Upload Artifacts to S3
To upload artifacts to AWS or other S3 providers, such as MinIO, you can either:
- Use the Upload Artifacts to S3 step with the optional Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin.
- Use the S3 Upload and Publish plugin.
To upload artifacts to S3, you need:
- Access to an S3 instance.
- A CI pipeline with a Build stage.
- Steps in your pipeline that generate artifacts to upload, such as by running tests or building code. The steps you use depend on what artifacts you ultimately want to upload.
- An AWS connector, if you want to use the Upload Artifacts to S3 step.
You can also upload artifacts to GCS, upload artifacts to JFrog, and upload artifacts to Sonatype Nexus.
Use the Upload Artifacts to S3 step
Add the Upload Artifacts to S3 step to your pipeline's Build stage, and configure the settings accordingly.
Here is a YAML example of a minimum Upload Artifacts to S3 step.
- step:
type: S3Upload
name: S3Upload
identifier: S3Upload
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_AWS_CONNECTOR_ID
region: YOUR_AWS_REGION
bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET_NAME
sourcePath: path/to/artifact.tar.gz
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>
Upload Artifacts to S3 step settings
The Upload Artifacts to S3 step has the following settings. Depending on the stage's build infrastructure, some settings might be unavailable or optional. Settings specific to containers, such as Set Container Resources, are not applicable when using a VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Name
Enter a name summarizing the step's purpose. Harness generates an Id (Entity Identifier) based on the Name. You can edit the Id.
AWS Connector
Select the Harness AWS connector to use when connecting to AWS S3.
- This step might not support all AWS connector authentication methods.
- You can use buckets with disabled ACLs.
- Additional stage variables are required for non-default ACLs or to assume IAM roles or use ARNs.
- The AWS IAM roles and policies associated with the AWS account for your AWS connector must allow pushing to S3. For more information, go to the AWS connector settings reference.
Stage variable required for non-default ACLs
S3 buckets use private ACLs by default. Your pipeline must have a PLUGIN_ACL stage variable if you want to use a different ACL.
- In the Pipeline Studio, select the stage with the Upload Artifacts to S3 step, and then select the Overview tab.
- In the Advanced section, add a stage variable.
- Enter
PLUGIN_ACLas the Variable Name, set the Type to String, and then select Save. - For the Value, enter the relevant ACL.
Stage variable required to assume IAM roles or use ARNs
Stages with Upload Artifacts to S3 steps must have a PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARN stage variable if:
- Your AWS connector's authentication uses a cross-account role (ARN). You can use
PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARNto specify the full ARN value corresponding with the AWS connector's ARN. - Your AWS connector uses Assume IAM Role on Delegate authentication. If your connector doesn't use AWS Access Key authentication, then the Upload Artifact to S3 step uses the IAM role of the build pod or build VM (depending on your build infrastructure). You can use
PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARNto select a different role than the default role assumed by the build pod/machine. This is similar tosts assume-role.
To add the PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARN stage variable:
- In the Pipeline Studio, select the stage with the Upload Artifacts to S3 step, and then select the Overview tab.
- In the Advanced section, add a stage variable.
- Enter
PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARNas the Variable Name, set the Type to String, and then select Save. - For the Value, enter the full ARN value.
- For cross-account roles, this ARN value must correspond with the AWS connector's ARN.
- For connectors that use the delegate's IAM role, the ARN value must identify the role you want the build pod/machine to use.
Region
Define the AWS region to use when pushing the image.
Bucket
The name of the S3 bucket name where you want to upload the artifact.
Source Path
Path to the file or directory that you want to upload.
If you want to upload a compressed file, you must use a Run step to compress the artifact before uploading it.
Endpoint URL
Endpoint URL for S3-compatible providers. This setting is not needed for AWS.
Target
Provide a path, relative to the S3 Bucket, where you want to store the artifact. Do not include the bucket name; you specified this in Bucket.
If you don't specify a Target, Harness uploads the artifact to the bucket's main directory.
Run as User
Specify the user ID to use to run all processes in the pod if running in containers. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
Set Container Resources
Maximum resources limits for the resources used by the container at runtime:
- Limit Memory: Maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number with the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalents,GiorMi. Do not include spaces when entering a fixed value. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed. For example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
Set the timeout limit for the step. Once the timeout limit is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution continues. To set skip conditions or failure handling for steps, go to:
Additional properties available through environment variables
Configuring Prefix Stripping in the "Upload to S3" Step
The out-of-the-box Upload to S3 step in Harness CI allows you to remove unwanted path prefixes when uploading files to Amazon S3. To customize this behavior, you can use the PLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIX environment variable.
