Kubernetes Traffic Routing Step
This topic describes the Kubernetes Traffic Routing step parameters and use cases. These configuration options can also be found as part of the Blue Green (BG) Deployment step as well as the Canary Deployment step.
This feature allows you to perform east-west routing of traffic. You would select a routing service mesh provider (currently supported SMI and Istio) and then configure one or more routes which are essentially groups of destinations and optional rules that applies for them.
Here is a video demo of traffic shifting in a Kubernetes deployments.
Name
Name of the step.
Config Type
Specify your configuration type here. Currently there are two choices:
- New Config: Select this option if you want to specify a new configuration for traffic routing in this step. If configuring this in a BlueGreen deployment step or a Canary step this option is implicitly assumed. This option will create a new resource(s).
- Inherit: Select this option if you want the traffic routing step to inherit a configuration from a previous Blue Green, Canary, or Traffic Routing step. This option will patch existing resources.
Provider
Specify your service mesh provider. Harness currently supports Service Mesh Interface (SMI) and Istio.
Each provider will have some common configuration options and some provider specific ones. We have listed all configuration options for each provider. Please look at the one relevant for you.
Service Mesh Interface (SMI) - New Config option
Before you begin, make sure you have an understanding on what SMI is and how it works by visiting their website.
Currently, we only support specs.smi-spec.io/v1alpha3 and specs.smi-spec.io/v1alpha4 TrafficSplit resource versions since these are the only versions that support having rules (such as uri, method, and headers described below).
- Parameters:
- Resource Name: This will be used in generating a name for a kubernetes traffic routing resources. Having that mind, the name needs to be kubernetes resource name compliant.
- Root Service: This should be a kubernetes service name which will be receiving incoming traffic (take a look in more details the SMI link provided above). Depending on which SMI implementation you are using this value may or may not be the same as one of the destination's host (described below)
- Routes:
-
Route type: Currently, Harness supports only the
httproute type - for http traffic. -
Route name: This will be used in generating kubernetes resources so the value should kubernetes name compliant. This should also be unique within the pipeline workflow as it is used as ID for updating purposes (described below)
-
Route Rules: This is the way incoming requests are filtered for the configured route destinations.
-
uri:
- Value: Enter the value that you want matched against incoming request URI.
- Match Type: Used to determine how URI of the incoming request is matched against the
valueconfig parameter. Available to choose one of three values (exact,prefix,regex).
-
method:
- Value: Used for matching the HTTP method of the incoming request.
-
headers:
- Values:
- Key: Specify the name of the request header
- Value: Specify the value of the header
- Match Type: Specify which kind of matching should be done against the incoming header. Available to choose one of three values (
exact,prefix,regex).
- Values:
-
-
Destinations: This is locations to which the filtered request will be routed to
-
Host: Should be the name of the Kubernetes service resource.
noteOnly applicable when using the Blue/Green deployment step - You can use placeholder
stableandstageresource names. Which would effectively be replaced with the name of the stable and stage services, respectively.Only applicable when using the Canary deployment step You can use the placeholder
stableandcanaryresource names. Which would effectively be replaced with the name of the stable and canary services, respectively. -
Weight: Specify the percentage of traffic that should be routed to this host. The weight should be a numeric value in range [0 - 100].
noteIf the total weights for all host destinations is not equal to 100, the weight values will be normalized into a percentage, and the pipeline will run with a warning.
-
-
Istio - New Config option
Before you begin, make sure you have an understanding of Istio and how it works by referring to their website.
- Parameters:
-
Resource Name: This name will be used to generate a kubernetes name for traffic resources. Hence the name needs to be kubernetes resource name compliant.
-
Hosts: Specify one or more host names. Hosts can be added individually using the +Add button or as a comma-separated list. This is specific to Istio, please take a look here.
-
Gateways: Specify one or more gateway names. This is specific to Istio, please take a look here.
-
Routes: Currently, Harness supports only the
httproute type.-
Route type: Currently, Harness supports only the
httproute type - for http traffic. -
Route name: This will be used in generating kubernetes resources so the value should be kubernetes name compliant. This should also be unique within the pipeline workflow as it is used as an ID for updating purposes (described below).
-
Route Rules: This is the way incoming requests are filtered for the configured route destinations.
-
uri:
- Value: Enter the value that you want matched against the incoming request URI.
- Match Type: Used to determine how the URI of the incoming request is matched against the
valueconfig parameter. Choose from one of the three available values (exact,prefix,regex).
-
method:
- Value: Used for matching the HTTP method of the incoming request.
- Match Type: Used to determine how the HTTP method of the incoming request is matched against the
valueconfig parameter. Choose from one of the three available values (exact,prefix,regex).
-
headers:
- Values:
- Key: Specify the name of the request header
- Value: Specify the value of the header
- Match Type: Specify which kind of matching should be done against the incoming header. Choose from one of the three available values (
exact,prefix,regex).
- Values:
-
scheme:
- Value: Specify which scheme you want to match with.
- Match Type: Specify which kind of matching should be done against the incoming request scheme. Choose from one of the three available values (
exact,prefix,regex).
-
authority:
- Value: Specify which authority you want to match with.
- Match Type: Specify which kind of matching should be done against the incoming request authority. Choose from one of the three available values (
exact,prefix,regex).
-
port:
- Value: Specify which port you want to match the incoming request port with.
-
-
Rewrite Rule: A rewrite rule in a traffic shifting step refers to modifying the incoming request’s path or URL before it's forwarded to the backend service.
noteCurrently, the support for re-write rule feature is behind the feature flag
CDS_K8S_TRAFFIC_ROUTE_REWRITE_RULE_SUPPORT. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.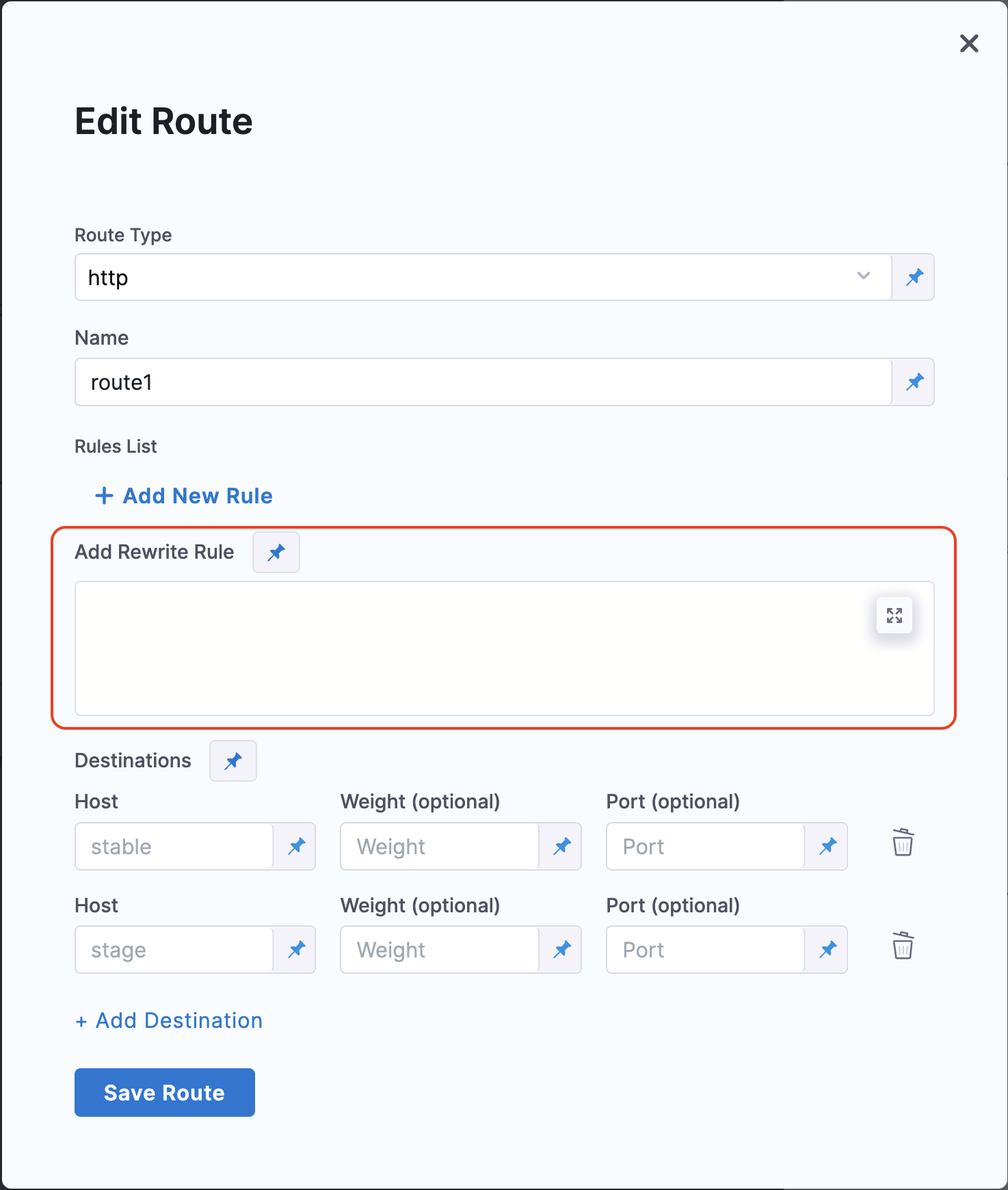
Here is a sample rewrite rule for reference. Note that each rule must begin with
rewrite:.Basic Path Rewrite Sample YAML
Add the following snippet in the Rewrite text box:
rewrite:
uri: /new-pathBelow is an example of the complete VirtualService YAML that gets compiled during execution:
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /old-path
rewrite:
uri: /new-path
route:
- destination:
host: my-service-
Destinations: The filtered requests will be routed to these locations.
-
Host: Should be the name of the Kubernetes service resource.
noteOnly applicable when using the Blue/Green deployment step - You can use placeholder
stableandstageresource names. Which would effectively be replaced with the name of the stable and stage services, respectively.Only applicable when using the Canary deployment step You can use the placeholder
stableandcanaryresource names. Which would effectively be replaced with the name of the stable and canary services, respectively.- Delegate Virtual Service Support
With the introduction of delegate virtual service support, the Host field can now be left empty when using custom rewrite logic. This allows for more dynamic traffic routing configurations, enabling users to rewrite traffic-routing logic to fit their deployment strategies. To configure this, you need to check the Delegate Service option, which creates a delegate virtual service. When this option is checked, the Host field will be left empty.
This is available for Canary Deployment, K8s Traffic routing, K8s Blue Green Deploy.
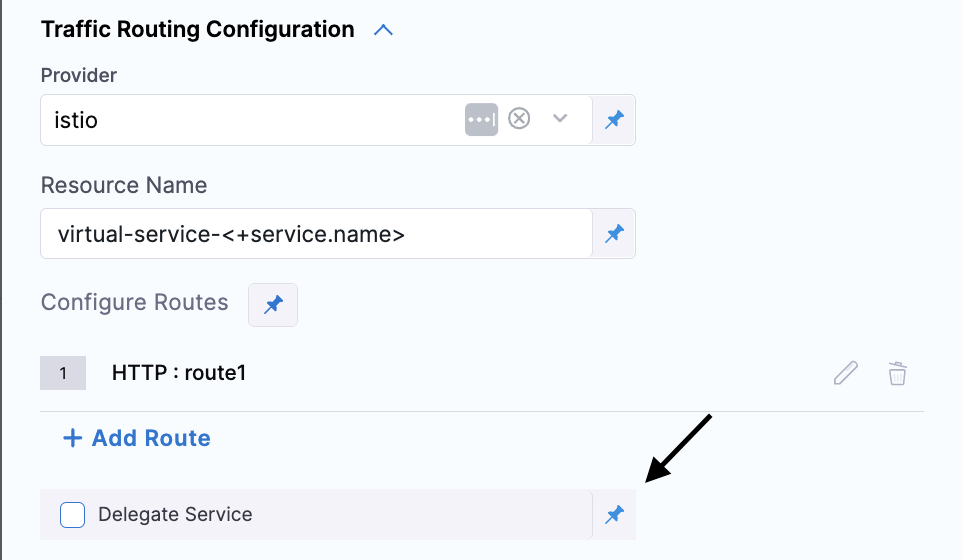
-
Weight: Specify the percentage of traffic that should be routed to this host. The weight should be a numeric value in range [0 - 100].
noteIf the total weights for all host destinations is not equal to 100, the weight values will be normalized into a percentage, and the pipeline will run with a warning.
-
-
-
SMI and Istio - Inherit option
This options provides a way to update an existing traffic routing configuration destination's weights. With this step configuration there are two logical parts.
First one is to configure the Route Name and second one is to configure destination(s) which you want to update. Route name is an ID for us to know which traffic routing resource we need to update. The value of the route name should match one of the route names defined during the New config step configuration.
You can configure one or more destinations and their weights.
You should also be aware that in case you configure lower number of destinations then the route contains, the update of the weights will occur, but it will respect [0-100] boundaries.
Example: In original setup you have configured 3 destinations for a route:
Destination1 -> Host: svc1, Weight: 60
Destination2 -> Host: svc2, Weight: 30
Destination3 -> Host: svc3, Weight: 10
Now in the update step you configured to update only one destination for that same route. Let's say you want to update Destination svc1 and you want to set its weight to 40
This will lead to having the remaining 60 (max limit of 100 - configured update weight of 40) to be split amongst the remaining destinations, but keeping the same ratio they have amongst themselves. Meaning the result would be:
Destination1 -> Host: svc1, Weight: 40
Destination2 -> Host: svc2, Weight: 45
Destination3 -> Host: svc3, Weight: 15
Configuration examples
Istio service mesh configuration
Here we have an example of an Istio service mesh traffic routing step which will take all the traffic that is coming from gateway testgateway and with host test.com.
It will filter all incoming request that have URI /login with HTTP method POST and header X-Request with value authxx.
This request will be split between PODs which are behind two service svc1 and svc2 in ratio 65 to 35, respectively.
The resource created would be a Virtual Service with name istio-vs-k8s-res
- step:
identifier: K8sTrafficRoutingConfig
type: K8sTrafficRouting
name: config
spec:
type: config
trafficRouting:
provider: istio
spec:
name: istio-vs-k8s-res
hosts:
- test.com
gateways:
- testgateway
routes:
- route:
type: http
name: route1
rules:
- rule:
type: uri
spec:
value: /login
matchType: prefix
- rule:
type: method
spec:
value: POST
- rule:
type: headers
spec:
values:
- value: authxx
key: X-Request
matchType: prefix
destinations:
- destination:
host: svc1
weight: 65
- destination:
host: svc2
weight: 35
SMI service mesh configuration
Here we have an example of an SMI service mesh traffic routing step which will take all the traffic that is coming into service svc1
It will filter all incoming request that have URI /login with HTTP method POST and header X-Request with value authxx.
This request will be split between PODs which are behind two service svc1 and svc2 in ratio 65 to 35, respectively.
The resource created would be a TrafficSplit with name smi-traffic-split-res-route1 and HTTPRouteGroup with name smi-traffic-split-res-route1-http-rule
- step:
identifier: K8sTrafficRoutingConfig
type: K8sTrafficRouting
name: config
spec:
type: config
trafficRouting:
provider: smi
spec:
rootService: svc1
name: smi-traffic-split-res
routes:
- route:
type: http
rules:
- rule:
type: uri
spec:
value: /login
matchType: prefix
- rule:
type: method
spec:
value: POST
- rule:
type: headers
spec:
values:
- value: authxx
key: X-Request
matchType: prefix
name: route1
destinations:
- destination:
host: svc1
weight: 65
- destination:
host: svc2
weight: 35
Advanced
See the following topics for advanced settings: