Using Feature Management & Experimentation with Harness Pipelines
Harness Feature Management & Experimentation (FME) integrates with Harness pipelinesA pipeline is a sequence of stages that define how services are deployed to an environment. Pipelines can include approvals, barriers, notifications, and other execution logic., allowing you to include feature flag logicA feature flag is a conditional toggle in Harness FME that enables or disables specific functionality without requiring a code deployment. Feature flags support controlled rollouts, experimentation, and quick rollbacks if issues arise. directly within your deployment or automation workflows. The Pipelines page in Harness FME displays a list of Harness pipelines created in your project.
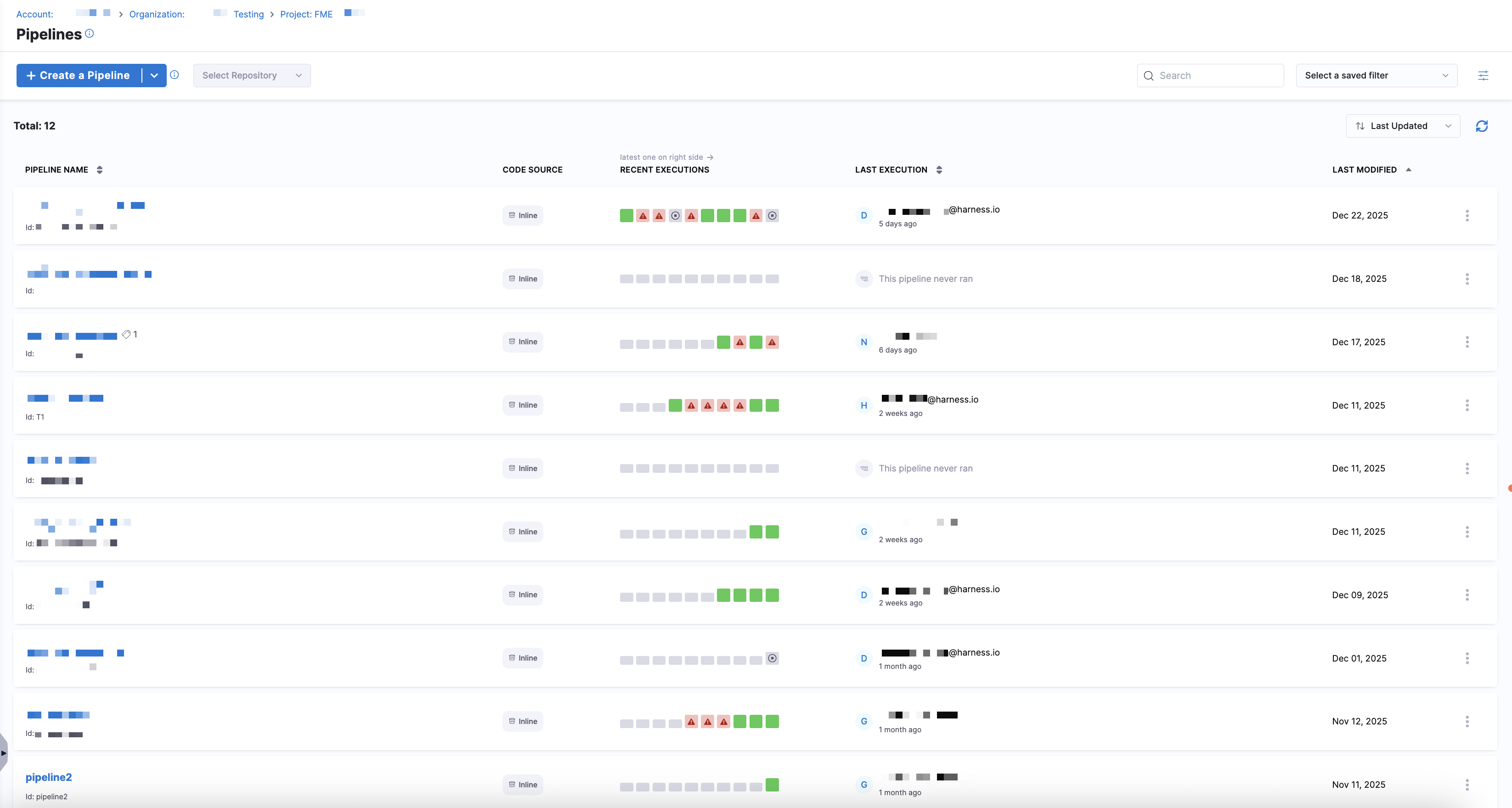
Create a Harness pipeline
To create a pipeline, click + Create a Pipeline. You can create a pipeline manually in the UI or import one from a Git repository. Clicking on a pipeline opens the Pipeline Studio, where you can design and manage the pipeline using either the Visual or YAML editor.
