Enable parallelism on a Run Tests step
While the Run Tests step remains backwards compatible until removal, Harness recommends using the new Test step as soon as possible to take advanced of improved functionality and avoid service interruptions upon removal of the deprecated step.
To enable parallelism/test splitting in the Test step, refer to the Test step documentation.
By default, Test Intelligence reduces test time by running only the necessary tests to validate your code changes. You can enable parallelism and test splitting in your Run Tests steps to further optimize test times.
This topic explains test splitting/parallelism in Run Tests steps only.
For test splitting/parallelism in Run steps, go to Split tests in Run steps.
For test splitting/parallelism in Test steps, go to the Test step documentation.
With parallelism, you specify how you want Harness to divide similar workloads. When you use parallelism and test splitting with Test Intelligence, Harness divides the work after test selection. This means that your test execution time is reduced by both test selection and parallelism.
Example: Time saved by combining TI with test splitting
Suppose you have a pipeline that runs 100 tests, and each test takes about one second to run. Here's how TI and parallelism can reduce your test times:
- By default, without TI or parallelism, all 100 tests run in sequence, taking 100 seconds.
- With TI, test selection reduces the number of tests based on the detected changes. Supposing only 20 out of the 100 tests are required, the build with TI runs 20 tests in sequence, taking 20 seconds. This reduces test run time by 80%.
- With TI and parallelism, the selected tests are divided into a number of workloads. Supposing a maximum of four workloads and 20 selected tests, the 20 tests are split into four concurrently-running groups. It takes only five seconds to run the tests, reducing test run time by 95% compared to the default.
Note that while parallelism for TI can improve the total time it takes to run all tests, some tests may still take a long time to run if, by their nature, they are intensive, long-running tests.
Enable test splitting for TI
To enable test splitting for TI, you must:
- Define a parallelism strategy.
- Enable test splitting on the Run Tests step.
- Use an expression to differentiate report names for each run.
Define a parallelism strategy
In the context of test splitting, the parallelism strategy defines the number of workloads into which tests can be divided. Each parallel instance (or workload) is a duplicate of the stage where you've defined a parallelism strategy, but each instance runs different tests.
- Visual editor
- YAML editor
Define the parallelism strategy on the stage with the Run Tests step.
You can configure parallelism strategies on stages or steps.
Harness recommends using stage-level parallelism for test splitting.
If you use step-level parallelism, you must ensure that your test runners won't interfere with each other because all parallel steps work in the same directory.
-
In your pipeline, select the stage where your tests run, and then select the Advanced tab.
-
Under Looping Strategies, select Parallelism.
-
Set the
parallelismvalue to the number of workloads that you want to divide your tests into. For example, if you want to create four workloads, setparallelism: 4.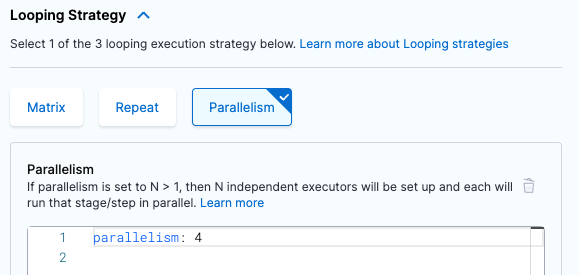
-
Optional: Define
maxConcurrency. This is a strategy to optimize parallelism.parallelism: 8
maxConcurrency: 2
Define the parallelism strategy (strategy.parallelism) on the stage with the RunTests step.
strategy: ## Declares a looping strategy.
parallelism: 8 ## Specify the number of workloads. This example creates 8 workloads.
maxConcurrency: 2 ## Optional setting to optimize parallelism. Limits the number of workloads that can run at once.
You can configure parallelism strategies on stages or steps.
Harness recommends using stage-level parallelism for test splitting.
If you use step-level parallelism, you must ensure that your test runners won't interfere with each other because all parallel steps work in the same directory.
Optimize parallelism
In general, a higher parallelism value means a faster pipeline run time, because the tests can be divided into more parallel instances. However, this depends on your test suite and resource limitations in your build infrastructure. For example, if you try to run 10 groups of tests, but your build infrastructure can't handle 10 parallel instances, the pipeline can fail or take longer than expected.
To optimize your parallelism strategy:
- Try different parallelism values to determine your infrastructure's limits. Parallelism impacts resource allocation for the pipeline. A pipeline with five sequential stages can require fewer resources than a pipeline running five parallel instances of a stage, because the second pipeline has to run all five instances at once.
- Use
maxConcurrencyto control the flow of parallel instances and avoid overtaxing infrastructure resources. Concurrency limits the number of parallel instances that can run at once and queues additional instances.- For example, if you set
parallelism: 12, Harness attempts to run 12 instances of the stage at once. If you setparallelism: 12andmaxConcurrency: 3, Harness generates 12 instances of the stage, but only runs three instances at a time. The remaining nine instances are queued, and the queued instances start running as space clears in the concurrency limit (when prior instances finish). - Concurrency allows you to divide tests into more workloads without overloading your system resources.
- There are resource requirements to generate parallel instances (even if they are not all running at the same time) and handle queues. Try different combinations of
parallelismandmaxConcurrencyvalues to determine your ideal configuration.
- For example, if you set
- Review the Best practices for looping strategies, including how to calculate ideal concurrency.
Enable Test Splitting on the Run Tests step
On the Run Tests step, set Enable Test Splitting (enableTestSplitting: true).
- step:
type: RunTests
identifier: Run_Tests_with_Intelligence
name: Run Tests with Intelligence
spec:
...
enableTestSplitting: true ## Required to enable test splitting.
testSplitStrategy: ClassTiming ## Optional. Can be ClassTiming or TestCount. Default is ClassTiming.
...
The Test Split Strategy is optional. The default test split strategy is class timing. If you would rather split tests by test count, you can set the Test Split Strategy to Test Count.
Class timing uses test times from previous runs to determine how to split the test workload for the current build. Test count uses simple division to split the tests into workloads. However, the maximum possible number of workloads is determined by the parallelism strategy you specified on the step or stage. For example, if you set parallelism: 5, then the tests are split into a maximum of five workloads.
Differentiate report names
With stage-level parallelism, results files are automatically output as separate stage artifacts.
If you want the individual results files to have unique names, you can use an expression or variable in the results file name, such as result_<+strategy.iteration>.xml or result_${HARNESS_NODE_INDEX}.xml.
You might need to modify your test tool configurations to support this report naming convention, and you must modify the Report Paths (reports.paths) value to include the Harness expression, such as <+strategy.iteration>. For example:
reports:
spec:
paths:
- "target/surefire-reports/result_<+strategy.iteration>.xml"
type: JUnit
Harness recommends stage-level parallelism for test splitting. However, if you defined the parallelism strategy on a step (instead of a stage), you must use an expression or variable in the results file name, such as The following modification is recommended when using test splitting in a Run Tests step with step-level The default maven-surefire-plugin configuration in When running tests, the default test reports ( However, when you run a CI pipeline with test splitting enabled, all test reports are generated in one This issue is only present in the Build details UI. In actuality, the tests are split. To correct the UI issue, make the following changes to Edit In your CI pipeline, edit the Run Tests step.result_<+strategy.iteration>.xml or result_${HARNESS_NODE_INDEX}.xml, to ensure each parallel instance produces a uniquely-named results file. If you don't use an expression or variable in the results file name, the files overwrite each other or fail due to same-name conflicts. How you enable this varies by language and test tool. For this reason, among others, Harness recommends using stage-level parallelism for test splitting.Recommended maven-surefire-plugin and pom.xml modifications for step-level test splitting
parallelism. This modification is recommended because it doesn't change the default behavior and preserves the default test report directory. If you are using stage-level parallelism, this modification has no impact and isn't required.pom.xml is as follows: <plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>*.xml) are generated in target/surefire-reports:<reportsDirectory default-value="${project.build.directory}/surefire-reports"/>surefire-reports directory. As a result, the Tests tab shows the same number of tests for all parallel runs.pom.xml and your Run Tests step:
pom.xml:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
<reportDir>target/surefire-reports</reportDir>
</properties>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
<configuration>
<reportsDirectory>${reportDir}</reportsDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
-DreportDir=reports-<+strategy.iteration> test
**/reports-<+strategy.iteration>/*.xml
Differentiate parallel runs in logs
You can also use environment variables and expressions to differentiate parallel runs in build logs.
-
Add two stage variables:
HARNESS_STAGE_INDEX: <+strategy.iteration>- This is the index of the current parallel run.HARNESS_STAGE_TOTAL: <+strategy.iterations>- This is the total parallel runs.
-
Add a
preCommandto echo the variables' values so you can easily see the values in build logs.
- step:
type: RunTests
identifier: Run_Tests_with_Intelligence
name: Run Tests with Intelligence
spec:
...
preCommand: |- ## Optional. Echo environment variables to differentiate parallel runs in build logs.
echo $HARNESS_STAGE_INDEX
echo $HARNESS_STAGE_TOTAL
...
YAML example: Test splitting for TI
This example shows a stage that uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure and runs Test Intelligence on a Java codebase. The parallelism strategy is set at the stage level.
- stage:
type: CI
identifier: Build_and_Test
name: Build and Test
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: RunTests
identifier: Run_Tests_with_Intelligence
name: Run Tests with Intelligence
spec:
language: Java ## Test splitting with TI is supported for all languages and tools that are supported by TI.
buildTool: Maven
envVariables: ## Optional environment variables to differentiate parallel runs.
HARNESS_STAGE_INDEX: <+strategy.iteration> # Index of current parallel run.
HARNESS_STAGE_TOTAL: <+strategy.iterations> # Total parallel runs.
preCommand: |- ## Optional. Echo environment variables to differentiate parallel runs in build logs.
echo $HARNESS_STAGE_INDEX
echo $HARNESS_STAGE_TOTAL
args: test
runOnlySelectedTests: true ## Enable TI.
enableTestSplitting: true ## Enable test splitting.
testSplitStrategy: ClassTiming ## Optional. Can be ClassTiming or TestCount. Default is ClassTiming.
postCommand: mvn package -DskipTests
reports:
spec:
paths:
- "target/surefire-reports/result_<+strategy.iteration>.xml" ## Use an expression to generate a unique results file for each parallel run.
type: JUnit
platform:
arch: Amd64
os: Linux
runtime:
spec: {}
type: Cloud
strategy:
parallelism: 3 ## Set the number of groups to use for test splitting.
Harness supports test splitting for any language.