Build and Push to JFrog Docker registries
This topic explains how to use the Build and Push an image to Docker Registry step to build and push an image to JFrog Artifactory Docker registries.
For JFrog non-Docker registries, you can use a script in a Run step to build the artifact, and then use the Upload Artifacts to JFrog step to upload the artifact.
You need:
- Access to a JFrog Artifactory instance with a Docker registry.
- A CI pipeline with a Build stage.
- A Harness Docker connector configured to your JFrog instance.
With Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures, Build and Push steps use Chainguard's maintained Kaniko fork by default. Kaniko can run as non-root in many cases. Root access is only required when your Dockerfile performs privileged operations (e.g., installing system packages, modifying root-owned directories).
If your build runs as non-root (runAsNonRoot: true), and you want to run the Build and Push step as root, you can set Run as User to 0 on the Build and Push step to use the root user for that individual step only.
If your security policy doesn't allow running as root, go to Build and push with non-root users.
Build and push to JFrog Docker registries
In your pipeline's Build stage, add a Build and Push an image to Docker Registry step and configure the settings for JFrog.
Here is a YAML example of a Build and Push an image to Docker Registry step configured for JFrog:
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: Build and push to JFrog Docker
identifier: Build_and_push_to_JFrog_Docker
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR_ID
repo: domain.jfrog.io/REPO/IMAGE
tags:
- <+pipeline.sequenceId>
When you run a pipeline, you can observe the step logs on the build details page. If the Build and Push step succeeds, you can find the uploaded image in JFrog.
You can also:
Using Local Tar Output
In scenarios where pushing a Docker image to a registry is not feasible, you can generate a local tarball of the built image instead. This approach is particularly useful for situations like local testing or when registry access is unavailable during the build process.
Once the tarball is generated, you can use a Security Testing Orchestration (STO) step, such as Aqua Trivy, to scan the image for vulnerabilities. This workflow ensures that images are built and scanned effectively, even without access to a remote registry.
Here’s a sample partial pipeline that demonstrates how build the image, generate the tarball, and push it to the registry:
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
identifier: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
spec:
connectorRef: docker_connector
repo: dockerhub/image_name
tags:
- linux-amd64
caching: false
dockerfile: ./docker/Dockerfile
envVariables:
PLUGIN_TAR_PATH: /harness/image_name.tar
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_2
identifier: Run_2
spec:
shell: Sh
command: ls /harness
The PLUGIN_NO_PUSH: "true" environment variable prevents the image from being pushed to the registry.Here’s a sample partial pipeline that demonstrates how build the image, generate the tarball, but skip pushing it to the registry:
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
identifier: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
spec:
connectorRef: docker_connector
repo: dockerhub/image_name
tags:
- linux-amd64
caching: false
dockerfile: ./docker/Dockerfile
envVariables:
PLUGIN_TAR_PATH: /harness/image_name.tar
PLUGIN_NO_PUSH: "true"
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_2
identifier: Run_2
spec:
shell: Sh
command: ls /harness
-
The local tar output feature is available only when using Kaniko as the build tool, which is commonly used in Kubernetes environments.
-
While the above examples show a push to a Docker registry, you can easily repurpose it for other registries by updating the step type, connector, and other relevant fields.
Step settings
These sections explain how to configure the Build and Push an image to Docker Registry step settings for JFrog. Depending on the build infrastructure, some settings might be unavailable or optional. Settings specific to containers, such as Set Container Resources, are not applicable when using a VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Name
Enter a name summarizing the step's purpose. Harness automatically assigns an Id (Entity Identifier) based on the Name. You can change the Id until the step is saved. Once save, the Id can't be changed.
Docker Connector
Specify a Harness Docker Registry connector configured for JFrog.
To create this connector:
- Go to Connectors in your Harness project, organization, or account resources, and select New Connector.
- Select Docker Registry under Artifact Repositories.
- Enter a Name for the connector. The Description and Tags are optional.
- For Provider Type, Select Other.
- In Docker Registry URL, enter your JFrog URL, such as
https://mycompany.jfrog.io. - In the Authentication settings, you must use Username and Password authentication.
- Username: Enter your JFrog username.
- Password: Select or create a Harness text secret containing the password corresponding with the Username.
- Complete any other settings and save the connector. For information all Docker Registry connector settings, go to the Docker connector settings reference.
The JFrog URL format depends on your Artifactory configuration, and whether your Artifactory instance is local, virtual, remote, or behind a proxy. To get your JFrog URL, you can select your repo in your JFrog instance, select Set Me Up, and get the repository URL from the server name in the docker-login command.
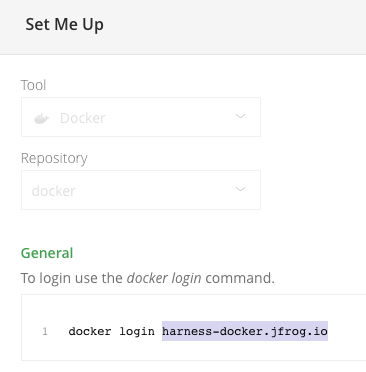
For more information, go to the JFrog documentation on Repository Management and Configuring Docker Repositories.
Docker Repository
The repo where you want to store the image and the image name, for example, mycompany.jfrog.io/REPO_NAME/IMAGE_NAME.
Tags
Add Docker build tags. This is equivalent to the -t flag.
Add each tag separately.
When you push an image to a repo, you tag the image so you can identify it later. For example, in one pipeline stage, you push the image, and, in a later stage, you use the image name and tag to pull it and run integration tests on it.
Harness expressions are a useful way to define tags. For example, you can use the expression <+pipeline.sequenceId> as a tag. This expression represents the incremental build identifier, such as 9. By using a variable expression, rather than a fixed value, you don't have to use the same image name every time.
For example, if you use <+pipeline.sequenceId> as a tag, after the pipeline runs, you can see the Build Id in the output.
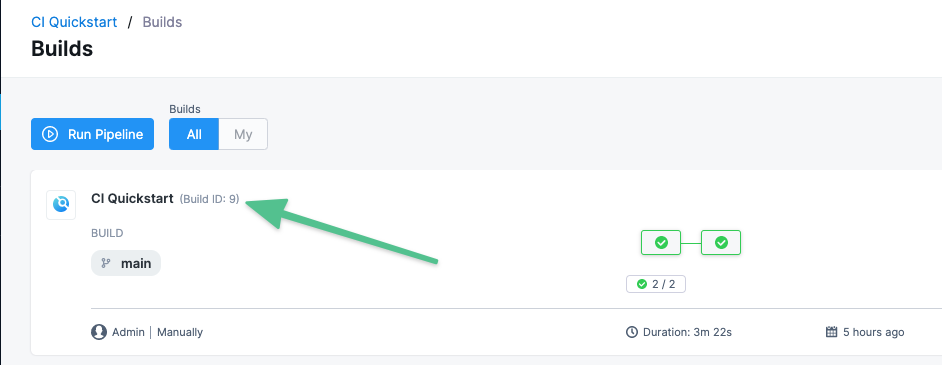
And you can see where the Build Id is used to tag your image in the container registry:
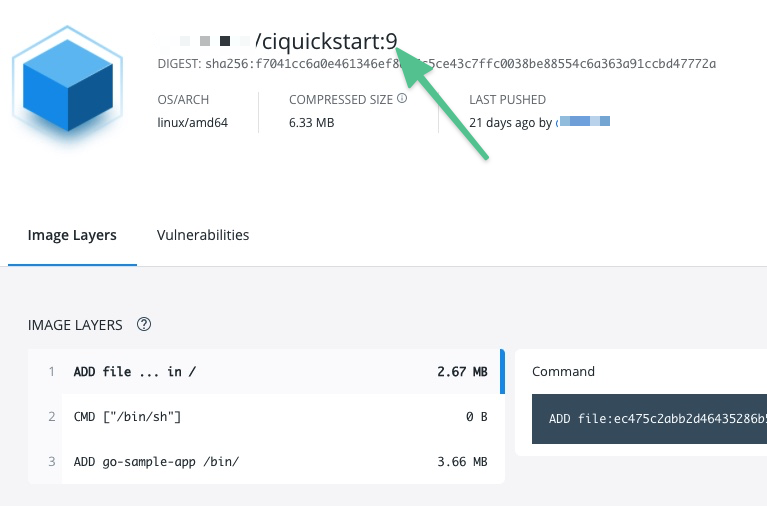
You can use the same expression to pull the tagged image, such as namespace/myimage:<+pipeline.sequenceId>.
Optimize
With Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures, select this option to enable --snapshotMode=redo. This setting causes file metadata to be considered when creating snapshots, and it can reduce the time it takes to create snapshots. For more information, go to the Kaniko documentation for the snapshotMode flag.
For information about setting other kaniko runtime flags, go to Environment variables.
Dockerfile
The name of the Dockerfile. If you don't provide a name, Harness assumes that the Dockerfile is in the root folder of the codebase.
Context
Enter a path to a directory containing files that make up the build's context. When the pipeline runs, the build process can refer to any files found in the context. For example, a Dockerfile can use a COPY instruction to reference a file in the context.
Kaniko, which is used by the Build and Push step with Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures, requires root access to build the Docker image. If you have not already enabled root access, you will receive the following error:
failed to create docker config file: open/kaniko/ .docker/config.json: permission denied
If your security policy doesn't allow running as root, go to Build and push with non-root users.
Labels
Specify Docker object labels to add metadata to the Docker image.
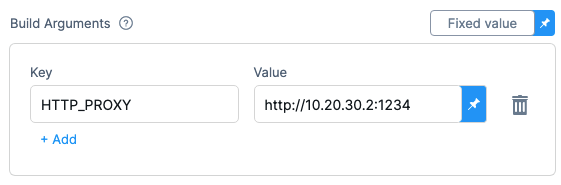
Build Arguments
The Docker build-time variables. This is equivalent to the --build-arg flag.
Target
The Docker target build stage, equivalent to the --target flag, such as build-env.
Docker layer caching and Remote cache image
There are two ways in which you can leverage Docker Layer Caching: Enable Docker layer caching ('caching' property) or Remote cache image ('remoteCacheRepo' property). Refer to Enable Docker layer caching for your build to learn more.
Environment Variables (plugin runtime flags)
Build and Push steps use plugins to complete build and push operations. With Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures, these steps use Chainguard's maintained Kaniko fork. With other build infrastructures, these steps use drone-docker.
These plugins have a number of additional runtime flags that you might need for certain use cases. For information about the flags, go to the Kaniko plugin documentation and the drone-docker plugin documentation.
In Environment Variables for your step, add the environment variable PLUGIN_BUILDX_OPTIONS to pass any supported options to the buildx command used by the build and push steps.
How you configure plugin runtime flags depends on your build infrastructure.
Set plugin runtime flags with Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure
When using the built-in Build and Push steps with a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure, you can use the Environment Variables setting to set kaniko plugin runtime flags.
Unlike in other Harness CI steps, the Environment Variables setting in Build and Push steps only accepts the known kaniko plugin runtime flags. You must set other types of environment variables in your Dockerfile, build arguments, or as stage variables, depending on their usage and purpose in your build.
In Environment Variables, you must input a Name and Value for each variable. Format the name as PLUGIN_FLAG_NAME.
For example, to set --skip-tls-verify, add an environment variable named PLUGIN_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY and set the variable value to true.
- step:
identifier: buildandpush
name: buildandpush
type: BuildAndPush---
spec:
...
envVariables:
PLUGIN_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY: true
To build without pushing, use the This YAML example shows a Build and Push to GAR step with several no-push kaniko flag.YAML example: Build and Push step with multiple environment variables
PLUGIN environment variables.- step:
identifier: pushGAR
name: push GAR
type: BuildAndPushGAR ## Type depends the selected Build and Push step, such as Docker, GAR, ACR, and so on.
spec: ## Some parts of 'step.spec' vary by Build and Push step type (Docker, GAR, ACR, etc).
connectorRef: GAR_CONNECTOR
host: "us-docker.pkg.dev/gar-prod-setup/harness-public"
projectID: "some-gcp-project"
imageName: "some-image-name"
tags:
- "1.0"
- "1.2"
buildArgs:
foo: bar
hello: world
labels:
foo: bar
hello: world
target: dev-env
context: "."
dockerfile: "harnessDockerfile"
remoteCacheImage: "test/cache"
envVariables: ## Specify plugin runtime flags as environment variables under 'step.spec'.
PLUGIN_TAR_PATH: ./harnesstarpath
PLUGIN_IMAGE_DOWNLOAD_RETRY: "2"
PLUGIN_COMPRESSED_CACHING: "false"
PLUGIN_USE_NEW_RUN: "true"
PLUGIN_GARBAGE: yoyo
Previously, you could set some kaniko runtime flags as stage variables. If you had done this and you are using Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure, then Harness recommends moving these kaniko plugin stage variables to the Environment Variables in your Build and Push step. Don't change non-kaniko plugin variables, such as PLUGIN_USER_ROLE_ARN.
For other types of environment variables (that aren't Build and Push plugin runtime flags), stage variables are still inherently available to steps as environment variables. However, where you declare environment variables depends on their usage and purpose in your build. You might need to set them in your Dockerfile, build args, or otherwise.
However some flags still require using a stage variable:
ignore-path: Set this flag to ignore a comma separated list of file paths when taking an image snapshot. Required when ignoring multiple paths.
Format these stage variables as PLUGIN_FLAG_NAME.
Set plugin runtime flags with other build infrastructures
With Harness Cloud, self-managed VM, or local runner build infrastructures, you can set some drone-docker plugin runtime flags as stage variable.
Currently, Harness supports the following drone-docker flags:
auto_tag: Enable auto-generated build tags.auto_tag_suffix: Auto-generated build tag suffix.custom_labels: Additional arbitrary key-value labels.artifact_file: Harness uses this to show links to uploaded artifacts on the Artifacts tab.dry_run: Disables pushing to the registry. Used to build without pushing.custom_dns: Provide your custom CNS address.
To set these flags in your Build and Push steps, add stage variables formatted as PLUGIN_FLAG_NAME.
For example, to set custom_dns, add a stage variable named PLUGIN_CUSTOM_DNS and set the variable value to your custom DNS address.
variables:
- name: PLUGIN_CUSTOM_DNS
type: String
description: ""
required: false
value: "vvv.xxx.yyy.zzz"
Mounting Docker Secrets
Harness now allows mounting Docker build secrets securely in 'Build and Push' steps. This feature enables you to pass sensitive data such as credentials or configuration files during Docker builds, either as environment variables or file-based secrets. It ensures secure handling of secrets, reducing the risk of exposing sensitive information.
- This feature is currently configurable only through YAML.
- In Kubernetes, unlike other build infrastructures (e.g., Harness Cloud), "Build and Push" steps default to Kaniko rather than Buildx. To enable this feature in Kubernetes, you must enable the feature flag
CI_USE_BUILDX_ON_K8. Additionally, note that Kubernetes build infrastructure using Buildx requires privileged access.
YAML example: Mounting Docker secrets
This example demonstrates how to configure a Build and Push step with Docker secrets passed as both environment variables and file-based secrets:
- step:
identifier: buildAndPush
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: Build and Push Docker Image
spec:
connectorRef: dockerConnector
repo: dockerRepo/imageName
tags:
- ci-<+pipeline.executionId>
envDockerSecrets:
USERNAME: a_user # Reference in Dockerfile:reference to env variable
PASSWORD: a_pass
fileDockerSecrets:
docker_user2: <+secrets.getValue("myusername")> # File secret defined in Harness
docker_pass2: <+secrets.getValue("mydockerpass")>
docker_user3: /harness/test.txt # path to local file in workspace containing the secret
caching: true
The envDockerSecrets field allows you to define Docker secrets that will be passed to the build process through environment variables.
- Key: The reference ID that will be used to identify the secret in the Dockerfile (used with
--mount=type=secret,id=USERNAME). - Value: The reference to the environment variable containing the secret value. If the value is a secret or contains a secret, Harness will implicitly create the environment variable for you.
The fileDockerSecrets field allows you to mount secrets as files into the Docker build process. This is useful for passing configuration files, certificates, or other file-based sensitive data.
- Key: The name of the secret as it will be referenced during the Docker build.
- Value: The path to the file or a dynamic reference to a secret in Harness that will be mounted as a file.
Using Local Tar Output
In scenarios where pushing a Docker image to a registry is not feasible, you can generate a local tarball of the built image instead. This approach is particularly useful for situations like local testing or when registry access is unavailable during the build process.
Once the tarball is generated, you can use a Security Testing Orchestration (STO) step, such as Aqua Trivy, to scan the image for vulnerabilities. This workflow ensures that images are built and scanned effectively, even without access to a remote registry.
Here’s a sample partial pipeline that demonstrates how build the image, generate the tarball, and push it to the registry:
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
identifier: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
spec:
connectorRef: docker_connector
repo: dockerhub/image_name
tags:
- linux-amd64
caching: false
dockerfile: ./docker/Dockerfile
envVariables:
PLUGIN_TAR_PATH: /harness/image_name.tar
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_2
identifier: Run_2
spec:
shell: Sh
command: ls /harness
The PLUGIN_NO_PUSH: "true" environment variable prevents the image from being pushed to the registry.Here’s a sample partial pipeline that demonstrates how build the image, generate the tarball, but skip pushing it to the registry:
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
identifier: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry_1
spec:
connectorRef: docker_connector
repo: dockerhub/image_name
tags:
- linux-amd64
caching: false
dockerfile: ./docker/Dockerfile
envVariables:
PLUGIN_TAR_PATH: /harness/image_name.tar
PLUGIN_NO_PUSH: "true"
- step:
type: Run
name: Run_2
identifier: Run_2
spec:
shell: Sh
command: ls /harness
-
The local tar output feature is available only when using Kaniko as the build tool, which is commonly used in Kubernetes environments.
-
While the above examples show a push to a Docker registry, you can easily repurpose it for other registries by updating the step type, connector, and other relevant fields.
Run as User
With Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures, you can specify the user ID to use to run all processes in the pod if running in containers. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
This step requires root access. You can use the Run as User setting if your build runs as non-root (runAsNonRoot: true), and you can run the Build and Push step as root. To do this, set Run as User to 0 to use the root user for this individual step only.
If your security policy doesn't allow running as root, go to Build and push with non-root users.
Set Container Resources
Set maximum resource limits for the resources used by the container at runtime:
- Limit Memory: The maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number using the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalentsGiandMi. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed; for example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
Set the timeout limit for the step. Once the timeout limit is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution continues. To set skip conditions or failure handling for steps, go to:
Conditions, looping, and failure strategies
You can find the following settings on the Advanced tab in the step settings pane:
- Conditional Execution: Set conditions to determine when/if the step should run.
- Failure Strategy: Control what happens to your pipeline when a step fails.
- Use looping strategies: Define a matrix, repeat, or parallelism strategy for an individual step.
Publish Build metadata to a Docker image in JFrog Docker Registry
Use the Harness plugin to publish build metadata to a Docker image in the JFrog Docker Registry. It's useful for tracking and managing Docker builds in Artifactory, ensuring that all relevant build information is stored alongside your images.
For example:
- step:
identifier: metadata
name: Artifactory - Publish build info to JFrog Docker Registry
type: Plugin
spec:
connectorRef: account.ArtifactoryDocker
image: plugins/artifactory-publish-docker-buildinfo
settings:
access_token: <+secrets.getValue("org.artifactory_token")>
url: https://artifactory.customer.com/artifactory/
build_name: <+pipeline.name>
build_number: <+pipeline.executionId>
build_url: <+pipeline.executionUrl>
docker_image: artifactory.customer.com/DOCKER_REPO/IMAGE_NAME:TAG_NAME
Plugin specification
- connectorRef: Harness Connector for the container registry where the plugin image is located.
- image: The Docker image containing the plugin to publish build info. For this example, it's
plugins/artifactory-publish-docker-buildinfo.
Settings:
- access_token: The access token for authenticating with Artifactory. In the example above it's retrieved from Harness secrets manager.
- url: The URL of the Artifactory instance where the build info will be published.
- build_name: The name of the build, typically set to the pipeline name.
- build_number: The build number, typically set to the pipeline execution ID.
- build_url: The URL to the pipeline execution in Harness, allowing quick access to the build details.
- docker_image: The Docker image for which to attach the build metadata, including its tag.
Using SSH Keys During Docker Builds
You can securely perform SSH-based operations in your Docker builds — such as cloning private Git repositories — by mounting an SSH key into the build using Docker BuildKit’s --ssh feature. The SSH key is mounted only during the build process and is never baked into the final image.
Below is a full working Harness CI pipeline example:
pipeline:
projectIdentifier: YOUR_PROJECT_ID
orgIdentifier: YOUR_ORG_ID
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: Build
identifier: Build
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: false
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Run
name: Create Dockerfile
identifier: Run
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: alpine
shell: Sh
command: |-
mkdir docker
cat > Dockerfile <<- "EOF"
FROM node:20-slim AS base
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install git -y
RUN mkdir -p ~/.ssh && ssh-keyscan github.com >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
RUN --mount=type=ssh,id=sshkey git clone git@github.com:GITHUB_ORG/PRIVATE_REPO.git
RUN ls -lR PRIVATE_REPO
EOF
cat Dockerfile
mv Dockerfile docker/
ls -al /harness
# docker pull harness/buildkit:1.0.1
- step:
type: Run
name: SSH Key Prep
identifier: SSH_Key_Prep
spec:
shell: Sh
command: |-
cat << EOF > /harness/id_ed25519
<+secrets.getValue("SSH_KEY")> # SSH_KEY is a file secret containing the private SSH key
EOF
chmod 400 /harness/id_ed25519
- step:
type: BuildAndPushDockerRegistry
name: Build and Push Image
identifier: Build_and_Push_Image
spec:
connectorRef: DOCKER_CONNECTOR
repo: DOCKER_ORG/DOCKER_REPO
tags:
- multiarch
caching: true # Required to enable BuildKit/buildx; without this, buildx will not be used
dockerfile: docker/Dockerfile
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 750m
envVariables:
PLUGIN_BUILDX_OPTIONS: "--ssh=sshkey=/harness/id_ed25519"
when:
stageStatus: Success
platform:
os: Linux
arch: Amd64
runtime:
type: Cloud
spec: {}
when:
pipelineStatus: Success
description: ""
identifier: SSH_Dockerfile_Example
name: SSH Dockerfile Example
Key points:
-
--mount=type=ssh,id=sshkeyin the Dockerfile matches--ssh=sshkey=/harness/id_ed25519inPLUGIN_BUILDX_OPTIONS. -
The SSH key comes from the Harness Secrets Manager, as shown in the SSH Key Prep step above where a file secret is used to create
/harness/id_ed25519. It is mounted only during the build. -
In this example, cloneCodebase is set to
falsebecause the Dockerfile is created in the pipeline itself. In your own pipelines, set this totrueif your Dockerfile (or other build context files) is stored in a repository that Harness needs to clone before the build.
Troubleshoot Build and Push steps
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related to building and pushing images, such as:
- What drives the Build and Push steps? What is kaniko?
- Does a kaniko build use images cached locally on the node? Can I enable caching for kaniko?
- Can I run Build and Push steps as root if my build infrastructure runs as non-root? What if my security policy doesn't allow running as root?
- Can I set kaniko and drone-docker runtime flags, such as skip-tls-verify or custom-dns?
- Can I push without building?
- Can I build without pushing?
- Is remote caching supported in Build and Push steps?
- Why doesn't the Build and Push step include the content of VOLUMES from my Dockerfile in the final image?
- Can I use a specific version of kaniko or drone-docker?
- How do I fix this kaniko container runtime error: kaniko should only be run inside of a container?
- Can I push and pull from two different docker registries that have same prefix for registry URL ?
- Why does the parallel execution of build and push steps fail when using Buildx on Kubernetes?
- Why do Build and Push steps fail with "Error while loading buildkit image: exit status 1" when /var/lib/docker is included in shared paths during DIND execution?