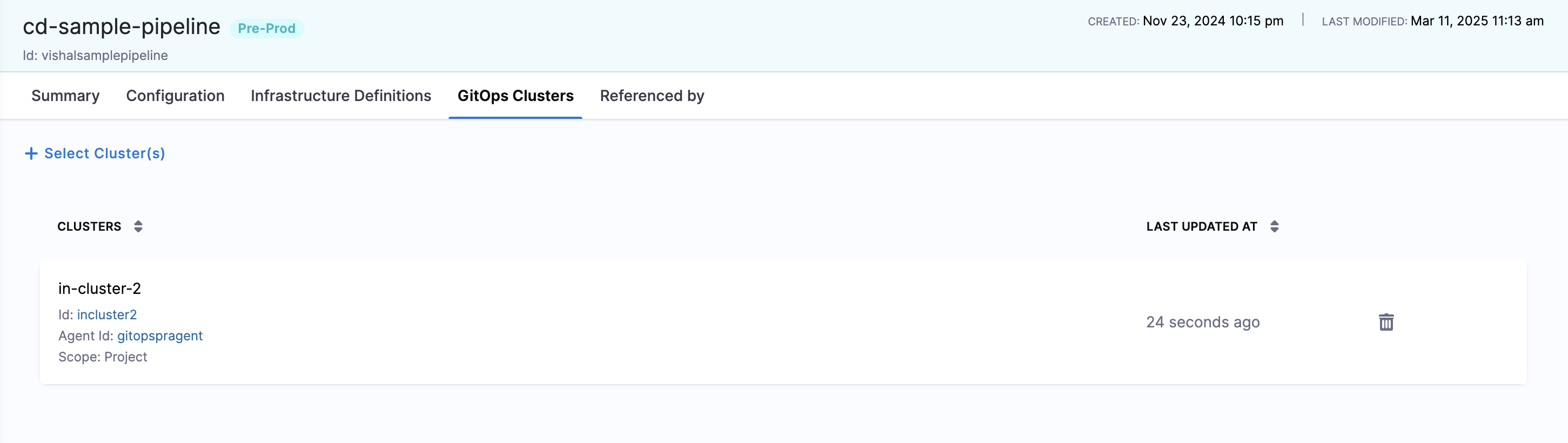
You can select your environment (Deployments → Environments → Your Environment), then click the GitOps Clusters tab to view the list of GitOps clusters associated with an environment. Each row's Cluster ID and Agent name is a link that opens the corresponding Cluster or Agent detail page in a new tab:
- Cluster ID: Click to open the Cluster's detail page in a new tab.
- Agent name: Click to open the linked Agent's detail page in a new tab.
To add a cluster to this list:
- Click + Select Cluster at the top of the page.
- In the Select GitOps Clusters to add to Environment popup, choose the scope tab—Project, Organization, or Account—to view clusters in that scope.
- Select the desired GitOps cluster from the list.
- Click Apply Selected. The selected cluster will now appear in the Environment's GitOps Clusters list.
Next, when you create a pipeline, you can select the environment and the GitOps cluster(s) to use.
GitOps clusters are used in a PR pipeline. A PR pipeline creates and merges a Git PR on the config.json for a destination cluster as part of an ApplicationSet. The PR Pipeline runs, merges a change to the config.json, and a GitOps sync on the ApplicationSet is initiated.
GitOps Clusters are not used in standard CD pipelines. They're used when using GitOps only.
Runtime inputs and expressions in environments
If you use runtime inputs in your environments, users will need to provide values for these when they run pipelines using these environments.
If you use expressions in your environments, Harness must be able to resolve these expressions when users run pipelines using these environments.
Select Runtime input for the environment.
When you run the pipeline, you can select the environment for runtime inputs.
For more information on runtime inputs and expressions, go to Fixed Values, Runtime Inputs, and Expressions.
Environments RBAC
Go to RBAC in Harness for examples of RBAC use cases for environments.
Access permission is needed to deploy to an environment
One of the most important advantages of environments is the ability to define roles that determines who can deploy them.
In order for a role to allow deployments using environments, the role must have the access permission enabled for environments.
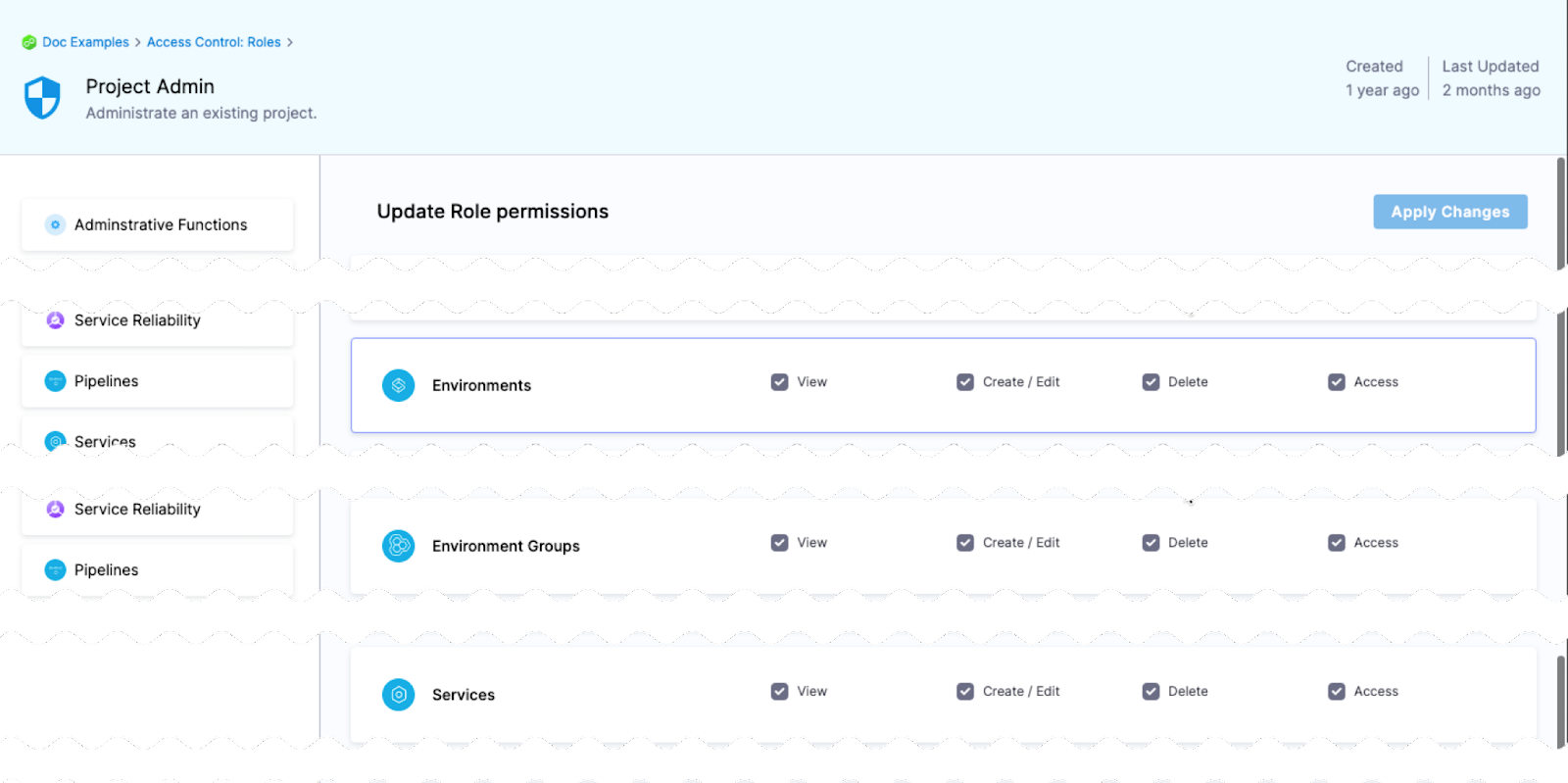
The View, Create, Edit, Delete, and Manage permissions enable you to deploy an environment.
If a role does not have the Access permission for Environments, a user or user group assigned that role cannot deploy to any environment.
Restrict access to specific environments for a user or user group
You can restrict a user or user group to using specific environments only.
If you want to restrict a user or user group to deploy to a specific environment only, do the following:
- Create a resource group and select the environment.
- Create a role and give the user or user group permissions. The Access permission is needed for deployments.
- Assign the role and resource group to the user or user group.
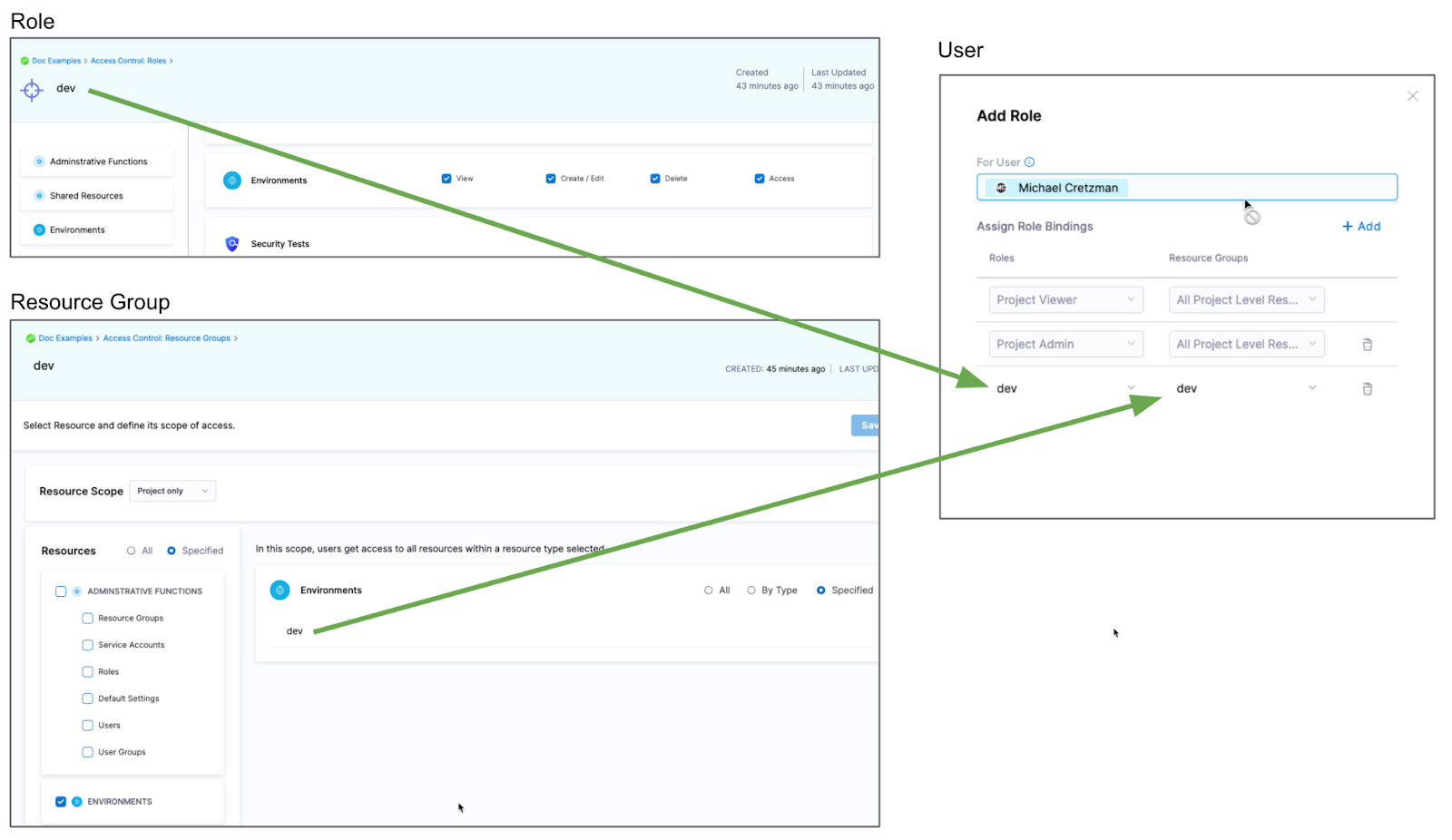
Environment groups
Environment groups are simply a way to group environments so you can assign permissions to multiple environments in a role.