Tutorial - Terraform Cloud notification triggers
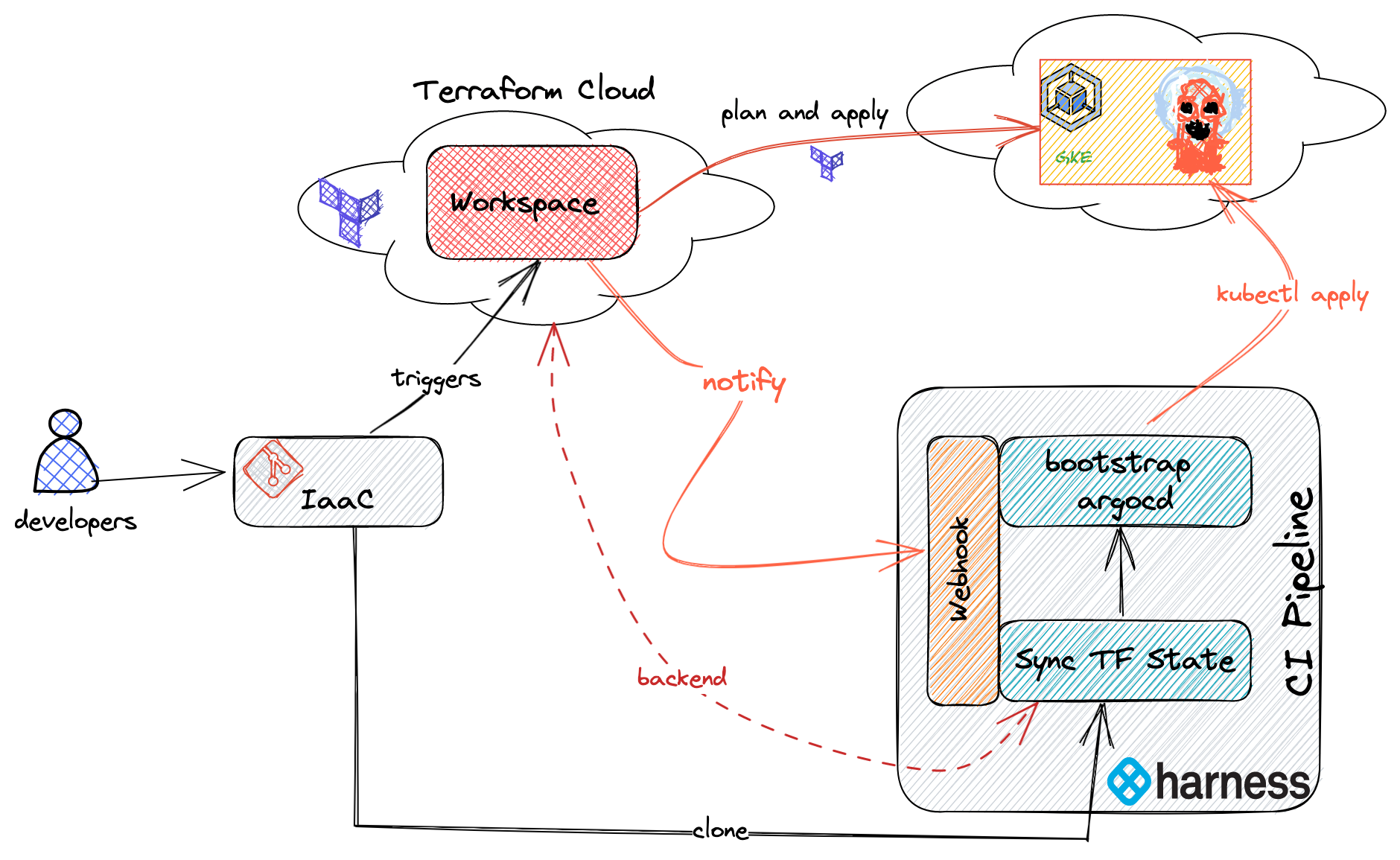
Harness CI/CD pipelines can deploy artifacts to a target infrastructure. Modern day architecture uses automation tools, like Terraform or Ansible, to provision the target infrastructure. This type of provisioning is called infrastructure-as-code (IaC).
Usually CI/CD and IaC don't run in tandem. Often, the CI pipeline is triggered only when the target infrastructure is ready to bootstrap with software components that are required by CI/CD pipelines. This tutorial users a custom trigger to address the following use case:
As CI/CD user, I want to provision a Kubernetes cluster on Google Cloud Platform (GKE) using Terraform. When the cluster is successfully provisioned, trigger a CI pipeline to start bootstrapping ArgoCD on to GKE.
Prerequisites
In addition to a Harness account, you need the following accounts for this tutorial:
- A GitHub account where you can fork the tutorial repos.
- A Terraform Cloud account.
- A Google Cloud account where you can create a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster.
Clone code repositories
This tutorial uses the following Git repositories. Fork these repos, and then clone them to your local machine.
- IaC vanilla-gke: The Terraform source repository used with Terraform Cloud to provision GKE. Code samples in this tutorial reference this repo by
$TFC_GKE_REPO. - Kubernetes manifests bootstrap-argocd: This repository holds Kubernetes manifests to bootstrap Argo CD on to the GKE cluster. Code samples in this tutorial reference this repo by
ARGOCD_BOOTSTRAP_REPO. - tfc-notification-demo: Contains a sample pipeline for this tutorial. Code samples in this tutorial reference this repo by
$TFC_NOTIFICATION_DEMO.
Fork and clone the tutorial repos
-
If you don't already have a Git command line tool on your machine, download the GitHub CLI tool, and then add
ghto your$PATH. -
Create a directory for your tutorial repos, for example:
mkdir -p "$HOME/tfc-notification-demo"
cd "$HOME/tfc-notification-demo"
export DEMO_HOME="$PWD" -
Clone and fork the
vanilla-gkerepo, for example:gh repo clone harness-apps/vanilla-gke
cd vanilla-gke
gh repo fork
export TFC_GKE_REPO="$PWD" -
Clone and fork the
bootstrap-argocdrepo, for example:cd ..
gh repo clone harness-apps/bootstrap-argocd
cd bootstrap-argocd
gh repo fork
export ARGOCD_BOOTSTRAP_REPO="$PWD" -
Clone and fork the
tfc-notification-demorepo, for example:cd ..
gh repo clone harness-apps/tfc-notification-demo
cd tfc-notification-demo
gh repo fork
export TFC_NOTIFICATION_DEMO="$PWD"
Create a Harness project
In Harness, create a project named terraform_integration_demos, and then go to the Continuous Integration module.
Create a project
- Select Projects, select All Projects, and then select New Project.
- For Name, enter
terraform_integration_demos. - Leave the Organization as default.
- Select Save and Continue.
- On Invite Collaborators, you can add others to your project, if desired. You don't need to add yourself.
- Select Save and Continue.
- On the Modules page, select Continuous Integration, and then select Go to Module.
If the CI pipeline wizard starts after you select Go to Module, you'll need to exit the wizard to complete the next step in this tutorial, creating the GitHub connector.
Create a GitHub connector
Harness uses connectors to connect to your Git repositories. You need a GitHub connector that can pull your forks of the tutorial repos.
-
In the GitHub account where you forked the tutorial repos, create a GitHub personal access token with all
repo,admin:repo_hook, anduserscopes.For information about the token's purpose in Harness, go to the GitHub connector settings reference.
-
Save the token as a Harness text secret named
GITHUB_PAT. -
In your Harness
terraform_integration_demosproject, go to Project Setup and select Connectors. -
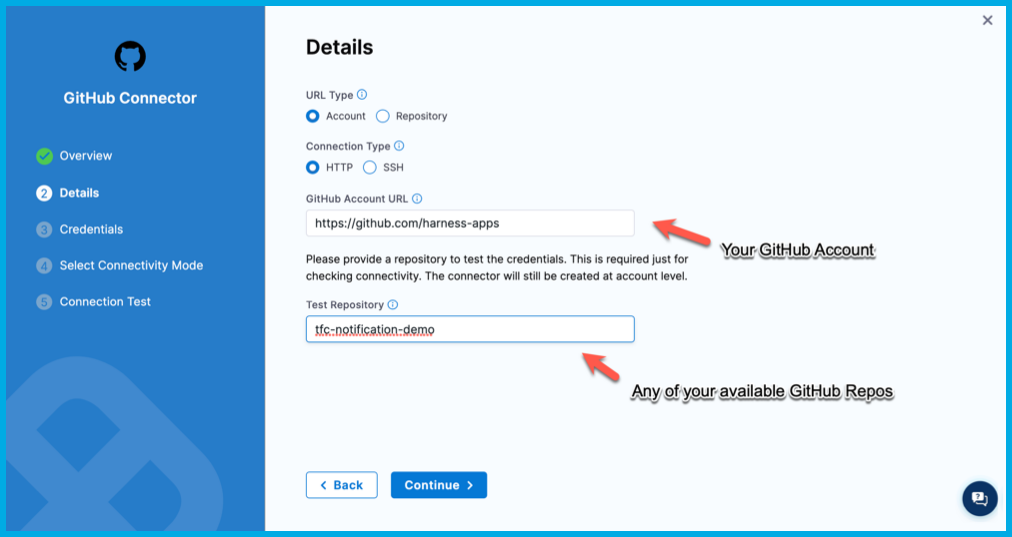
Create a GitHub code repository connector configured as follows:
-
Overview: Enter a Name for the connector. Description and Tags are optional.
-
Details:
- URL Type: Select Account.
- Connection Type: Select HTTP.
- GitHub Account URL: Enter the URL for the GitHub account where you forked the tutorial repos, such as
https://github.com/my-account. - Test Repository: Enter the repo name for any repo in your GitHub account, such as
tfc-notification-demos. This is only used to verify connectivity.
-
Credentials:
- Username: Enter the username for the GitHub account where you forked the tutorial repos.
- Personal Access Token: Select your
GITHUB_PATtext secret. - Enable API access: Select this option and select the same personal access token secret.
-
Select Connectivity Mode: Select Connect through the Harness Platform.
-
-
Select Save and Continue, wait while Harness tests the connection, and then select Finish.
Create a GSA key
You need Google Service Account (GSA) credentials, in JSON key format, to query your GKE cluster's details and create resources on it.
Run these commands in Cloud Shell. For more information, go to the Google Cloud documentation on Exporting your Google Cloud resources to Terraform format.
-
Set the environment.
export GCP_PROJECT=YOUR_GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT_ID_WHERE_YOUR_GKE_CLUSTER_EXISTS
export GSA_KEY_FILE=PATH/TO/STORE/KEY/FILE -
Create the service account.
gcloud iam service-accounts create gke-user \
--description "GKE User" \
--display-name "gke-user" -
