Passing data in custom triggers
Various stages of a pipeline might require input data or parameters to function properly. You can set runtime inputs in your Harness pipelines and provide their values when executing the pipeline manually or you can pass in this data when the pipeline execution is triggered automatically.
Passing variables and parameters to a pipeline when triggering it can help streamline the pipeline execution based on the specific needs of each run.
Harness variable expressions are not supported in triggers for pipeline or stage variables.
How data is passed in the trigger cURL command
Once you create a custom trigger, Harness provides the Webhook URL and cURL command to initiate the trigger.
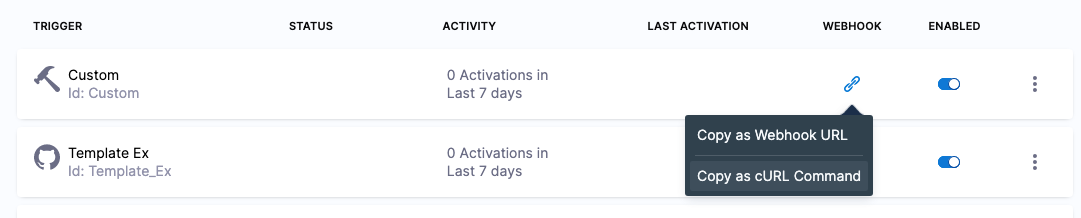
For information on creating Custom triggers, go to Trigger pipelines using custom triggers.
You can use the Custom trigger cURL command to initiate the trigger and pass in data.
The cURL command will look something like this:
curl -X POST -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'X-Api-Key: sample_api_key' --url 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/pipeline/api/webhook/custom/v2?accountIdentifier=H5W8iol5TNWc4G9h5A2MXg&orgIdentifier=default&projectIdentifier=CD_Docs&pipelineIdentifier=Custom&triggerIdentifier=Custom' -d '{"sample_key": "sample_value"}'
The -d '{"sample_key": "sample_value"}' section is where you can pass data to the target pipeline. The -d option specifies the data to be sent in the HTTP request body.
The value you specify for sample_key can be referenced in the triggered pipeline using the Harness expression <+trigger.payload.[key_name]>.
For example, in the following cURL command, the key name is my_key:
curl -X POST -H 'content-type: application/json' --url 'https://app.harness.io/gateway/pipeline/api/webhook/custom/v2?accountIdentifier=H5W8iol5TNWc4G9h5A2MXg&orgIdentifier=default&projectIdentifier=CD_Docs&pipelineIdentifier=Custom&triggerIdentifier=Custom' -d '{"my_key": "hello world"}'
You would reference this data using the expression <+trigger.payload.my_key>. The expression would resolve to hello world.
You can use the <+trigger.payload.[key_name]> expression as a script, a variable value, or any setting configured as an expression.
Passing data to the pipeline
This cURL command can be used in the terminal or program, but it can also be used in the Shell Script step of a pipeline's CD stage.
If you use the command in a Shell Script step, you can pass data from one pipeline to another pipeline.
Let's look at a few examples.
Passing a Harness expression
Let's look at an example where we pass a source pipeline's artifact location expression (<+artifact.image>) into a target pipeline using its trigger.
In the target pipeline, copy its Custom trigger cuRL command.
In the source pipeline, use a Shell Script step to run the cURL command.
In the command, use the Harness <+artifact.image> expression to reference the source pipeline's deployment artifact.
curl -X POST -H 'content-type: application/json' --url 'webhook_url' -d '{"artifact_image": "<+artifact.image>"}'
In the target pipeline, create a pipeline variable and set its value as <+trigger.payload.artifact_image>.
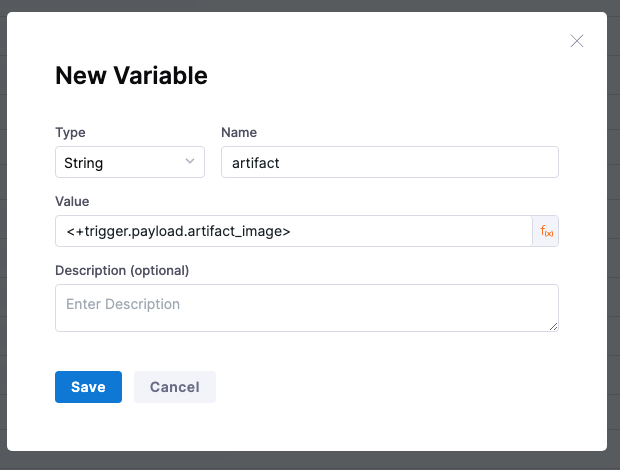
When the source pipeline runs, it will resolve the expression <+artifact.image> in the cURL command to its pipeline artifact location and then run the command.
In the target pipeline, you can retrieve the data from the command using a variable containing <+trigger.payload.artifact_image> as its value.
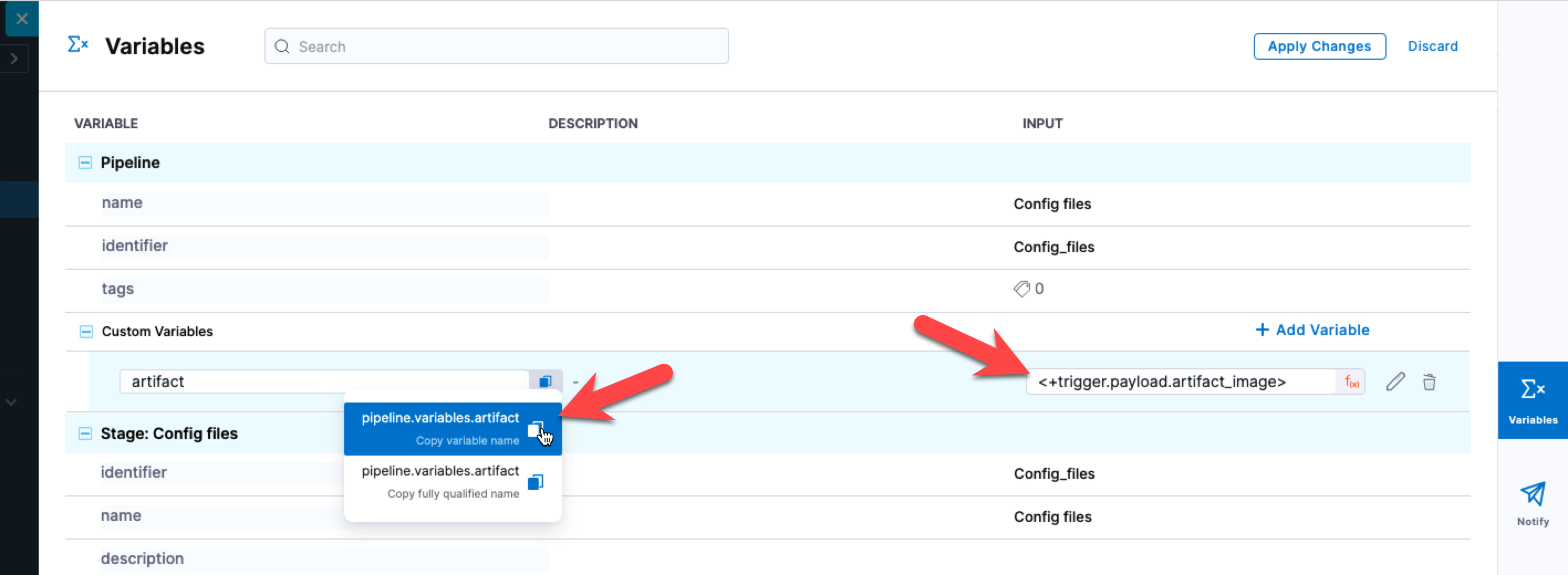
Now you can use the variable anywhere you want to view the source pipeline's artifact location.
Passing an environment variable
Let's look at an example where you want to pass an environment variable to the pipeline you are triggering using the cURL command. For example, let's say you want to trigger a specific version of tests in a test suite after deploying your service.
Here's the command passing in the $version:
version="1.5.3"
curl -X POST -H 'content-type: application/json' --url 'webhook_url' -d '{"version": "'"$version"'"}'
In the target pipeline, simply create a pipeline variable that references <+trigger.payload.version> and then use that variable in the scripts or settings that need the version number.
Passing matrix axes
Harness stages and steps include looping strategies. These strategies enable you to run a stage or step multiple times without the need to copy the same stage or step.
Let's look at an example where we pass multiple values in the cURL command, use the split() method in our target pipeline variable to get each value, and then use the matrix strategy to use each value in the same step.
For an example, we'll use the Email step. We'll pass 5 email addresses using the cURL command.
Here's the cURL command:
curl -X POST -H 'content-type: application/json' --url 'webhook_url' -d '{"emailIds": "emaild1@gmail.com,emaild2@gmail.com,emaild3@gmail.com,emaild4@gmail.com,emaild5@gmail.com"}'
In the target pipeline, create a pipeline variable named emailIds that uses the <+trigger.payload.emailIds> expression.
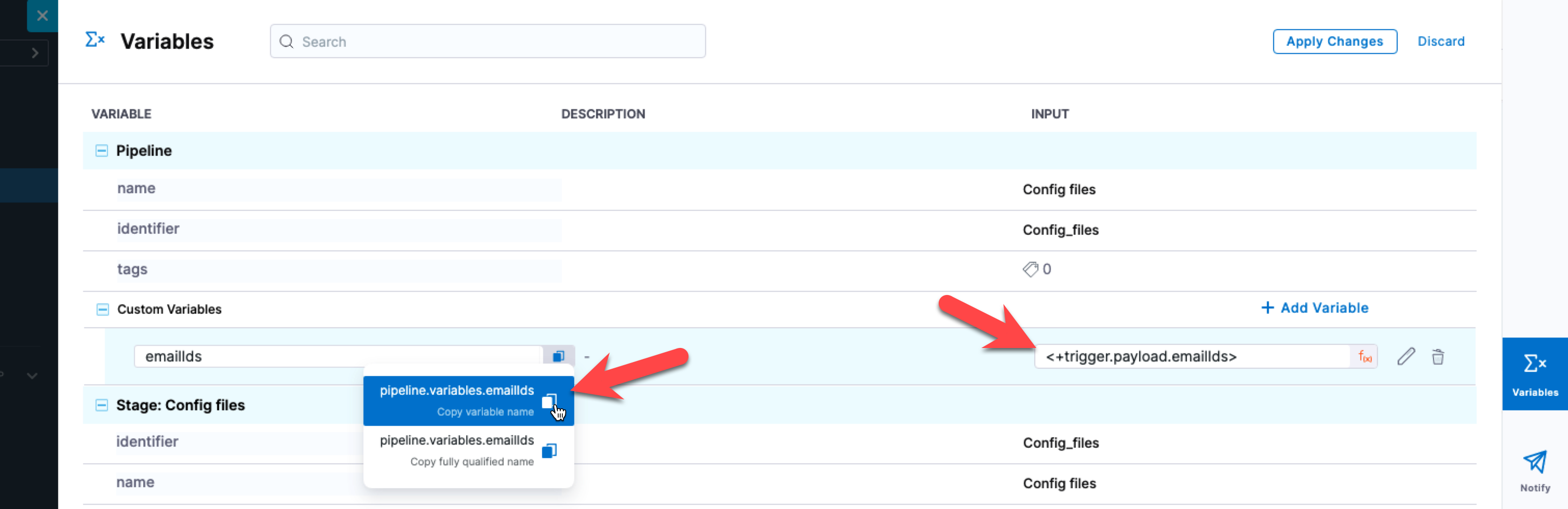
In the Email step, in Advanced, in Looping Strategy, select Matrix and enter the following.
matrix:
emailId: <+pipeline.variables.emailIds>.split(',')
maxConcurrency: 2
You can see the split() method is used to parse the email addresses in the JSON payload.
In the To setting of the Email step, you can reference the matrix using <+matrix.emaild>.
Now the Email step is run for each address in the matrix.