2. Administrator Day-to-Day Guide
This guide is intended to get users in the Admin role started with Harness CD. The intended audience is an administrator or anyone who will be configuring and/or piloting Harness on behalf of their organization.
Most of the items in this guide align with the onboarding wizard that is shown within the application, and we include additional suggested configurations and setups in Next Steps.
Set up a delegate at the account level
The Harness Delegate is a service you run in your local network or VPC to connect Harness SaaS with your artifacts, infrastructure, collaboration, verification, and other providers.
The first time you connect Harness to a third party resource, the Harness Delegate is installed in your target infrastructure, such as a Kubernetes cluster.
After the delegate is installed and registers with Harness, you connect Harness to third party resources.
The delegate performs all operations on your behalf, including deployment and integration.
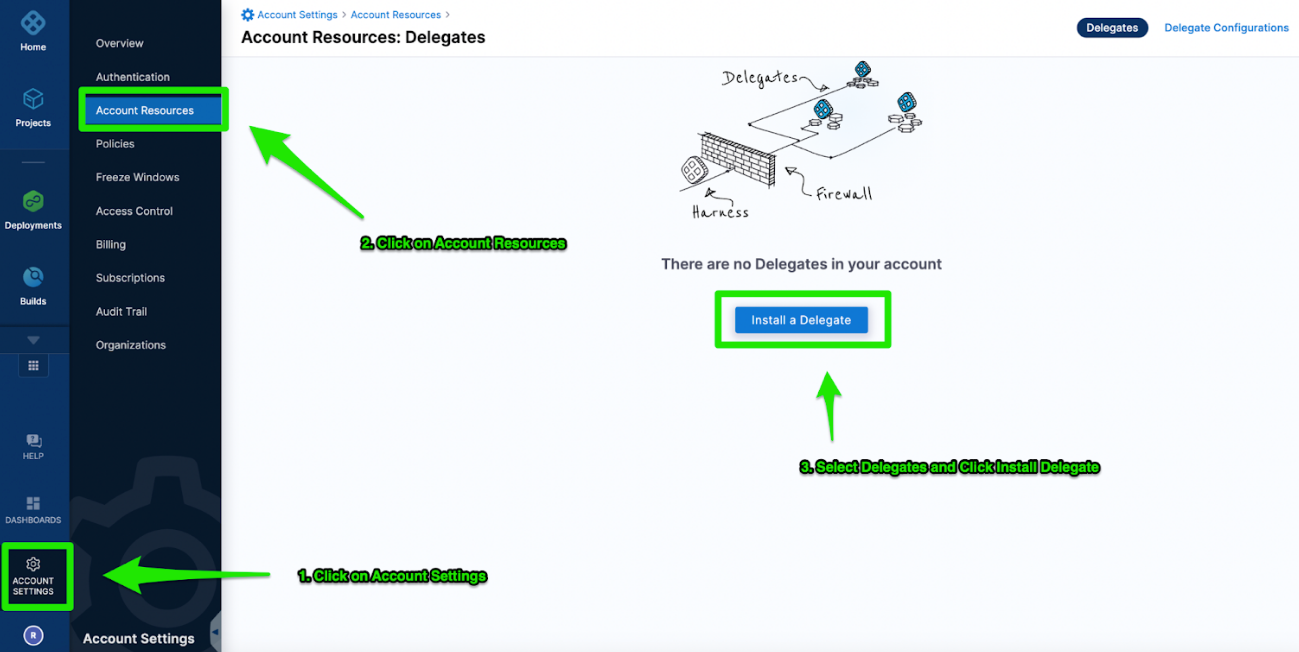
For more information, go to Delegate overview and Delegate installation overview.
Configure the account structure (project and organization setup)
Harness uses a three level hierarchy of account, organizations, and projects. Accounts contains organizations, and organizations contain projects.
Projects overview
A project is everything an application team needs to get started with Harness.
A project is a group of services that serves the same business goal (several components for the same application, for example) and it is usually managed by the same development team. The idea is to treat the project as a common space for teams of similar or related technologies to be managed.
For example, imagine Customer A has 1 application that is comprised of numerous microservices. These microservices leverage the same Git connector, the same secrets managers, and deploy the same way. All of the components for deployment, the pipelines, stages, resources, and infrastructure, are shared across the microservices.
In this scenario, the entire application can be managed in one project. Each of these microservices can be owned by different teams, however, as they all work on the same project.
For more information, go to What is a project?.
Organizations overview
An organization allows users to group several projects that share the same objective. For example, different business units, divisions, etc.
Within an organization, users can create several projects using resources that are scoped at the organization level. This scoping allows child projects to leverage the resources provided at their parent organization level.
Users can invite people to an organization to gain membership and start leveraging resources based on specific roles and permissions. These roles and permissions are covered in the RBAC section later in this topic.
For more information, go to What is an organization?.
Account overview
Account level resources are available globally for all projects and organizations to access and leverage in their respective scopes.
Go to View account info and subscribe to downtime alerts for more information.
Configure the Harness connectors your teams needs to get started
Once you have set up the delegate, project, organization, account structure, you can now begin to integrate into the Harness platform.
Harness connectors are access points used by Harness to connect to a specific tool to perform an action on the user’s behalf.
Please see our connectors documentation to add connectors for your integrations:
Configure RBAC
Once you have configured your project, organization, and account structure, you can begin configuring the RBAC model.
You can model how developers and teams access the delegate and connectors you have created in the above steps.
By default, Harness provides some default roles to get you started. As you operationalize Harness, you can customize these roles and make them more granular.
For more information, go to Manage users.
Onboard and invite your team members
You have finally spun up your first delegate, configured your account, and added a few connectors. You can now onboard your existing teammates and get them building their pipelines within a project.
To help you onboard users and user groups from your tool of choice, Harness supports provisioning with SCIM, and SSO with LDAP, SAML, and OAuth.
For more information, go to Manage users.
Next Steps
By now, you should have done a basic walkthrough of Harness, including setting up a delegate, a few connectors, a project, and an organization. Getting started on software delivery is now at your fingertips!
To experience the full power of Harness Continuous Delivery, we recommend the following next steps:
- Build your first pipeline.
- Harness suggests you build your first pipeline in a project and get it deploying successfully before expanding into other areas of the product.
- Add various steps and integrations to model the pipeline to your specifications and deployment needs.
- Harness supports various deployment types, so feel free to explore the ones that match your business needs.
- Template your pipelines and configurations.
- After building your first pipeline, we recommend templating and building generic delivery components for other projects and organizations to leverage.
- Add your services.
- Add your environments.
- Automate your onboarding of teams:
- After the initial team is onboarded, Harness recommends automating onboarding for the next set of teams.
- Using the Harness Terraform Provider, you can automate your onboarding of projects, orgs, connectors, services, pipelines, etc.
- Using Harness Git Experience, you can manage and clone pipelines and templates in Git and share across projects.
- Automate your pipeline deployments and experiment with steps and conditions.
- Harness offers triggers and APIs to automate the execution of pipelines. Harness recommends you automate the pipeline execution once the pipeline design and structure is relatively mature and not going to change. For more information on triggers and APIs, go to:
- You can customize you pipelines further by adding steps such as approvals, policy checks, Jira change management, etc. For more information, go to:
- Jira Approval step.
- Verify step (integrating logging and application monitoring tools).
- Configure deployment dashboards.
- Harness provides out of the box dashboards for development teams to track their deployed services. For more information, go to Monitor deployments and services in CD dashboards.
- You can also customize the dashboards and build your own via our custom dashboards.
If there are questions at any time, please reach out to our Support team, the Adoption team, or the Harness account manager that is working with you.