Configure the IAM policy binding. The service account must be able to provision Kubernetes resources.
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $GCP_PROJECT \
--member="serviceAccount:$GSA_NAME@$GCP_PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/container.admin" -
Download and save the GSA key. The Google Cloud user you are using must have the Security Admin role to generate GSA keys.
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create "${GSA_KEY_FILE}" \
--iam-account="gke-user@${GCP_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" -
In your Harness project, save the GSA key as a Harness file secret.
Create a Terraform workspace
-
In your Terraform Cloud account, create a workspace called
vanilla-gke. -
Update the workspace settings to use Version Control and point to
$TFC_GKE_REPO, which is thevanilla-gketutorial repo.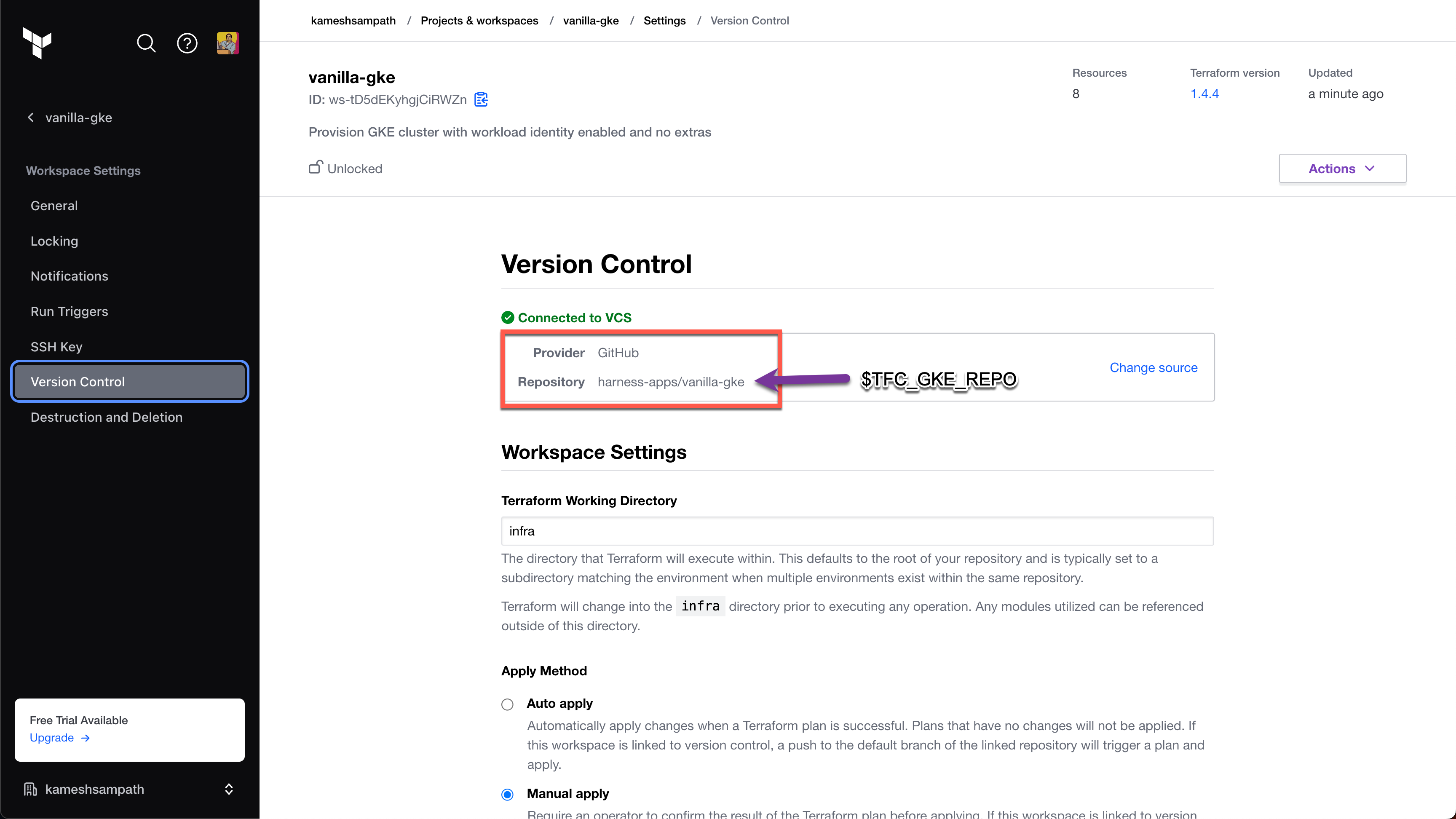
-
Configure the workspace with the following variables:
Key Value Category gcp_projectSensitive - write only terraform gcp_regionSelect a region terraform GOOGLE_CREDENTIALSSensitive - write only env 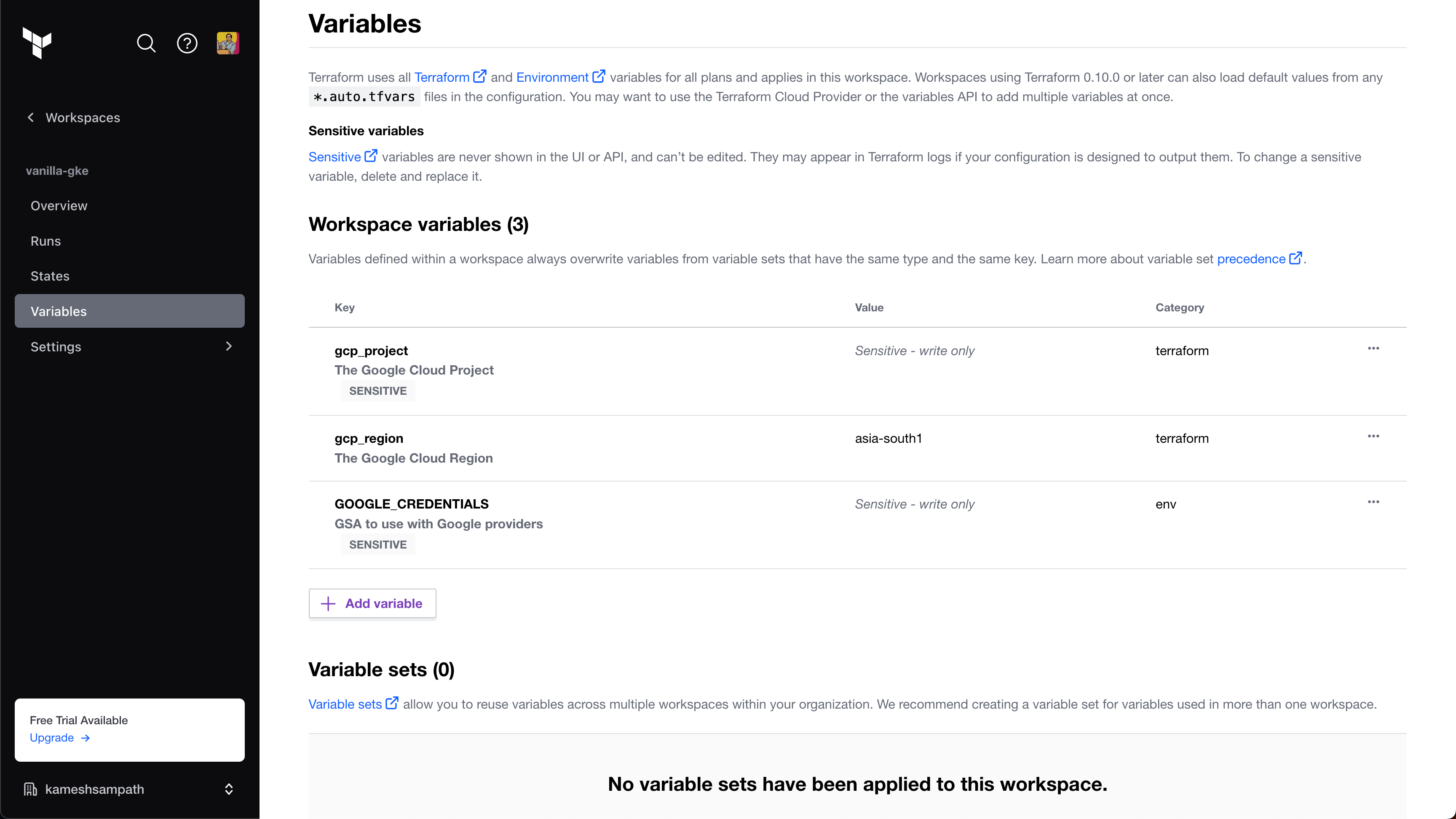
GOOGLE_CREDENTIALSis a Google Service Account JSON key with permissions to create GKE clusters. Terraform uses this key to create the GKE cluster. When you add the key to your Terraform variables, it must be base64 encoded. For example, the following command encodesYOUR_GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS_KEY_FILEin base64 format:cat YOUR_GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS_KEY_FILE | tr -d \\nFor required roles and permissions, go to the
vanilla-gketutorial repo documentation: Prerequisites.For more information, go to the
vanilla-gketutorial repo documentation: Terraform Inputs. -
Create a variable called
$TF_WORKSPACEand set the value to the name of your Terraform Cloud organization.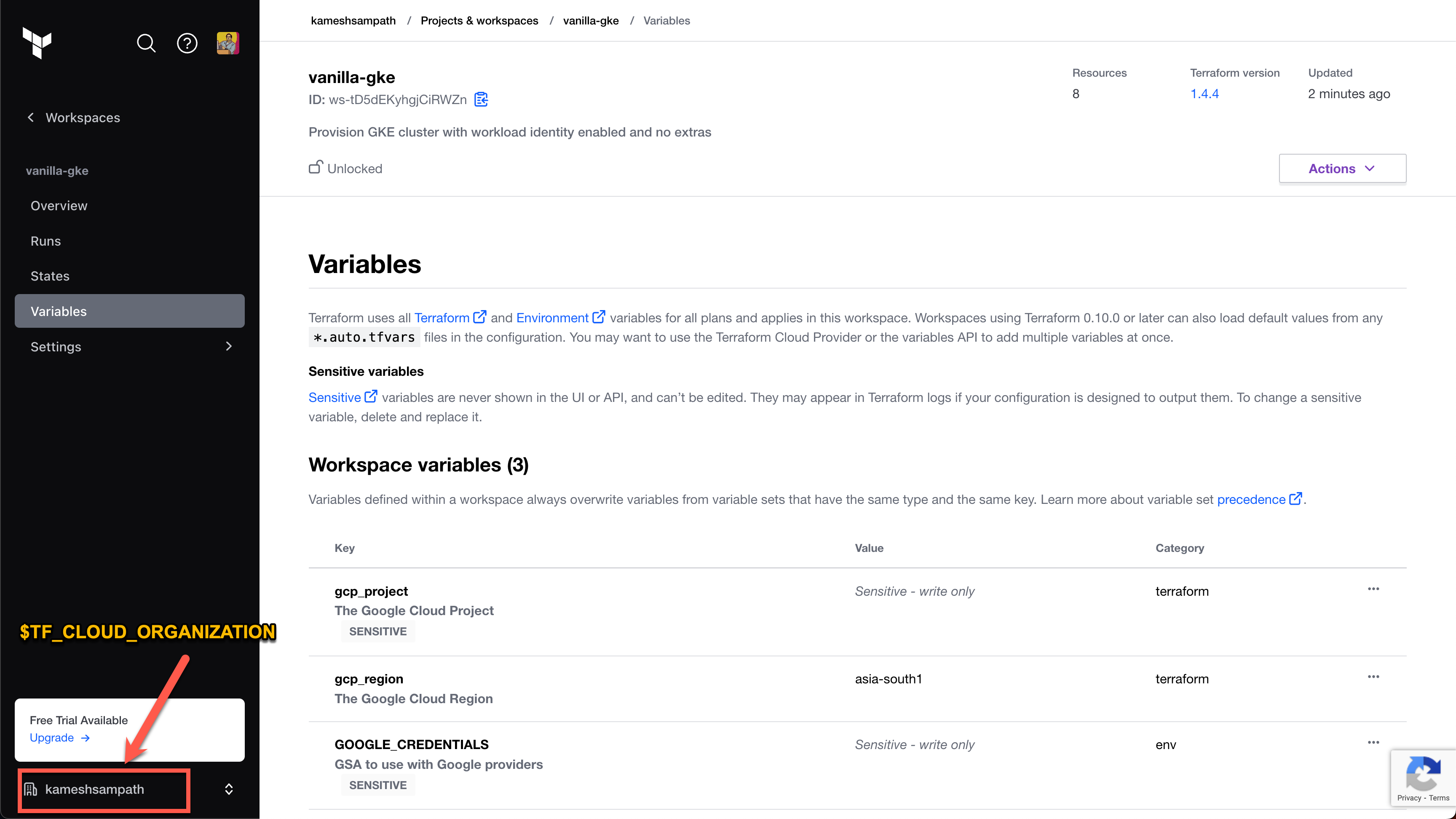
-
In your Terraform Cloud user settings, Create an API token. This token is used to pull outputs from Terraform runs.
