Key Concepts
This topic covers the fundamental concepts and terminology used in Harness Release Orchestration.
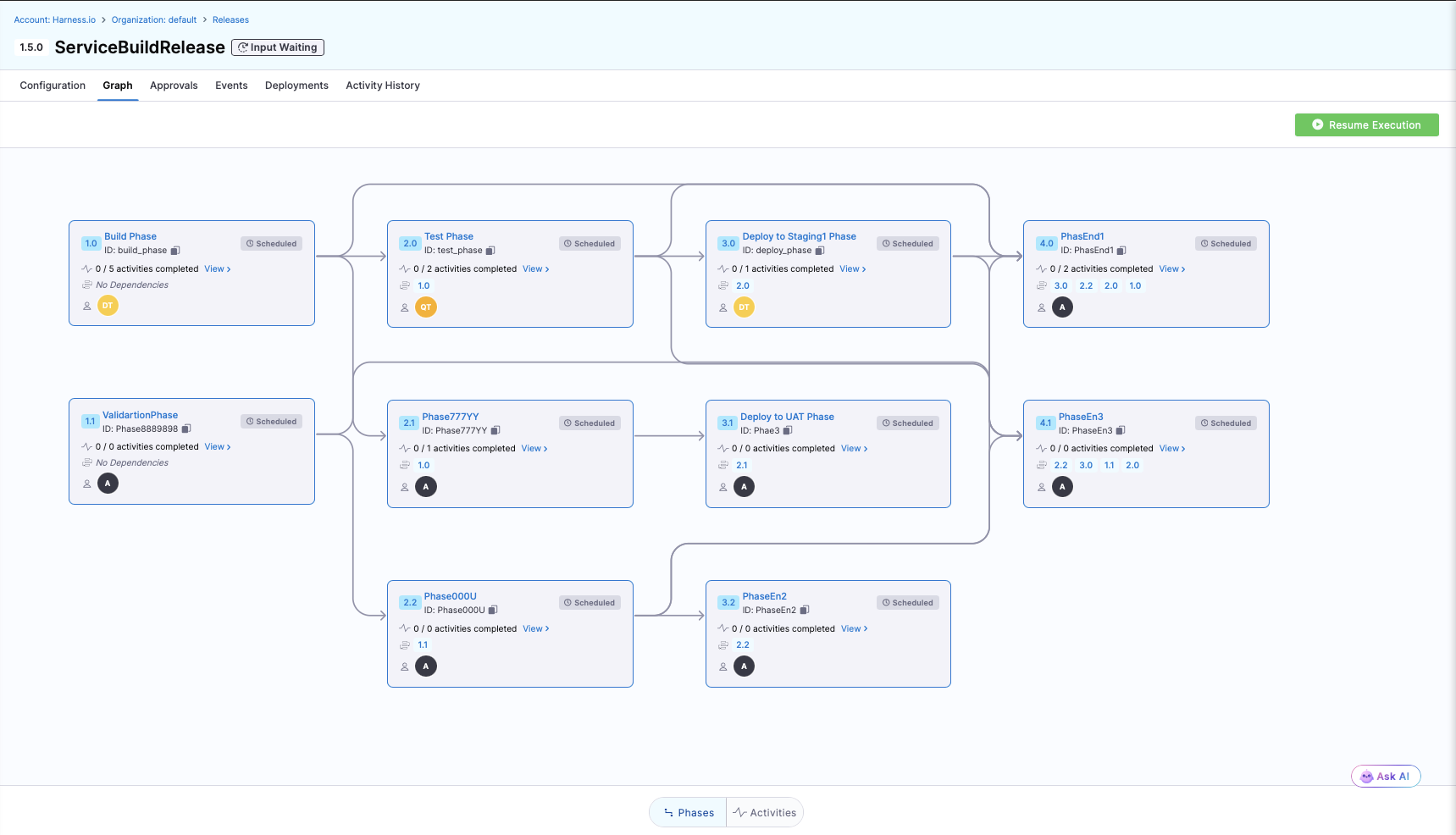
Release
A release represents a software delivery comprising different functions across teams, tools, and environments. Releases are modeled using processes that define the phases, activities, and dependencies required to complete the release.
