Install using Helm
This document explains how to use Helm to install, upgrade, or uninstall Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition. This document describes an installation on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The same installation process, however, applies to installations on Kubernetes versions 1.x and later.
Helm package manager provides a declarative approach to Kubernetes application management in which software packages are specified as "charts." For more information, go to the Helm documentation.
Helm client version compatibility
Harness validates Helm client compatibility against the following versions:
- 3.9.4
- 3.10.3
- 3.11.3
- 3.12.3
- 3.13.3
- 3.14.2
You can also install Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition in an air-gapped environment. For more information, go to Install in air-gapped environment.
Role requirements
The account you use to install Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition must have the Account Admin role to create service accounts. For more information on role-based permissions, go to RBAC in Harness.
Update the override.yaml file
Helm chart values, default value definitions, and field descriptions are available in the Harness Helm chart repo.
Depending on your target environment, you'll need to update the override.yaml file to specify a load balancer or to specify the Harness modules to be deployed.
Add a load balancer
You can use either Istio or Nginx as your ingress controller based on your specific technical requirements. Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition integrates with your chosen solution, providing enhanced traffic management, security, and streamlined DevOps workflows.
Use the following procedure to add a load balancer.
- NLB
- Ingress ALB
To add the URL for a load balancer, do the following:
-
In the
values.yamlfile, set theglobal.loadbalancerURLfield to the URL of your load balancer. This is the URL you use for Harness.global:
# -- Harness Application URL
loadbalancerURL: http://<load-balancer-IP-address> -
Set the
host_namefield to the IP address of the load balancer. -
Save the file.
To an ingress ALB, do the following:
-
Copy the following YAML, then save it to an
ingress-alb.yamlfile.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/inbound-cidrs: 10.0.0.0/8
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP":80}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-attributes: deletion_protection.enabled=false
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internal
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-policy: ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS-1-2-Ext-2018-06
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/subnets: <subnets>
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes: stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=300
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
ingress.kubernetes.io/tls-minimum-version: "1.2"
name: harness-public-ingress
namespace: harness
spec:
ingressClassName: alb
rules:
- host: <YOUR_HOST_URL>
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: harness-ingress-controller
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix -
Replace
<YOU_HOST_URL>with your load balancer's URL. -
Replace
<YOUR_SUBNETS>with your subnets.This sets traffic to internal only
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internal. -
Run the following command.
kubectl apply -f ingress-alb.yaml -n <namespace>
Optional: Configure a vanity URL based on your load balancer
You can use the script provided below to configure a vanity URL based on your load balancer. The script is available in the Harness Helm chart and also accessible at the following path within your Helm manifest: harness/configure-vanity-url.sh.
Prerequisites
Before using this script, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- You must have a subdomain URL mapped to your load balancer's static IP. The subdomain URL must adhere to one of the following example formats:
http://mysubdomain.mysite.comhttps://mysubdomain.mysite.com
Execution
Execute this script within your cluster environment, providing three argument inputs:
- Namespace
- Account ID
- Subdomain URL
if [ "$#" -ne 3 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <namespace> <accountId> <subdomainUrl>"
exit 1
fi
# Assign the first argument to namespace
namespace="$1"
# Assign the second argument to accountId
accountId="$2"
# Assign the second argument to subdomainUrl
subdomainUrl="$3"
MONGO_PASS=$(kubectl get secret -n $namespace mongodb-replicaset-chart -o jsonpath={.data.mongodb-root-password} | base64 --decode)
kubectl exec -it mongodb-replicaset-chart-0 -n $namespace -- mongo <<EOF
use admin
db.auth('admin', '${MONGO_PASS}')
use gateway
db.account_refs.update({"uuid":"${accountId}"},{\$set:{"subdomainUrl": "${subdomainUrl}"}})
db.account_refs.find()
use harness
db.accounts.update({"_id":"${accountId}"},{\$set:{"subdomainUrl": "${subdomainUrl}"}})
db.accounts.find()
EOF
kubectl patch configmap ng-auth-ui -n $namespace --type merge -p '{"data":{"EXPECTED_HOSTNAME":"app.harness.io"}}'
kubectl rollout restart -n $namespace deployment -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=ng-auth-ui"
The app.harness.io value in the command, kubectl patch configmap ng-auth-ui -n $namespace --type merge -p '{"data":{"EXPECTED_HOSTNAME":"app.harness.io"}}' should NOT be replaced with your created subdomain value, it should be set to "app.harness.io" itself.
Example command
The example command below executes the configure-vanity-url.sh script file for the mynamespace namespace, abc123 account ID, and http://smp.harnessurl.com subdomain URL.
./configure-vanity-url.sh mynamespace abc123 http://smp.harnessurl.com
Deploy Harness modules
Harness Helm chart includes Harness Platform components. You can add modules by editing the override.yaml file.
The Platform component and the module below is enabled by default:
- Harness Continuous Deployment (CD) - Next Generation
The Harness modules below can be enabled or disabled conditionally:
- Harness Chaos Engineering (CE)
- Harness Cloud Cost Management (CCM)
- Harness Continuous Integration (CI)
- Harness Security Testing Orchestration (STO)
- Harness Service Reliability Management (SRM)
- Harness Feature Flags (FF)
- Harness Supply Chain Security (SCS)
You can conditionally disable or enable the modules by specifying a boolean value in the enabled field of the YAML:
Deploy the CI module
ci:
# -- Enable to deploy CI to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the SRM module
srm:
# -- Enable to deploy SRM to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the FF module
ff:
# -- Enable to deploy FF to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the STO module
sto:
# -- Enable to deploy STO to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the CCM module
ccm:
# -- Enable to deploy Cloud Cost Management (CCM) to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the CE module
chaos:
# -- Enable to deploy Chaos Engineering (CE) to your cluster
enabled: true
Deploy the SCS module
ssca:
# -- Enable to deploy SSCA to your cluster
enabled: true
Add a Harness license
Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition needs a license to be provisioned for the Harness NextGen platform. Contact Harness Support to procure the license and add it to the override.yaml file.
license:
# -- Insert NG License String to enable NG license
ng: ''
Install the Helm chart
To use the charts, you must install Helm. To get started with Helm, go to the Helm documentation. After you install Helm, follow the instructions below.
To install the Helm chart, do the following:
-
Add the repository.
helm repo add harness https://harness.github.io/helm-charts -
Create a namespace for your installation.
kubectl create namespace <namespace> -
Modify the
override.yamlfile with your environment settings. -
Install the Helm chart.
helm install my-release harness/harness -n <namespace> -f override.yaml
Verify the installation
After the installation completes, the services that were installed are enumerated with their status.
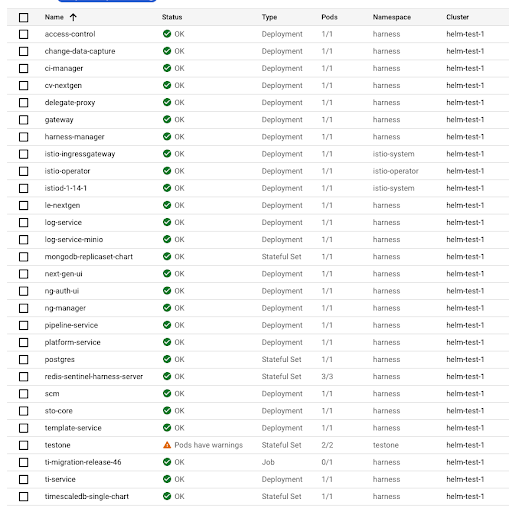
The services that appear depend on the modules that were installed.
To verify installation, do the following:
-
Review the list of services.
-
In your browser, type the following instruction:
http://<load-balancer-IP-address>/auth/#/signupIf the installation was successful, the Harness Sign up page appears.
Helm chart values
For details about the chart values, explanations of the default values, and descriptions of the fields, go to https://github.com/harness/helm-charts#values.
Use self-signed certificates with Helm-based installations
There are additional steps for self-signed certificates:
- Install delegates with custom certificates
- Configure a Kubernetes build farm to use self-signed certificates
- Configure GitOps Agent with self-signed certificates
Next steps
After installation is complete, you should create the initial Harness account, and then create organizations and projects.
To get started with the modules, review the following topics:
- For Harness Continuous Integration, go to the CI key concepts.
- For Harness Continuous Delivery & GitOps, go to the CD key concepts.
- For Harness Security Testing Orchestration, go to the STO overview.
- For Harness Chaos Engineering, go to Get started with Harness Chaos Engineering.
- For Harness Cloud Cost Management, go to Manage cloud costs by using Harness Self-Managed Enterprise Edition.