Maven settings.xml
This topic provides guidance on storing and using Maven settings.xml with Harness CI. It is not exhaustive. This information is provided primarily to address some specific use cases for settings.xml.
Where do I store Maven project settings.xml in Harness CI?
There are several options for handling settings.xml in Harness CI:
- Store
settings.xmlexternally from Harness, such as in a version control repo, and then use a Git Clone or Run step to clone that repo (or subdirectory of a repo) into your pipeline. - Store
settings.xmlas a file secret in Harness and then use a shell script in a Run step to copy the file to the relevant directory when your build runs. - Store values for
settings.xmlas text secrets, and then add those values to a newsettings.xmlfile that is created when your build runs. An example of this is shown in Override secrets in settings.xml at runtime.
You can use expressions to reference secrets in step commands, such as:
cat > settings.xml <<- EOM
<+secrets.getValue("account.[settingsXMLSecretID]")>
EOM
If you need to share settings.xml with multiple steps in the same stage, declare it in Shared Paths. For more information, go to Share data between steps in a stage.
Override secrets in settings.xml at runtime
Use the following steps to override secrets in a Maven settings.xml file by modifying the Build stage settings when the pipeline runs.
These steps assume you have an understanding of the Harness Secret Manager or that you know how to add your own secrets manager. You should also be familiar with adding text secrets, adding file secrets, and adding SSH secrets.
Create a secret at the account scope
Create a text secret at the account scope that contains the content of your settings.xml file.
You need permissions to create, edit, and view secrets at the account scope to be able to do this. For more information, go to the Permission Reference.
- Go to Account Settings, select Account Resources, and then select Secrets.
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
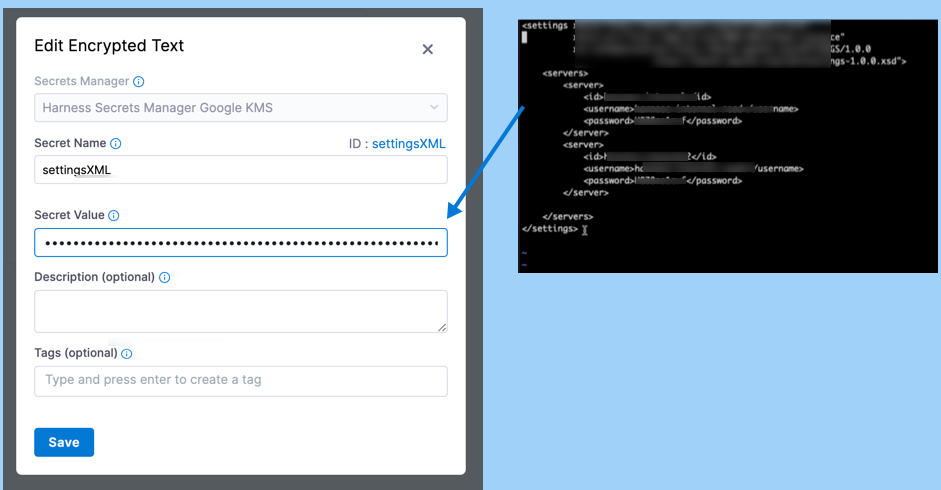
- Enter a Secret Name, such as
settingsXML. Take note of the ID. You need it to reference the secret in your pipeline. - In Secret Value, paste the XML settings content from your
settings.xmlfile, and then select Save.
Transcribe the text secret into settings.xml
Create a new settings.xml file in the Harness working directory (/harness) and include a command in your pipeline to assign the value of your settings XML text secret to that file. To do this, modify the Run step or Test step where your Maven tests run.
- Run or Test step
- Run Tests step (deprecated)
If your Maven tests run in a Run or Test step, add the following to the Command:
cat > settings.xml <<- EOM
<+secrets.getValue("account.settingsXML")>
EOM
If your Maven tests run in a Run Tests step, add the following to the Pre-Command:
cat > settings.xml <<- EOM
<+secrets.getValue("account.settingsXML")>
EOM
Modify the Maven test command
Once the settings.xml file exists in the Harness working directory, Maven can read your text secret from this file if you run mvn test with the -s flag. For example:
mvn test -s settings.xml
Optional: Use the .m2 directory
If your settings.xml file is in the ~/.m2/ directory, Maven can read the secrets from the default location and you don't need to run mvn test with -s flag.
For example, if you can use the following command to transcribe the settings.xml text secret to ~/.m2/:
cat > ~/.m2/settings.xml <<- EOM
<+secrets.getValue("account.settingsXML")>
EOM
And then you only need mvn test to run the test.