Default settings
The Harness Default Settings are broadly scoped configurations that apply to your entire account, an entire organization in your account, or a specific project. These settings control configurations for certain Harness Platform features and high-level module settings.
To manage default settings at the account, org, or project scope, you need view and edit permissions for Default Settings at the corresponding scope.
Managed Default Settings
Default Settings include configurable module-specific parameters that you can customize based on your needs, such as enabling or disabling features at specific scopes.
When configuring default settings, be mindful of your current scope. For example, editing settings at the account scope applies the setting across the entire account.
- Account scope
- Organization scope
- Project scope
To access the Default Settings at the Account scope:
-
Go to Account Settings.
-
Select Default Settings.
To access the Default Settings at the Org scope:
- Select Organizations and select the organization you want to modify.
- Select Organization Settings, and then select Default Settings.
To access the Default Settings at the Project scope:
- Select Projects and select the project you want to modify.
- Select Project Settings, and then select Default Settings.
On the Default Settings screen, settings are divided into Platform (General), cross-module feature (Connectors, Notifications, Pipelines, Harness AI), and module-specific settings (CCM, CD, Git Experience, SCS).
Expand each section to configure the settings in that section. Available settings vary by scope.
Allow Overrides
If necessary, you can configure the Default Settings differently at the account, org, and project scopes.
To do this you must enable Allow Overrides at the account and/or org scope. This allows the setting to be overridden at lower scopes. Allow Overrides is not available at the project scope because that is the lowest scope.
To force lower scopes to inherit the configuration from a higher scope, disable Allow Overrides.
Restore to Default
All Default Settings are initially set to their default values. Once you modify a setting, you can quickly set it back to the default by selecting Restore to Default..
Default Settings reference
These are the Default Settings available for configuration at the Account scope. You can also configure Default Settings at the Org and Project scopes, but some options are not available at lower scopes.
General
Enable Force Delete of Harness Resources: You can force delete a Harness entity even if your pipelines or other entities reference it. For more information, go to Force delete.
Connectors
Disable Harness Secret Manager: You can choose to disable the Harness built-in Secret Manager at any point and use any other Secret Manager to store secrets. For more information, go to Disable built-in secret manager.
Continuous Deployment
These settings are for the Harness CD module.
- Enable Emails to be sent to non-Harness Users: To send emails to non-Harness users, you must configure your own SMTP server and enable this default setting.
- Project Scoped Resource Constraint Queue: Resource Constraints protect resource capacity limits by preventing simultaneous deployments to the same Service + Infrastructure combination. For more information, go to Resource constraints.
- Enable Native Helm steady state for jobs: By default, the steady state check is only performed for Harness-managed workloads. To perform steady state check for jobs in Native Helm Deployment, you must enable this setting.
- Fetch files from Git using provider-specific APIs: Utilize provider-specific APIs (works with GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure Repos) for efficient file retrieval from Git, instead of relying on JGit. This approach can encounter API rate limits. Refer to your Git provider's documentation for limit details.
- Disable addition of Harness track selector in Kubernetes deployments: During canary deployments, Harness adds a selector (
harness.io/track: stable) in deployment objects during the rolling deployment phase. If there are pre-existing deployment objects in the cluster (not deployed by Harness), this can cause an errors. For more information, go to Skip Harness label selector tracking on Kubernetes deployments. - Ignore status code for HTTP connections: This setting is only relevant for HTTP steps and HTTP Helm repositories. When enabled, Harness only requires a valid response from the target HTTP server and does not verify the response code. This is useful when the Harness Delegate is configured with a proxy, because socket connection tests conducted by Harness from the delegate do not account for proxy details.
Pre Flight check
Pre Flight check includes a series of check on the Pipeline such as verifying Pipeline YAML, accessibility of connectors, services, secrets and others.
Skip Pre Flight is not checked by default in the Pipeline Run Form that means that the Pre Flight checks do not run by default.
You can enable Pre Flight Check by default by following these steps:
In Pipeline settings, you will see the default setting Run Pre Flight checks by Default for Pipeline Execution.
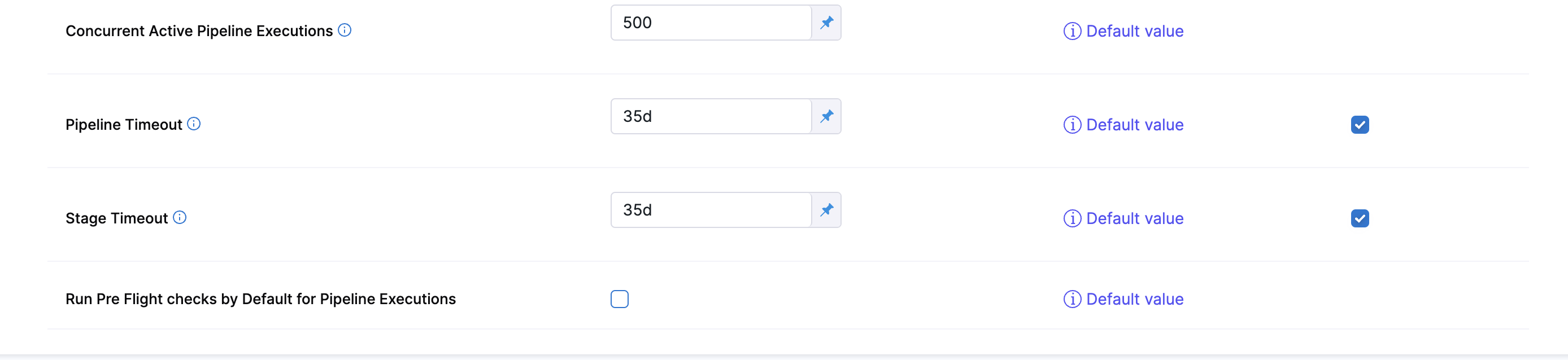
If this setting is enabled Skip Pre Flight will be checked by default.
Continuous Integration
Build Intelligence
-
Automatically Enable Build Intelligence - This setting applies only to newly created CI stages. When set to
True, CI stages will be set with Build Intelligence Intelligence enabled (users will still have the option to enable/disable the feature in stage settings as well). Using Build Intelligence requires S3-compatible storage to be set in Default Settings for self-hosted builds. -
Maven Repository URL - Applicable only in self-hosted builds. By default, the Build Intelligence plugin is downloaded from Maven Central. If you prefer using a custom Maven repository, provide a different URL.
-
Cache Server Port - Applicable only in self-hosted builds. Enter port to for the cache service proxy, in case the default port, 8082, cannot be used.
Learn more about Build Intelligence.
Cache Intelligence
-
Automatically Enable Cache Intelligence - This setting applies only to newly created CI stages. When set to
True, CI stages will be set with Cache Intelligence enabled (users will still have the option to enable/disable the feature in stage settings as well). Using Cache Intelligence requires S3-compatible storage to be set in Default Settings for self-hosted builds. -
Always Override - Enable cache override to always update the cache, regardless of cache changes. This is useful if you have infrequent builds and want to ensure your cache remains fresh.
Learn more about Cache Intelligence.
S3-Compatible Object Store for Self-Managed Build Infrastructure
To use Harness CI Intelligence caching features (Build Intelligence, Docker layer caching, and Cache Intelligence) with self-managed build infrastructures, you must provide S3-compatible object store where Harness can store and manage your caches.
Use the S3-Compatible Object Store for Self-Managed Build Infrastructure settings to connect your S3-compatible object store to your Harness account. If you want to define different object store for individual organizations or projects, you must allow overrides and then change these settings at the lower scopes.
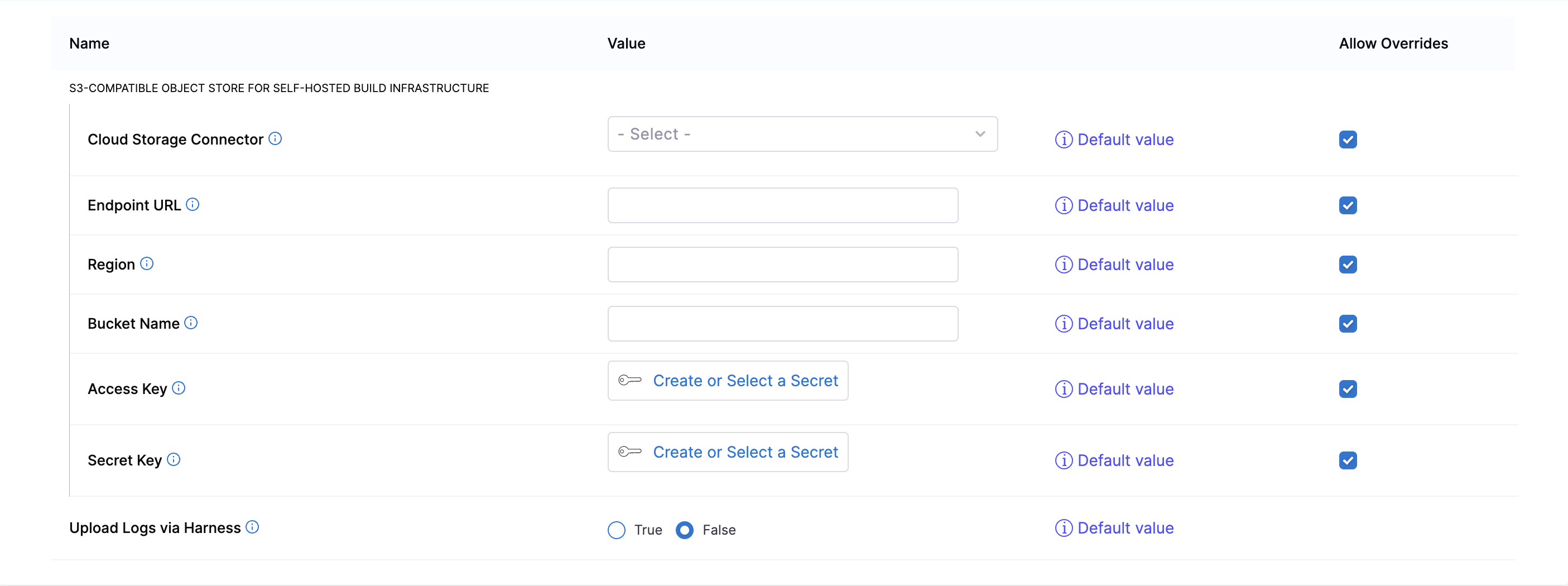
- Cloud Storage Connector: Provide an AWS connector or GCP connector configured to authenticate with your object store.
- Endpoint URL: S3-compatible storage URL.
- Region: Geographical region where your storage is hosted. This is optional for some providers.
- Bucket Name: The name of the bucket to use for Harness-managed caches.
- Access Key and Secret Key: Access key and secret key to access your S3-compatible storage. NOTE: If you're using 'Cloud Storage Connector' (recommended) then there is no need to enter values for access/secret key fields.
Upload Logs Via Harness
When set to True, CI step execution logs will route through Harness' log service instead of getting uploaded directly to the object store (GCS bucket). This is useful if your network settings do not allow direct access to the object store.
By Default, Upload Logs Via Harness is set to False. This is an account level setting only, it cannot be overriden in organization or project default settings.
Note: Enabling this setting may introduce some latency in log uploads so we advise to only use this option if truly needed.
Git Experience
For information about these settings, go to Git Experience settings.
Pipeline
For information about these settings, go to Pipeline settings.
Cloud Cost Management
For information about these settings, go to Set up perspective preferences and View and apply recommendations.
Notifications
For information about these settings, go to Notification settings.
Supply Chain Assurance
These settings are for Harness SCS.
- Use Base64 encoded secrets for attestation
- Enable SSCA Airgap
Harness AI
Enable this setting to use Harness AI.
Visible Modules in this Account
This feature is currently behind the feature flag CDS_NAV_MODULE_VISIBILITY. To enable this feature, contact Harness Support.
Use this setting to enable/disable which modules are visible to all users of this account.