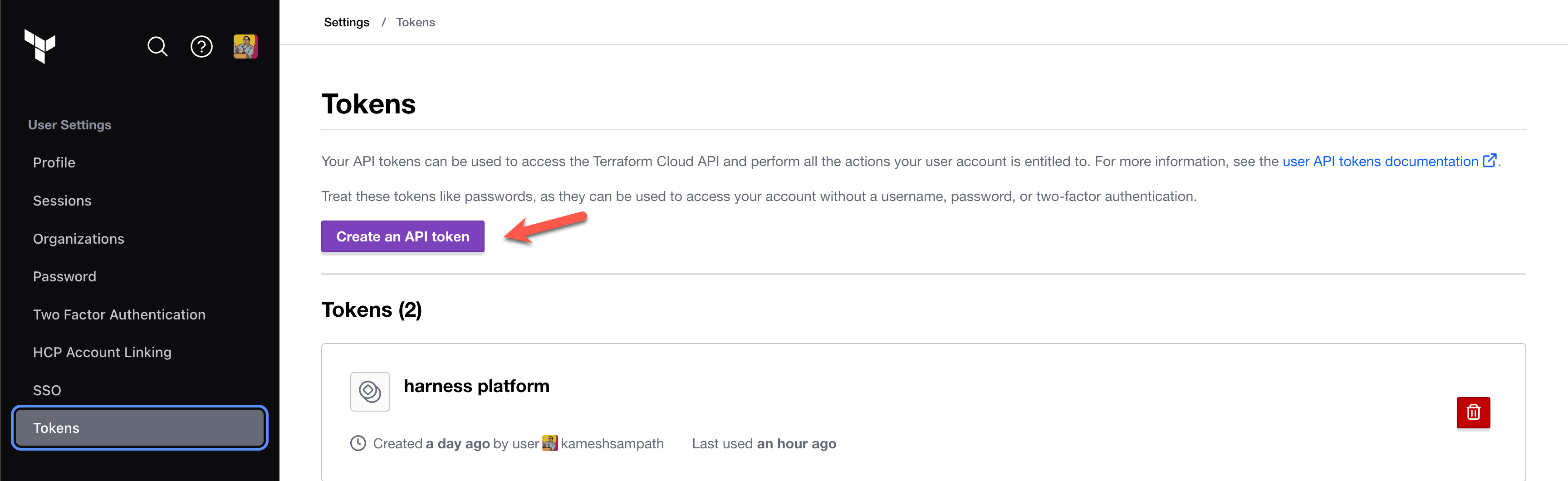
-
Save the API token to a variable named
$TF_TOKEN_app_terraform_io. You will refer to this token in your Harness CI pipeline later in this tutorial.
Create the pipeline
In Harness, import a premade pipeline from one of the tutorial repos.
- In Harness, go to your
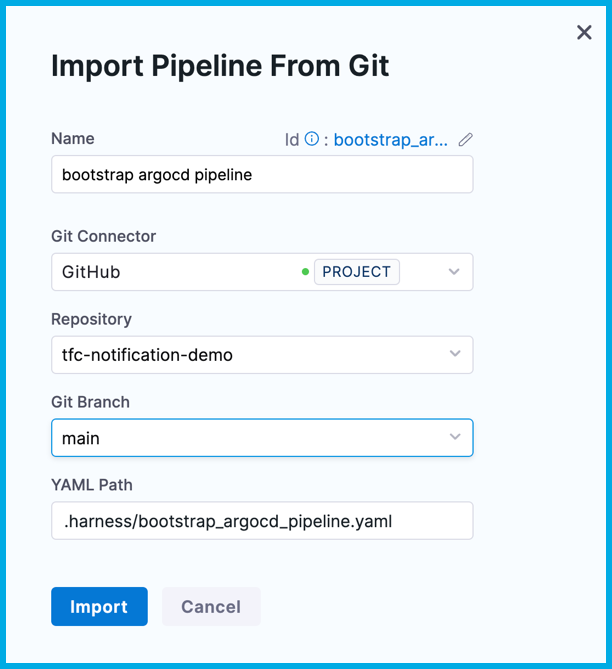
terraform_integration_demosproject, and select Pipelines. - Select Create a Pipeline, select Import From Git, and complete the Import Pipeline From Git fields as follows:
- Name:
bootstrap argocd pipeline - Git Connector: Your GitHub connector
- Repository:
tfc-notificaiton-demo - Git Branch:
main - YAML Path:
.harness/bootstrap_argocd_pipeline.yaml
- Name:
- Select Import.
Add secrets to the pipeline
-
On the list of pipelines, select the bootstrap argocd pipeline, and then select the Bootstrap Argo CD stage.
