Build Intelligence Overview
Build Intelligence is part of Harness CI Intelligence, a suite of features in Harness CI designed to improve build times. By storing these outputs remotely and retrieving them when inputs haven't changed, Build Intelligence avoids unnecessary rebuilds, significantly accelerating the build process and enhancing efficiency.
Build Intelligence is currently available for Gradle, Bazel and Maven build tools. Regardless of the programming language used in your projects, as long as you're building with a supported build tool, you can leverage Build Intelligence to optimize your builds.
Build Intelligence is now available in beta for the Maven build tool (version 3.9+). To join the beta program, please contact Harness Support or your account representative.
- Build Intelligence is now Generally Available (GA).
- Build Intelligence is enabled by default for newly created CI stages. This is configurable in CI default settings.
- Build Intelligence currently supports Linux only (AMD and ARM).
- Build Intelligence currently supports Cloud and Kubernetes Build infrastructures only.
Using Build Intelligence
Build Intelligence seamlessly integrates into your workflow without requiring changes to your build commands. Harness automatically detects supported build tools in your pipeline and injects the necessary configurations into the relevant files within the build workspace. This ensures Build Intelligence optimizes your builds during Gradle or Bazel operations performed in Test or Run steps.
To enable Build Intelligence, use the UI editor to enable the stage property Build Intelligence in Build stage overview tab. Alternatively, it can be enabled from YAML editor as shown below.
Below is an example of a CI stage using Build Intelligence:
- stage:
identifier: build
name: build
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
buildIntelligence:
enabled: true # Build intelligence enabled
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Action
name: Set up Gradle
identifier: Set_up_Gradle
spec:
uses: gradle/gradle-build-action@v2
with:
gradle-version: "8.5"
- step:
type: Run
name: build
identifier: build
spec:
shell: Sh
command: ./gradlew build --profile # '--profile' is optional but advised for gradle
You can also enable or disable Build Intelligence based on an expression directly in the YAML. For example, you can conditionally set whether Build Intelligence is on or off using a pipeline variable expression like <+pipeline.variables.someVar>.
- Harness Cloud
- Self Hosted
The cache storage limit depends on your subscription plan type. Please visit Subscriptions and licenses page to learn more about usage limits.
Harness doesn't limit the number of caches you can store, but, once you reach your storage limit, Harness continues to save new caches by automatically evicting old caches.
The cache retention window is 15 days, which resets whenever a cache is updated.
- Build Intelligence is only supported for Kubernetes on self-hosted build infrastructure.
- By default, Build Intelligence uses port 8082, and downloads the Build Intelligence plugin from Maven Central. You can change the default behaviour in CI default settings.
- When using a Build Intelligence with self-hosted infrastructure, an S3-compatible bucket is required for cache storage. Please visit configure default S3-compatible object storage for more information.
- By default, the Build Intelligence step configures a proxy on port 8082. However, for self-hosted setups, you can configure the port by setting the stage variable
CACHE_SERVICE_HTTPS_BIND, or in CI default settings.
Example Pipeline YAML:
pipeline:
projectIdentifier: YOUR_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: default
properties:
ci:
codebase:
connectorRef: YOUR_CONNECTOR_REF
build: <+input>
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
caching:
enabled: false
buildIntelligence:
enabled: true
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: k8
namespace: harness-delegate-ng
os: Linux
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_1
identifier: Run_1
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_IMAGE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR
image: gradle:8.1.1-jdk17
shell: Sh
command: |-
./gradlew build
variables:
- name: MAVEN_URL
type: String
required: false
value: https://your-artifactory-domain/artifactory/your-repository/
- name: CACHE_SERVICE_HTTPS_BIND
type: String
description: "Custom port for self-hosted Build Intelligence proxy"
required: false
value: "8284" # Example custom port
identifier: YOUR_PIPELINE_ID
name: YOUR_PIPELINE_NAME
- By default, the Build Intelligence plugin is downloaded from Maven Central. If your environment does not have access to Maven Central or you prefer using a custom Maven repository, you can configure this by setting a stage variable named
MAVEN_URL, or in CI default settings. See Build Intelligence plugin
How does Build Intelligence work
Harness auto-detects supported build tools (Gradle and Bazel). It auto injects required configuration to appropriate files on the build workspace. This will allow Build Intelligence to automatically optimize your builds when bazel/gradle operation are done in Test or Run steps.
Gradle Config
When using gradle, Harness creates an init.gradle file in ~/.gradle/init.d or $GRADLE_HOME/init.d or $GRADLE_USER_HOME/init.d folder if not found, with the required configuration.
Bazel Config
When using bazel, Harness create a ~/.bazelrc file (if it does not exist), with the required configuration.
The config will look like:
build --remote_cache=http://endpoint:port/cache/bazel (endpoint is localhost:8082)
Maven Config
For Maven builds, the following configuration files are injected into the environment:
.mvn/maven-build-cache-config.xml
.mvn/extensions.xml
~/.m2/settings.xml
There are two ways to apply settings.xml:
-
Maven installation-wide:
${maven.home}/conf/settings.xml -
User-specific:
${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml
These configurations enable build caching and repository access based on your pipeline’s setup.
Using a Private Maven Repository for Build Intelligence Extensions
If your environment restricts access to Maven Central, you can configure Build Intelligence to download required extensions (like the Maven build cache extension) from your private or third-party artifact registry.
This support is built-in and requires the following:
- Upload Required Maven Artifacts
Ensure the following artifacts are available in your private Maven repository under the correct path structure (i.e.,
org/apache/maven/extensions/maven-build-cache-extension/1.2.0/):
This ensures Maven clients can resolve the artifacts properly using the standard package coordinates, which are required by Build Intelligence to enable caching for Maven builds.
- Update Your
pom.xml
Point your Maven build to use your private registry:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>maven-dev</id>
<url>https://your-private-maven-registry.example.com/repository/maven-releases</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
- (Optional) Add Authentication
If your registry requires authentication, add this to your
settings.xmlfile:
<settings>
<servers>
<server>
<id>maven-dev</id>
<username>YOUR_USERNAME</username>
<password>YOUR_PASSWORD</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>
Make sure the <id> in settings.xml matches the one in the <repository> section of your pom.xml.
Using '--profile'
Appending `--profile' to your build command, enables publishing Build Intelligence savings to Harness. This will allow you to clearly view the performance and benefits of using Build Intelligence. Note that even when omitted, Build Intelligence will continue to work and optimize your run as expected, but the savings will not be visible in the UI and relevant dashboards.
For example: ./gradlew build --profile
This is currently supported with Gradle build tool only .
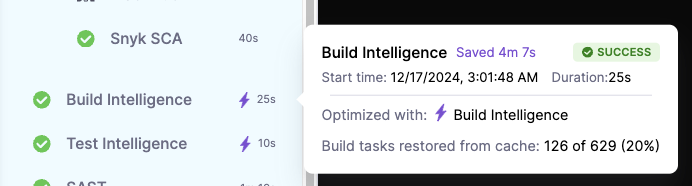
Visit Intelligence Savings for more information.
Troubleshooting
Ignoring Build Intelligence Directories in Apache RAT Scans
If you are using the Apache RAT plugin for license compliance, it may incorrectly mark Harness Build Intelligence directories as invalid files. This can cause unnecessary failures in your build pipeline.
To avoid this, explicitly exclude the following directories in your pom.xml file.
Directories to Ignore
-
Build Intelligence:
/harness/.mvn -
Cache Intelligence:
/harness/.m2/harness/.mvn(also applies to cache-related scans)
Example: Update to pom.xml
Add the following snippet under the <build> section to configure the apache-rat-plugin to ignore these paths:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.rat</groupId>
<artifactId>apache-rat-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.15</version> <!-- Or use the latest version -->
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>/harness/.mvn</exclude>
<exclude>/harness/.m2</exclude> <!-- Optional, but recommended -->
</excludes>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>verify</phase>
<goals>
<goal>check</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>