ECS container network latency
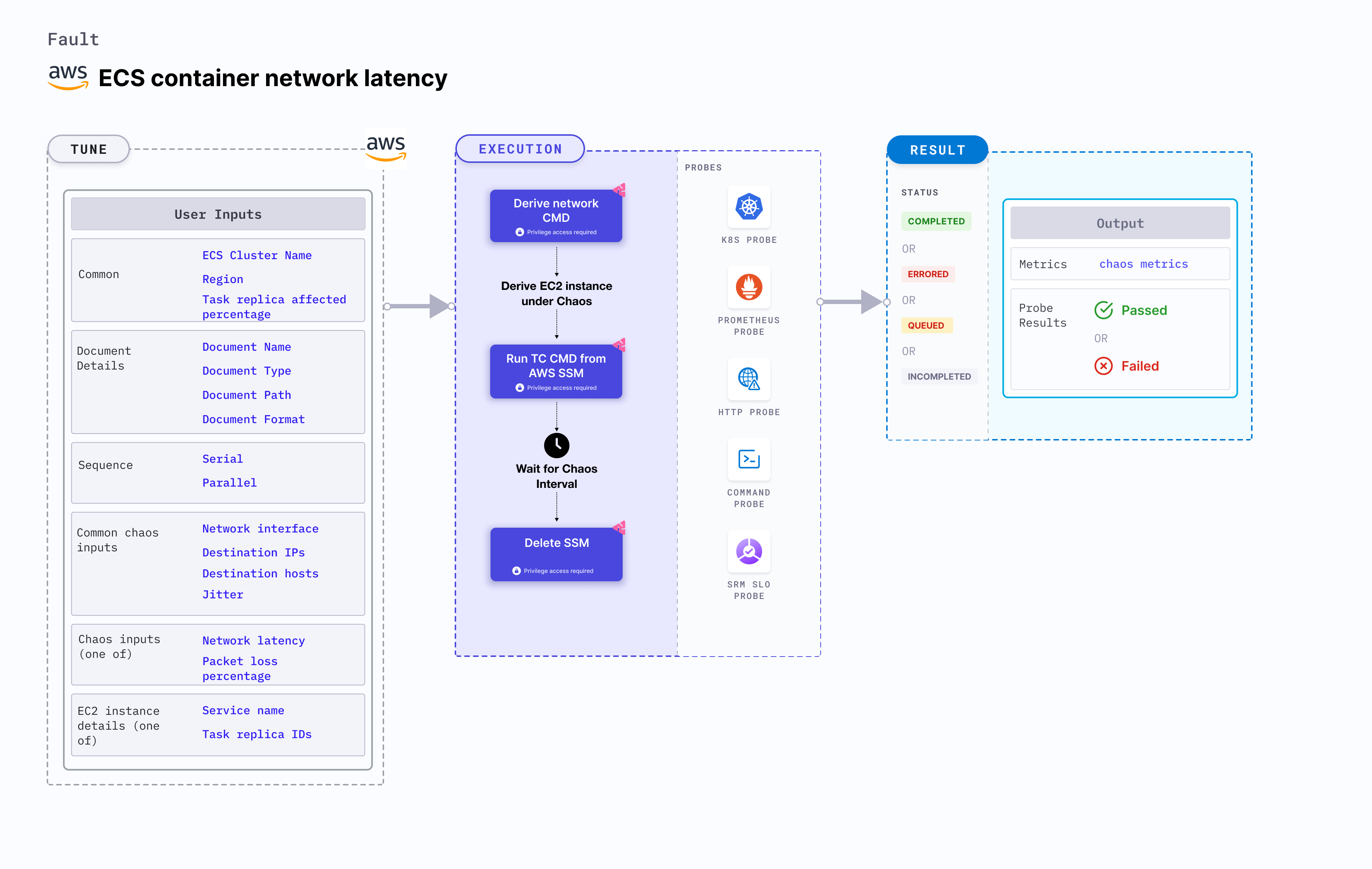
ECS container network latency disrupts the state of infrastructure resources. It brings delay on the AWS ECS container using Amazon SSM Run command, which is carried out using SSM docs which is in-built into the fault.
- It causes network stress on the containers of the ECS task using the given
CLUSTER_NAMEenvironment variable for a specific duration. - To select the Task Under Chaos (TUC), use the service name associated with the task. If you provide the service name along with the cluster name, all the tasks associated with the given service will be selected as chaos targets.
- It tests the ECS task sanity (service availability) and recovery of the task containers subject to network stress.
- This experiment induces chaos within a container and depends on an EC2 instance. Typically, these are prefixed with "ECS container" and involve direct interaction with the EC2 instances hosting the ECS containers.
Use cases
This fault degrades the network of the task container without the container being marked as unhealthy/ (or unworthy) of traffic. It simulates issues within the ECS task network or communication across services in different availability zones (or regions). This can be resolved using middleware that switches traffic based on certain SLOs (or performance parameters). This can also be resolved by highlighting the degradation using notifications (or alerts). It also determines the impact of the fault on the microservice. The task may stall or get corrupted while waiting endlessly for a packet. The fault limits the impact (blast radius) to only the traffic you wish to test by specifying the service to find TUC (Task Under Chaos). This fault helps improve the resilience of the services over time.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes >= 1.17
- Adequate AWS access to stop and start an EC2 instance.
- Create a Kubernetes secret that has the AWS access configuration(key) in the
CHAOS_NAMESPACE. Below is a sample secret file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: cloud-secret
type: Opaque
stringData:
cloud_config.yml: |-
# Add the cloud AWS credentials respectively
[default]
aws_access_key_id = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
aws_secret_access_key = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
HCE recommends that you use the same secret name, that is, cloud-secret. Otherwise, you will need to update the AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE environment variable in the fault template with the new secret name and you won't be able to use the default health check probes.
Below is an example AWS policy to execute the fault.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:UpdateContainerInstancesState",
"ecs:RegisterContainerInstance",
"ecs:ListContainerInstances",
"ecs:DeregisterContainerInstance",
"ecs:DescribeContainerInstances",
"ecs:ListTasks",
"ecs:DescribeClusters"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssm:GetDocument",
"ssm:DescribeDocument",
"ssm:GetParameter",
"ssm:GetParameters",
"ssm:SendCommand",
"ssm:CancelCommand",
"ssm:CreateDocument",
"ssm:DeleteDocument",
"ssm:GetCommandInvocation",
"ssm:UpdateInstanceInformation",
"ssm:DescribeInstanceInformation"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2messages:AcknowledgeMessage",
"ec2messages:DeleteMessage",
"ec2messages:FailMessage",
"ec2messages:GetEndpoint",
"ec2messages:GetMessages",
"ec2messages:SendReply"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
- The ECS container instance should be in a healthy state.
- Refer to AWS Named Profile For Chaos to know how to use a different profile for AWS faults.
- Refer to the superset permission/policy to execute all AWS faults.
- Refer to the common attributes and AWS-specific tunables to tune the common tunables for all faults and aws specific tunables.
Mandatory tunables
| Variables | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CLUSTER_NAME | Name of the target ECS cluster. | For example, cluster-1. |
| REGION | Region name of the target ECS cluster. | For example, us-east-1. |
Optional tunables
| Variables | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration that you specify, through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| CHAOS_INTERVAL | Interval between successive instance terminations (in seconds). | Default: 30 s. For more information, go to chaos interval. |
| AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE | Path to the AWS secret credentials. | Defaults to /tmp/cloud_config.yml. |
| SERVICE_NAME | Target ECS service name. | For example, app-svc. For more information, go to ECS service name. |
| NETWORK_LATENCY | Latency you wish to induce within the service (in milliseconds). | Default: 2000 ms. For more information, go to latency. |
| DESTINATION_IPS | IP addresses of the services or the CIDR blocks(range of IPs), the accessibility to which is impacted | Comma-separated IP(S) or CIDR(S) can be provided. if not provided, it will induce network chaos for all ips/destinations. For more information, go to destination IPs. |
| DESTINATION_HOSTS | DNS Names of the services, the accessibility to which, is impacted | If not provided, it will induce network chaos for all ips/destinations or DESTINATION_IPS if already defined. For more information, go to destination hosts. |
| NETWORK_INTERFACE | Name of ethernet interface considered for shaping traffic | Default: eth0. For more information, go to network interface. |
| JITTER | Specify the value of jitter. | Default: 0. For more information, go to jitter. |
| SEQUENCE | It defines sequence of chaos execution for multiple instance | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
Network latency
Delay (in ms) to be injected in the target container. Tune it by using the NETWORK_LATENCY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# injects network latency for a certain chaos duration
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# network latency to be injected
- name: NETWORK_LATENCY
value: '2000' #in ms
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
Network interface
Name of the ethernet interface considered for shaping traffic. Tune it by using the NETWORK_INTERFACE environment variable. Its default value is eth0.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# provide the network interface
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# name of the network interface
- name: NETWORK_INTERFACE
value: 'eth0'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
Jitter
Jitter (in ms), a parameter that allows introducing a network delay variation. Tune it by using the JITTER environment variable. Its default value is 0.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# provide the network latency jitter
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# value of the network latency jitter (in ms)
- name: JITTER
value: '200'
Destination IPs and destination hosts
The network faults interrupt traffic for all the IPs/hosts by default. Tune the interruption of specific IPs/Hosts using DESTINATION_IPS and DESTINATION_HOSTS environment variables.
DESTINATION_IPS: It contains the IP addresses of the services or pods or the CIDR blocks(range of IPs), the accessibility to which is impacted.DESTINATION_HOSTS: It contains the DNS Names/FQDN names of the services, the accessibility to which, is impacted.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it inject the chaos for the ingress/egress traffic for specific ips/hosts
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-container-network-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# supports comma-separated destination ips
- name: DESTINATION_IPS
value: '8.8.8.8,192.168.5.6'
# supports comma-separated destination hosts
- name: DESTINATION_HOSTS
value: 'nginx.default.svc.cluster.local,google.com'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
ECS service name
Service name whose tasks are stopped. Tune it by using the SERVICE_NAME environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# stop the tasks of an ECS cluster
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: ecs-task-stop
spec:
components:
env:
# provide the name of ECS cluster
- name: CLUSTER_NAME
value: 'demo'
- name: SERVICE_NAME
vale: 'test-svc'
- name: REGION
value: 'us-east-1'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'