Create Entities Manually
This documentation is only relevant to IDP 2.0. This will not be valid for IDP 1.0 since the experience there is different.
In IDP 2.0, entity creation is simplified with full UI support and optional YAML-based creation. Entities are now "inline," which means their entire lifecycle can be managed through the UI or API, without Git integration.
You can create entities directly via the Harness IDP UI; no YAML required for a streamlined, code-free experience. Alternatively, you can use your existing catalog YAML files, and Harness will automatically convert legacy Backstage YAML into the new Harness Catalog Entity Model.
Prerequisites
Before creating entities manually, ensure:
- You have the necessary permissions to create entities at your desired scope (Account, Organization, or Project)
- You are familiar with the Catalog Data Model and entity types
- IDP 2.0 is enabled behind the
IDP_2_0Feature Flag. Contact Harness Support to enable it on your account.
Method 1: Visual View (UI-Based Creation)
The Visual View provides an intuitive interface for creating entities without writing YAML.
- Interactive Guide
- Step-by-Step
Create Entity Manually via UI
To create a new entity, navigate to the Harness IDP portal and click on "Create" from the side-bar menu. Choose the desired entity type, and follow these steps:
-
You'll be redirected to the "Visual View", where you can input entity details and begin the creation process.
-
Enter the required entity information. The Visual view is synced in real-time with the YAML view for full transparency.
-
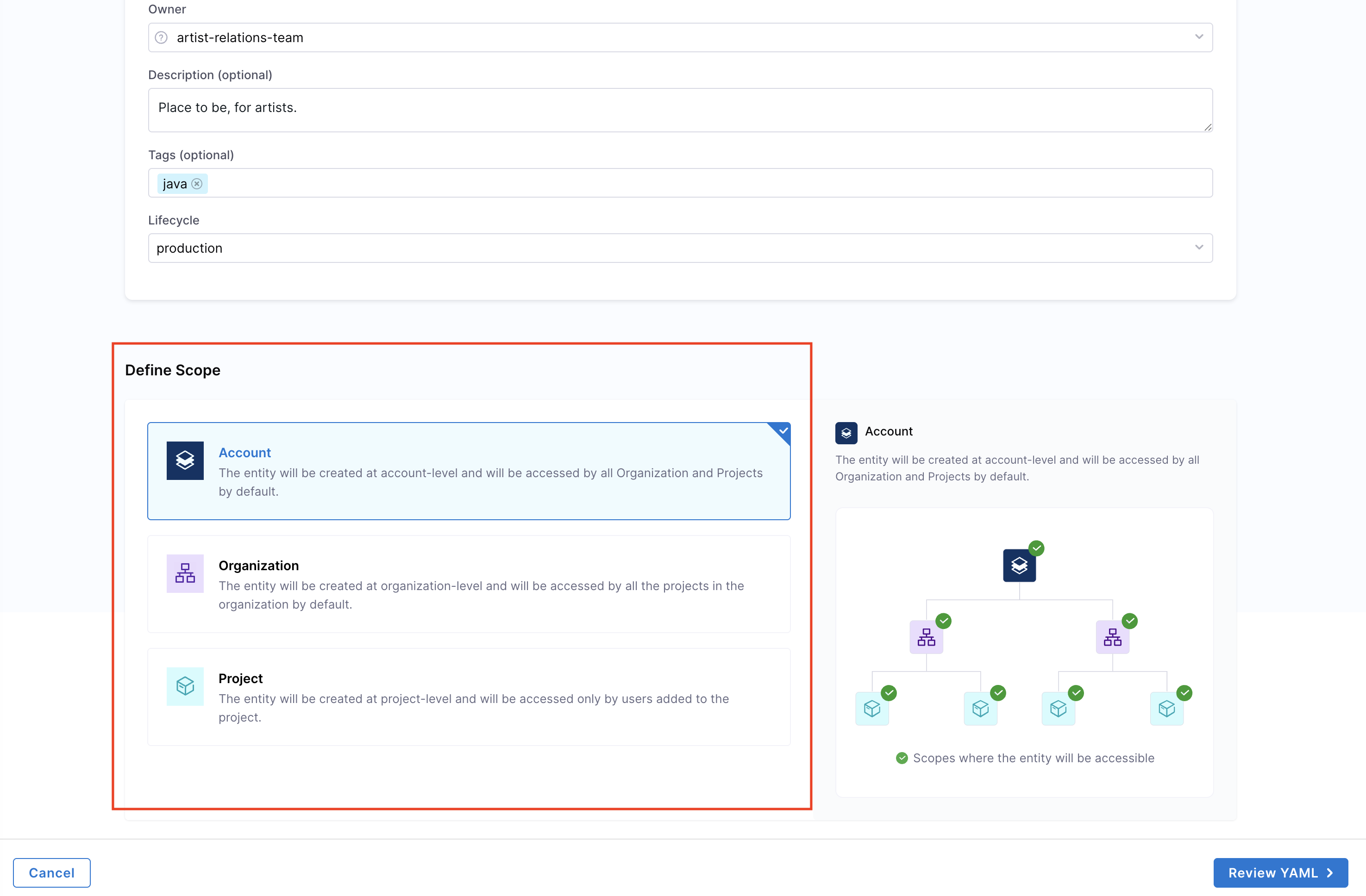
Define the entity scope — choose whether the entity should reside at the Account, Project, or Organization level. Read more about Catalog RBAC.
-
Associate with System Entities Systems in Harness IDP are high-level catalog entities used to logically group related components, APIs, and resources. Associating your component with one or more Systems helps organize the catalog and improves visibility. Learn more about System entities.
You can select one or more Systems from the dropdown. This creates a relationship between your component and the selected Systems, making it easier to discover related entities and understand your software ecosystem.
-
Link to Source Code Repository Configure the source code repository associated with this component. This link enables several key capabilities, such as:
- Automatically configuring plugins like Scorecards, TechDocs, and STO
- Displaying the View Source option in the UI
You can connect repositories from multiple supported providers:
- Harness Code Repository – Native Harness Git management
- GitHub – Cloud or enterprise GitHub instances
- GitLab – Cloud or self-managed GitLab instances
- Bitbucket – Cloud or server-hosted Bitbucket repositories
- Azure Repos – Repositories from Azure DevOps Services or Server
infoFor authentication with the Bitbucket connector, both Access Token and API Token authentication modes are supported. For more details, see the reference documentation on Access Token mode and API Token mode.
You also get the option to connect mono repository (monorepo) is a single repository that contains multiple projects or services, often organized in subdirectories.
- Yes – Select this if the component's code is located inside a specific subdirectory of a larger repository. You must also provide the Subdirectory Path (for example
/harness/java-service). - No – Select this if the repository is dedicated to a single component or service.
This field is optional, but strongly recommended if your component is tied to a Git-based workflow or needs source-aware plugins. For Harness Code Repo, note that the source code repository link is scoped to the same level as the entity itself (Account, Organization, or Project).
infoWhen configuring Link to Source Code, ensure that the selected Git connector has permissions matching the scope at which the entity is created (Account, Organization, or Project). For example, if the entity is created at the Project level, the Git connector must have access to all three scopes. The same applies to the Harness Code Repository — it should be configured with access rights that align with the selected scope.
Harness IDP also auto-generates the legacy
backstage.io/source-locationannotation for backwards compatibility. -
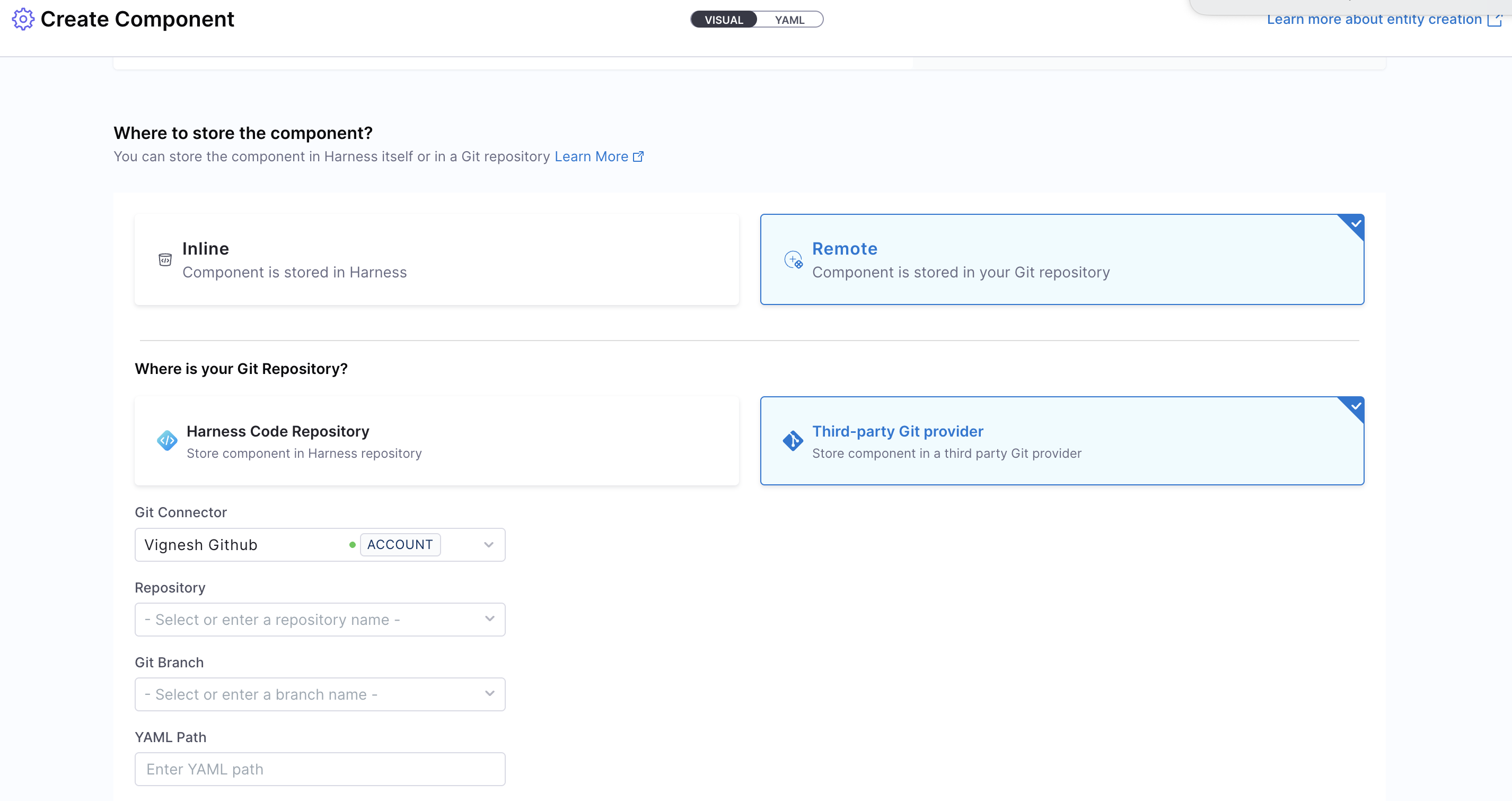
Choose how you want to manage the entity:
- Inline (default): Manage the entity YAML directly within Harness.
- Remote: Choose to store your entity YAML in a Git repository for version control, collaboration, and change tracking. You can either use a Harness Code Repository or connect to a Third-party Git provider like GitHub or GitLab by selecting a Git connector, repository, branch, and YAML path.
The Git Experience is ideal for teams who prefer to manage entities as code. Learn more in the Git Experience Journey.
- Click on "Review YAML" to view the auto-generated YAML. Since there's a live sync between the Visual and YAML views, changes in one will reflect in the other.
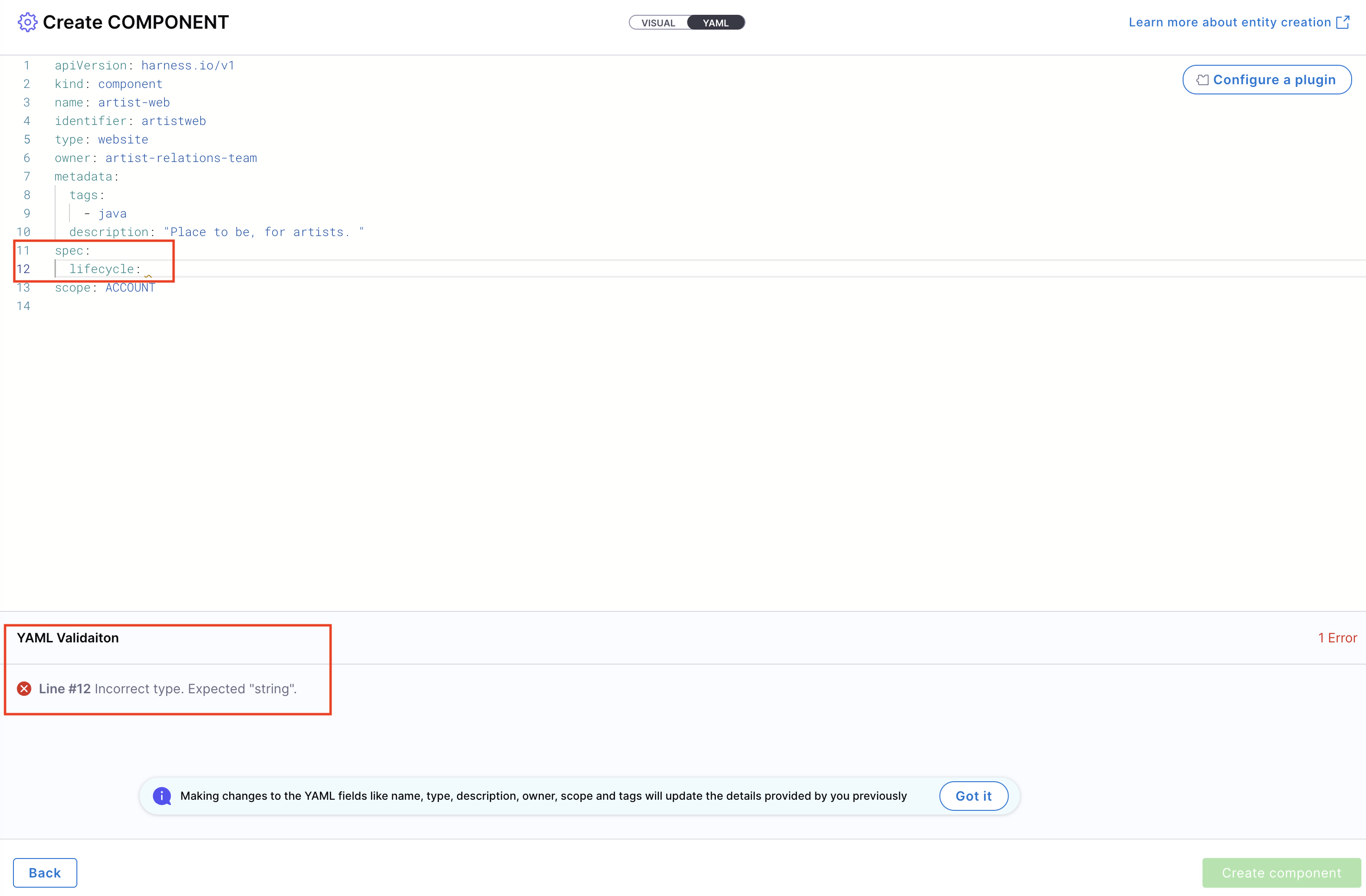
YAML validation is performed to ensure compatibility with the Harness-native Catalog YAML model. Any errors will be shown in the Validation logs.
