Insert step and stage in existing Template
Currently this feature is behind the feature flag PIE_FLEXIBLE_TEMPLATES and PIE_FLEXIBLE_TEMPLATES_PHASE2. Please contact Harness support to enable this feature.
Insert blocks provide a way to customize pipelines without affecting the main template.
Steps and stages included in the insert block will behave the same as normal steps and stages in the pipeline.
Insert block is supported for CI, CD, Custom and Approval Stages.
Pros of Using Insert blocks in a template
- Only the Template Editor has the flexibility to allow additional steps or stages at any given point where they want.(At beginning of all steps/stage or at the end of all steps/stages or in between the steps/stages)
- The YAML is simple and inline with existing Harness steps/stages YAML. Here the Insert is simply a new type of step which starts with the key
insert.
Now, let's dive into who can add insert block in the pipeline and stage template and how other users can utilise it in their pipelines.
Insert stage block in Pipeline Template
Template editors will be able to add insert stage block in the pipeline template at any position between a stage.
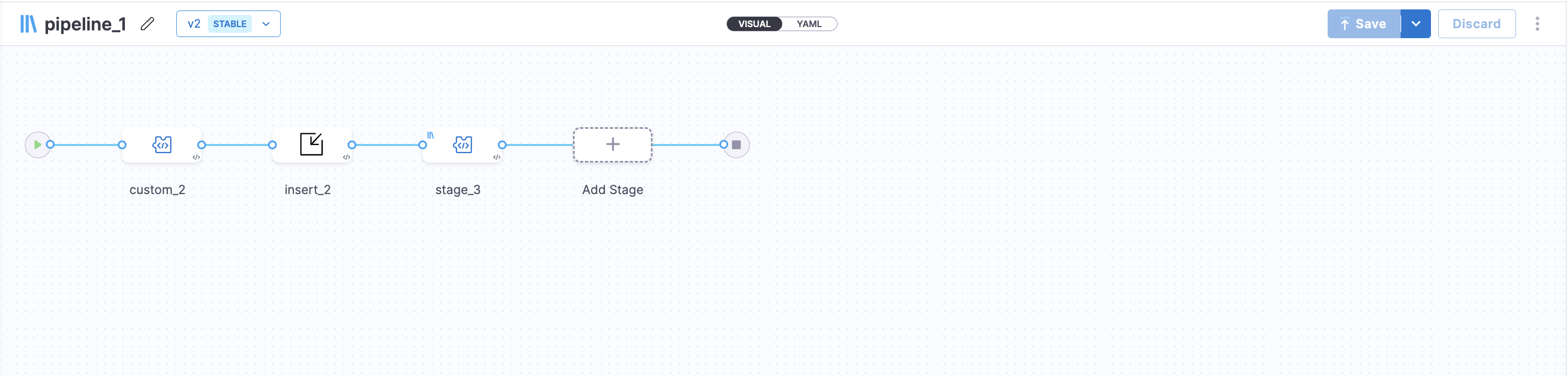
Sample YAML of a pipeline template with insert stage block will look like:
template:
name: pipeline_1
identifier: pipeline_1
versionLabel: v2
type: Pipeline
projectIdentifier: Krishika_test_autocreation
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
spec:
stages:
- stage:
name: custom_2
identifier: custom_2
description: ""
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: ShellScript_1
identifier: ShellScript_1
spec:
shell: Bash
executionTarget: {}
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: echo hello_2
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
tags: {}
- insert:
name: insert_2
identifier: insert_2
stages: <+input>
- stage:
name: stage_3
identifier: stage_3
tags: {}
template:
templateRef: stage_1
versionLabel: v2
templateInputs:
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- parallel:
- insert:
identifier: insert_1
steps: <+input>
Insert step block in Stage Template
Similarly, as a Template Editor you can add a insert step block in the stage template at any position between a step.
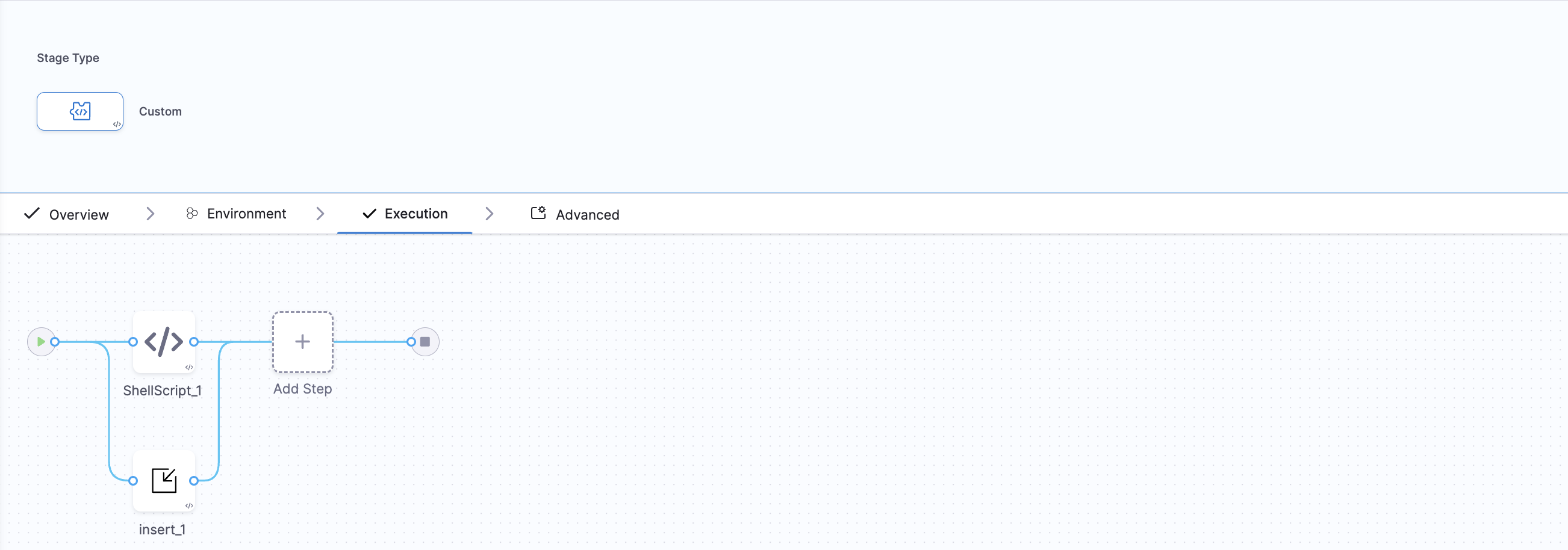
Sample YAML of a stage template with an insert step block will look like:-
template:
name: stage_1
identifier: stage_1
versionLabel: v2
type: Stage
projectIdentifier: Krishika_test_autocreation
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
spec:
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- parallel:
- step:
type: ShellScript
name: ShellScript_1
identifier: ShellScript_1
spec:
shell: Bash
executionTarget: {}
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: |
echo hello
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
- insert:
name: insert_1
identifier: insert_1
steps: <+input>
This allows you, as the template editor, to maintain control over the template, ensuring its integrity is preserved.
Now, if you use a template with a insert step/stage block in a pipeline, suppose you are using a pipeline template while creating a pipeline in a pipeline studio those insert stages will come under templateInputs.
Sample YAML:
pipeline:
name: pipeline_insert_sample
identifier: pipeline_insert_sample
tags: {}
template:
templateRef: pipeline_insert_template
versionLabel: v2
templateInputs:
stages:
- insert:
identifier: insertStages1
stages: <+input>
- insert:
identifier: insertStages2
stages: <+input>
projectIdentifier: Insert_block
orgIdentifier: default
In the above YAML as you can see, we have used pipeline template pipeline_insert_template which are having two insert blocks and those insert blocks are under templateInputs.
Template user can add additional step and stage wherever an insert block has been defined. The insert block support inclusion of stages and steps along with runtime inputs, failure strategies, and conditional execution.
Consider a YAML using stage template in a pipeline with an insert step block:-
pipeline:
name: pipeline_sample
identifier: pipeline_sample
projectIdentifier: Krishika_test_autocreation
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: stage_1
identifier: stage_1
tags: {}
template:
templateRef: stage_insert_template
versionLabel: v2
templateInputs:
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- insert:
identifier: insertSteps1
steps:
- parallel:
- step:
identifier: shell1
type: ShellScript
name: shell1
spec:
shell: Bash
executionTarget: {}
source:
type: Inline
spec:
script: echo hello_3
environmentVariables: []
outputVariables: []
timeout: 10m
failureStrategies:
- onFailure:
errors:
- AllErrors
action:
type: Ignore
- insert:
identifier: insertSteps2
steps: <+input>
In this, under the first insert block we have added one Shell Script step. Now, when we run the pipeline the execution will look like :-
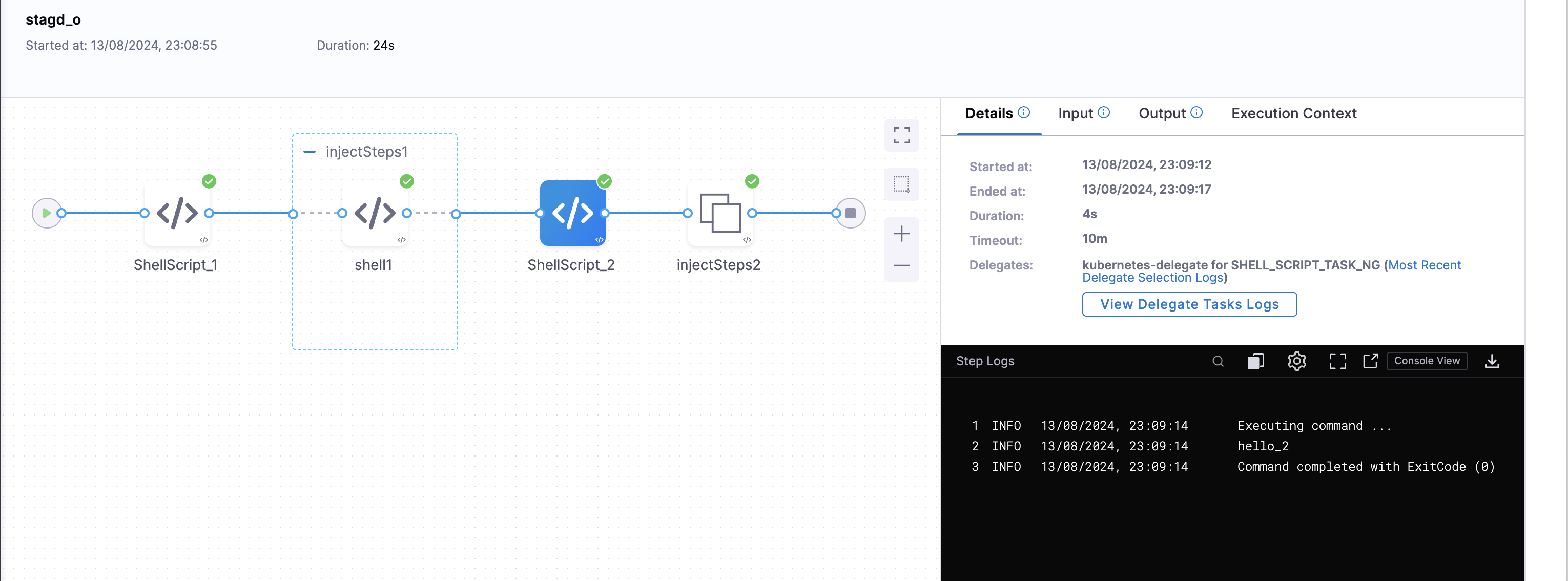
If no actions are provided in the insert block the pipeline will proceed without any additonal steps and stages.
For example, in the below yaml, we have used this stage template in the pipeline with 2 insert blocks and we have not added any additional steps in it:-
pipeline:
name: pipeline_insert_sample
identifier: pipeline_insert_sample
projectIdentifier: Krishika_test_autocreation
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: stage_1
identifier: stage_1
tags: {}
template:
templateRef: stage_insert_template
versionLabel: v2
templateInputs:
type: Custom
spec:
execution:
steps:
- insert:
identifier: insertSteps1
steps: <+input>
- insert:
identifier: insertSteps2
steps: <+input>
Now when we will run the pipeline the execution will look like:-
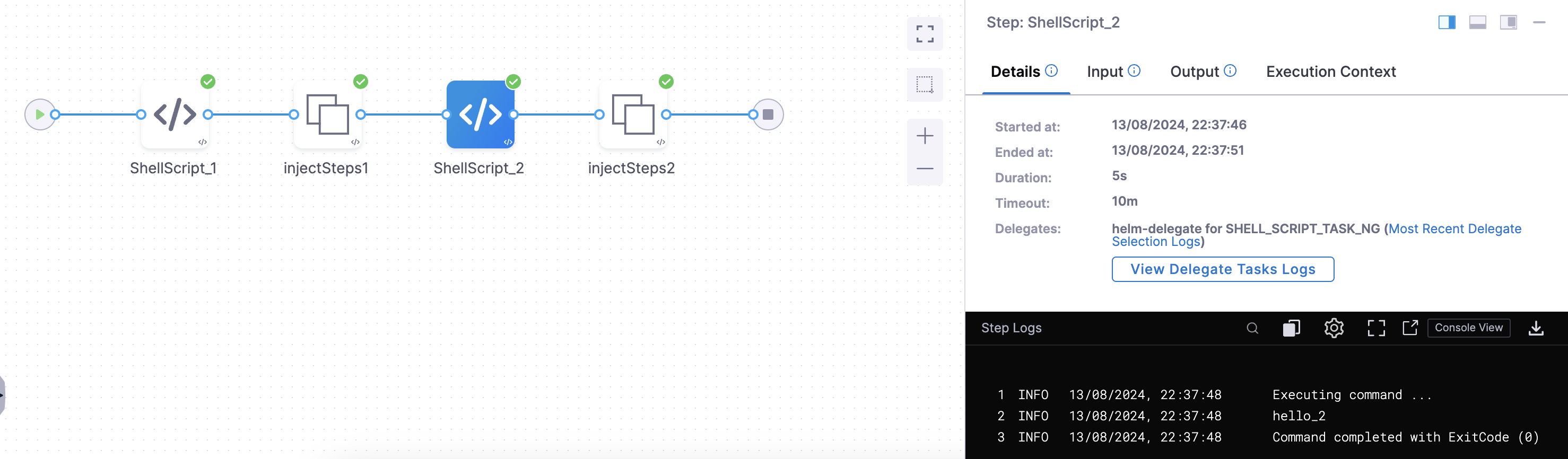
If you will check the compiled YAML it will show the steps input as empty and thus will not fail the pipeline as well with a null error.
Limitations
- Insert block can not be output of any step, it has to be provided.
- Nested insert blocks are not allowed.
- Insert blocks cannot be added in parallel to any other stage.
- In the step group template, insert step cannot be added.
- Only service, environment, and infrastructure definitions can be propagated within an insert block; they cannot be propagated outside the insert block for other stages that are not part of it.
Demo Video
Expressions
If we intend to utilize expressions for the properties within the insert, it will be necessary to specify the complete path for each one.
Example: <+execution.steps.insert1.steps.ShellScript_1.description>
RBAC required
- Users must possess the Template Create/Edit Permission in order to insert an insert block into the template at any desired location.
- In order to provide the steps/stages input to insert block when specifying runtime inputs in the pipeline, users must have Pipeline Create/Edit Permission. Otherwise, if they intend to provide input values in the parent template, Template Create/Edit Permission will be required.