Harness SAST Scanner
Harness native SAST scanner integrates directly into your CI/CD pipelines to scan source code for security vulnerabilities, secrets, and open-source dependencies - without requiring external scanners or connectors.
With one-click configuration, Harness automatically manages authentication and licensing, while providing built-in data flow visualization, reachability analysis to determine whether a vulnerability is exploitable, and AI-powered remediation to help developers quickly understand and fix issues.
The SAST step works natively within STO, with all findings unified and visible alongside results from other security scanners.
Licensing
Running the Harness SAST step in STO pipelines requires a Harness SAST Enterprise license.
For licensing details or to enable the Enterprise license, contact Harness Sales.
Free Trial
A 45-day free trial is available. If you are an existing Harness STO customer and want to access the Harness scanners, contact the Harness sales representative to have them enabled for your account.
The following topics contain useful information for setting up scanner integrations in STO:
Harness SAST scanner is being gradually rolled out and is currently enabled for some customers. Full availability across all accounts is coming soon.
Harness SAST step settings for STO scans
Setting up the Harness SAST scanner is the same as configuring any other built-in scanner step. The required configuration is handled automatically, making the setup process simple and straightforward. Here’s how to set it up:
-
In your Build or Security stage, open the step palette by clicking the Add Step option in your pipeline.
-
Navigate to the Harness Security Scanners section under the Security Tests category.

-
By default, all the below fields are configured automatically by the Harness SAST scanner.
- Set the Scan Mode to Orchestration.
- Set the Scan Configuration to Default
- Set the Target Type to Repository.
To run the Harness SAST scan step in the pipeline, no further configuration is required; If you want to add additional scan settings, you can configure the following below fields in the step.
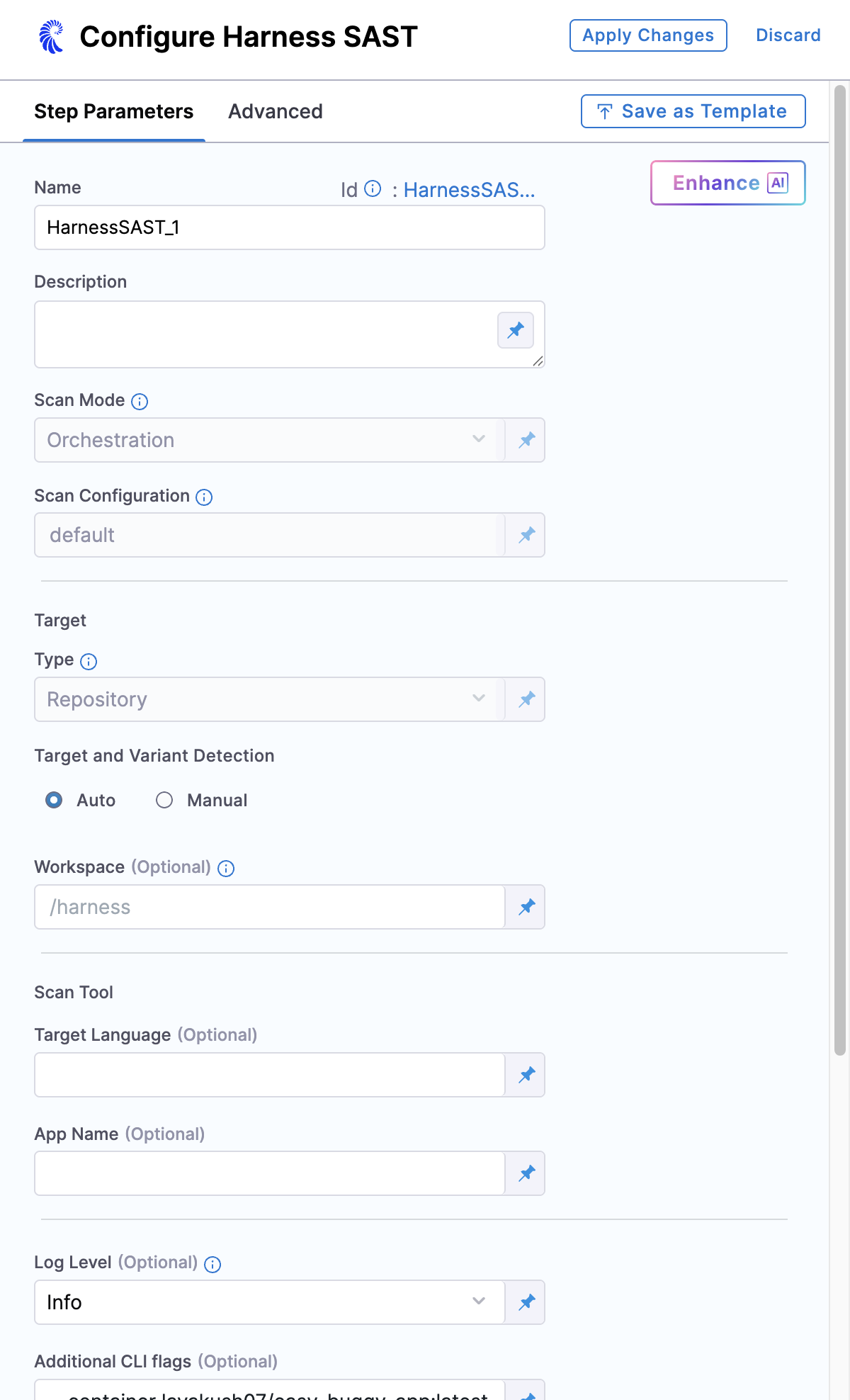
Target and Variant Detection
When Auto is enabled for code repositories, the step detects these values using git:
- To detect the target, the step runs
git config --get remote.origin.url. - To detect the variant, the step runs
git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD. The default assumption is that theHEADbranch is the one you want to scan.
When you select it as Manual, specify the name and variant of the code repo.
Name
The identifier for the target, such as codebaseAlpha or jsmith/myalphaservice. Descriptive target names make it much easier to navigate your scan data in the STO UI.
It is good practice to specify a baseline for every target.
Variant
The identifier for the specific variant to scan. This is usually the branch name, image tag, or product version. Harness maintains a historical trend for each variant.
Workspace (repository)
The workspace path on the pod running the scan step. The workspace path is /harness by default.
You can override this if you want to scan only a subset of the workspace. For example, suppose the pipeline publishes artifacts to a subfolder /tmp/artifacts and you want to scan these artifacts only. In this case, you can specify the workspace path as /harness/tmp/artifacts.
Additionally, you can specify individual files to scan as well. For instance, if you only want to scan a specific file like /tmp/iac/infra.tf, you can specify the workspace path as /harness/tmp/iac/infra.tf
-
The Harness SAST scanner is not supported in SMP.
-
With a Harness SAST Enterprise license, you also get access to the Qwiet AI by Harness platform. AppSec users can log in to the platform.
-
The Qwiet AI dashboard does not support exemptions, so any issues you mark as exempt in Harness STO will not appear as exempted in Qwiet AI. Exemptions must be managed in Harness STO only.
Scan Tool
Target Language
Specify which programming language needs to be analyzed in the scan by passing the corresponding parameter. Learn more about the supported languages.
| Language | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Apex | --apex |
| C/C++ | --c |
| C# | --csharp |
| Go | --go |
| Java | --java |
| JavaScript/TypeScript | --javascript / --jssrc* |
| Kotlin (Beta) | --kotlin |
| PHP (Beta) | --php |
| PL/SQL (Beta) | --plsql |
| Python | --python |
| Ruby (Beta) | --ruby |
| Scala | --java (uses Java flag) |
| Swift (Alpha) | --swift (if applicable) |
| Terraform | --terraform |
App Name
Provide a unique name to identify the scanning application. All scan results for this application are grouped and tracked under this name in the Qwiet AI by Harness dashboard.
Log Level
The minimum severity of the messages you want to include in your scan logs. You can specify one of the following:
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARNING
- ERROR
Additional CLI flags
Use this field to run the scanner binary with additional flags supported by the scanner.
- Instead of running two separate Harness SAST and SCA scans, you can use the Harness SAST scanner to scan container images and determine dependency reachability by adding the
--containerflag with the image name. Example:--container docker.io/shiftleft/demoContainer:latest. This requires an active Harness SCA license
Passing additional CLI flags is an advanced feature. Harness recommends the following best practices:
-
Test your flags and arguments thoroughly before you use them in your Harness pipelines. Some flags might not work in the context of STO.
-
Don't add flags that are already used in the default configuration of the scan step.
To check the default configuration, go to a pipeline execution where the scan step ran with no additional flags. Check the log output for the scan step. You should see a line like this:
Command [ scancmd -f json -o /tmp/output.json ]In this case, don't add
-for-oto Additional CLI flags.
Fail on Severity
Every STO scan step has a Fail on Severity setting. If the scan finds any vulnerability with the specified severity level or higher, the pipeline fails automatically. You can specify one of the following:
CRITICALHIGHMEDIUMLOWINFONONE— Do not fail on severity
The YAML definition looks like this: fail_on_severity : critical # | high | medium | low | info | none
Settings
You can use this field to specify environment variables for your scanner.
Additional Configuration
The fields under Additional Configuration vary based on the type of infrastructure. Depending on the infrastructure type selected, some fields may or may not appear in your settings. Below are the details for each field
- Override Security Test Image
- Privileged
- Image Pull Policy
- Run as User
- Set Container Resources
- Timeout
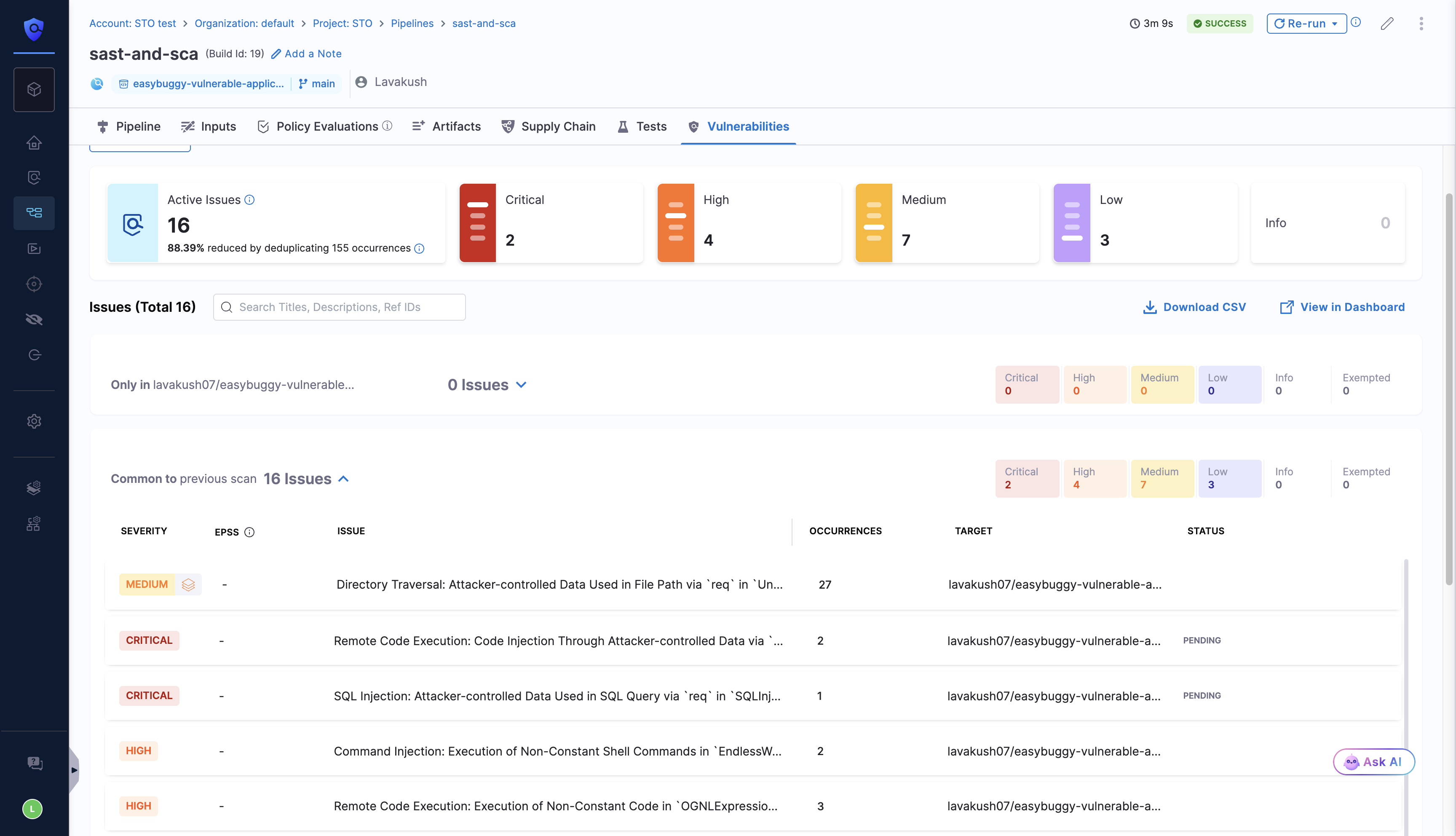
View Harness SAST Scanner results in the Vulnerabilities tab
After running the Harness SAST scanner in your pipeline, navigate to the Vulnerabilities tab. Use the Issue Type filter to view all vulnerabilities detected by the scanner, including SAST, SCA (Open Source dependencies), and Secrets.
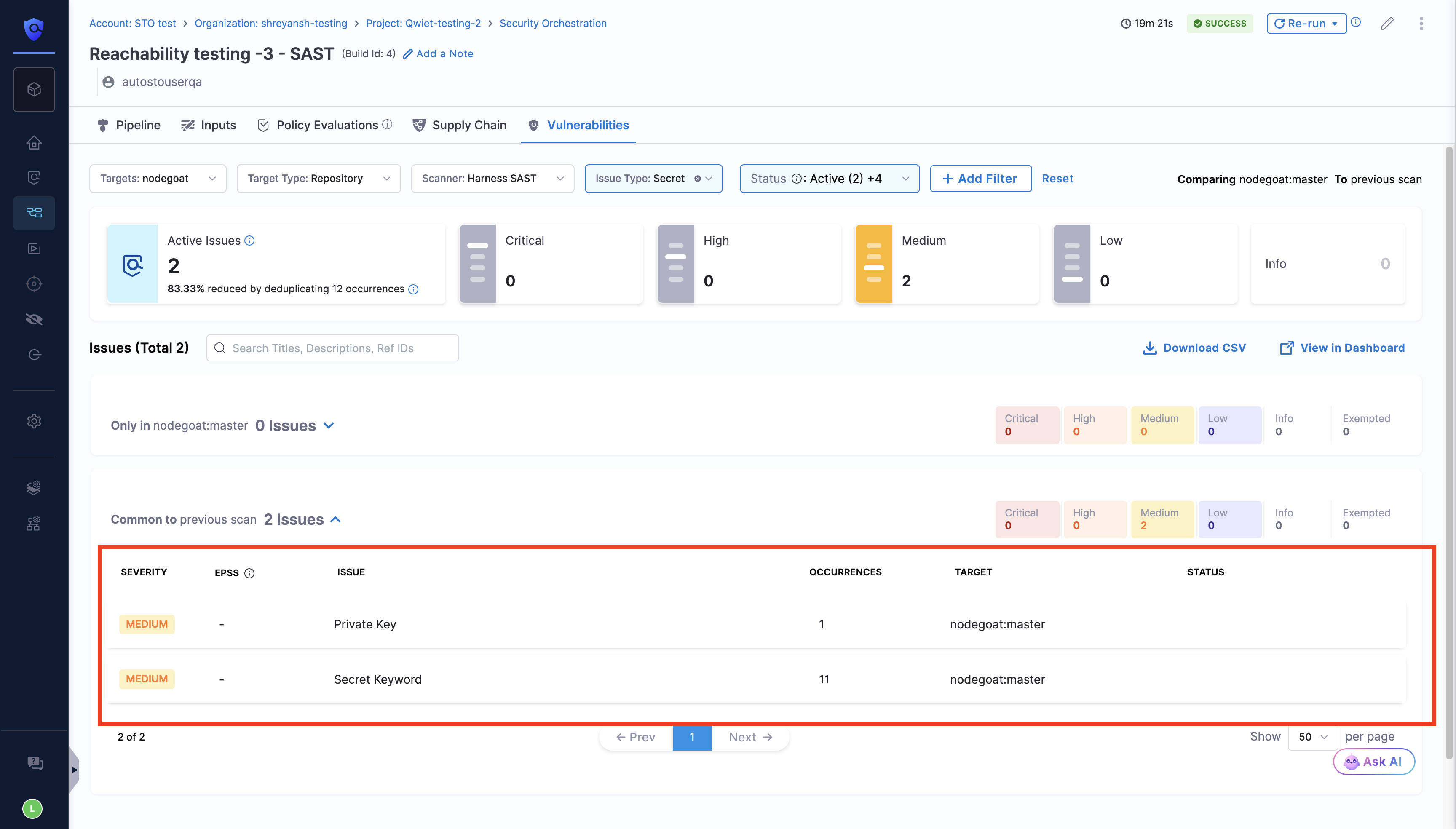
Secret Detection
Harness SAST detects hardcoded secrets in your code, such as API keys, tokens, and passwords, helps you prevent accidental credential leaks early in the development lifecycle. After the successful pipeline run, in the vulnerabilities tab, apply the Issue Type filter as Secret to view the Secrets identified by the Harness SAST scanner.
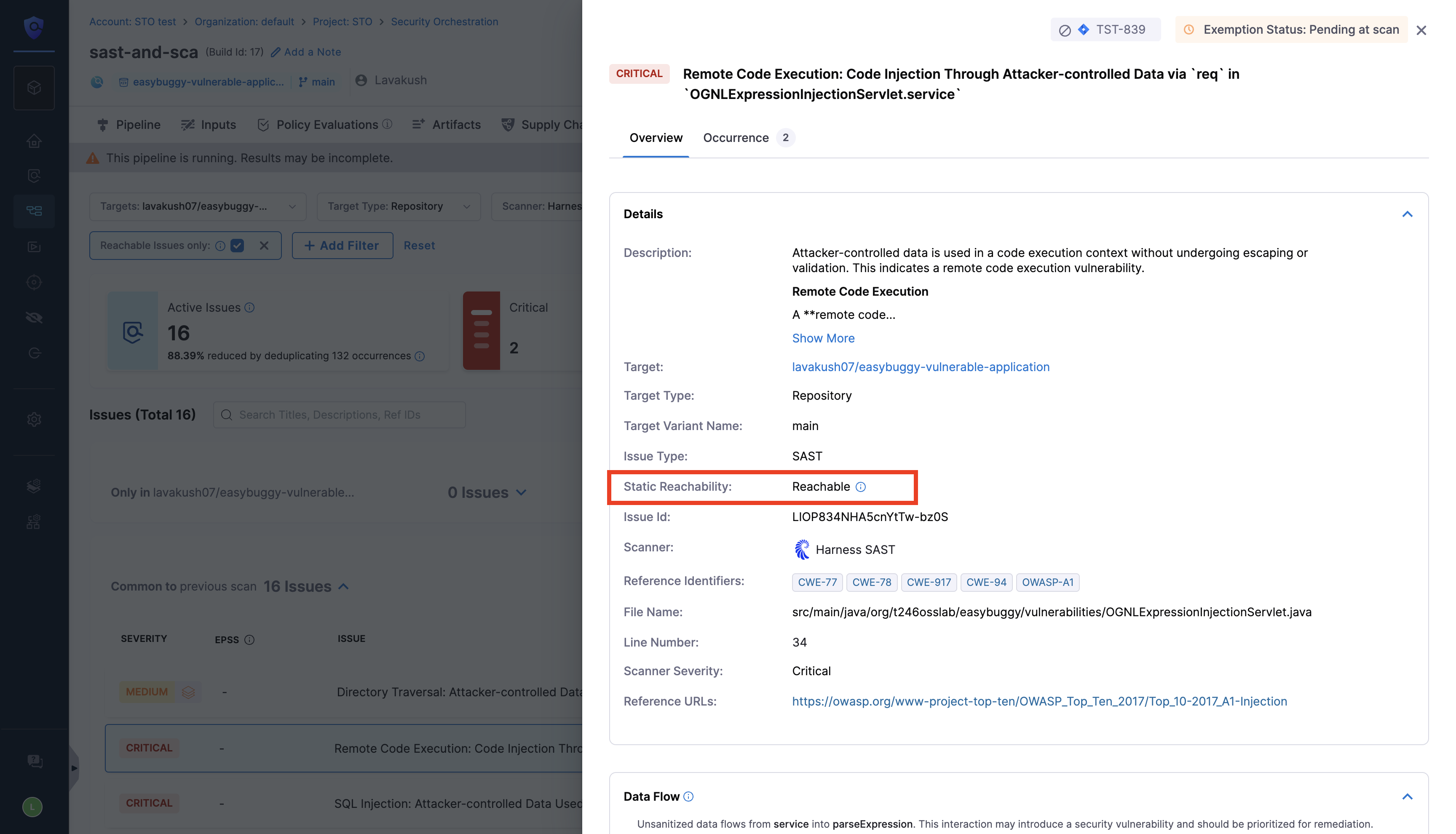
Static Reachability
A vulnerability is considered as Reachable when an attacker can reach the affected code (CVE) through a controlled path from application input. A vulnerability is marked as Reachable if at least one of its occurrences is reachable. Exempted occurrences are not considered. You can view the Reachability for each of the occurrences of a security issue in the Vulnerabilities and Issues page.
After a successful pipeline run, the Vulnerabilities tab shows whether a vulnerability is marked as Reachable. On the Vulnerabilities page, use the Reachability filter to view findings by reachability. This helps reduce noise and focus on vulnerabilities that pose real risk. Learn more.
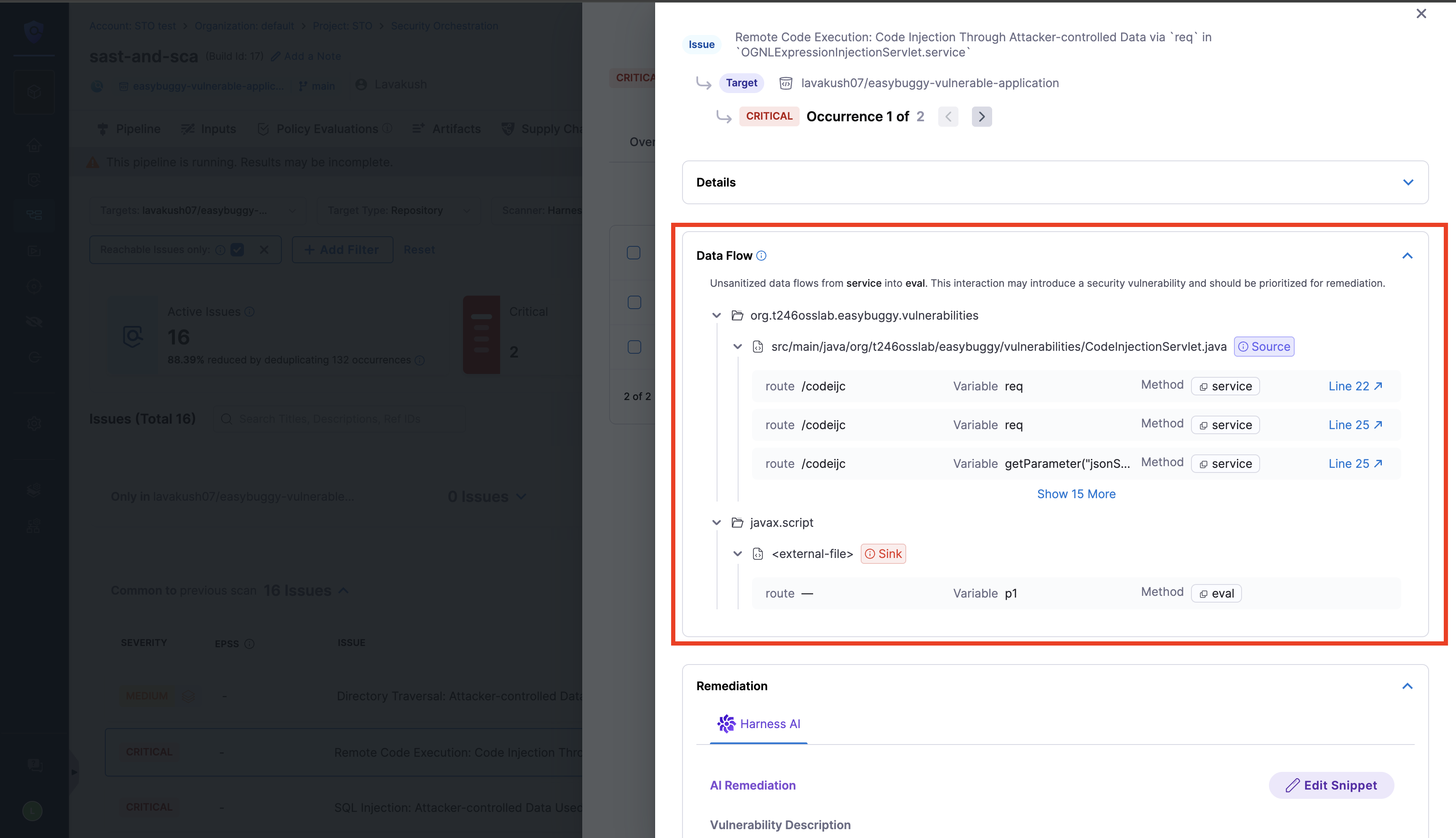
Data Flow
The Data Flow helps you understand how an issue propagates through your application by leveraging the Code Property Graph (CPG), making it easier to assess risk and prioritize remediation by showing the path from the source to the sink.
SOURCE: The part of the code that allows the issue to occur. For example, a function that accepts user input could be the source of a command injection vulnerability.
SINK: The point where the issue is triggered or exploited. For example, a command executed using unvalidated user input would be the sink.
You can view the Dataflow for each of the occurrences of a security issue in the Vulnerabilities page.
IDE Integration
Harness provides a code extension that helps you shift security even further left by allowing you to identify and fix vulnerabilities as you write code. It integrates directly into the developer workflow through IDE plugins for VS Code and JetBrains, with support for AI-native IDEs such as Cursor and Windsurf coming soon.
Harness also provides a CLI to run SAST and SCA scans locally, to help you identify code vulnerabilities and dependency risks before pushing code to your repository. Learn more on how to install, authenticate, and use the CLI commands in the Harness CLI.
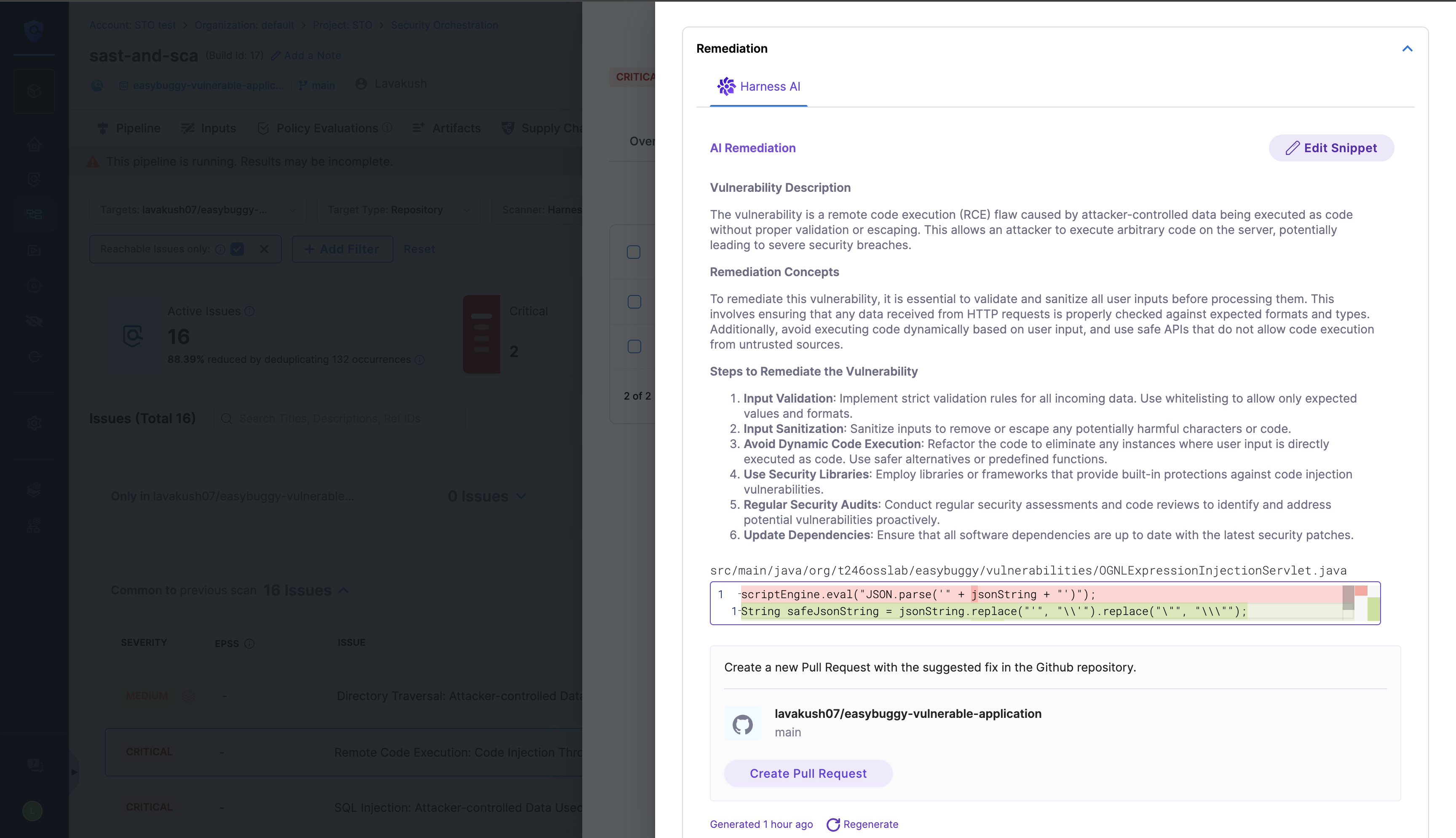
AI remediation for Harness SAST Security Issues
Harness AI analyzes security issues and provides AI remediation within the security details for each specific issue. This includes an analysis of the issue, remediation concepts, and step-by-step instructions to fix them, along with example code snippets. Additionally, AI remediation details can be found for each occurrence of an issue. You also have the option to make a Code Suggestion or create a Pull Request to apply the suggested remediation.
You can view the PR by clicking on the View Fix button. Make sure to read the configuration details to understand the requirements and what is supported for this feature.
Enforce OPA Policy to block the Static Reachable Vulnerabilities
Enforce OPA Policy to automatically warn or block pipelines based on static reachability, exploitability, and license metadata, to help you prevent risky deployments and maintain security and compliance.
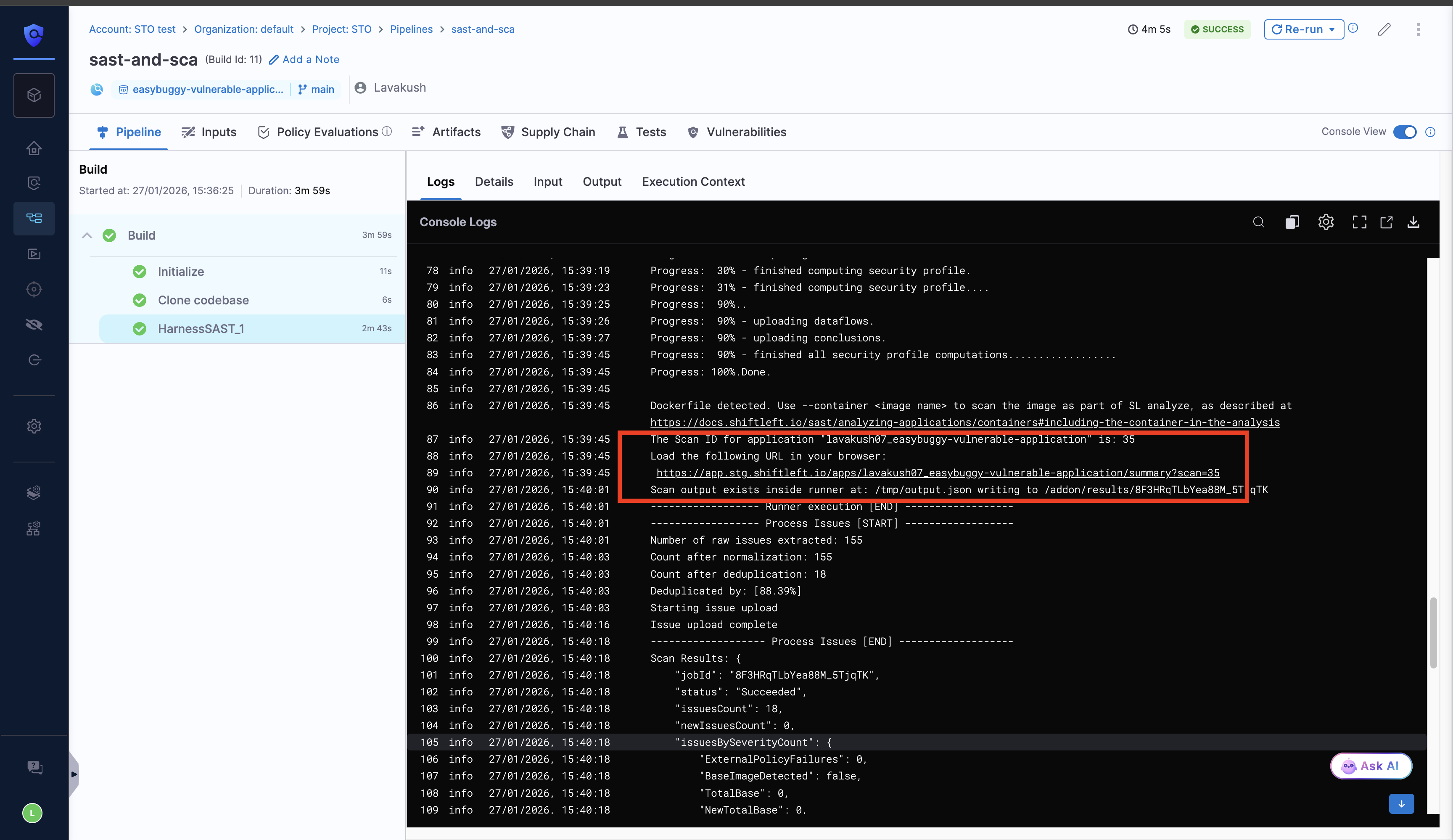
View Harness SAST Scan results in the Qwiet AI Dashboard
After running the Harness SAST scanner in your pipeline in the scan logs, you can click the provided shiftleftlink, which redirects you to the Qwiet AI dashboard, where you can explore detailed scan results and analyze identified issues.
Alternatively, you can manually log in to the Qwiet AI dashboard and search for the application name that corresponds to the target name used in the scan.
You can view the generated SBOM for application dependencies, along with the scan summary and compliance results, in the Qwiet AI by Harness dashboard. These details are currently available only in Qwiet AI by Harness dashboard and are not currently supported in Harness STO.
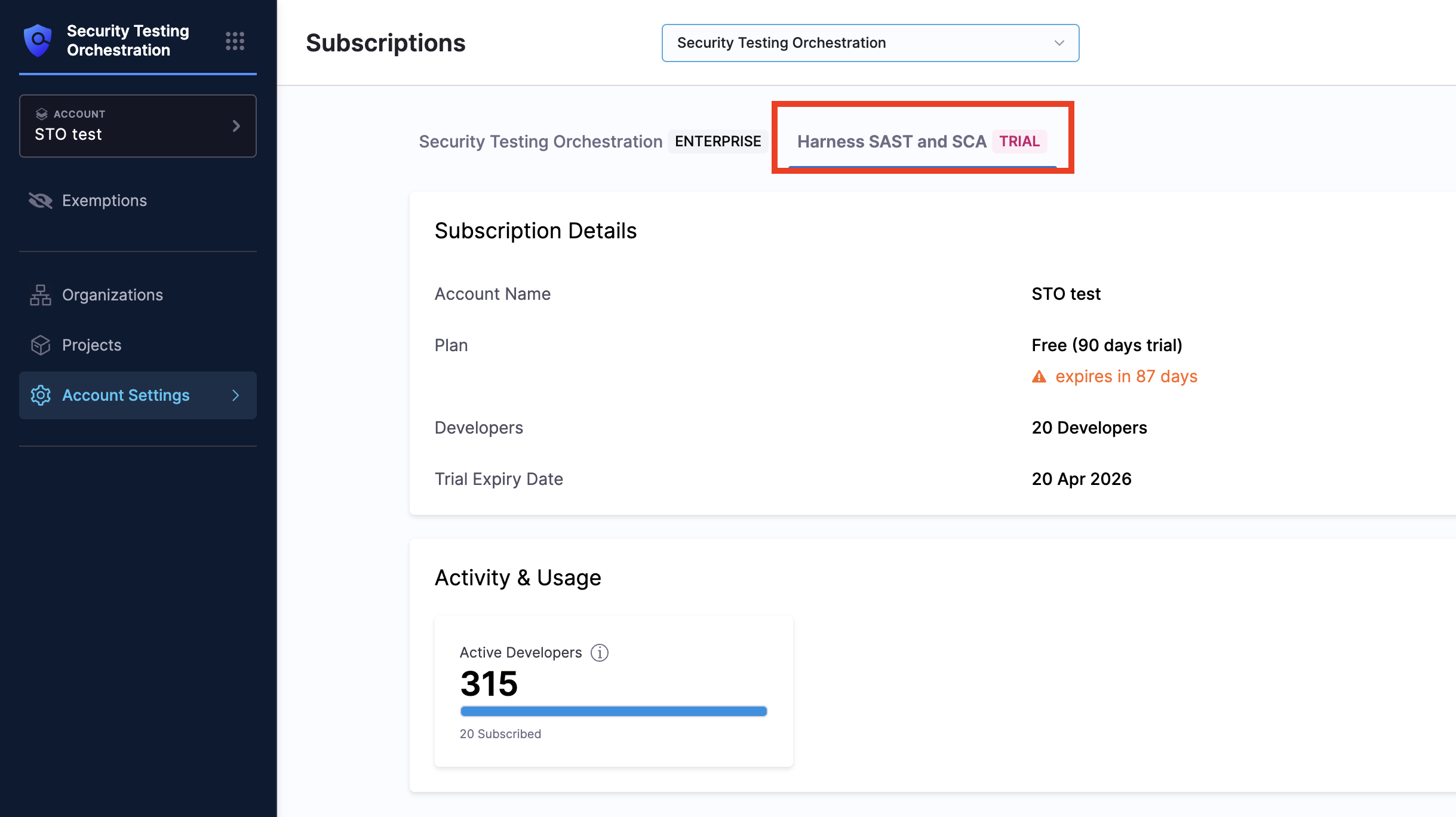
License Usage
Usage is calculated based on Active Developers. An Active Developer is an individual who, within the last 90 days, has created or modified code, configurations, content, or artifacts that are scanned by STO. An individual is counted only once, even if they contribute to multiple scanned repositories.
You can view your current usage and subscription details on the STO subscription page under the Harness SAST and SCA sub-tab.