Ensure your identifier follows naming rules. Invalid identifiers may lead to entity registration errors.
- If needed, configure a plugin by referring to its documentation and adding the required annotations in the Catalog YAML.
- Once everything is set, click "Create Component" to finalize and create the entity.
Catalog with Git Experience (GitX)
When you choose to manage your entity YAML via a Git repository (Remote mode), Harness IDP enables full Git integration through GitX.
This adds advanced capabilities to your catalog experience, including:
- Branch selection: Choose from any available Git branches (e.g.,
main,dev, or feature branches) from a dropdown in the Catalog view. - File path visibility: Easily identify which YAML file and location are powering your entity.
- Real-time sync: Changes made to the YAML file in Git (e.g., via PR or commit) are reflected in the IDP UI, and updates made via the UI are pushed to the Git repo.
- Pull request collaboration: Git-backed entities enable auditability and team collaboration using version control workflows. This makes it easy to track, version, and collaborate on entity definitions as code, while still leveraging the UI for updates and metadata insights.
This Git-backed entity mode requires a Git connector and a repository path configuration during entity creation.
While you can view and edit entity YAML across multiple Git branches, the entity registered in the Software Catalog will always reflect the YAML from the repository's default branch (e.g., main). Ensure that any final changes are merged to the default branch to be considered active in IDP.
Method 2: YAML View
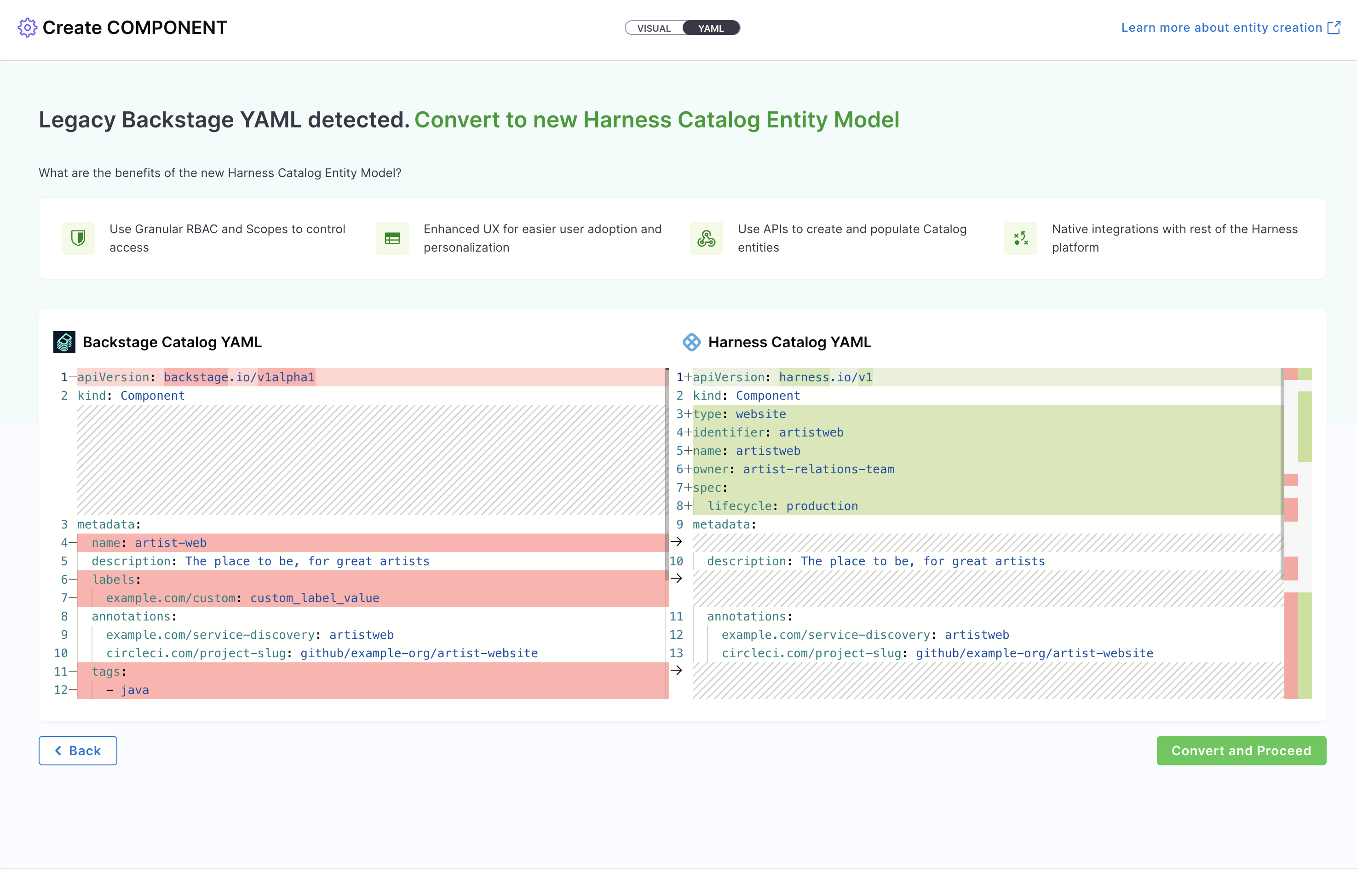
You can also use the Catalog YAML to create entities in Harness IDP. With IDP 2.0, you are required to follow the new Harness-native Data Model and structure when defining entities in Catalog YAML. If you have existing entities defined using legacy Backstage YAML, you can still use them—Harness will automatically convert them into the Harness-native Data Model format. Learn more about the new data model here. To create a new entity, navigate to the Harness IDP portal and click "Create" from the side-bar menu.
If you have a legacy Backstage YAML, you can still use it to create an entity. Harness will automatically convert it into the native Catalog Entity Model format.
If you have existing entities defined using legacy Backstage YAML (from IDP 1.0), you can convert them to the new Harness-native data model schema. For detailed instructions on converting your existing entity YAMLs, refer to Convert Existing Entity YAMLs.
- Interactive Guide
- Step-by-Step
- You'll be redirected to the Visual View. You can switch to the YAML View using the toggle at the top of the screen. This allows you to directly edit the entity's YAML definition.
- If you're using a legacy Backstage YAML, paste it into the YAML view. Harness will convert it into the Harness-native format automatically. You can then proceed to finalize and create the entity. Since the Visual and YAML views are live-synced, changes made in one view will reflect in the other.
Note: YAML validation is automatically performed to ensure compatibility with the Harness-native Catalog YAML model. Any validation errors will be displayed in the Validation Logs. Ensure your identifier follows naming rules. Invalid identifiers may lead to entity registration errors.
- You can define the scope of the entity in two ways: either switch to the Visual View and select the desired scope, or specify the projectIdentifier or orgIdentifier directly in the YAML to set the project or organization scope.
- To associate your entity with System Entities in YAML, add the
systemfield to thespecsection. You can specify multiple Systems by providing an array of System entity references:
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: System
name: Payment System
identifier: paymentsystem
type: system
owner: team-payment
spec:
lifecycle: ""
metadata:
description: This system groups services and libraries related to payment processing.
tags:
- rest
- java
This creates a relationship between your component and the specified Systems, making it easier to discover related entities and understand your software ecosystem. Each System reference follows the format system:[scope]/[identifier].
- Define Link to Source Code Repository to configure the source code repository associated with this component. This link enables several key capabilities, such as, Automatically configuring plugins and Displaying the View Source option in the UI This field is optional, but strongly recommended if your component is tied to a Git-based workflow or needs source-aware plugins.
spec:
sourceCode:
monoRepo: false
provider: Github
repoName: java-service_svc
connectorRef: account.ShibamDhar // Empty in case of Harness Code Repository
Supported Repository Providers in YAML
The provider field defines the Git-based source hosting service. Harness IDP supports:
provider: Harness # Harness Code Repository
provider: Github # GitHub Cloud or Enterprise
provider: Gitlab # GitLab Cloud or Self-Managed
provider: Bitbucket # Bitbucket Cloud or Server
provider: AzureRepo # Azure DevOps Repositories
You should select the correct provider according to where your code is hosted. The connectorRef should point to a valid Harness Connector for that provider.
When configuring Link to Source Code, ensure that the selected Git connector has permissions matching the scope at which the entity is created (Account, Organization, or Project). For example, if the entity is created at the Project level, the Git connector must have access to all three scopes. The same applies to the Harness Code Repository — it should be configured with access rights that align with the selected scope.
Mono Repository Setup in YAML
A mono repository (monorepo) contains multiple projects or services in separate subdirectories within the same repository. This is useful for organizations managing many services in a unified repository.
When monoRepo is set to true, you must also define the monoReposubDirectoryPath to indicate the folder containing this component's source code.
Example for a mono repository setup:
spec:
sourceCode:
monoRepo: true
provider: Github
repoName: java-service_svc
connectorRef: account.ShibamDhar
monoReposubDirectoryPath: /harness
Harness IDP also auto-generates the legacy
backstage.io/source-locationannotation for backwards compatibility. Currently, Scorecard computation uses the GitX connector and the Git Integration connector. An upcoming enhancement, available behind theUSE_LOCAL_GIT_CONNECTOR_FOR_SCORE_COMPUTATIONfeature flag, will enable Scorecard computation to directly use the connector from Link to Source Code.
-
Choose how you want to manage the entity:
- Inline (default): Manage the entity YAML directly within Harness.
- Remote: Choose to store your entity YAML in a Git repository for version control, collaboration, and change tracking.
You can either use a Harness Code Repository or connect to a Third-party Git provider like GitHub or GitLab by selecting a Git connector, repository, branch, and YAML path.
The Git Experience is ideal for teams who prefer to manage entities as code. Learn more in the Git Experience Journey.
-
If needed, configure a plugin by referring to the plugin's documentation and adding the appropriate annotations in the Catalog YAML.
-
Once all details are complete, click "Create Component" to finalize and register your entity in the catalog.
YAML Template Examples
Component YAML Example
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: Component
name: anomaly-detection
identifier: anomaly-detection
type: service
owner: group:ccmplayacc
spec:
lifecycle: production
dependsOn:
- component:ng-manager
metadata:
description: CCM anomaly detection backend service
annotations:
backstage.io/kubernetes-label-selector: app=anomaly-detection
github.com/project-slug: wings-software/ce-anomalyDetection
pagerduty.com/service-id: PFVOX97
jira/project-key: CCM
backstage.io/source-location: url:https://github.com/wings-software/ce-anomalyDetection/tree/main
links:
- title: repo
url: https://github.com/wings-software/ce-anomalyDetection
tags:
- python
API YAML Example
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: API
type: openapi
identifier: cenextgen
name: cenextgen
owner: johndoe
spec:
lifecycle: production
definition:
$text: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/main/examples/v2.0/json/api-with-examples.json
metadata:
description: The official CE NEXTGEN service REST APIs
Resource YAML Example
apiVersion: harness.io/v1
kind: Resource
name: Payment Database
identifier: payment-database
type: database
owner: group:ccmplayacc
spec:
system:
- system:account/ccm_platform
dependsOn:
- resource:account/ccm-backup-storage
metadata:
description: MongoDB database for CCM platform data storage
annotations:
harness.io/db-instance: mongodb-ccm-prod-01
harness.io/db-region: us-east-1
harness.io/backup-schedule: daily-2am-UTC
links:
- title: Database Dashboard
url: https://harness-monitoring.grafana.net/d/mongodb-ccm
- title: Backup Policy
url: https://harness.atlassian.net/wiki/spaces/CCM/pages/123456/Database+Backup+Policy
tags:
- mongodb
- database
- production
Next Steps
After creating your entities manually, you can refer to: