Linux process kill
The Linux process kill fault kills the target processes running on the Linux machines. It checks the performance of the application or process running on the Linux machine.
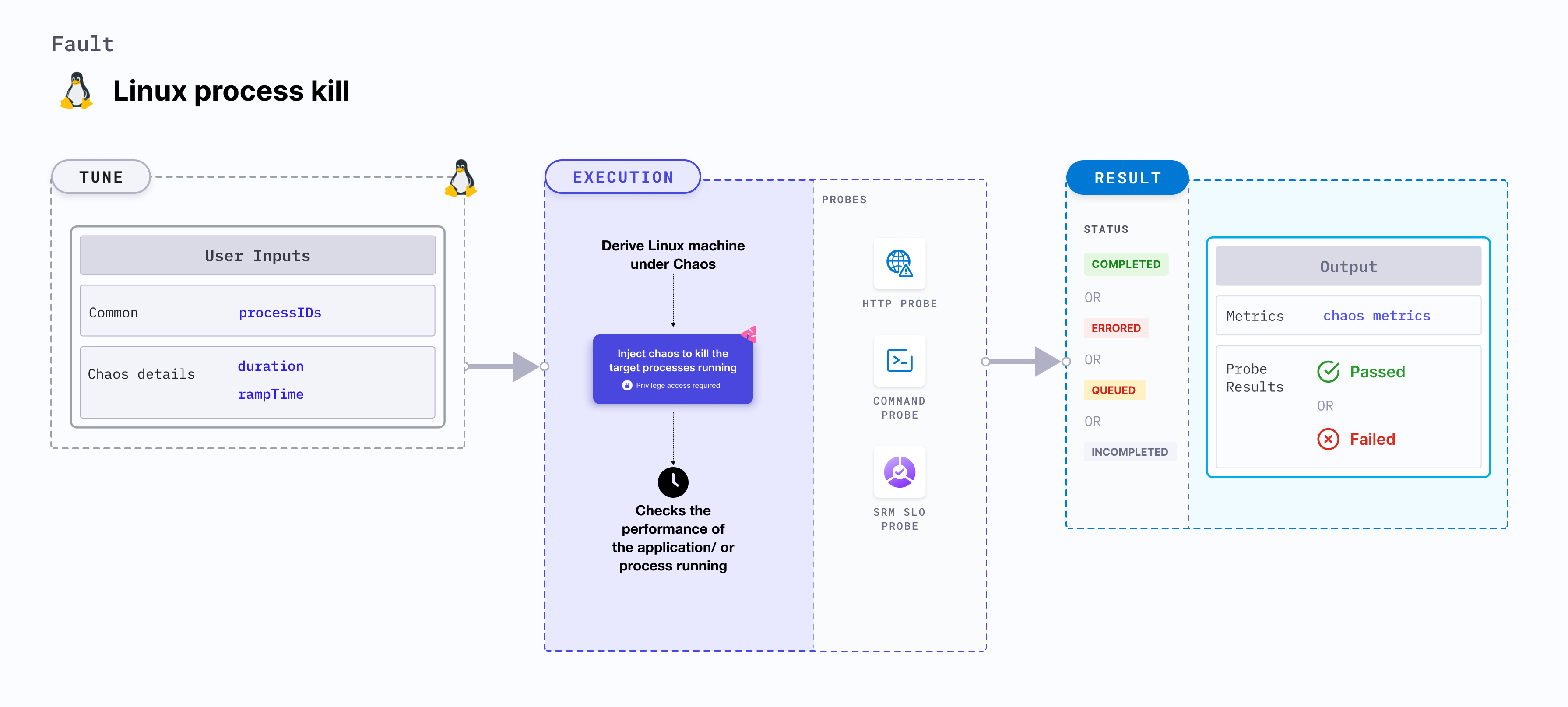
Use cases
Linux process kill:
- Induces process kill on the target Linux machines.
- Disrupts the application-critical processes such as databases or message queues by killing the underlying processes or threads.
- Determines the resilience of applications when processes on a Linux machine are unexpectedly killed (or disrupted).
- This fault can be executed on Ubuntu 16 or higher, Debian 10 or higher, CentOS 7 or higher, RHEL 7 or higher, Fedora 30 or higher, and openSUSE LEAP 15.4 or higher.
- The
linux-chaos-infrastructuresystemd service should be in an active state, and the infrastructure should be inCONNECTEDstate.
Fault permissions
The fault uses the root Linux user and root user group.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| processIDs | Comma-separated process IDs of the target processes. | Takes precedence over processNames and processCommand when all three parameters are defined. For example, 13453,32444,27436 |
| processCommand | Command used to start the target processes. A substring match is performed to determine the target process. | Takes precedence over processNames when both are defined. For example, /usr/lib64/thunderbird/thunderbird |
| processNames | Comma-separated target process names. | For example, nginx,redis |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| forceKill | Whether to force kill the process using the SIGKILL signal or SIGTERM signal for graceful killing. | Default: false. |
| Duration | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 30s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
| rampTime | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 0s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
Process IDs
The processIDs input variable targets process IDs to kill.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# process ids of target processes
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-process-kill
labels:
name: process-kill
spec:
processKillChaos/inputs:
processIDs: "13453,32444,27436"
duration: 30s
Process names
The processNames input variable targets process names to kill.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# process names of target processes
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-process-kill
labels:
name: process-kill
spec:
processKillChaos/inputs:
processNames: "nginx,redis"
duration: 30s
Process command
The processCommand input variable targets the processes, based on the command used to start processes, if available. A substring match is made on the given command to determine the target processes.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# process command of the target process
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-process-kill
labels:
name: process-kill
spec:
processKillChaos/inputs:
processCommand: "/usr/lib64/thunderbird/thunderbird"
duration: 30s
Force kill
The forceKill input variable specifies whether to force kill the target processes using the SIGKILL signal or gracefully kill the target processes with the SIGTERM signal.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
# force kill processes
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-process-kill
labels:
name: process-kill
spec:
processKillChaos/inputs:
processNames: "nginx"
duration: 30s
forceKill: true