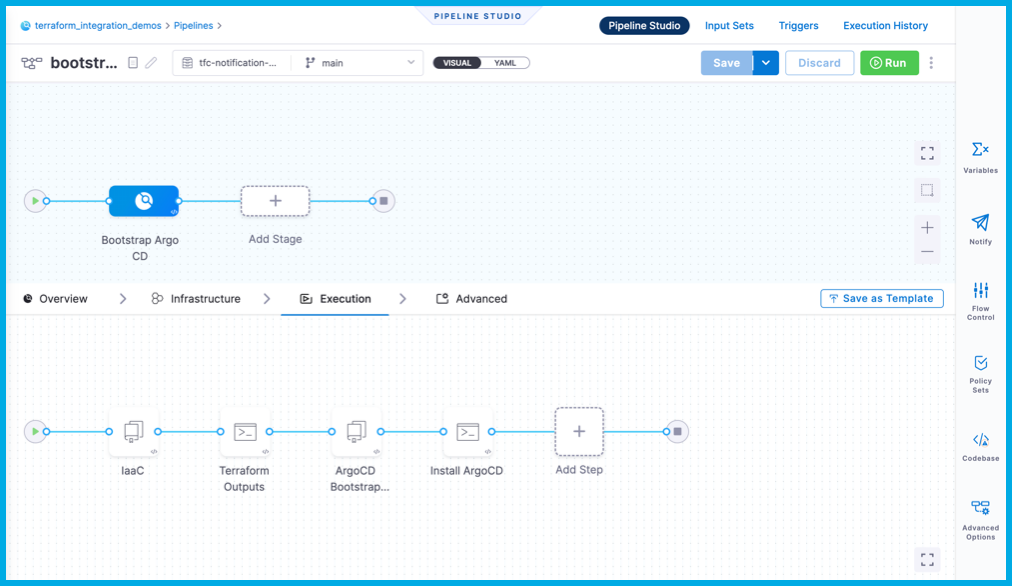
-
Select each step to examine its configuration. Notice that the pipeline uses the following secrets, which need to be populated:
google_application_credentials: The GSA credentials to manipulate GKEterraform_cloud_api_token: The value of$TF_TOKEN_app_terraform_ioterraform_workspace: The value of$TF_WORKSPACEterraform_cloud_organization: The value of$TF_CLOUD_ORGANIZATION
-
To populate these values, add Harness text secrets for
terraform_cloud_api_token,terraform_workspaceandterraform_cloud_organization.Make sure the secret names are exact, or the pipeline will fail.
You added the
google_application_credentialssecret earlier in the tutorial.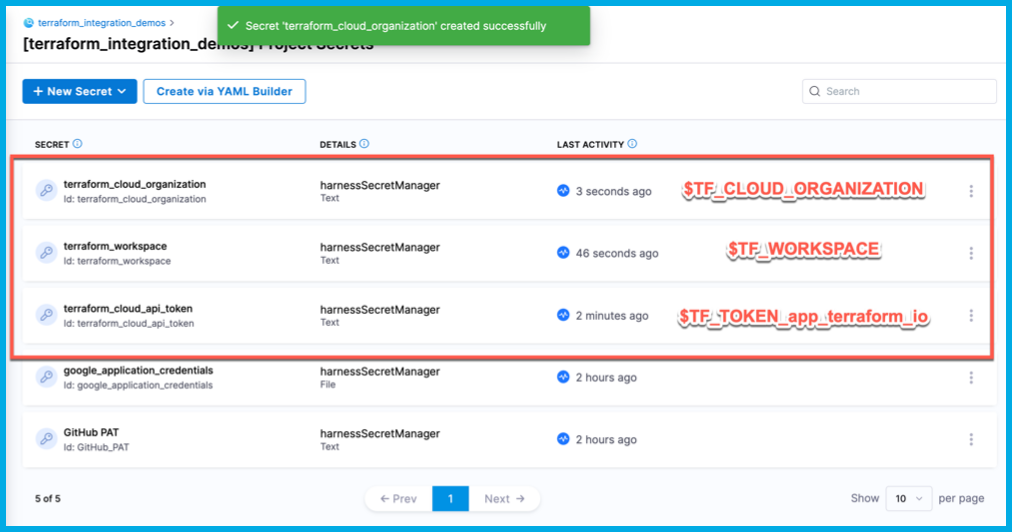
Alternately, you can extract the values for terraform_workspace and terraform_cloud_organization from the trigger webhook payload by replacing their <+secret> expressions with the expressions <+trigger.payload.workspace_name> and <+trigger.payload.organization_name> respectively.
Add the trigger
For the pipeline to listen for Terraform Cloud events, you must add a custom webhook trigger.
-
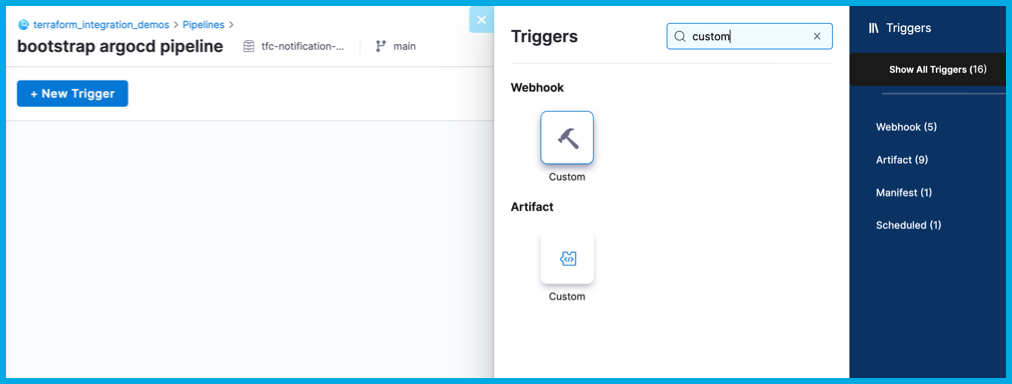
In Harness, go to your bootstrap argocd pipeline, and then select Triggers in the header.
-
Select Add New Trigger, and select the Custom trigger type under Webhook.
-
On the Configuration tab, enter
tfc notificationfor the Name, and then select Continue.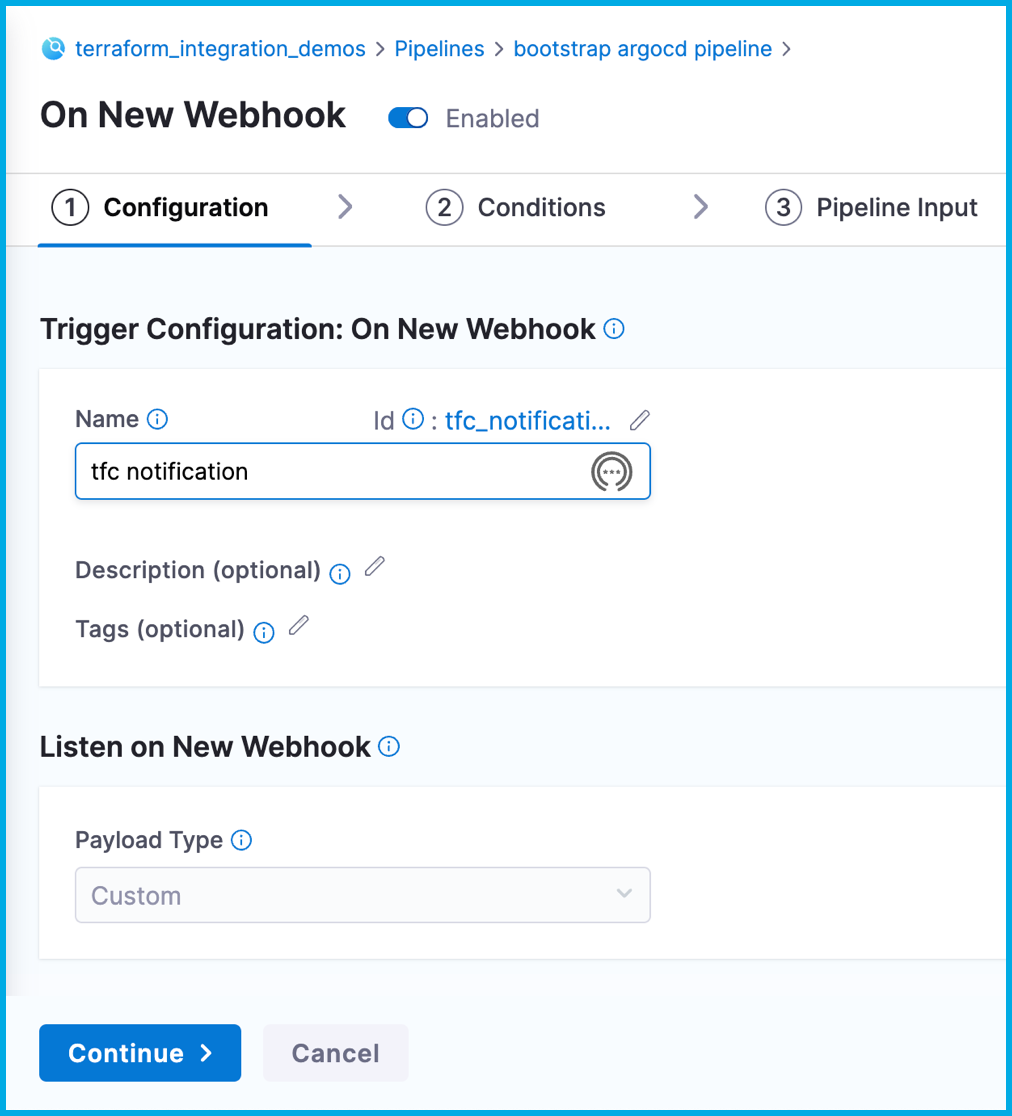
-
Don't change the Conditions tab. Select Continue.
-
On the Pipeline Input tab, enter
mainfor Pipeline Reference Branch.This field is required to create the trigger; however, it doesn't have any relevance to this tutorial, because this pipeline manually clones code repos.
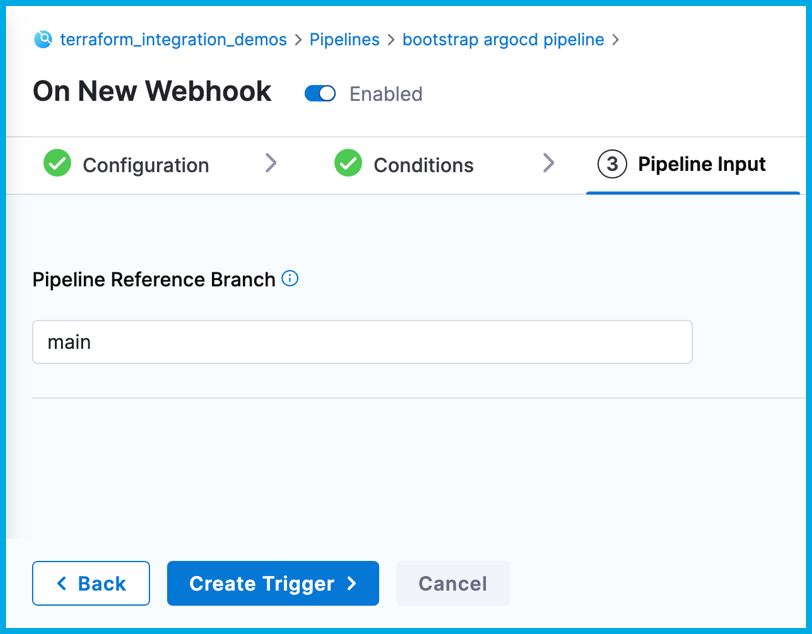
-
Select Create Trigger.
-
On the list of triggers, select the icon in the Webhook column, and then select Copy as Webhook URL. This value is referred to as
$TRIGGER_WEBHOOK_URLin the rest of this tutorial.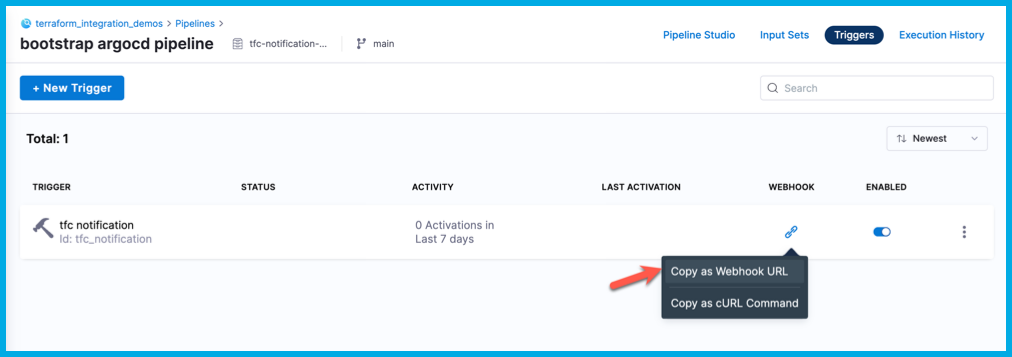
-
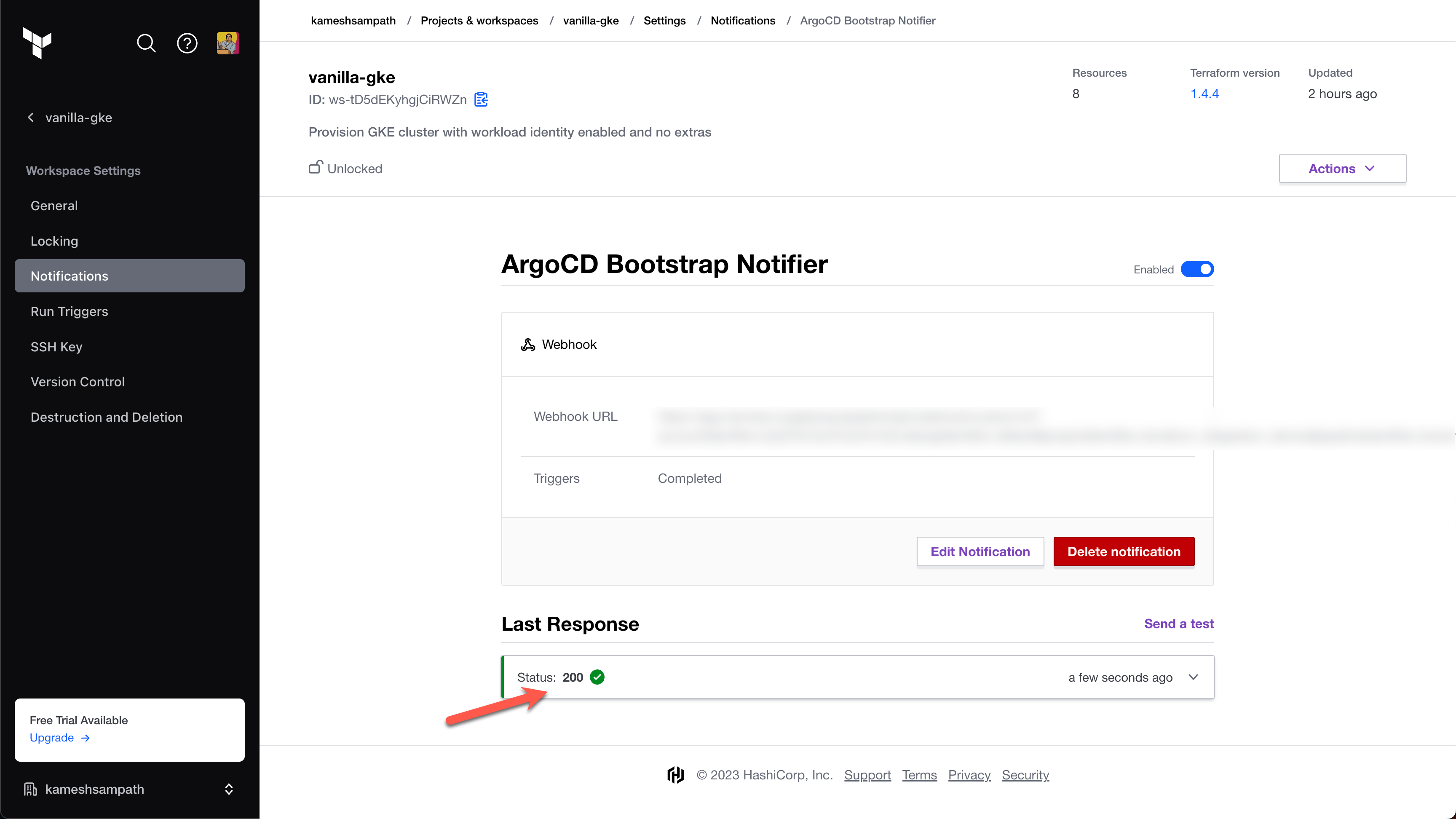
In your Terraform Cloud workspace, go to the notification settings, and select Create a Notification.
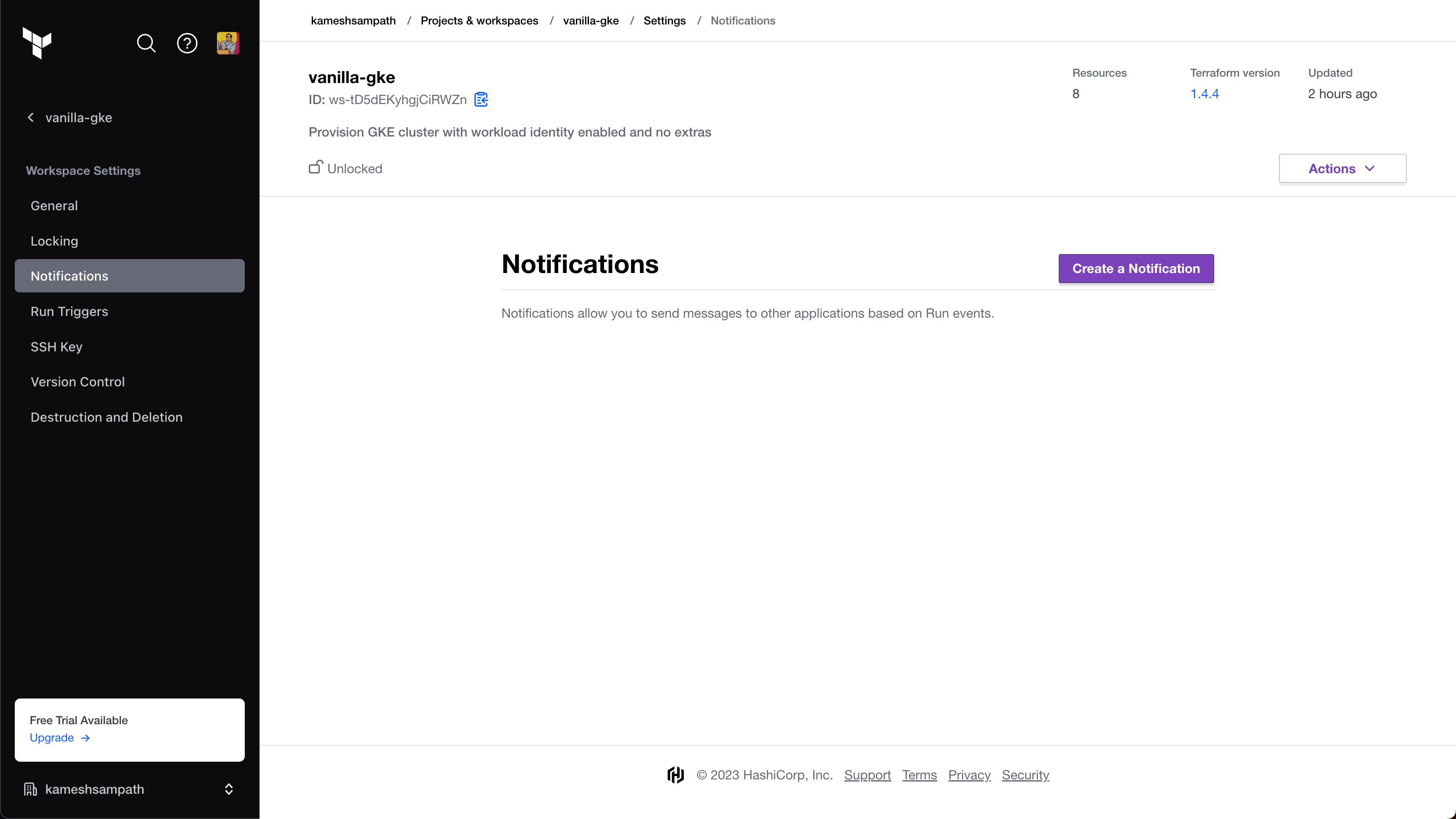
-
Configure the notification as follows:
- Destination: Select Webhook.
- Name: Enter
Argo CD Bootstrap Notifier. - Webhook URL: Enter your custom webhook trigger URL.
- Triggers: Select Only certain events, and then select Completed. This ensures the pipeline only runs when events are successfully completed.