Learn more: Releases Overview | Modeling Releases
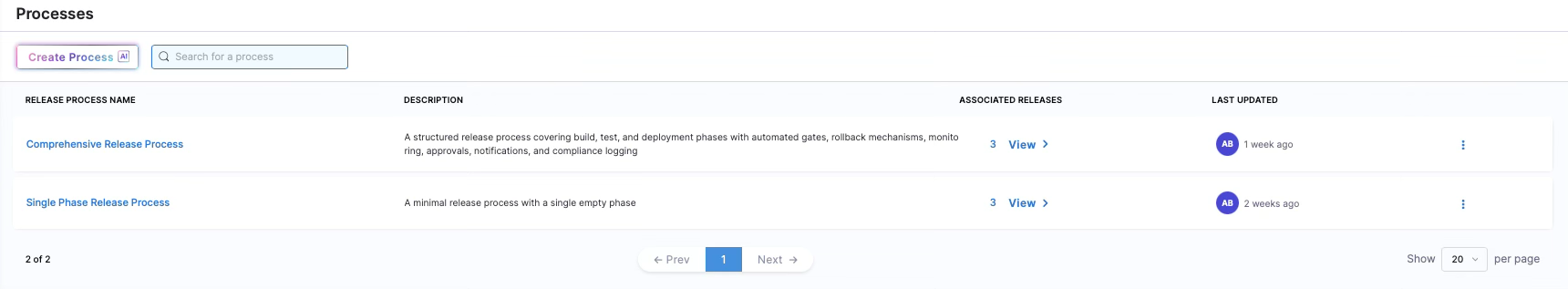
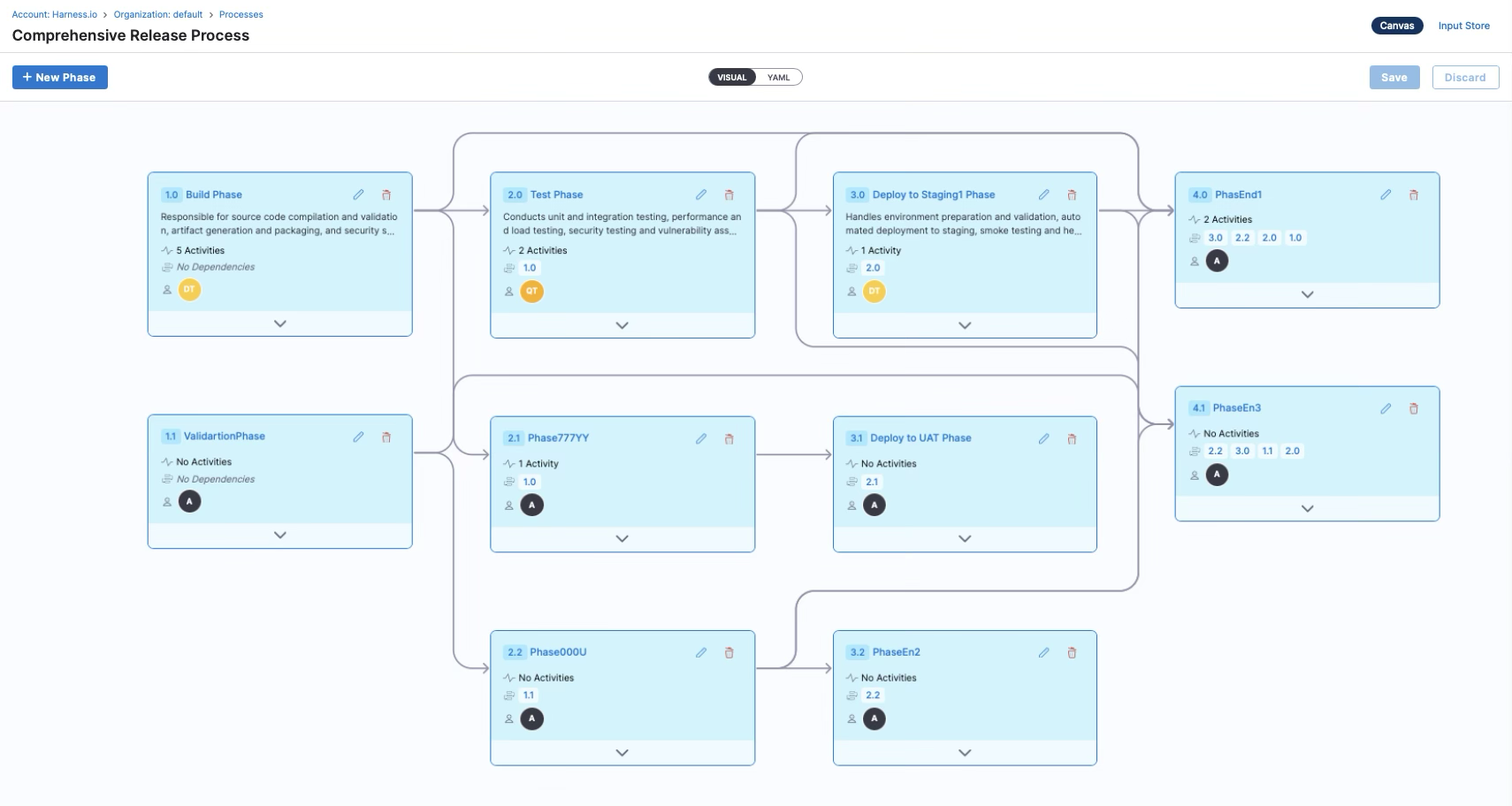
Process
A process is a reusable blueprint that defines the structure of a release. It consists of phases, activities, dependencies, inputs, and variables. Processes can be created manually or using AI-based process creation.
Learn more: Processes Overview | Process Modeling | AI-Based Process Creation
Phases & Activities
A phase is a collection of activities which represents one logical group of functions. Phases are a logical grouping of activities within a release process. Phases represent major milestones or stages in the release lifecycle, such as "Planning and Coordination", "Testing and Validation", "Feature Flag Enablement", "Deployment", and "Monitoring". Phases can have dependencies on other phases.
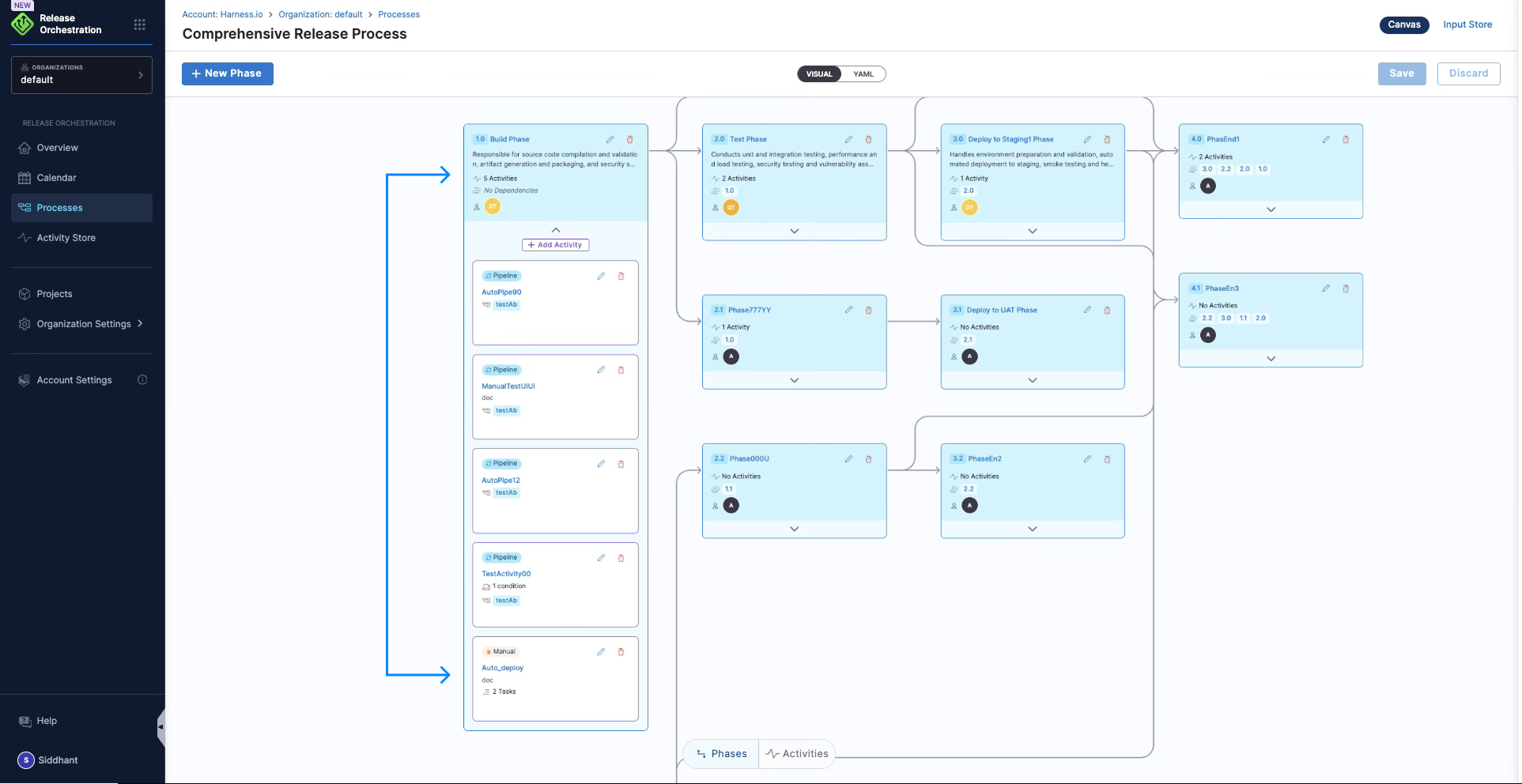
An activity is a single unit of work within a phase. Activities can be of three types:
-
Automated Activity: An activity that encapsulates a pipeline. Th activity contains or references a Harness pipeline that executes automatically.
-
Manual Activity: An activity where users can create tasks, record their actions, and finalize their actions in a manual fashion. Used for approvals, sign-offs, and manual verification steps.
-
Subprocess Activity: An activity of process type, where a process can be referred within a process (called a subprocess).
Learn more: Phases Overview | Activities Overview | Automated Activities | Manual Activities | Subprocess Activities
Activity Store
The activity store contains a collection of reusable activities with inputs and outputs encapsulating the pipelines. Harness Release Orchestration provides activity stores where all the reusable activities pertaining to different processes can be modeled and selected. Activities can be reused across different processes, promoting consistency and reducing duplication.
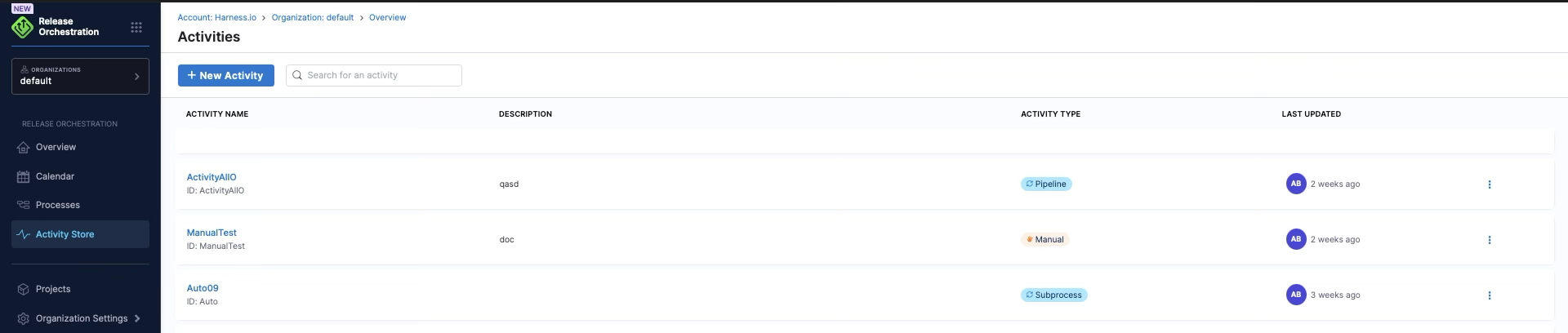
Learn more: Activity Store | Reusable Activities
Input Store
The Input Store is a collection of inputs for every process. There can be different sets of inputs for the same process, allowing you to execute the release multiple times with different sets of inputs. The Input Store holds the concrete values for:
- Process-level inputs
- Phase-level inputs
- Activity instance inputs within an execution
- Each process can posses multiple inputs instances
Input Store is a centralized place to manage the configuration inputs required to run your processes. Each automated activity needs to have an input set.
Process Input Set: A collection of activity input sets that apply across the entire release process
Activity Input Set: Defines the inputs needed for a specific activity within a phase of the process. Each activity must be linked to one input set for the process to run successfully.
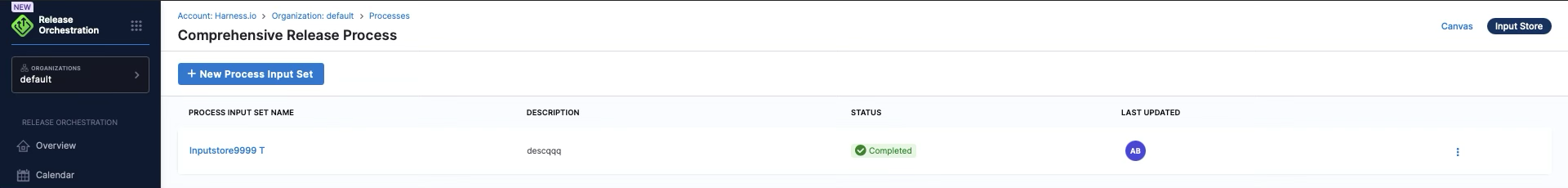
Learn more: Inputs and Variables Overview
Release Group & Release Calendar
A release group is a collection of releases created and executed in a certain cadence.
The release calendar provides a visual representation of all planned and scheduled releases. It helps teams coordinate releases and avoid conflicts.
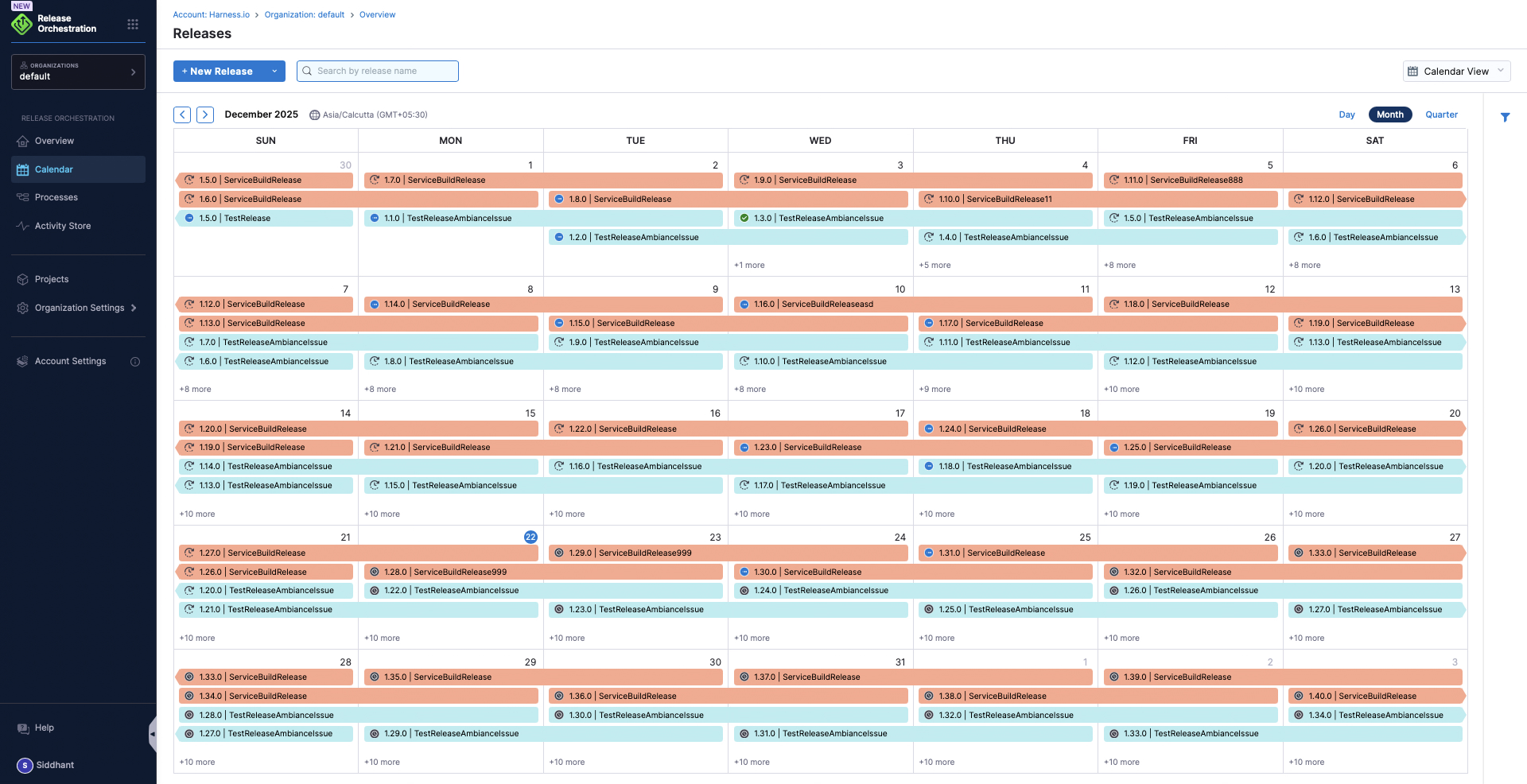
Learn more: Modeling Releases
Variables
Inputs are parameters that are provided when creating or executing a process. Variables are values that can be used throughout the process and can be defined at different levels:
- Global variables: Available across the entire process
- Phase variables: Available within a specific phase
- Activity variables: Available within a specific activity
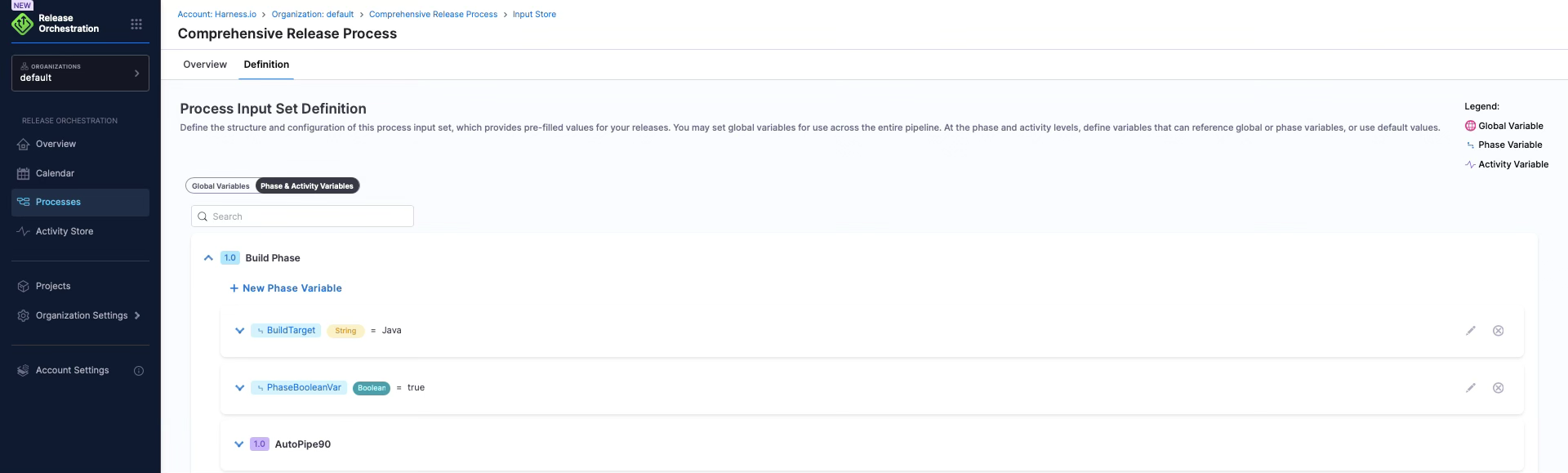
Learn more: Inputs and Variables Overview | Global Variables | Phase Variables | Activity Variables
Process Execution
Process Execution refers to the actual running of a release. During execution, activities are executed according to their dependencies and configuration. The system tracks the status of each activity and the overall release progress.
Learn more: Executing a release | Activity Execution Flow | Parallel vs Sequential Execution