Using Secure Connect for Gitspaces
This feature is only relevant for Harness Hosted Gitspaces.
This guide explains how to enable and use Secure Connect for your Harness Hosted Gitspaces. With Secure Connect, you can directly fetch and pull private Docker images from privately-hosted assets, such as internal Artifact Repositories and on-premises repositories.
Secure Connect for Harness Gitspaces is currently gated behind the feature flag CI_SECURE_TUNNEL. To enable this feature, please reach out to support@harness.io.
Secure Connect for Gitspaces
Harness Gitspaces offers the Secure Connect feature, providing a robust and secure proxy solution. This feature allows seamless integration with your on-premises, privately-hosted assets such as Docker Registries and Artifact Repositories. Additionally, you can customize your configurations using proxy environment variables for enhanced flexibility.
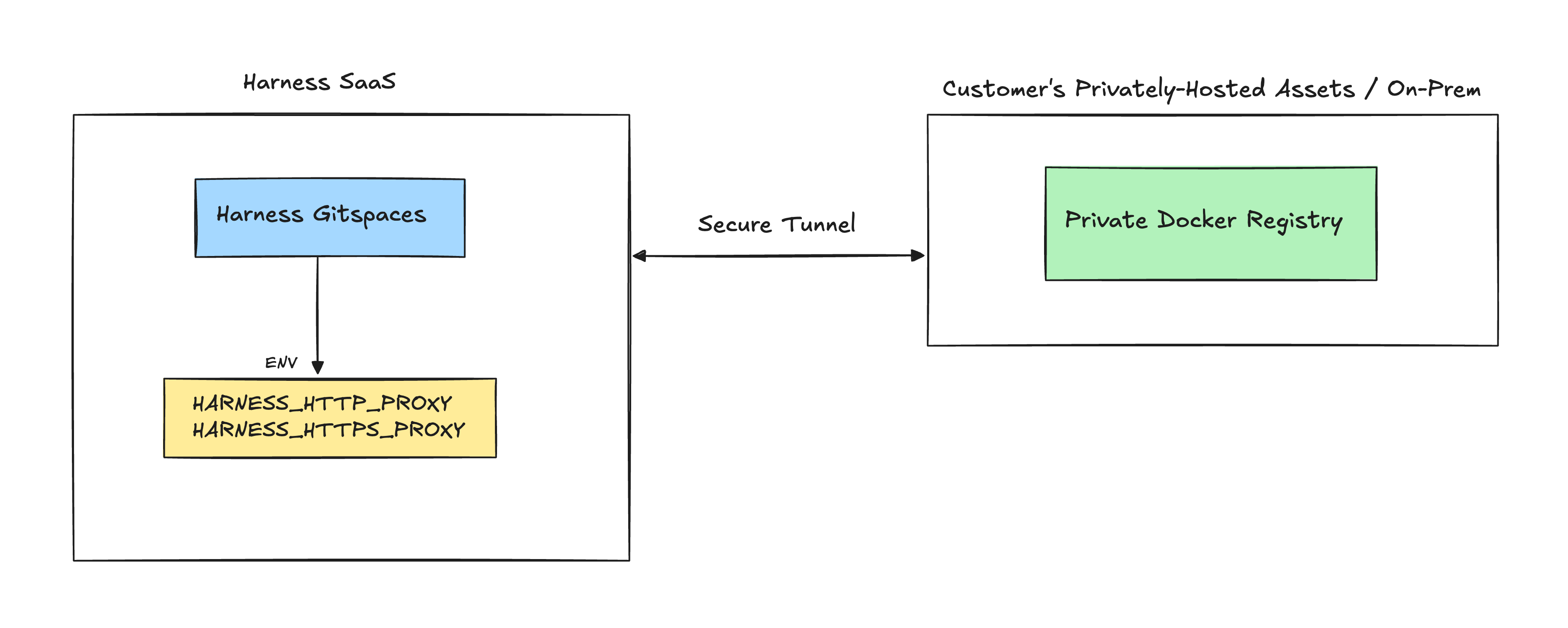
Here’s a step-by-step guide to enabling and using this feature.
Configuring Secure Connect
-
Create a Harness API Key: You can start by creating a Harness API key with at least RBAC:core_pipeline_view and ABAC:All permissions.
-
Run the Secure Connect Docker Client: You’ll have to run a Docker client within your firewalled environment. This client will act as a proxy server in your network, establishing a secure connection with the Harness server. Use the following command to start the client:
docker run -it \
-e REMOTE_PORT=ANY_PORT_FROM_30000_TO_30099 \
-e REMOTE_SERVER=sc.harness.io \
-e API_KEY=YOUR_HARNESS_API_KEY \
harness/frpc-signed- REMOTE_PORT: Specify any port from 30000 to 30099.
- API_KEY: Replace with a valid Harness API key.
-
Enable Secure Connect: Once the client is installed, enable the "Secure Connect" flag while adding your artifact repository connector. (Refer to this guide for detailed steps on adding an artifact repository connector.)
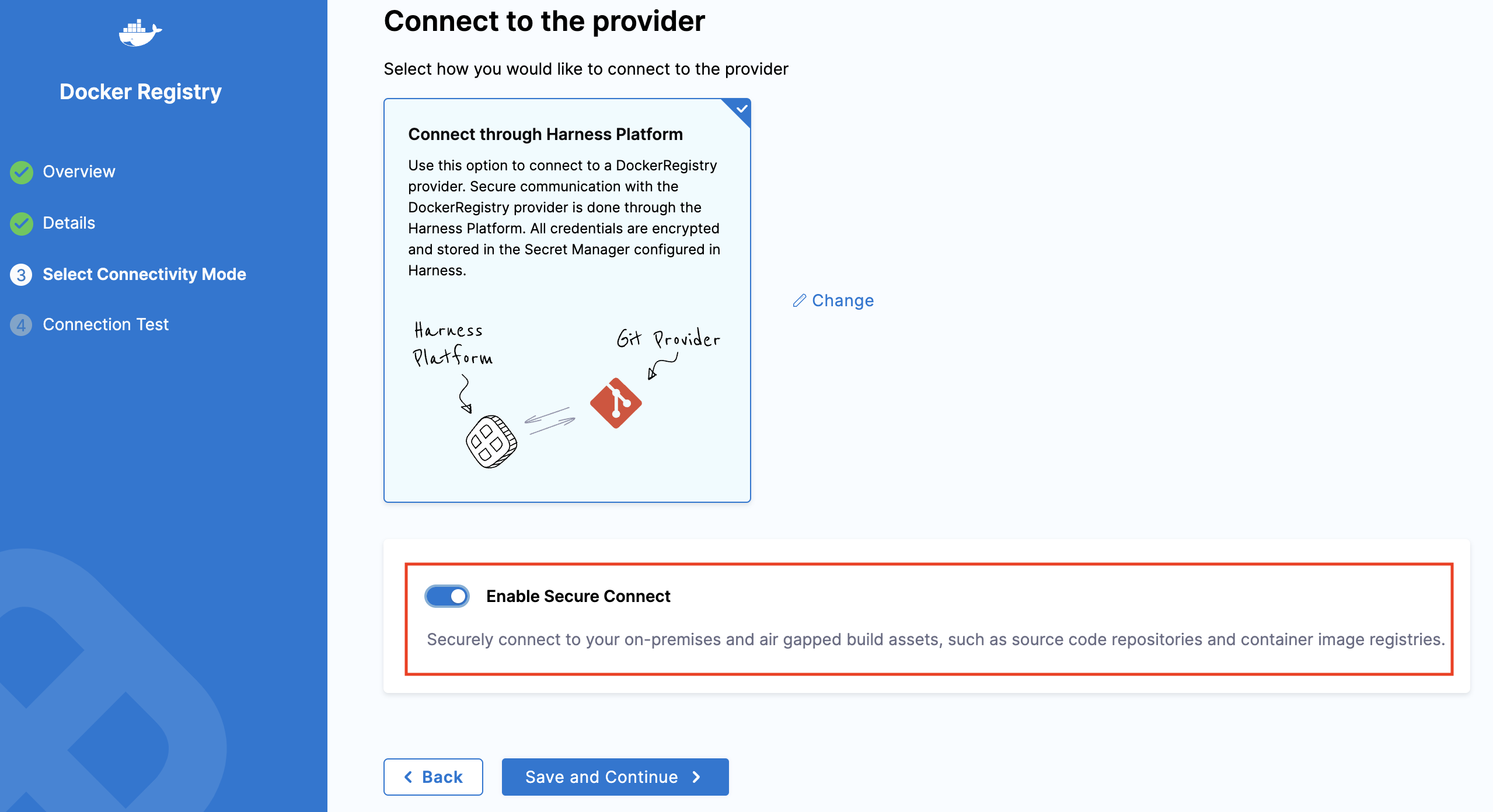
Secure Connect is now successfully configured. You can proceed to create a Gitspace using your privately hosted Docker image. (Follow this guide to learn more.)
Secure Connect Environment Variables
During the Secure Connect setup, the proxy URLs are exposed through the following environment variables: HARNESS_HTTP_PROXY and HARNESS_HTTPS_PROXY. You can configure these environment variables to redirect outbound calls through the specified proxy, ensuring secure and efficient connectivity.
Example Configuration
You can configure your proxy settings in the following way:
$ env | grep -i PROXY
HARNESS_HTTPS_PROXY=https://<username>:<password>@sc.harness.io:<port>
HARNESS_HTTP_PROXY=http://<username>:<password>@sc.harness.io:<port>
Now, you can configure Gradle to use a proxy server for downloading plugins or dependencies explicitly specified. You can define the proxy settings in the gradle.properties file:
# Proxy settings for Gradle
systemProp.http.proxyHost=sc.harness.io
systemProp.http.proxyPort=<port>
systemProp.https.proxyHost=sc.harness.io
systemProp.https.proxyPort=<port>
systemProp.http.proxyUser=<username>
systemProp.http.proxyPassword=<password>
systemProp.https.proxyUser=<username>
systemProp.https.proxyPassword=<password>
Now when you'll run gradle build, Gradle downloads plugins and dependencies specified in the build.gradle file. With these proxy settings, Gradle will route all its HTTP and HTTPS requests through the proxy server.