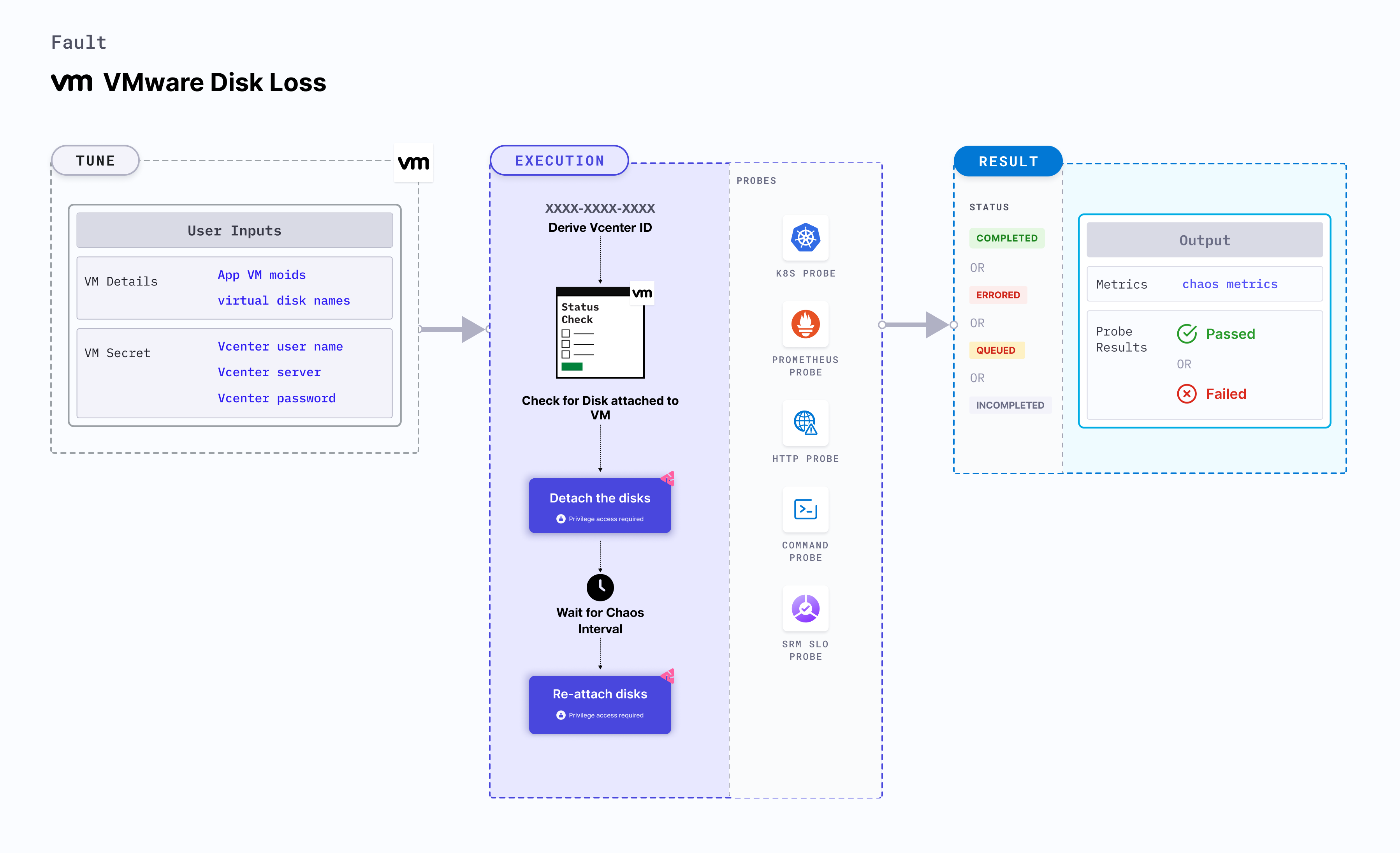
VMware disk loss
VMware disk loss detaches the disks that are attached to a Linux OS based VMware VM.
Use cases
- VMware disk loss determines the resilience of an application to the unplanned scaling of K8s pods.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes > 1.16 is required to execute this fault.
- The VM should be in a healthy state before and after injecting chaos.
- The target disks should be attached to the VM.
- Execution plane should be connected to vCenter and host vCenter on port 443.
- VMware tool should be installed on the target VM with remote execution enabled.
- Appropriate vCenter permissions should be provided to access the hosts and the VMs.
- Create a Kubernetes secret that has the Vcenter credentials in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. Below is a sample secret file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vcenter-secret
namespace: litmus
type: Opaque
stringData:
VCENTERSERVER: XXXXXXXXXXX
VCENTERUSER: XXXXXXXXXXXXX
VCENTERPASS: XXXXXXXXXXXXX
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| APP_VM_MOIDS | MOIDs of the VMware instance. After you open the VM in VCenter WebClient, you can find the MOID in the address field (VirtualMachine:vm-5365). Alternatively you can use the CLI to fetch the MOID. | For example, vm-5365. For more information, go to MOIDs of the VMware instance. |
| VIRTUAL_DISK_NAMES | Name of the target disks provided as comma-separated values. | For example, disk-1.vmdk,disk-2.vmdk. For more information, go to virtual disk names. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Defaults to 30s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | Time interval between two successive instance terminations (in seconds). | Defaults to 30s. For more information, go to chaos interval. |
| SEQUENCE | Sequence of chaos execution for multiple instances. | Defaults to parallel. Supports serial sequence as well. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
| DEFAULT_HEALTH_CHECK | Determines if you wish to run the default health check which is present inside the fault. | Default: 'true'. For more information, go to default health check. |
Virtual disk names
It specifies the name of the target disks attached to a particular VM. Tune it by using the VIRTUAL_DISK_NAMES environment variable.
Use the following example to tune it:
# Disk loss in the VMware VM
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: VMware-disk-loss
spec:
components:
env:
# Name of the VM
- name: APP_VM_MOIDS
value: 'vm-2055'
# Name of target disk
- name: VIRTUAL_DISK_NAMES
value: 'disk-1.vmdk'