Use config files in your deployments
You can add files to your Harness services and then reference and use the files in your service manifests/specifications and pipelines.
Files are added to the Config Files section in your Harness services.
Files can be stored in the following locations.
- Harness file store: All platform integrations (Kubernetes, etc.) support config files stored in the Harness file store.
- Git providers: You can use config files in any Git provider, including GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. You connect to these providers using Harness connectors. Ensure that the connector credentials have read permissions on the target repository.
Important notes on config files
- Files must be 1MB or less.
- All text files are supported (JSON, txt, XML, etc.) .
- You cannot use Harness variables in an encrypted text config file.
- You cannot reference other config files within a config file.
- Config files cannot be binaries.
Expressions are not allowed in references
Config files are referenced using the <+configFile.getAsString("CONFIG_FILE_ID")> format, as described in Referencing and encoding config files.
You cannot use Harness expressions in the parameter field of the getAsString() and getAsBase64() functions. For example, this expression will fail: <+configFile.getAsString(“<+serviceVariable.var_name>”)>.
Config file capabilities
You can add plain or encrypted text files. Both types can be referenced using a Harness expression, discussed below.
With a plain text config file, Harness renders the contents of the file.
With an encrypted text config file, you need to base64 decode it before you can reference it within the deployment.
Add config files to a service
You can add config files to any Harness service deployment type (Kubernetes, ECS, etc.).
- YAML
- Pipeline Studio
Here's an example of a service with both a plain text and encoded config file added from the Harness file store.
service:
name: Config files
identifier: Config_files
tags: {}
serviceDefinition:
spec:
configFiles:
- configFile:
identifier: plainText
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
files:
- /Config files/my-plain-text-file.txt
- configFile:
identifier: encodedTextFile
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
secretFiles:
- sshnov7
type: Ssh
The encoded file is added as a Harness secret. The secret must be created separately if you are using YAML.
You will use the configFile.identifier value to reference the config file.
You can attach multiple files in a config file. Simply add a new line:
files:
- /Config files/file1.json
- /dev/file2.json
- In the Harness service, in Config Files, select Add Config File.
- In Config File Source, select Harness, and select Continue.
- In Config File Identifier, enter a name for the file.
- In Select file type, select File Store or Encrypted. Encrypted files are stored as Harness secrets.
- Select Add to attach multiple files as a single config file.
- Select Submit.
You will use the value you entered in Config File Identifier to reference the config file as an expression in the format <+configFile.getAsString("CONFIG_FILE_ID")>.
Multiple files can be added to one config file
You can attach multiple files to one config file. All the files must be either plain text or encoded. You cannot mix types.
Referencing and encoding config files
Files added in the Config Files section of a service are referenced using the following Harness expressions.
- Plain text file contents:
<+configFile.getAsString("CONFIG_FILE_ID")> - Base64-encoded file contents:
<+configFile.getAsBase64("CONFIG_FILE_ID")>
If the config file has multiple text or encrypted files attached, you must use fileStore or secrets variables expressions:
<+fileStore.getAsString("SCOPED_FILEPATH")><+fileStore.getAsBase64("SCOPED_FILEPATH")><+secrets.getValue("SCOPED_SECRET_ID")>
Here are some examples:
<+configFile.getAsString("cf_file")><+configFile.getAsBase64("cf_file")><+fileStore.getAsString("/folder1/configFile")><+fileStore.getAsBase64("account:/folder1/folder2/configFile")><+secrets.getValue("account.MySecretFileIdentifier")>
Use Base64 to avoid new lines
If you are going to use a config file in a manifest or shell script, be aware that <+configFile.getAsString()> can cause problems by adding new lines to your manifest (unless you have formatted the file very carefully).
Instead, use <+configFile.getAsBase64()>. This ensures that the contents of the file are rendered as a single line.
In a Shell Script step or service command it would look like this:
echo <+configFile.getAsBase64("myFile")>
Decoding a config file in a manifest
In a Kubernetes manifest (in our example, a ConfigMap), you decode the base64 config file and indent it for the YAML syntax.
Here's the values.yaml:
my_file:`my_file:\<+configFile.getAsBase64("myFile")>`
Here's the ConfigMap:
data:
keyname: |
{{.Values.my_file | b64dec | indent 4}}
At runtime, the config file is decoded and used as plaintext.
Using Harness variables in config files
Plain text config files support the following Harness variables:
- Pipeline variables
- Service variables
- Environment variables
- Environment override variables
- Secrets
You cannot use Harness variables in an encrypted text config file.
Override service config files at the environment level
You can override service config files at the environment level. When the service is deployed to that environment, the environment's config files will override the service's config files.
Override config files for all services
To override the config files for all services used with an environment, do the following.
- YAML
- Pipeline Studio
Here's an example of an environment with config file overrides in its overrides.
environment:
name: Config Files
identifier: Config_Files
tags: {}
type: PreProduction
orgIdentifier: default
projectIdentifier: CD_Docs
variables: []
overrides:
configFiles:
- configFile:
identifier: EnvironmentPlainText
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
files:
- /Config files/my-plain-text-file.txt
- configFile:
identifier: EnvironmentEncodedFile
spec:
store:
type: Harness
spec:
secretFiles:
- account.Dpk
- In Environments, select an environment.
- In the environment's Configuration, in Config Files, select New Config File Override.
- Follow the same steps as you would when adding a config file in a service and then select Submit.
Override config files for specific services
You can override the config files of specific services' deployed to an environment.
- In Environments, select an environment.
- In the environment's Service Overrides, select New configuration overrides.
- In Service, select the service to override.
- In Override Type, select Config file, and then select New Config File Override.
- In Config File Selection, select the config file to override, and select Override.
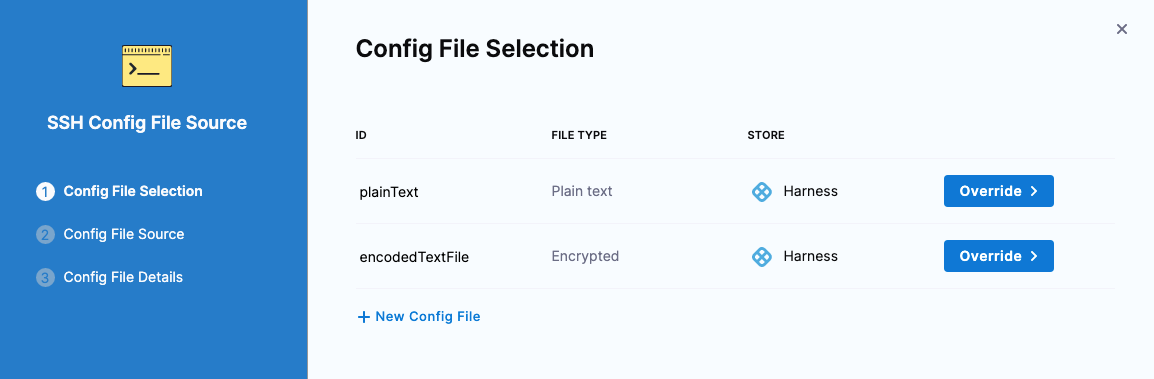
- Follow the steps to select the override file, and then select Submit.
When the selected service is deployed to this environment, the environment's config files will override that service's config files.
Fully overriding config files and variables
Harness supports overriding service config files at the environment level.
Config files are a black box that can contain multiple formats and content, such as YAML, JSON, plain text, etc. Consequently, they cannot be overridden like Values YAML files.
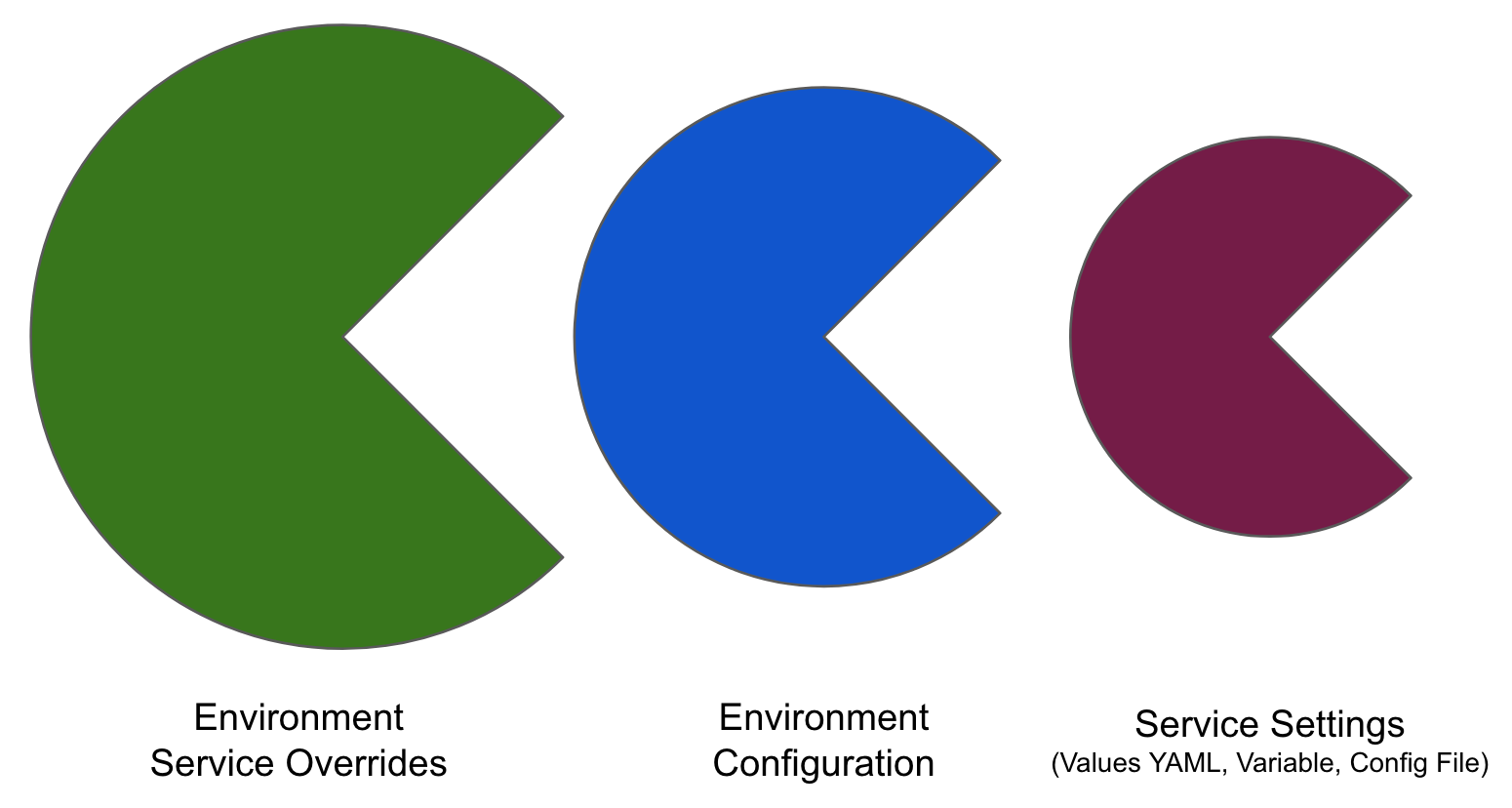
When you have config files at two or more of the environment Service Overrides, Configuration, and the service itself, the standard override priority is applied.
The priority from top to bottom is:
- Environment service overrides
- Environment configuration
- Service settings
When you have Variables with the same name at two or more of the environment Service Overrides, Configuration, and the service itself, the standard override priority is applied.
Use the Copy Configs command
In most cases, you can use the Copy command to copy the config files to your target hosts.
- YAML
- Pipeline Studio
Here's an example of a Command step copying a config file to all target hosts.
- step:
type: Command
name: Copy
identifier: Copy
spec:
onDelegate: false
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
commandUnits:
- identifier: Copy
name: Copy
type: Copy
spec:
sourceType: Config
destinationPath: /
timeout: 10m
failureStrategies: []
strategy:
repeat:
items: <+stage.output.hosts>
Note the use of strategy.repeat.items: <+stage.output.hosts>. This runs the command on all target hosts.
- In your CD stage, add a Command step.
- In the Command step, in Run the following commands, select Add Command.
- In Add Command, in Command Type, select Copy.
- In Select file type to copy, select Config.
- In Destination Path, enter the path on the target host where you want the config file copied.
- Select Add.
- In the Command step Advanced settings, select Looping Strategy.
- Select the Repeat strategy and enter the following:
repeat:
items: <+stage.output.hosts>
This runs the command on all target hosts.