- Visual
- YAML
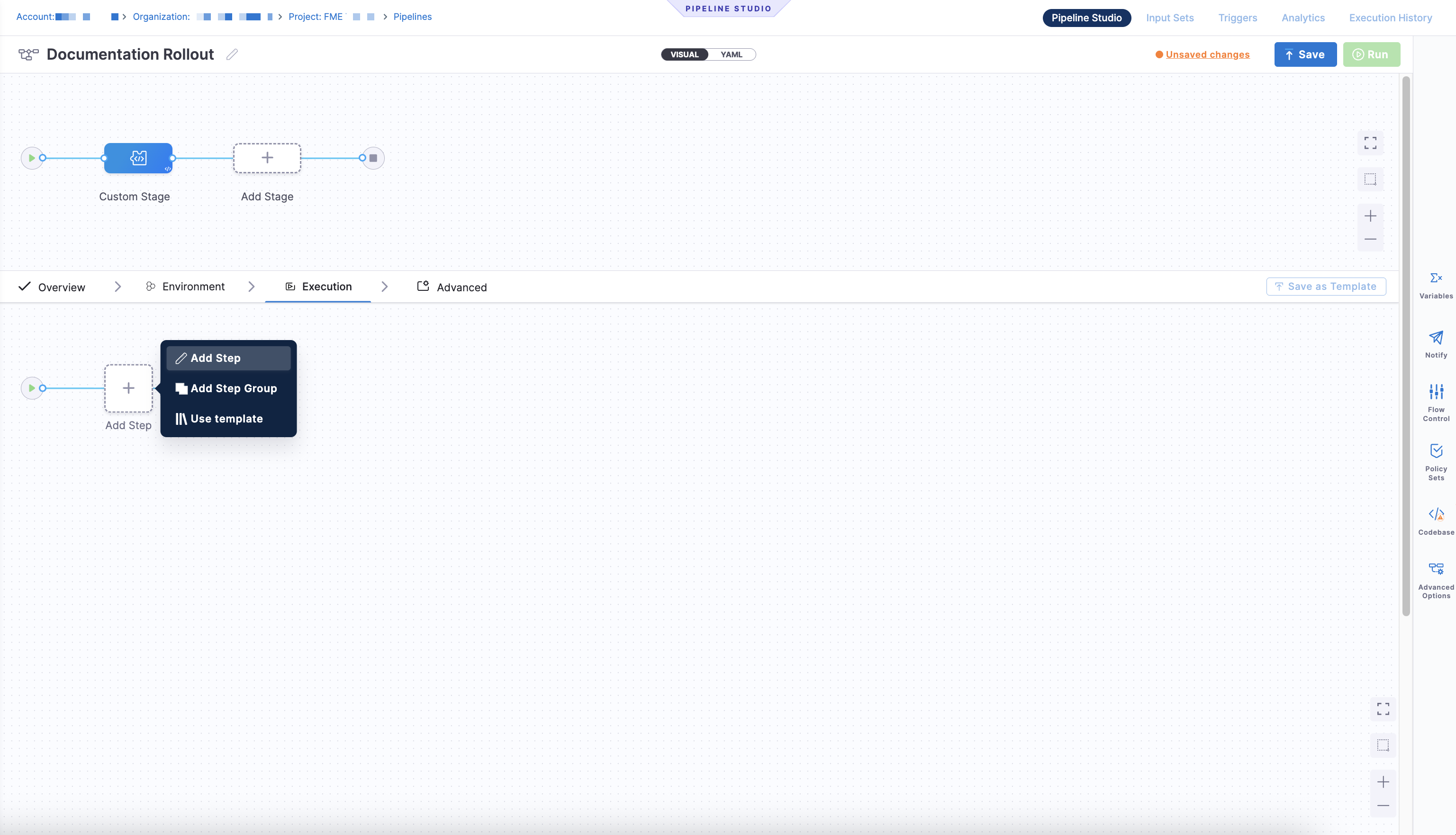
The Visual tab lets you configure stages and steps using the UI, including adding FME steps supported in Custom stagesA custom stage is a user-defined stage in a pipeline that allows you to run custom logic or actions as part of a pipeline. FME steps are only supported in Custom stages.. Add a custom stage and click Add Step to open the Step Library.
The YAML tab displays the full pipeline definition as YAML. Click Edit YAML to modify the pipeline configuration in code.
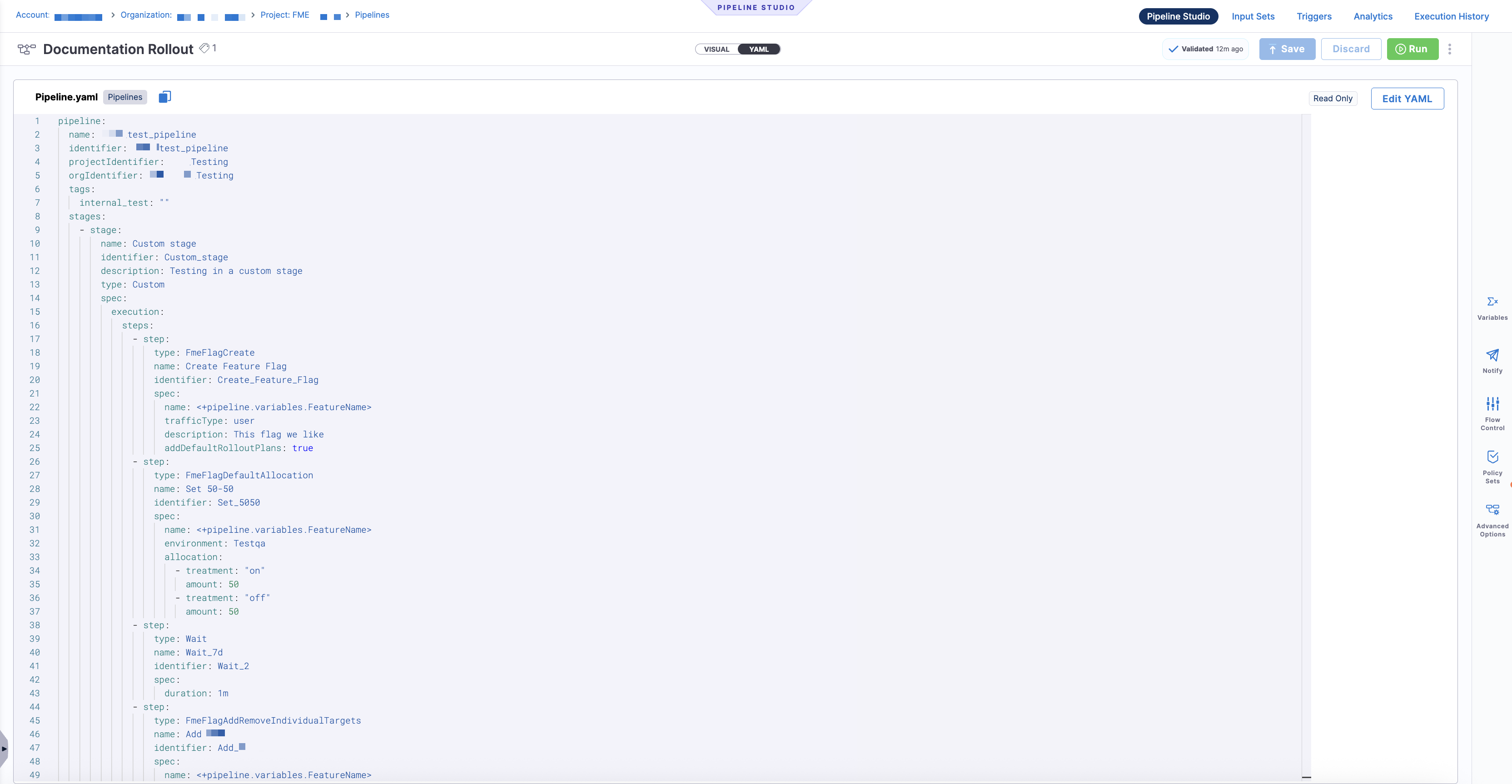
Both views stay in sync; changes made in the Visual editor are reflected in the YAML, and changes made in YAML are reflected back in the Visual editor.
When you configure a pipeline, you set it up like any standard pipeline, with the addition of FME stepsA step is an individual action within a stage. FME steps include operations such as creating or updating a feature flag, modifying rollout behavior, or killing a flag. at the stage levelA stage represents a discrete phase of a pipeline, such as testing, experimentation, or production rollout. You can add FME steps to any Custom stage, whether newly created or existing.. These steps let you integrate feature flag operations directly into your deployment workflow.
Permissions
Pipeline permissions are controlled through Harness RBAC for FME. Pipeline runs that include FME steps require the same permissions you would need to edit feature flags in Harness FME.
- You need view (
core_pipeline_view), create/edit (core_pipeline_edit), and execute (core_pipeline_execute) pipeline permissions. - You also need create/edit (
fme_fmefeatureflag_edit) permissions for feature flags in any FME environment the pipeline modifies. If a pipeline run tries to update a flag in an environment where you don't have edit access, the step will fail.
How FME steps work in Harness pipelines
When you add a stepA step is an individual action within a stage. FME steps include operations such as creating or updating a feature flag, modifying rollout behavior, or killing a flag. to a Custom stageA custom stage is a user-defined stage in a pipeline that allows you to run custom logic or actions as part of a pipeline. FME steps are only supported in Custom stages. in the Pipeline Studio, the Step Library includes a Feature Management & Experimentation section with FME-specific steps.
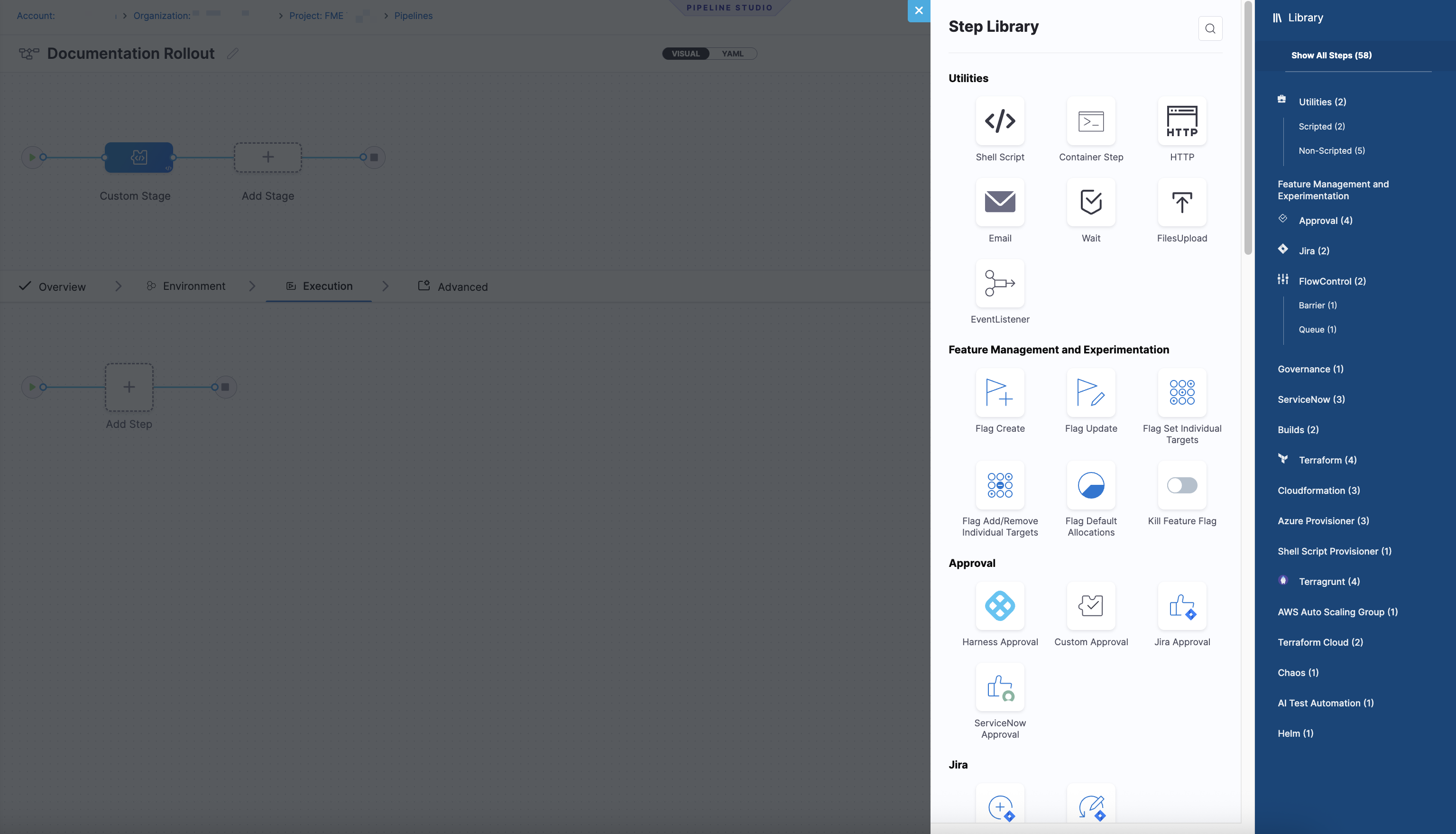
Each FME step runs like any other Harness pipeline step and performs a single, discrete feature flag operation, such as creating a flag, updating metadata, modifying individual targets, or killing a flag. These steps execute in sequence with the rest of your pipeline logic and support standard pipeline capabilities, including approvals, notifications, and custom failure strategies.
How approvals work with FME steps
Approvals can be added in Harness pipelines to prevent the execution from proceeding without approval. An Approval stage or step pauses the pipeline and requires an approver to approve or reject before the pipeline continues. For more information about approval stages or steps, see the Platform documentation.
When using FME steps in pipelines, these Harness approvals control the execution flow. FME environment-level approval settings do not apply to pipeline runs.
This approach lets teams coordinate automated workflows and feature flag changes within a single, auditable pipeline. By adding FME steps to your pipeline stages, you can:
- Create and manage feature flags as part of your deployment or promote workflows using Flag Create and Flag Update, including defining flags across all environments and updating metadata such as status, owners, and tags
- Manage individual targeting lists deterministically with Set Individual Targets and Add/Remove Individual Targets, allowing you to define or modify explicit target membership during a pipeline run
- Control default rollout behavior using Set Default Allocations, configuring how traffic is allocated when no targeting rules apply
- Immediately disable a feature flag with Kill Feature Flag as part of an incident runbook
FME steps in Harness pipelines allow feature flag operations to be predictable, reusable, and executed alongside application deployments, helping teams coordinate releases while reducing manual configuration and operational risk.
Add FME steps to a pipeline stage
FME steps are compatible with the Custom stage in Harness pipelines.
To add FME steps to a pipeline:
-
Navigate to the Pipelines page from the FME navigation menu.
-
Click + Create a Pipeline or click +Import From Git to import a pipeline from an existing Git repository.
-
Enter a name for the pipeline. Optionally, add a description and include tags for this pipeline.
-
Click Inline to store the pipeline in Harness or Remote to store the pipeline in a Git repository.
-
Click Start.
-
Click Add Stage and select Custom Stage.
-
Click + Add Step. The Step Library panel opens on the right.
-
Navigate to the Feature Management & Experimentation (FME) section and select a step.
FME step Primary use case When to use it Flag Create Create a new feature flag Use when introducing a new feature flag as part of deployment or feature development. This step instantiates the flag across all environments with default rollout plans. Flag Update Update flag metadata Use when you need to edit flag properties such as the description, rollout status, owners, or tags without changing targeting or traffic allocation. Set Individual Targets Define the full set of individual targets Use when you want to deterministically set the complete list of individual targets for a flag in an environment, replacing any existing list. Add/Remove Individual Targets Incrementally modify targeting Use when you need to add or remove specific users or segments without overwriting existing individual target lists. Useful for gradual rollouts or hand-picked targets. Set Default Allocations Control default rollout percentages Use when you want to define how traffic is split across treatments for users who do not match any targeting rules (for example, 50/50, 75/25, or 100% on). Kill Feature Flag Immediately disable a feature Use to kill the flag in the specified environment, serving the default treatment. -
Configure the step in the Step Parameters tab.
-
Optionally, add additional configuration in the Advanced tab.
-
Click Save to add the step to the stage.
Example Pipeline YAML Configuration
The following example shows a Harness pipeline that uses multiple FME stepsA step is an individual action within a stage. FME steps include operations such as creating or updating a feature flag, modifying rollout behavior, or killing a flag. within a Custom stageA step is an individual action within a stage. FME steps include operations such as creating or updating a feature flag, modifying rollout behavior, or killing a flag. to coordinate feature flag creation, rollout, targeting, and kill actions alongside standard pipeline steps:
pipeline:
name: <PIPELINE_NAME>
identifier: <PIPELINE_ID>
projectIdentifier: Default
orgIdentifier: <ORG_ID>
tags: {}
variables:
- name: flagName
type: String
description: "The feature flag name for this feature rollout."
required: true
value: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: demo_stage
identifier: demo_stage
description: "Custom stage with FME steps for this feature rollout."
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: FmeFlagCreate
name: initial setup
identifier: initial_setup
spec:
name: <+pipeline.variables.flagName>
trafficType: user
description: live demo flag
addDefaultRolloutPlans: true
- step:
type: FmeFlagSetIndividualTargets
name: add testers to on
identifier: add_testers_to_on
spec:
flagName: <+pipeline.variables.flagName>
environment: Prod-Default
treatments:
- treatment: "on"
keys:
- user1
- user2
segments: []
- step:
type: Wait
name: Wait_1
identifier: Wait_1
spec:
duration: 10s
- step:
type: FmeFlagDefaultAllocation
name: 50-50 Rollout
identifier: _rollout
spec:
flagName: <+pipeline.variables.flagName>
environment: Prod-Default
allocation:
- treatment: "on"
amount: 50
- treatment: "off"
amount: 50
- step:
type: FmeFlagUpdate
name: Change status to ramping
identifier: FmeFlagUpdate_1
spec:
name: <+pipeline.variables.flagName>
tags:
- demo
rolloutStatus: Ramping
addDefaultRolloutPlans: true
- step:
type: HarnessApproval
name: Harness Manual Approval
identifier: Harness_Manual_Approval
spec:
approvalMessage: Please review the change and approve.
includePipelineExecutionHistory: true
isAutoRejectEnabled: false
approvers:
userGroups:
- account._fme_admins
minimumCount: 1
disallowPipelineExecutor: false
approverInputs: []
timeout: 1d
- step:
type: FmeFlagDefaultAllocation
name: Rollout out to everyone
identifier: FmeFlagDefaultAllocation_2
spec:
flagName: <+pipeline.variables.flagName>
environment: Prod-Default
allocation:
- treatment: "on"
amount: 100
- treatment: "off"
amount: 0
tags: {}
Configure FME steps
Each FME step is configured at the stage levelA stage represents a discrete phase of a pipeline, such as testing, experimentation, or production rollout. You can add FME steps to any Custom stage, whether newly created or existing. of a CD pipeline. After adding an FME step from the Step Library, you can configure its behavior using the Step Parameters tab, and optionally refine execution behavior using the Advanced tab.
The following section walks through how to configure each FME step.
Flag Create
Use this step to create a feature flag and define it across all environments with default rollout plans.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Flag Create under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name (such as
Create Feature Flag). - Feature Flag Name: Add a name for the feature flag or use a pipeline variable (for example,
<+pipeline.variables.FeatureName>). - Traffic Type: Select the traffic type (for example,
user). - Description: Optionally, enter a description for the feature flag.
- Owners: Optionally, select one or more owners for the feature flag.
- Tags: Optionally, add tags to help organize and filter feature flags.
- Name: Add a step name (such as
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Flag Update
Use this step to update feature flag metadata without changing rollout behavior or targeting.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Flag Update under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name (such as
Update Feature Flag). - Feature Flag Name: Add a name of the existing feature flag.
- Description: Optionally, update the feature flag description.
- Owners: Optionally, update feature flag ownership.
- Tags: Optionally, add or modify tags.
- Name: Add a step name (such as
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Set Individual Targets
Use this step to define the complete set of individual targets for a feature flag in a specific environment. This replaces any existing individual targeting configuration.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Set Individual Targets under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name.
- Environment: Specify the environment where targeting should be applied.
- Feature Flag: Add the feature flag name.
-
Under the Set Individual Targets section, for the specific configure one or more treatments where you want to override the current individual targets list by clicking + Add Treatment:
- For Treatment: Select a treatment to apply.
- Keys: Optionally, enter individual target keys desired list.
- Segments: Optionally, enter individual segments to include.
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Add/Remove Individual Targets
Use this step to incrementally add or remove individual targets without replacing the existing target list.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Add/Remove Individual Targets under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name.
- Environment: Specify the target environment.
- Feature Flag: Add the feature flag name.
-
Under the Flag Change section, configure one or more treatments by clicking + Add Treatment:
- For Treatment: Select a treatment to apply.
- Add Segments: Optionally, enter segments to include.
- Add Keys: Optionally, enter individual target keys to include.
- Remove Segments: Optionally, enter segments to remove.
- Remove Keys: Optionally, enter individual keys to remove.
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Set Default Allocations
Use this step to control how traffic is allocated across treatments for users who do not match any targeting rules.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Set Default Allocations under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name.
- Environment: Specify the environment.
- Feature Flag: Add the feature flag name.
-
Under the Flag Change section, define one or more allocations by clicking + Add Allocation:
- Treatment: Select a treatment to apply.
- Allocation Percentage: Enter the percentage of traffic.
-
Ensure the total allocation equals 100%.
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Kill Feature Flag
Use this step to immediately disable a feature flag in a specific environment.
-
In your pipeline stage, click + Add Step.
-
Select Kill Feature Flag under Feature Management & Experimentation in the Step Library.
-
In the Step Parameters tab, configure the following:
- Name: Add a step name.
- Environment: Specify the environment.
- Feature Flag: Add the feature flag name.
-
Click Apply Changes to add the step to the pipeline.
Once you have added FME steps to a Custom stage and designed your pipeline, click Save and execute the pipeline by clicking Run.
Advanced Pipeline Configuration
You can also control how an FME step runs or recovers by configuring conditional execution, failure strategy, and looping strategy settings on the Advanced tab of each step.
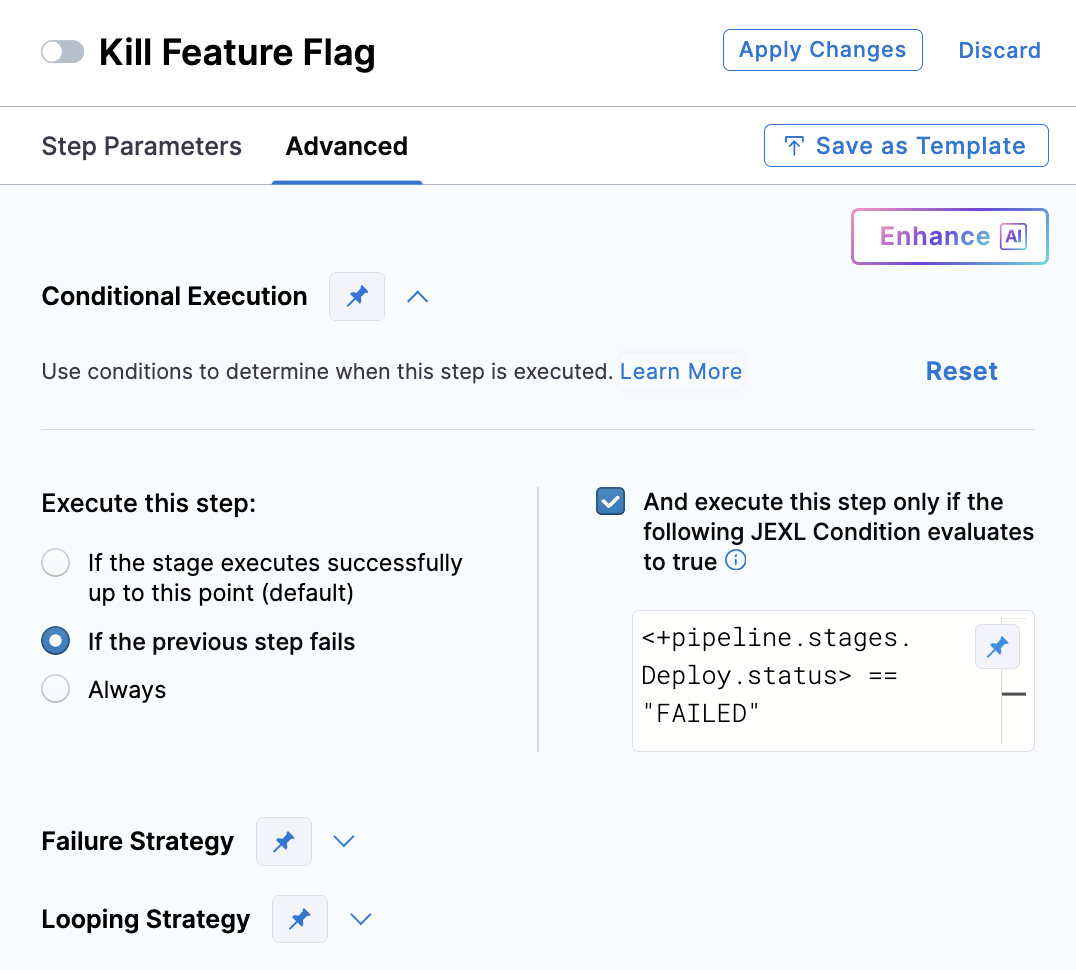
Conditional execution lets you run or skip FME steps based on pipeline variables, expressions, or runtime inputs. For example, you can update a feature flag only in production or configure a flag kill step to run only if the previous deployment step fails.
If both a stage and a step define conditional execution rules, the step-level condition takes precedence and overrides the stage-level condition.
Pipeline notifications
You can create notification rules to send notifications about events in your pipeline and notify your team using Slack, Microsoft Teams, Email, or PagerDuty as one of the notification channels.
Advanced options
To configure how your pipeline executes and behaves under different conditions, click Advanced Options in the Pipeline Studio sidebar.
- Pipeline Timeout Settings
- Stage Execution Settings
- Re-run Settings
Set a timeout for the entire pipeline. If a pipeline run exceeds the configured duration, it will automatically fail.
Choose whether to allow selective stage execution. This setting controls whether stages can be run or skipped based on stage-level execution rules.
Control whether input data is editable when re-running a pipeline. If set to No, inputs cannot be modified during reruns.