Steps to Configure Prefix Stripping:
- Set Up the
PLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIXVariable:
- In your pipeline stage, add a variable named
PLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIX. - Assign it a value representing the prefix path segment you want to strip. This path will be removed from the beginning of the file paths before they are uploaded to S3.
- Example Usage:
- If your files are located in a subdirectory (e.g.,
/build/output), and you want onlyoutputto be uploaded without the build prefix, setPLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIXtobuild.
Here's an example for reference:
pipeline:
name: s3upload
identifier: s3upload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_PROJECT_NAME
orgIdentifier: YOUR_ORG_NAME
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: test-artifact-linux-arm64
identifier: Pull
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: false
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_1
identifier: Run_1
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
mkdir -p /harness/configfiles/filesconfig
echo "this is a test" > /harness/configfiles/filesconfig/upload-<+pipeline.sequenceId>.txt
- step:
type: S3Upload
name: S3Upload_1
identifier: S3Upload_1
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_AWS_CONNECTOR
region: us-east-1
bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET
sourcePath: /harness/configfiles/**/*
target: config
caching:
enabled: false
paths: []
sharedPaths:
- ""
buildIntelligence:
enabled: false
variables:
- name: PLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIX
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: /harness/configfiles
Impact on Multiple Upload Steps:
Since PLUGIN_STRIP_PREFIX is defined at the stage level, it will apply to all Upload to S3 steps within the same stage. If your stage has multiple upload steps, each one will strip the specified prefix from file paths.
If you need different prefix behavior for each upload step, you may want to use the Upload to S3 plugin directly in each step, instead of using the out-of-the-box step, to allow for customized configurations on a per-step basis.
View artifacts on the Artifacts tab
You can use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin to view artifacts on the Artifacts tab on the Build details page.
Add the Plugin step after the Upload Artifacts to S3 step.
- Visual
- YAML
Configure the Plugin step settings as follows:
- Name: Enter a name.
- Container Registry: Select a Docker connector.
- Image: Enter
plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher. - Settings: Add the following two settings as key-value pairs.
file_urls: Provide the URL to the artifact that was uploaded in the Upload Artifacts to S3 step, such ashttps://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs. If your S3 bucket is private, use the console view URL, such ashttps://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/object/BUCKET?region=REGION&prefix=TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Add a Plugin step that uses the artifact-metadata-publisher plugin.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION
artifact_file: artifact.txt
connectorRef: Use the built-in Docker connector (account.harness.Image) or specify your own Docker connector.image: Must beplugins/artifact-metadata-publisher.file_urls: Provide the URL to the target artifact that was uploaded in the Upload Artifacts to S3 step, such ashttps://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs. If your S3 bucket is private, use the console view URL, such ashttps://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/object/BUCKET?region=REGION&prefix=TARGET/ARTIFACT_NAME_WITH_EXTENSION.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Use the S3 Upload and Publish plugin
You can use the S3 Upload and Publish plugin to upload an artifact to S3 and publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
If you use this plugin, you do not need an Upload Artifacts to S3 step in your pipeline. This plugin provides the same functionality as the Upload Artifacts to S3 step combined with the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin; however it may not be appropriate for use cases that require advanced configuration.
- Visual
- YAML
In your pipeline's Build stage, add a Plugin step that uses the drone-s3-upload-publish plugin, and configure the settings as follows:
- Name: Enter a name.
- Container Registry: Select a Docker connector.
- Image: Enter
harnesscommunity/drone-s3-upload-publish. - Settings: Add the following seven settings as key-value pairs.
aws_access_key_id: An expression referencing a Harness secret or pipeline variable containing your AWS access ID, such as<+pipeline.variables.AWS_ACCESS>.aws_secret_access_key: An expression referencing a Harness secret or pipeline variable containing your AWS access key, such as<+pipeline.variables.AWS_SECRET>.aws_default_region: Your default AWS region, such asap-southeast-2.aws_bucket: The target S3 bucket.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.source: Provide the path, in the build workspace, to the file or directory that you want to upload. If you want to upload a compressed file, you must use a Run step to compress the artifact before uploading it.target: Optional. Provide a path, relative to theaws_bucket, where you want to store the artifact. Do not include the bucket name; you specified this inaws_bucket. If the specified path doesn't exist in the bucket, Harness creates the folder or folders when uploading the artifact. If you don't specify atarget, Harness uploads the artifact to the bucket's main directory. You might want to use expressions, such as<+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>, which would automatically organize your artifacts into directories based on the pipeline name and incremental build ID.
- Image Pull Policy: Select If Not Present.
In your pipeline's CI stage, add a Plugin step that uses the drone-s3-upload-publish plugin, for example:
- step:
type: Plugin
name: s3-upload-publish
identifier: custom_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: harnesscommunity/drone-s3-upload-publish ## Required.
settings:
aws_access_key_id: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_ACCESS> ## Reference to your AWS access ID.
aws_secret_access_key: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_SECRET> ## Reference to your AWS access key.
aws_default_region: ap-southeast-2 ## Set to your default AWS region.
aws_bucket: bucket-name ## The target S3 bucket.
artifact_file: artifact.txt ## Provide any '.txt' file name. Harness uses this to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
source: path/to/target/artifact.tar.gz ## Provide the path to the file or directory that you want to upload.
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId> ## Optional. Provide a path, relative to the 'aws_bucket', where you want to store the artifact. Do not include the bucket name. If unspecified, Harness uploads the artifact to the bucket's main directory.
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
For aws_access_key_id and aws_secret_access_key, use expressions to reference Harness secrets or pipeline variables containing your AWS access ID and key. You could also use expressions for target, such as <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>, which would automatically organize your artifacts into directories based on the pipeline name and incremental build ID.
If you want to upload a compressed file, you must use a Run step to compress the artifact before uploading it.
Build logs and artifact files
When you run the pipeline, you can observe the step logs on the build details page.
If the build succeeds, you can find the artifact on S3.
If you used the Artifact Metadata Publisher or S3 Upload and Publish plugin, you can find the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
On the Artifacts tab, select the step name to expand the list of artifact links associated with that step.
If your pipeline has multiple steps that upload artifacts, use the dropdown menu on the Artifacts tab to switch between lists of artifacts uploaded by different steps.
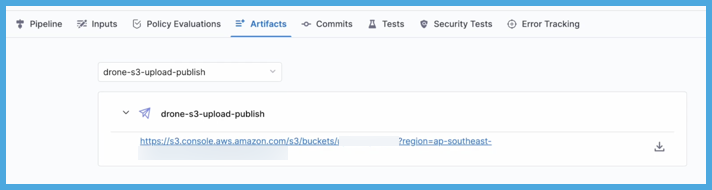
Pipeline YAML examples
- Upload Artifacts to S3 step
- S3 Upload and Publish plugin
The following pipeline examples use the Upload Artifacts to S3 step and the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin.
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed
This example pipeline uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure. It produces a text file, uploads the file to S3, and uses the Artifact Metadata Publisher to publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: default
identifier: default
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: upload artifact
identifier: upload_artifact
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: write file
identifier: write_file
spec:
shell: Bash
command: |-
echo "some file" > myfile.txt
date >> myfile.txt
- step:
type: S3Upload
name: S3Upload
identifier: S3Upload
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_AWS_CONNECTOR_ID
region: YOUR_AWS_REGION
bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET
sourcePath: path/to/myfile.txt
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step:
type: Plugin
name: artifact metadata
identifier: artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/SOURCE_PATH/myfile.txt
artifact_file: artifact.txt
This example pipeline uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure. It produces a text file, uploads the file to S3, and uses the Artifact Metadata Publisher to publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: allure-report-upload
identifier: allurereportupload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
automountServiceAccountToken: true
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: write file
identifier: write_file
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: alpine:latest
shell: Bash
command: |-
echo "some file" > myfile.txt
date >> myfile.txt
- step:
type: S3Upload
name: S3Upload
identifier: S3Upload
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_AWS_CONNECTOR_ID
region: YOUR_AWS_REGION
bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET
sourcePath: path/to/myfile.txt
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>
- step:
type: Plugin
name: artifact metadata
identifier: artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://BUCKET.s3.REGION.amazonaws.com/TARGET/SOURCE_PATH/myfile.txt
artifact_file: artifact.txt
The following pipeline examples use the S3 Upload and Publish plugin.
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed
This example pipeline uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure. It produces a text file and uses the S3 Upload and Publish plugin to uploads the file to S3 and publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: default
identifier: default
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: upload artifact
identifier: upload_artifact
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: write file
identifier: write_file
spec:
shell: Bash
command: |-
echo "some file" > myfile.txt
date >> myfile.txt
- step:
type: Plugin
name: s3-upload-publish
identifier: custom_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: harnesscommunity/drone-s3-upload-publish
settings:
aws_access_key_id: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_ACCESS>
aws_secret_access_key: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_SECRET>
aws_default_region: YOUR_AWS_REGION
aws_bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET
artifact_file: artifact.txt
source: path/to/myfile.txt
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
This example pipeline uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure. It produces a text file and uses the S3 Upload and Publish plugin to uploads the file to S3 and publish the artifact URL on the Artifacts tab.
pipeline:
name: allure-report-upload
identifier: allurereportupload
projectIdentifier: YOUR_HARNESS_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
repoName: YOUR_CODE_REPO_NAME
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
description: ""
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
automountServiceAccountToken: true
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: write file
identifier: write_file
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: alpine:latest
shell: Bash
command: |-
echo "some file" > myfile.txt
date >> myfile.txt
- step:
type: Plugin
name: s3-upload-publish
identifier: custom_plugin
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: harnesscommunity/drone-s3-upload-publish
settings:
aws_access_key_id: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_ACCESS>
aws_secret_access_key: <+pipeline.variables.AWS_SECRET>
aws_default_region: YOUR_AWS_REGION
aws_bucket: YOUR_S3_BUCKET
artifact_file: artifact.txt
source: path/to/myfile.txt
target: <+pipeline.name>/<+pipeline.sequenceId>
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
Download Artifacts from S3
You can use the S3 Drone plugin to download artifacts from S3. This is the same plugin image that Harness CI uses to run the Upload Artifacts to S3 step. To do this,add a Plugin step to your CI pipeline. For example:
- step:
type: Plugin
name: download
identifier: download
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR
image: plugins/s3
settings:
access_key: <+secrets.getValue("awsaccesskeyid")>
secret_key: <+secrets.getValue("awssecretaccesskey")>
region: YOUR_BUCKET_REGION
bucket: YOUR_BUCKET_NAME
source: path/to/directory/to/download
target: download/destination
download: "true"
Configure the Plugin step settings as follows:
| Keys | Type | Description | Value example |
|---|---|---|---|
connectorRef | String | Select a Docker connector. | YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR |
image | String | Enter plugins/s3. | plugins/s3 |
access_key | String | Reference to a Harness text secret containing your AWS access key ID. | <+secrets.getValue("awsaccesskeyid")> |
secret_key | String | Reference to a Harness text secret containing your AWS secret access key. | <+secrets.getValue("awssecretaccesskey")> |
region | String | The S3 bucket region | us-east-2 |
bucket | String | The S3 bucket name. | my-cool-bucket |
source | String | The path to the directory to download from your S3 bucket. | path/to/artifact/directory |
target | String | Path to the location where you want to store the downloaded artifacts, relative to the build workspace. | artifacts (downloads to /harness/artifacts) |
download | Boolean | Must be true to enable downloading. If omitted or false, the plugin attempts to upload artifacts instead. | "true" |
Mount an S3 bucket using s3fs-fuse
s3fs-fuse allows files and directories in an S3 bucket to act like a local file system. Harness Cloud supports using s3fs-fuse on Linux infrastructure.
The s3fs command supports the standard AWS credentials file, or AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY environment variables.
Here is an example pipeline step that installs s3fs and mounts an S3 bucket using aws_access_key_id and aws_secret_access_key text secrets.
- step:
type: Run
name: Setup s3fs
identifier: Setup_s3fs
spec:
shell: Sh
envVariables:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: <+secrets.getValue("aws_access_key_id")>
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: <+secrets.getValue("aws_secret_access_key")>
AWS_REGION: <+input>
S3_BUCKET_NAME: <+input>
S3FS_MOUNT_DIR: <+input>
command: |-
apt-get update
apt-get install s3fs
s3fs $S3_BUCKET_NAME $S3FS_MOUNT_DIR \
-o use_cache=/tmp \
-o allow_other \
-o uid=1000 \
-o gid=1000 \
-o umask=0022 \
-o url=https://s3.${AWS_REGION}.amazonaws.com
In the above example, AWS_REGION, S3_BUCKET_NAME and S3FS_MOUNT_DIR are input parameters.
Any following steps in the stage can access the directory mounted at S3FS_MOUNT_DIR to read and write files in the S3 bucket.
- step:
type: Run
name: Write file to bucket
identifier: Write_file_to_bucket
spec:
shell: Sh
envVariables:
S3FS_MOUNT_DIR: <+input>
command: |-
echo "Write file" > $S3FS_MOUNT_DIR/example.txt
- step:
type: Run
name: Read file from bucket
identifier: Read_file_from_bucket
spec:
shell: Sh
envVariables:
S3FS_MOUNT_DIR: <+input>
command: |-
cat $S3FS_MOUNT_DIR/example.txt
When using Docker in a Run step, S3FS_MOUNT_DIR must be added as a shared path.
Troubleshoot uploading artifacts
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related uploading artifacts, such as: