Use the HTTP step to set unsupported fields when creating Jira issues
This article talks about using the HTTP step to set the fields that are not supported by Harness using an example.
By default, Harness doesn't support cascading lists and other custom field types. For the list of supported Jira fields, go to Add issue fields.
We will discuss how to set a cascading list using the HTTP step. This unblocks integration with Jira projects that mark such fields as mandatory.
Create a pipeline with a Custom stage and configure the following steps under the Execution tab of the pipeline.
Configure the HTTP step
In the HTTP step's Step Parameters, configure the following fields.
-
URL: Enter your Jira server details. For example,
https://<your_JIRA_domain>/rest/api/2/issue. -
Method: Select POST HTTP method.
-
Request Body: Enter the cURL command to create a task in project
TESwith a summary and cascading field with IDcustomfield_10500. Here's a sample:{
"fields": {
"project": {
"key": "TES"
},
"summary": "Testing select list (cascading)",
"issuetype": {
"id": "10003"
},
"customfield_10500": {
"value": "Parent 1",
"child": {
"value": "P1 Child 1"
}
}
}
} -
Optional Configuration: Enter the following optional configurations.
- Headers: Enter the following Key:Value information:
- Content-Type:
application/json - Authorization:
Basic <authorization_key_to_your_Jira_server>
- Content-Type:
- Output: Enter the variable name and value to get the Jira Issue Id from the pipeline output. For example:
- Variable Name:
<issue_key> - Value: Choose Expression input type and enter
<+json.select("key", httpResponseBody)>
- Variable Name:
- Headers: Enter the following Key:Value information:
Configure the Jira Update step
Now, create a Jira Update step to update the Jira issue as a step during pipeline execution.
In the Jira Update step's Step Parameters, configure the following fields.
- Jira Connector: Select your Jira connector.
- Issue Key: Enter the Jira issue key as an expression:
<+pipeline.stages.testJiraCustomFields.spec.execution.steps.Http_1.output.outputVariables.issue_key>.
Sample pipeline YAML
Here's a sample pipeline:
pipeline:
name: testJiraCustomFields
identifier: testJiraCustomFields
projectIdentifier: testNaman
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: testJiraCustomFields
identifier: testJiraCustomFields
description: ""
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Http
name: Http_1
identifier: Http_1
spec:
url: https://<your_JIRA_domain>/rest/api/2/issue
method: POST
headers:
- key: Content-Type
value: application/json
- key: Authorization
value: Basic <authorization_key_to_your_Jira_server>
inputVariables: []
outputVariables:
- name: issue_key
value: <+json.select("key", httpResponseBody)>
type: String
requestBody: |-
{
"fields": {
"project": {
"key": "TES"
},
"summary": "Testing select list (cascading)",
"issuetype": {
"id": "10003"
},
"customfield_10500": {
"value": "Parent 1",
"child": {
"value": "P1 Child 1"
}
}
}
}
assertion: <+httpResponseCode>==201
timeout: 10s
- step:
type: JiraUpdate
name: JiraUpdate_1
identifier: JiraUpdate_1
spec:
connectorRef: jiraServer
issueKey: <+pipeline.stages.testJiraCustomFields.spec.execution.steps.Http_1.output.outputVariables.issue_key>
fields:
- name: Assignee
value: aut************@mailinator.com
- name: Description
value: This is updated description
- name: Priority
value: Medium
issueType: Task
projectKey: TES
timeout: 10m
tags: {}
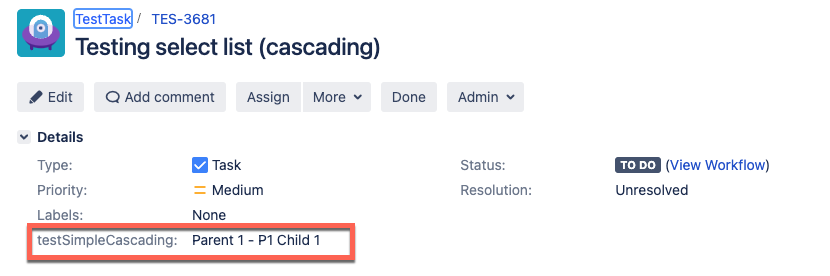
Viewing the cascading list in the Jira issue
After configuring the HTTP and Jira Update steps, run the pipeline. From the pipeline Output tab, copy the issue URL. In the Jira issue, you can see the cascading field as shown in the image below: