Trigger pipelines on a new artifact
Currently, this feature is behind the feature flag CD_TRIGGERS_REFACTOR. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
You can trigger Harness pipelines in response to a new artifact version being added to a registry.
For example, every time a new Docker image is pushed to your Docker Hub account, it triggers a CD pipeline that deploys it automatically.
On New Artifact Triggers listen to the registry where one or more of the artifacts in your pipeline are hosted.
You can set conditions on the triggers, such as matching a Docker tag or label or a traditional artifact build name or number.
This trigger is a simple way to automate deployments for new builds.
An artifact source does not need to be defined in the service definition for the trigger to work. The only possible scenario of failure is during the initial collection of the artifact within one minute of creating the trigger. For instance, suppose the Docker registry contains 10 tags for a specific image and a trigger is created. In that case, the delegate's polling job retrieves all 10 tags and sends them to the manager, which does not initiate any pipelines. This is because running the pipeline for all 10 tags that were pushed before creation of the trigger could leave the system in an undesirable state. However, when an 11th or any subsequent tag is pushed, the trigger executes and initiates the pipeline.
Harness variable expressions are not supported in triggers for pipeline or stage variables.
Supported artifact providers for artifact triggers
You can use the following artifact providers to triggers pipelines:
- Harness Artifact Registry
- ACR (Azure Container Registry)
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Amazon S3
- Artifactory Registry
- Azure Artifacts
- Bamboo
- Custom Artifact
- Docker Registry
- ECR (Amazon Elastic Container Registry)
- GCR (Google Container Registry)
- Github Package Registry
- Google Artifact Registry
- Google Cloud Storage
- Jenkins
- Nexus3 Registry
Important notes
-
One artifact triggers deployment: If more than one artifact is collected during the polling interval (one minute), only one deployment will be started and will use the last artifact collected.
-
All artifacts trigger deployment: All artifacts collected during the polling interval will trigger a deployment, with one deployment triggered for each artifact collected.
noteTo enable this feature, go to your Harness project/org/account Default Settings, select Pipeline, and then enable Execute Triggers With All Collected Artifacts or Manifests.
-
Trigger based on file name: The trigger is executed based on file names and not metadata changes.
-
Do not trigger on the latest tag of an artifact, such as a Docker image. With latest, Harness only has metadata, such as the tag name, which has not changed, and so Harness does not know if anything has changed. The trigger will not be executed.
-
In Harness, you can select who is able to create and use triggers within Harness, but you must use your repository's RBAC to control who can add the artifacts or initiate the events that start the Harness trigger.
-
Whenever you create a trigger for the first time, Harness recommends submitting a tag or pushing an artifact to verify its functionality. By doing this, the trigger will execute and the pipeline will run as expected when subsequent tags are pushed.
noteWhen you link a Docker repository to a trigger, the trigger status will remain
pendinguntil there are available tags. After the first artifact push, the trigger status changes tosuccessbecause of new tags, but this alone will not activate the pipeline. The pipeline will only be triggered after a second push to Docker. -
Whenever a trigger is created or updated, it takes about five to ten minutes for the polling job to start, and for the trigger to be in a working state. Harness recommends that you wait for five to ten minutes after a trigger is created or updated to push the artifact.
-
The polling stops when you disable a trigger. Artifact polling restarts after reenabling the trigger. Harness recommends that you submit a tag or push an artifact and verify the flow as this is treated as a new polling job.
-
Due to a Docker API limitation, image build numbers/tags are always listed in lexical order. To ensure that executions are triggered with the image pushed last, a best practice is to create build numbers or tags that can be sorted lexically using their creation date. Using this method, higher build numbers are assigned for higher creation dates. This ensures that the image pushed last is used when more than one image is pushed over a short period of time, such as less than 5 minutes.
Familiarize yourself with Harness CD pipelines, such as the one you create in the Kubernetes CD Quickstart.
Visual summary
This 5 minutes video walks you through building an app from source code and pushing it to Docker Hub using Harness CIE, and then having an On New Artifact Trigger execute a CD pipeline to deploy the new app release automatically.
Artifact polling
Once you have created a trigger to listen for new artifacts, Harness will poll for new artifacts continuously.
Polling is immediate because Harness uses a perpetual task framework that constantly monitors for new builds/tags.
Using the <+trigger.artifact.build> and <+lastPublished.tag> expressions
When you add a Harness service to the CD stage, you can set the artifact tag to use in Artifacts Details.
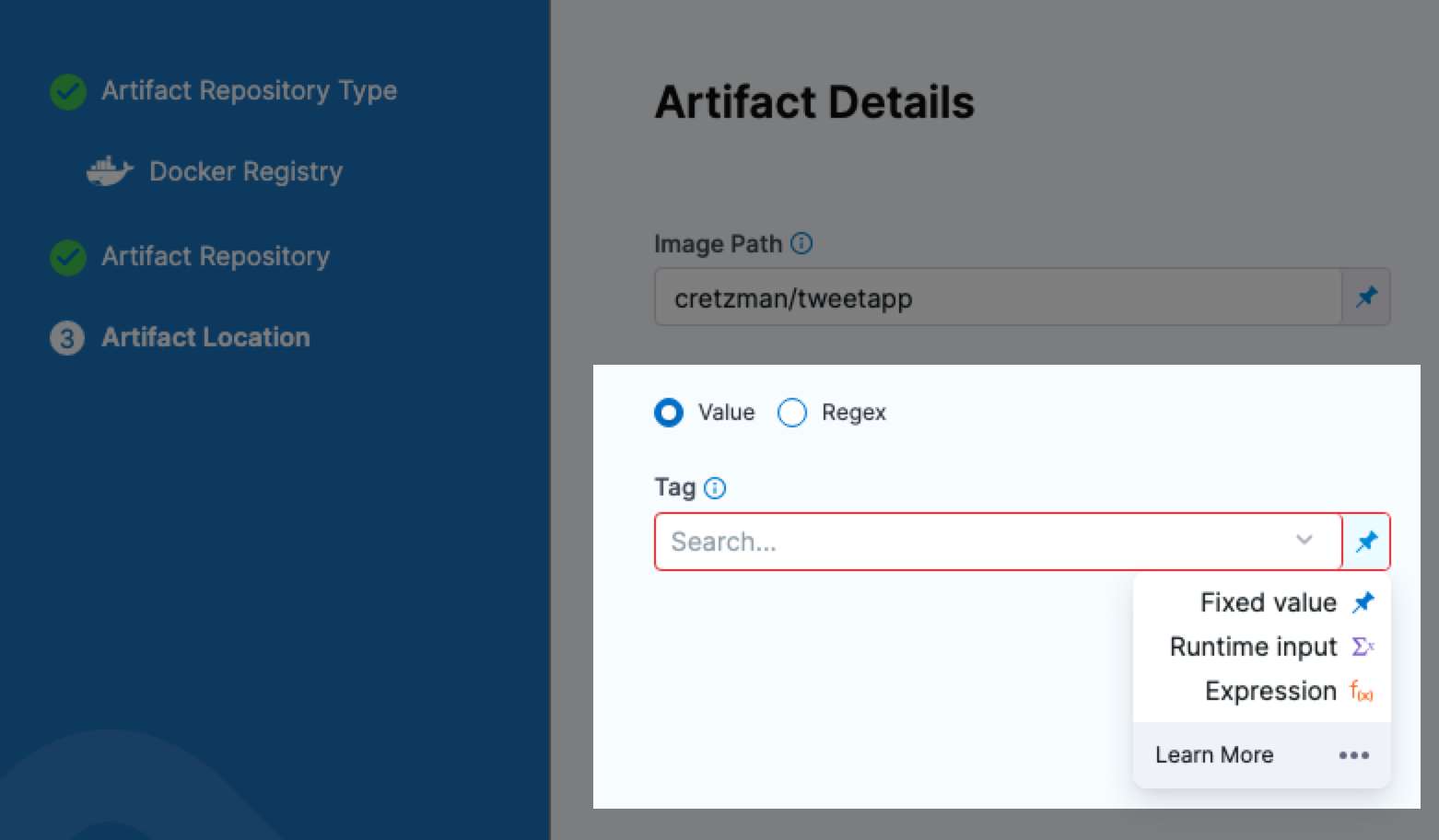
If you use a Fixed Value for the artifact Tag (for example, 2), when the trigger executes the pipeline, Harness will deploy the artifact with that tag (2).
If you want the pipeline to deploy the artifact version that initiated the trigger, use the expression <+trigger.artifact.build>.
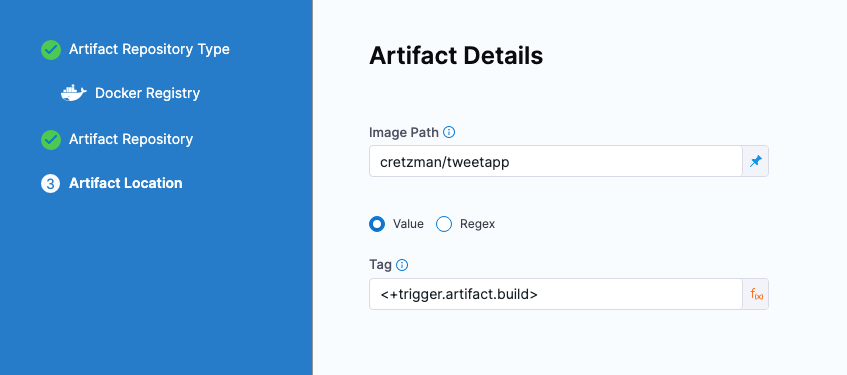
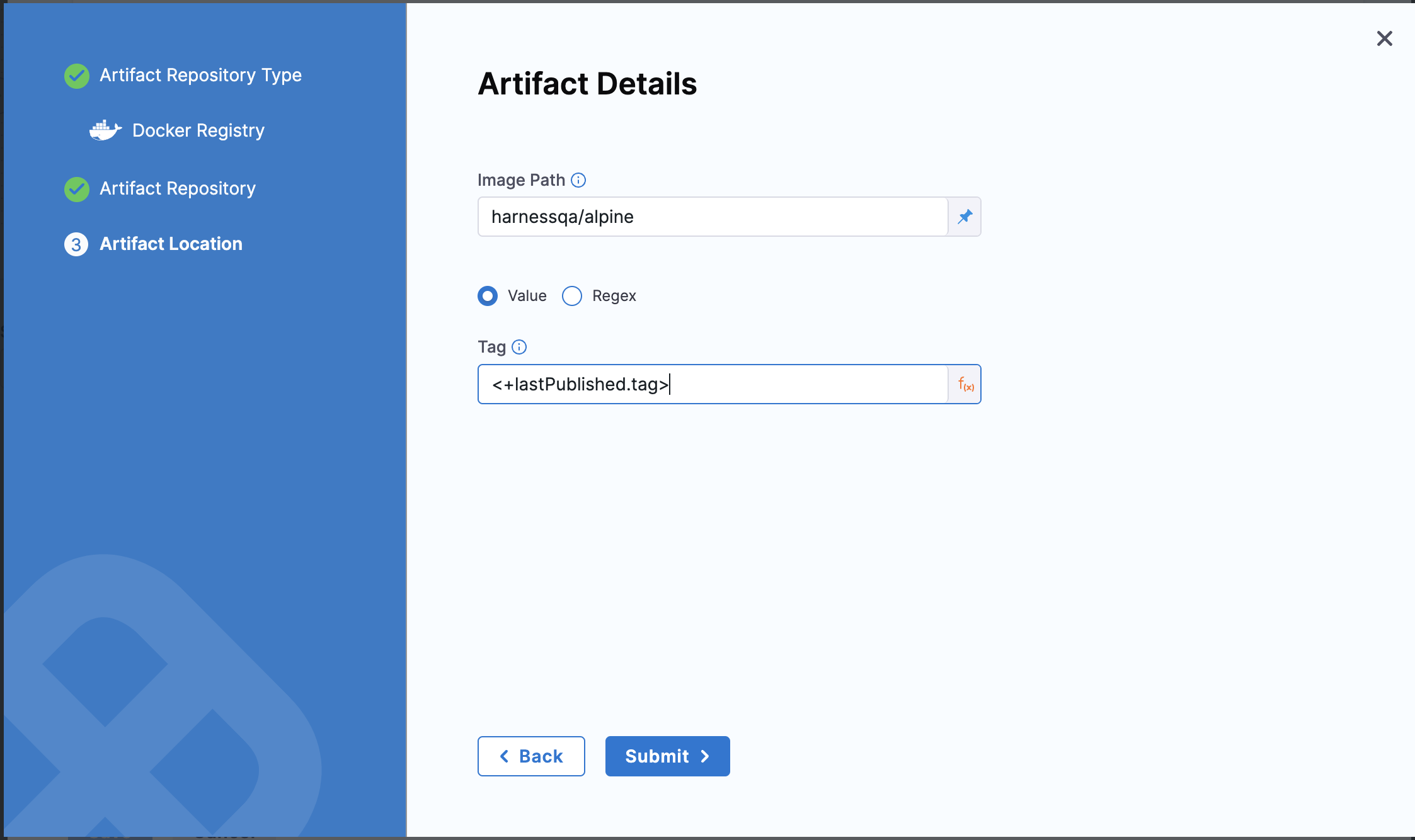
If you want the pipeline to deploy the last successful published artifact version, use the expression, <+lastPublished.tag>.
The lastPublished tag returns the lexicographically last published tag for container image based artifact sources.
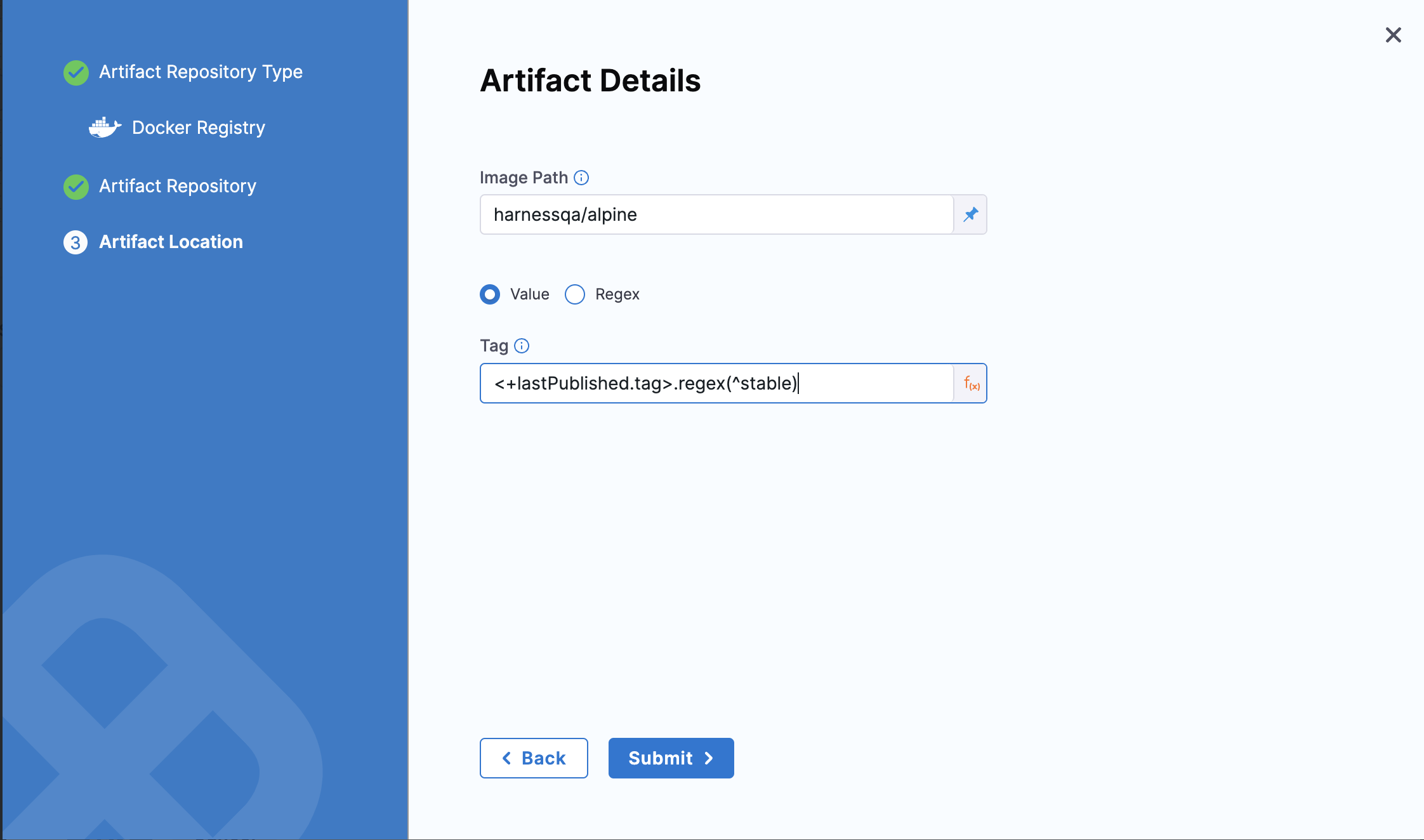
If you want the pipeline to deploy the last successful published artifact version of matching regex, use the expression, <+lastPublished.tag>.regex(regex).
You can also set tag as a runtime input and then use <+trigger.artifact.build> in the trigger's Pipeline Input settings.
Create an artifact trigger
-
Select a Harness pipeline that includes an artifact in the stage's Service Definition.
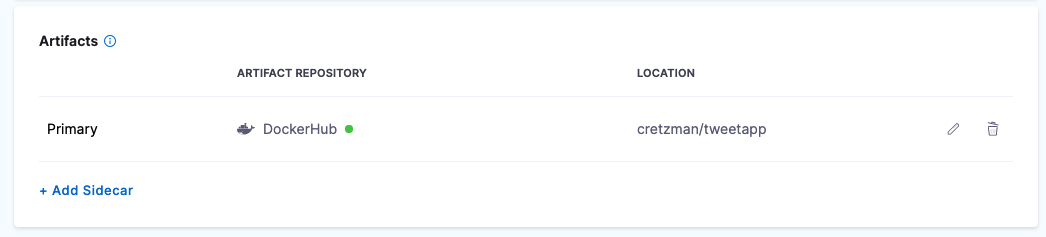
You reference an artifact in the stage's service definition in your manifests using the expression
<+artifact.image>. Go to Add Container Images as Artifacts for Kubernetes Deployments for more details. -
Select Triggers.
-
Select New Trigger.
-
The On New Artifact Trigger options are listed under Artifact. Each of the Artifact options are described below.
-
Select the artifact registry where your artifact is hosted. If you artifact is hosted on Docker Hub and you select GCR, you won't be able to set up your trigger.
- Docker Registry Artifacts
- GCR Artifacts
- ECR Artifacts
- AWS S3
- Artifactory
- ACR
- Bamboo
-
In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
-
In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source. This is where you tell Harness what artifact repository to poll for changes.
-
Create or select the connector to connect Harness to the repository, and then select Continue. For steps on Docker Registry connectors, go to docker registry connectors.
-
In Artifact Details, enter the artifact for this trigger to listen for and select Submit. For example, in Docker Hub, you might enter
library/nginx. The artifact is now listed in trigger.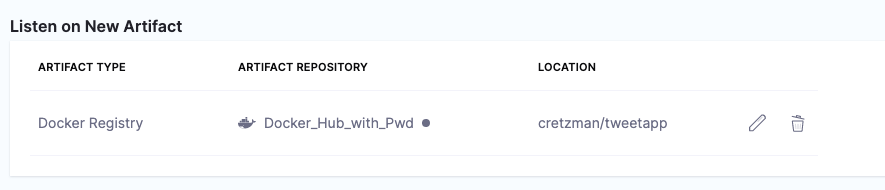
-
Select Continue.
In your Docker Registry connector, to connect to a public Docker registry like Docker Hub, use
https://registry.hub.docker.com/v2/. To connect to a private Docker registry, usehttps://index.docker.io/v2/.
-
In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
-
In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source.
-
Create or select the GCP connector to connect Harness to GCR, and then select Continue. For steps on GCP connectors, go to Add a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Connector.
-
In Artifact Details, in GCR Registry URL, select the location of the registry, listed as Hostname in GCR.
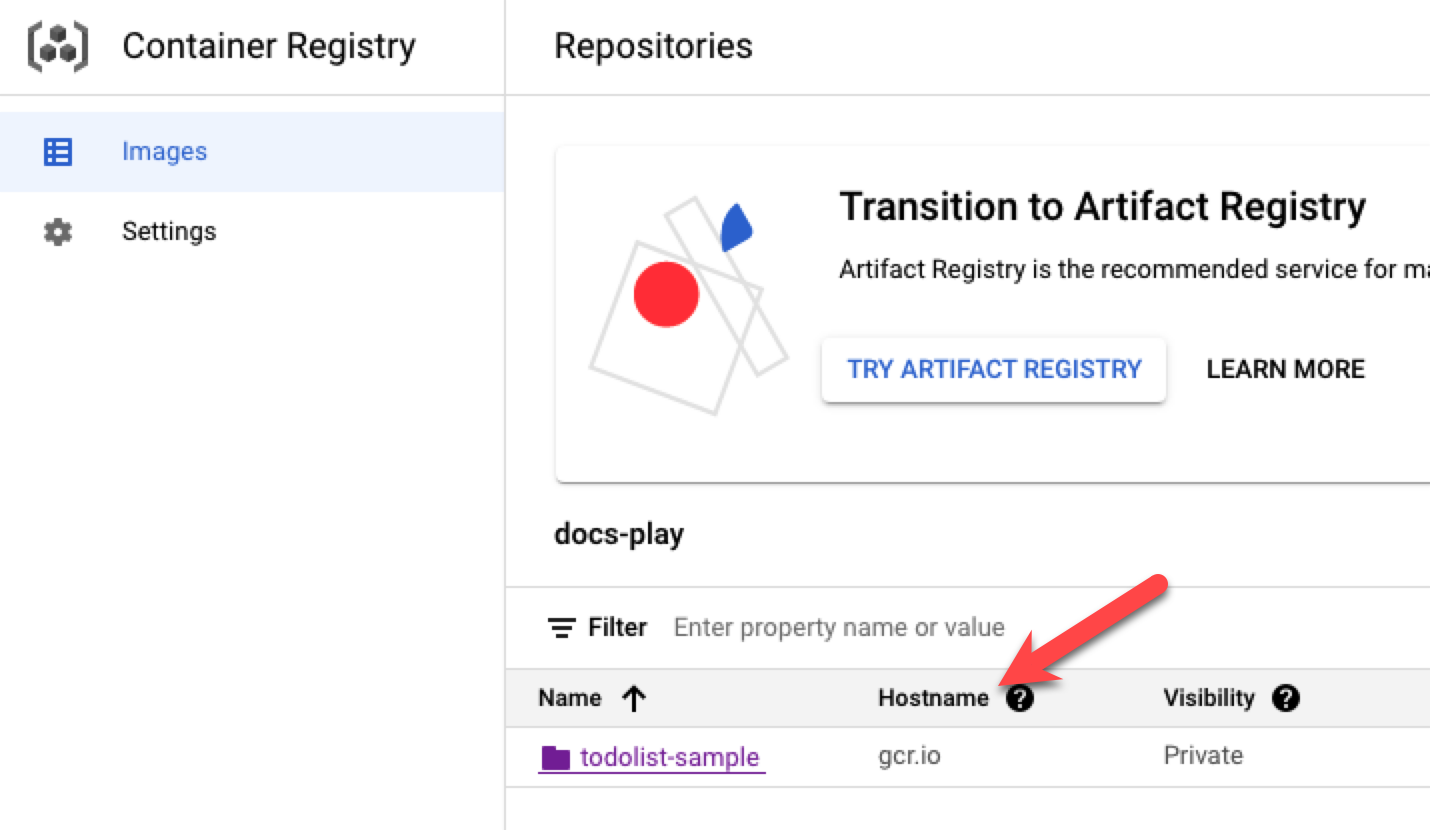
-
In Image Path, enter the artifact for this trigger to listen for. You can click the copy button in GCR and then paste the path into Harness.
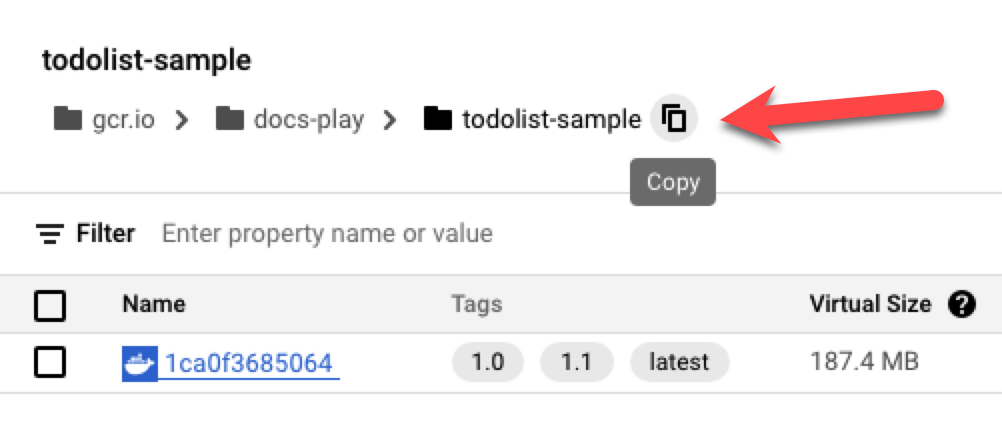
-
Select Submit, and then select Continue.
- In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
- In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source.
- In Artifact Repository, create or select the AWS Connector to connect Harness to ECR, and then select Continue. For information about configuring AWS connectors, go to AWS Connector Settings Reference.
- In Artifact Location, in Region, select the region for the ECR service you are using.
- (Optional) In Registry ID, enter the AWS account ID of the ECR registry you want to use. This field is useful when the AWS connector can access AWS accounts other than the one it is configured with. If you do not specify a registry ID, Harness uses the default registry associated with the AWS account.
- In Image Path, enter the path to the repo and image. You can copy the URI value from the repo in ECR. For example,
public.ecr.aws/l7w9l6a8/todolist(public repo) or085111111113.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/todolist(private repo). - Select Continue.
- In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
- In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source.
- Create or select the AWS Connector to connect Harness to S3, and then select Continue. For steps on AWS Connectors, go to AWS Connector Settings Reference.
- In Artifact Details, in Region, select the region for the S3 service you are using. While S3 is regionless, Harness needs a region for the S3 API.
- In Bucket Name, enter the S3 bucket name.
- In File Path Regex, enter a regex like
todolist*.zip. The expression must either contain a*or end with/.notePlease use
*for regex matching and not.*. For example -*.tgz,todolist-v*.zip - Select Continue.
- In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
- In Listen on New Artifact, click Define Artifact Source.
- Create or select the Artifactory connector to connect Harness to Artifactory, and then select Continue. For steps on Artifactory connectors, go to Artifactory Connector Settings Reference.
- In Artifact Details, in Repository Format, select Generic or Docker.
- Generic:
- Repository: enter the Name of the repo.
- Artifact Directory: enter the path to the Directory that is inside the repo.
- Docker:
- Repository: enter the Name of the repo.
- Artifact/Image Path: enter the path to the Artifact/Image that is inside the repo.
- Repository URL (optional): enter the URL to file.
- Generic:
- Select Continue.
- In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
- In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source.
- Create or select the Azure connector to connect Harness to ACR, and then select Continue. For steps on Azure connectors, go to Add a Microsoft Azure Cloud Connector.
- In Artifact Details, in Subscription Id, select the Subscription Id from the ACR registry.
- In Registry, select the registry you want to use.
- In Repository, select the repository to use.
- Select Continue.
- In Configuration, in Name, enter a name for the trigger.
- In Listen on New Artifact, select Define Artifact Source.
- Create or select the Bamboo connector to connect Harness to Bamboo, and then select Continue.
- In Artifact Details, specify the plan name, artifact paths, and builds to monitor.
- Select Continue.
Set conditions
In Conditions, enter any conditions that must be matched in order for the trigger to execute.
Regex and wildcards
You can use wildcards in the condition's value and you can select Regex.
For example, if the build is todolist-v2.0:
- With regex selected, the regex
todolist-v\d.\dwill match.
If the regex expression does not result in a match, Harness ignores the value.
Harness supports standard Java regex. For example, if regex is enabled and the intent is to match any branch, the wildcard should be .* instead of simply a wildcard *. If you wanted to match all of the files that end in -DEV.tar you would enter .*-DEV\.tar.
Set metadata conditions
On New Artifact Triggers support conditions based on artifact metadata expressions.
You can define conditions based on metadata apart from the artifact build and JEXL conditions.
To configure a condition based on artifact metadata, do the following:
- In the configuration of an artifact trigger, select Conditions.
- In Metadata Conditions, select Add.
- Enter an expression in Attribute.
- Select an operator and a value to match to the metadata attribute when the expression is resolved.
When the trigger is executed, the metadata condition is evaluated and, if the condition matches, the pipeline is executed.
Here are the artifact metadata expressions you can use:
- Docker registry
- ECR
- ACR
- GAR
- Artifactory
- Jenkins
- Nexus 2
- Nexus 3
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.image>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.tag>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHAV2>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHA>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.dockerConfigJsonSecret>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.image>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.tag>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHAV2>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHA>
<+pipeline.stages.DS.spec.artifacts.primary.dockerConfigJsonSecret>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.image>
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.registryHostname>
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.tag>
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHAV2>
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHA>
<+pipeline.stages.s1.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
Here are the expressions for Google Artifact Registry (GAR).
<+pipeline.stages.firstS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.image>
<+pipeline.stages.firstS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.registryHostname>
<+pipeline.stages.firstS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHAV2>
<+pipeline.stages.firstS.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.SHA>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.tas_0.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.fileName>
<+pipeline.stages.tas_0.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Jenkins_ArtifactSource.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.fileName>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.package>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.repositoryName>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.version>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
You can use the following expressions:
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus3_Maven.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.extension>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus3_Maven.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.fileName>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus3_Maven.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.imagePath>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.repositoryName>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.version>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus2_NPM.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.url>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus3_Maven.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.artifactId>
<+pipeline.stages.SSH_Nexus3_Maven.spec.artifacts.primary.metadata.groupId>
Define multi-region artifact source
Once you've selected an artifact in the trigger, you will see the Define Multi Region Artifact Source option.
When artifact repositories such as Google Artifact Registry (GAR) are enabled with multiregion support, artifacts of the same version are available across different regions for easy consumption.
Each region can have similar artifacts. This support enables the configuration of Harness triggers using artifacts from multiple regions.
In On New Artifact triggers, you can configure the regions and conditions associated with the artifact across regions. This enables the pipeline to be triggered based on the availability of artifacts in different regions.
To configure multi region for the artifact, do the following:
-
In your pipeline, select Triggers.
-
Create an On New Artifact trigger for your artifact registry.
-
In Configuration, in the Listen on section, add an artifact. This will be the primary region where the artifact is available. The Harness connector you use should be pointing to the region.
Once you have added an artifact you will see the Define Multi Region Artifact Source option.
-
Select Define Multi Region Artifact Source and add artifacts corresponding to other regions. Add as many regions as needed for the trigger.
-
When you are done, select Continue to move to Conditions.
-
Select the conditions required for the artifacts across different regions.
When the artifact version is available across different regions, the condition is evaluated for all the artifacts and the pipeline is triggered.
-
Complete the trigger setup.
Select pipeline inputs
If your pipeline uses input sets, you can select the input set to use when the trigger executes the pipeline.
Customize trigger input configuration using override YAML
To use an input set for both trigger and manual runs,you can easily achieve this by overriding input parameters in trigger inputYAML configuration. This provides the flexibility to modify a specific parameter within the associated Input Set.
For more details, go to Customize trigger input configuration using override YAML
Enable or disable trigger
You can enable or disable triggers using the enabled toggle:

Reuse trigger YAML to create new triggers
You can reuse triggers by copying and pasting trigger YAML. This can be helpful when you have advanced conditions you don't want to set up each time.
Trigger artifact expressions used in a pipeline are resolved when you rerun a pipeline that was activated by a trigger.