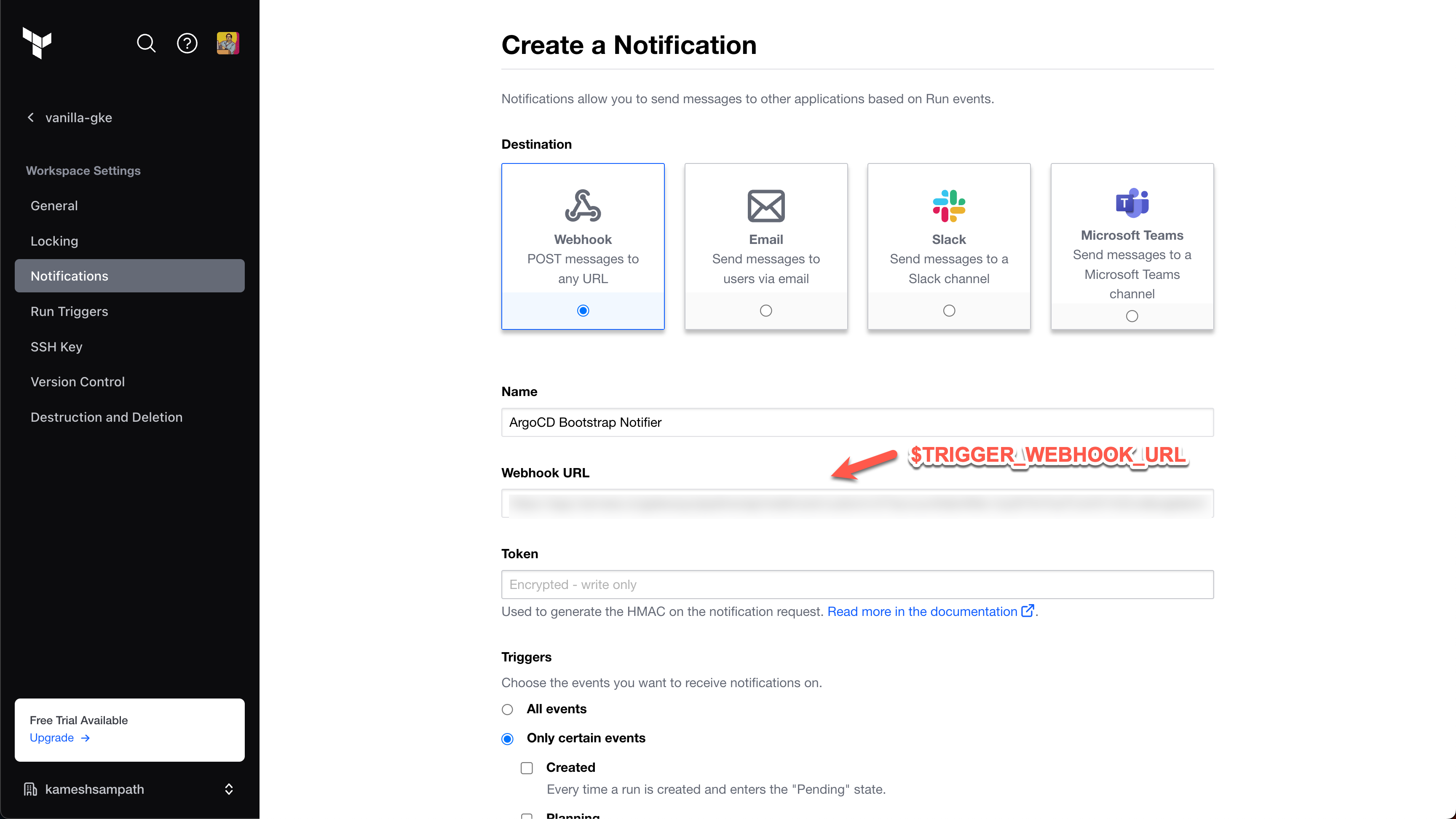
-
Select Create Notification. Creating the notification triggers a notification event. If the cluster is not ready yet, the pipeline fails. You can select Send a test to reattempt the trigger.
Summary
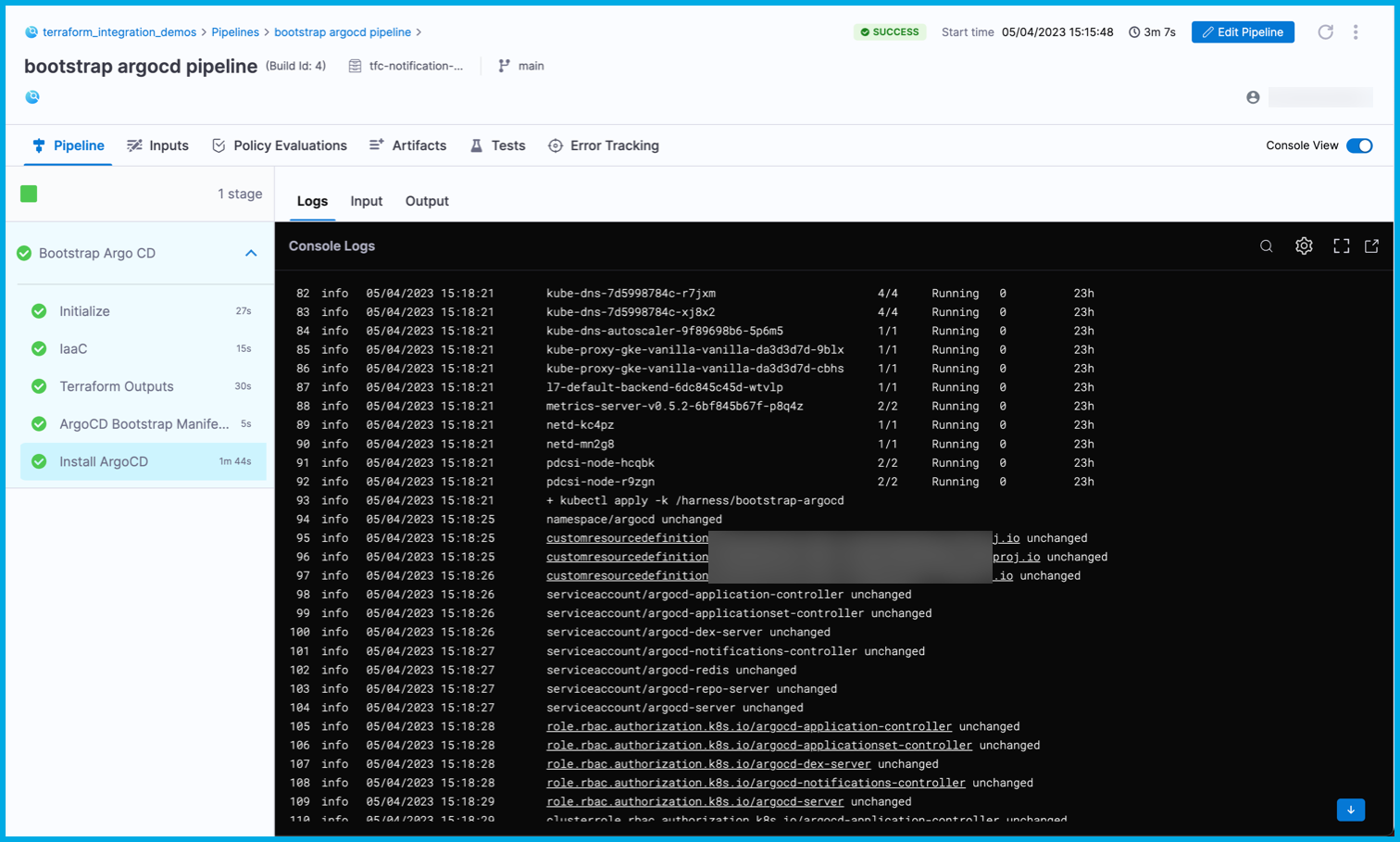
This pipeline is now configured to listen for notifications of IaC events from Terraform, and the pipeline only runs when it's necessary. Specifically in this pipeline, any changes to the $TFC_GKE_REPO trigger a plan and apply on Terraform Cloud. A completed plan triggers the bootstrap argocd pipeline to run and apply the manifests from $BOOTSTRAP_ARGOCD_REPO on the GKE cluster.
Here's an example of logs from a successful run: