Configuring Workflow Actions
The backend of Harness IDP workflows consists of a library of steps and actions that define the workflow logic.
Workflow Actions in IDP are integration points with third-party tools that take inputs from workflows and execute specific tasks based on user input. Workflows include built-in actions for fetching content, registering services in the catalog, and creating/publishing Git repositories.
Defining Workflow Actions
You can configure the backend using the spec.steps field in your YAML configuration. These steps serve as core execution units, triggering actions and orchestrating pipelines. Input details from the frontend are passed to the backend, enabling task execution.
YAML Syntax
steps:
- id: step_id
name: Step Name
action: action_name
input:
key: value
output:
key: value
YAML Breakdown
id– A unique identifier for the step, used to reference it in later steps.name– A human-readable label for the step.action– Specifies the workflow action to execute (e.g., trigger:harness-custom-pipeline, publish:github).input– Defines the parameters required by the action. These vary depending on the action used.
Example (for trigger:harness-custom-pipeline):
input:
url: "https://app.harness.io/ng/account/..."
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
github_repo: ${{ parameters.github_repo }}
Here, url specifies the Harness pipeline, and inputset are the parameters provided by the user, to be used as an input for the pipeline mentioned in the URL.
output– Stores results from the action, which can be used in later steps.
Example (for storing a generated file path):
output:
filePath: '{{ steps.generate.outputs.file }}'
This allows other steps to reference the generated filePath.
Supported Actions
You can find a list of all registered Workflow actions under:
- Click on the three dots in the top right corner of the Workflows page. Select Installed Actions.
- You'll be able to see all the supported actions here.
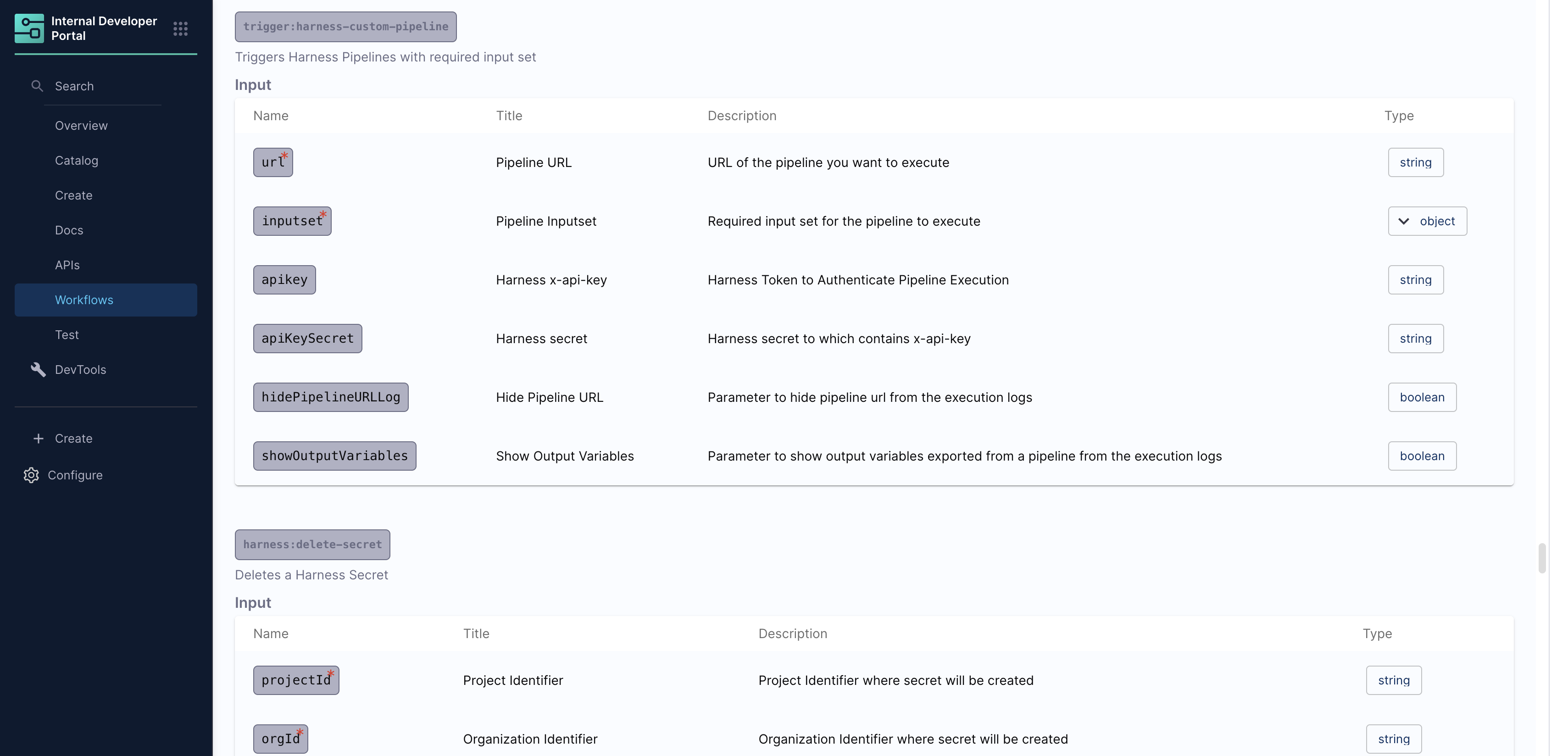
Let's dive deeper into each supported action.
1. trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
This action triggers a Harness pipeline using a provided URL and user-defined input variables. It supports various pipeline configurations, including:
-
Custom Stage (Harness CD License or Free Tier required)
-
codebase disabled Build Stage (Harness CI License required)
##Example
...
steps:
- id: trigger
name: Creating your React app
action: trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
input:
url: "https://app.harness.io/ng/account/..."
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
github_repo: ${{ parameters.github_repo }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
hidePipelineURLLog: true
output:
text:
- title: Pipeline Execution
content: "Execution URL: `${{ steps.trigger.output.url }}`"
Inputs
Here's a list of inputs required to use the action:
| Name | Title | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| url (Mandatory) | Pipeline URL | URL of the pipeline you want to execute | string |
| inputset (Mandatory) | Pipeline Inputset | Required input set for the pipeline to execute | object |
| apikey | Harness x-api-key | Harness Token to Authenticate Pipeline Execution | string |
| apiKeySecret | Harness secret | Harness secret to which contains x-api-key | string |
| hidePipelineURLLog | Hide Pipeline URL | Parameter to hide pipeline url from the execution logs | boolean |
| showOutputVariables | Show Output Variables | Parameter to show output variables exported from a pipeline from the execution logs | boolean |
Let's dive into these inputs in detail:
url: Pipeline execution URL
Note: For pipelines using Git Experience make sure your URL includes
branchandrepoNamee.g.,https://app.harness.io/ng/account/accountID/module/idp/orgs/orgID/projects/projectID/pipelines/pipelineID?repoName=repo-name&branch=branch
inputset: Key-value pairs of pipeline variables
In the YAML example above, under inputset, values such as project_name and github_repo are placeholders for pipeline variable names. You can use the reference format <+pipeline.variables.VARIABLE_NAME> directly within the inputset key-value pairs. For example, instead of simply specifying the variable name, you can reference the pipeline variable like this:
...
inputset:
pipeline.variables.project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
pipeline.variables.github_repo: ${{ parameters.github_repo }}
...
...
To obtain these references, simply copy the variable path from the Harness Pipeline Studio UI. Please make sure to remove <+ & > from the expression copied from UI.
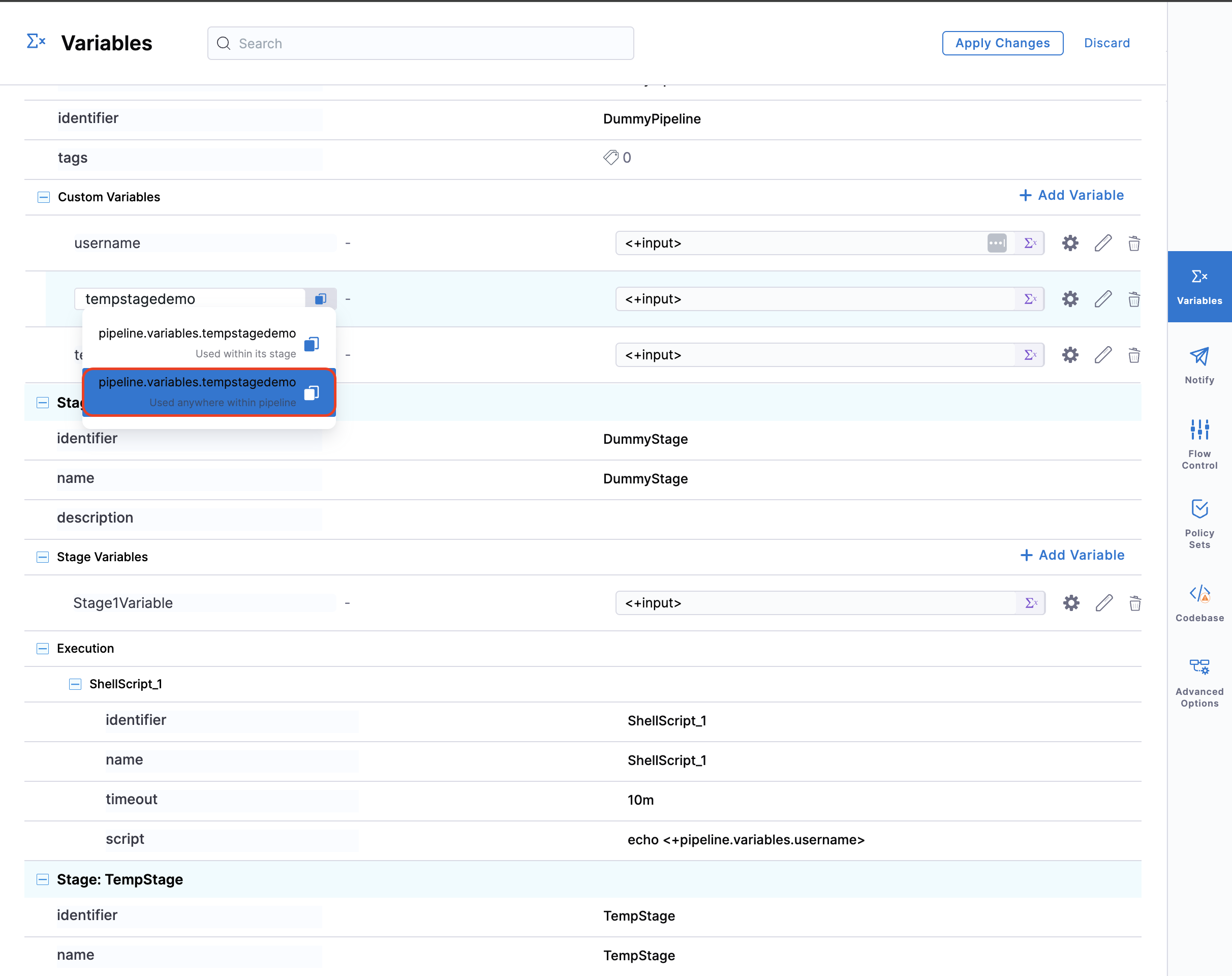
Support for Stage Variables and Pipeline Templates
In addition to pipeline variables, you can also reference stage variables within the inputset. Here’s how each type of variable can be referenced:
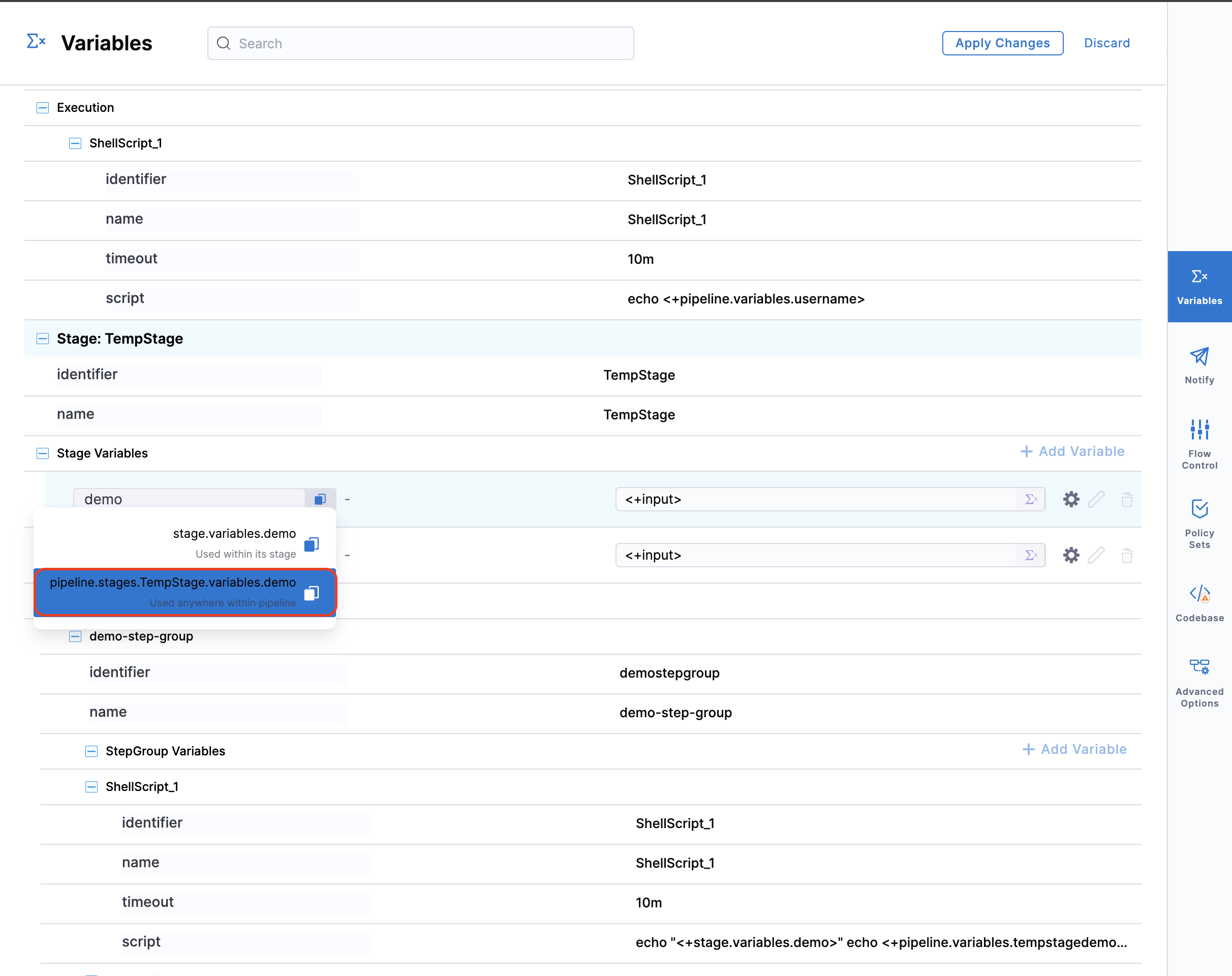
- Stage variable reference:
pipeline.stages.STAGE_IDENTIFIER.variables.VARIABLE_NAME
If you need to reference lower-level variables (such as stage, step group, and step variables) from outside their original scope, you must include the relative path to that variable. For instance, if you want to reference a stage variable from a different stage, you should use the format, pipeline.stages.originalStageID.variables.variableName
Instead of the simpler stage.variables.variableName. This fully qualified path ensures the correct variable is referenced across stages, step groups, or steps.
inputset:
pipeline.variables.project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
pipeline.stages.originalStageID.variables.github_repo: ${{ parameters.github_repo }}
To obtain these references, simply copy the variable path from the Harness Pipeline Studio UI and remove the special characters <+ and >.
Note: This is the only way to reference stage variables and pipelines using templates with variables under
inputset. Without the fully qualified path, the input will not be valid.
Variables under inputset | What's Supported |
|---|---|
Variable name (variable_name) | Supported with Pipelines Variables for IDP stage, custom stage and Codebase Disabled build stage along Pipelines not containing any templates. |
Variable name with Fully Qualified Path (pipeline.variables.variable_name) | Supported with Pipelines Variables for all supported stages and Pipelines containing any templates. |
apikey: User Session Token
Learn more about this authentication mode in detail here.
- The user's session token is used to trigger the Harness Pipeline.
- The user must have execute permissions for the underlying pipeline(s) to ensure successful execution.
You can trigger a pipeline in Harness IDP Workflows using the user session token mode by specifying the token setup in your parameters.properties section of the Workflow YAML.
1. Defining the token setup:
This is defined under the parameter.properties spec to extract the user session token. This token is then used to execute the pipeline.
The token property used to fetch the Harness Auth Token is hidden on the Review Step using ui:widget: password. However, for this to function correctly in a multi-page workflow, the token property must be included under the first page.
parameters:
- title: <PAGE-1 TITLE>
properties:
property-1:
title: title-1
type: string
property-2:
title: title-2
token:
title: Harness Token
type: string
ui:widget: password
ui:field: HarnessAuthToken
- title: <PAGE-2 TITLE>
properties:
property-1:
title: title-1
type: string
property-2:
title: title-2
- title: <PAGE-n TITLE>
```YAML
token:
title: Harness Token
type: string
ui:widget: password
ui:field: HarnessAuthToken
2. Referencing the token in the steps spec of the Workflow YAML:
You'll need to reference the token within the steps section using the following format:
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
apiKeySecret: Harness API Key Secret
Learn more about this authentication mode in detail here.
- A pre-configured Harness API Key is used to trigger the Harness Pipeline.
- The user does not need direct access to the underlying pipeline(s); however, the API key must have the execute permissions for the underlying pipeline(s).
You can also trigger a pipeline in an IDP Workflow using a pre-configured Harness API Key. Here's how you can set this up:
- Create a Harness API Key Secret.
- Store it in your Harness Secret Manager.
- The secret must be stored in the Account Scope to ensure accessibility for workflow execution.
- The secret must have
execute permissionsto the underlying pipeline(s).
Referencing the secret in the steps spec:
apiKeySecret: ${{ secretId }}
Here, secretId refers to the identifier of the secret which stores the Harness API Key. You can retrieve this secretId from the Harness Secret Manager.
-
hidePipelineURLLog: Boolean to hide logs (optional) -
showOutputVariables: Boolean to display pipeline output variables (optional)
Outputs
Title: Name of the Pipeline.url: Execution URL of the Pipeline e.g.:https://app.harness.io/ng/account/********************/module/idp-admin/orgs/default/projects/communityeng/pipelines/uniteddemo/executions/**********/pipeline?storeType=INLINE
Once you create the workflow with this Workflow action, you can see the pipeline URL running in the background and executing the flow.
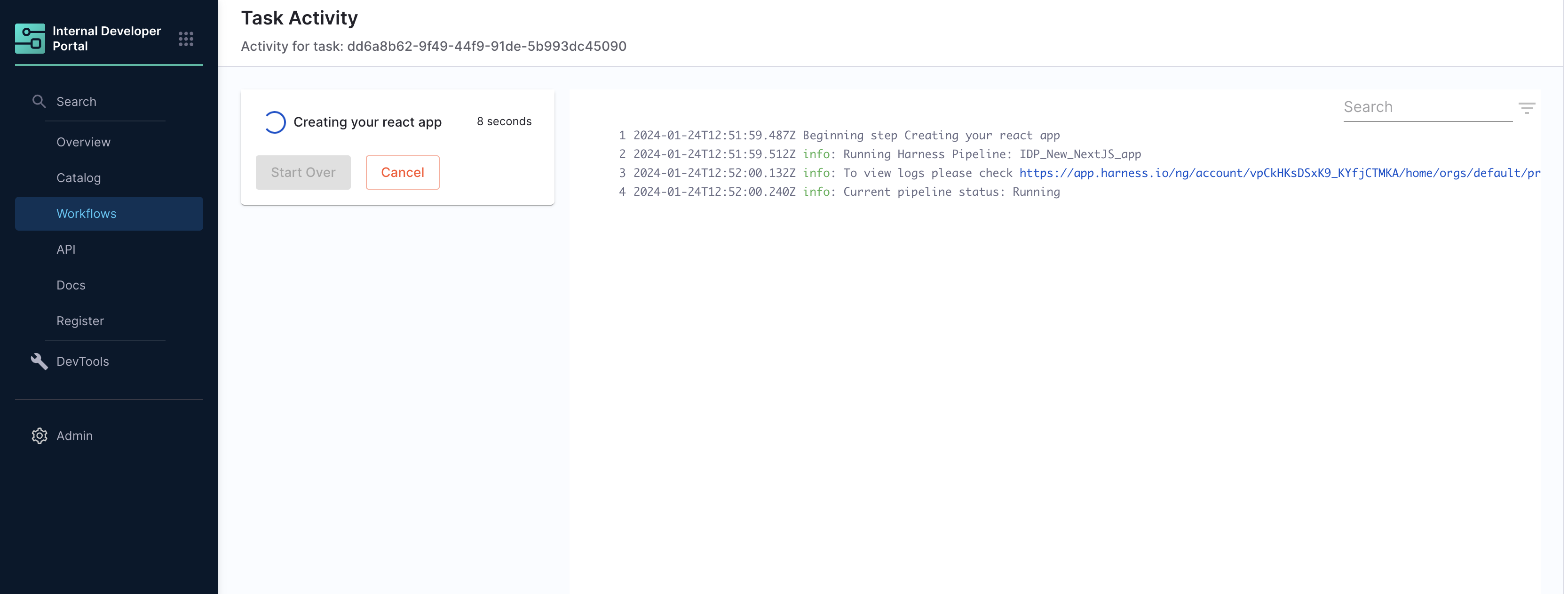
You can now optionally remove the pipeline URL from the workflow execution logs, for this you need to use the boolean property hidePipelineURLLog and set the value as true.
## Example
steps:
- id: trigger
name: Creating your react app
action: trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
input:
url: "Pipeline URL"
hidePipelineURLLog: true
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
- You can as well configure the output to display the pipeline output variables, by setting the
showOutputVariables: trueunderinputsand addingoutputas shown in the example below:
...
## Example
steps:
- id: trigger
...
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
showOutputVariables: true
output:
text:
- title: Output Variable
content: |
Output Variable **test2** is `${{ steps.trigger.output.test2 }}`
- title: Another Output Variable
content: |
Output Variable **test1** with fqnPath is `${{ steps.trigger.output['pipeline.stages.testci.spec.execution.steps.Run_1.output.outputVariables.test1'] }}`
...
Only user defined output variables are allowed, but you can as well use the system generated variables by assigning them as a new variable under shell script step as displayed below. For e.g. we have mentioned the system generated output as jira_id and under Optional Configuration added a test-var which becomes a user defined output variable and could be displayed as output in the IDP workflows.
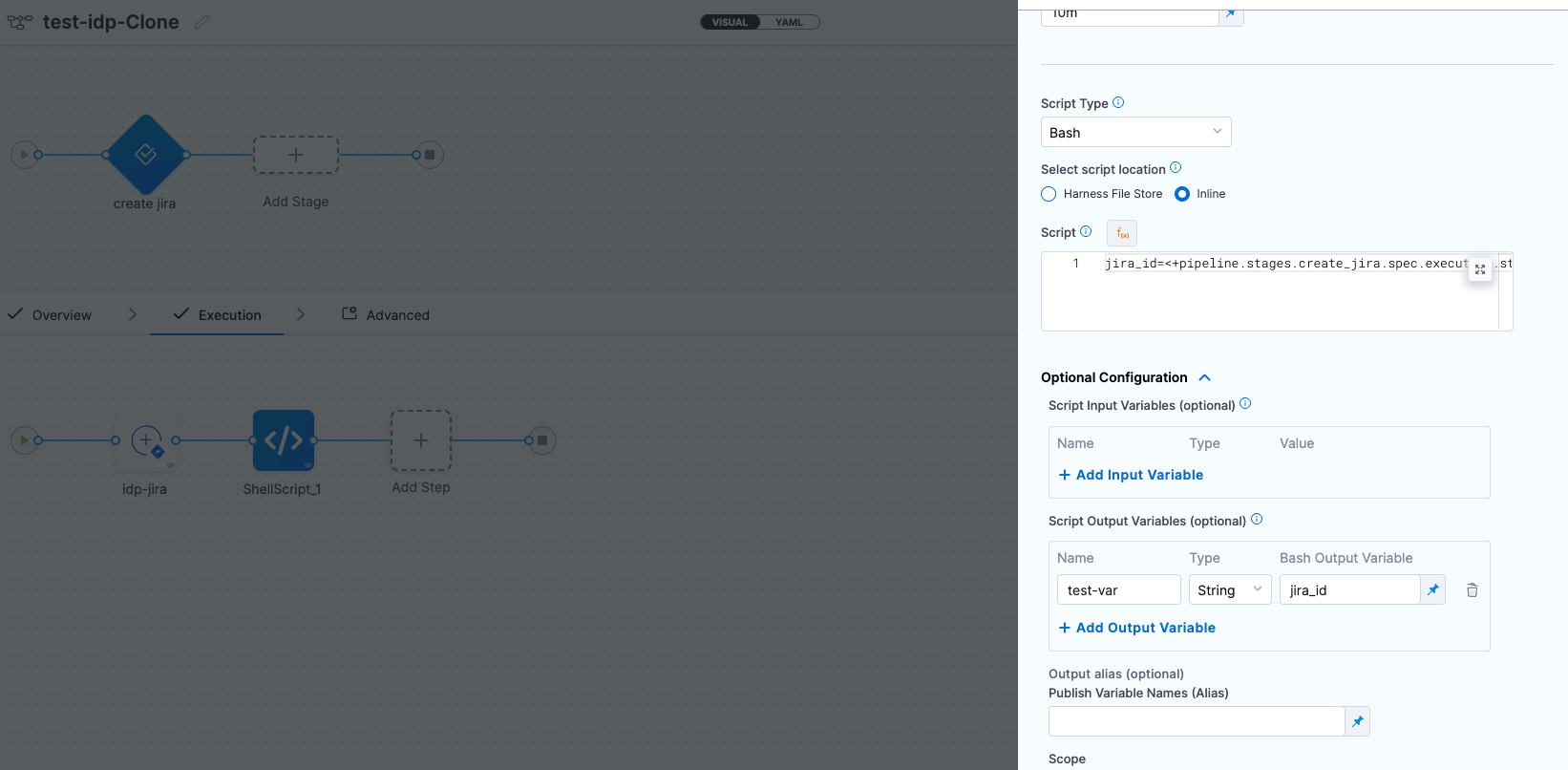
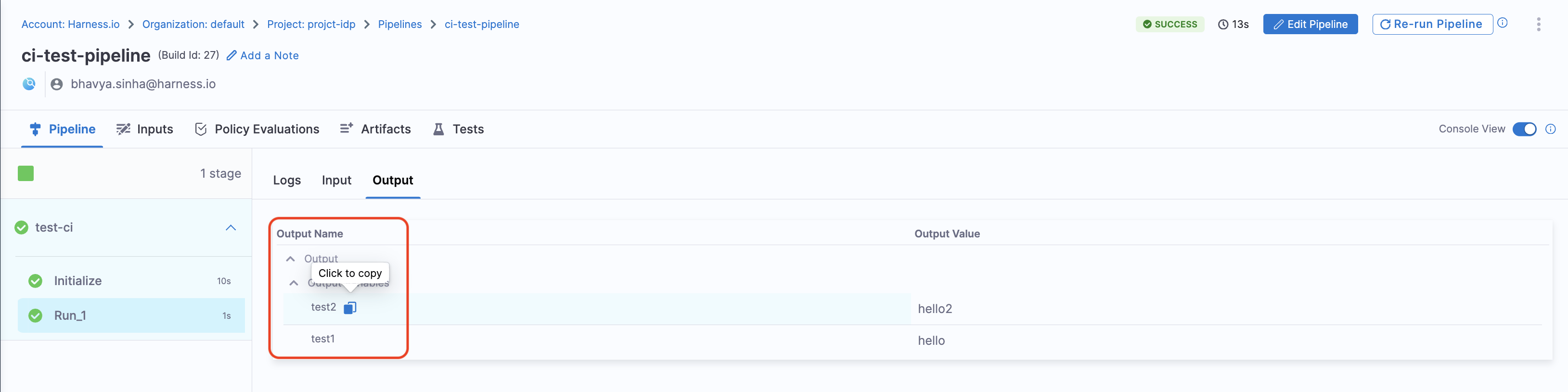
There are two ways in which you can add the output variable to the template syntax.
-
You can directly mention the output variable name
${{ steps.trigger.output.test2 }}, heretest2is the output variable name we created in the pipeline. -
You can copy the JEXL expression of the output variable and remove the JEXL constructs,
${{ steps.trigger.output['pipeline.stages.testci.spec.execution.steps.Run_1.output.outputVariables.test1'] }}, here the partpipeline.stages.testci.spec.execution.steps.Run_1.output.outputVariables.test1comes from<+pipeline.stages.testci.spec.execution.steps.Run_1.output.outputVariables.test2>copied from execution logs.
Example
...
## Example
steps:
- id: trigger
name: Creating your react app
action: trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
input:
url: "https://app.harness.io/ng/account/..."
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
github_repo: ${{ parameters.github_repo }}
pipeline.variables.cloud_provider: ${{ parameters.provider }}
db: ${{ parameters.db }}
cache: ${{ parameters.cache }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
showOutputVariables: true
output:
text:
- title: Output Variable
content: |
Output Variable **test2** is `${{ steps.trigger.output.test2 }}`
- title: Another Output Variable
content: |
Output Variable **test1** with fqnPath is `${{ steps.trigger.output['pipeline.stages.testci.spec.execution.steps.Run_1.output.outputVariables.test1'] }}`
...
2. trigger:trigger-pipeline-with-webhook
This Workflow action could be used to trigger a pipeline execution based on the input-set identifier and a webhook name. Usually a single deployment pipeline has different input-set as per the environment it's going to be deployed and developers can just specify the input-set ID aligning with the environment name to trigger the deployment pipeline.
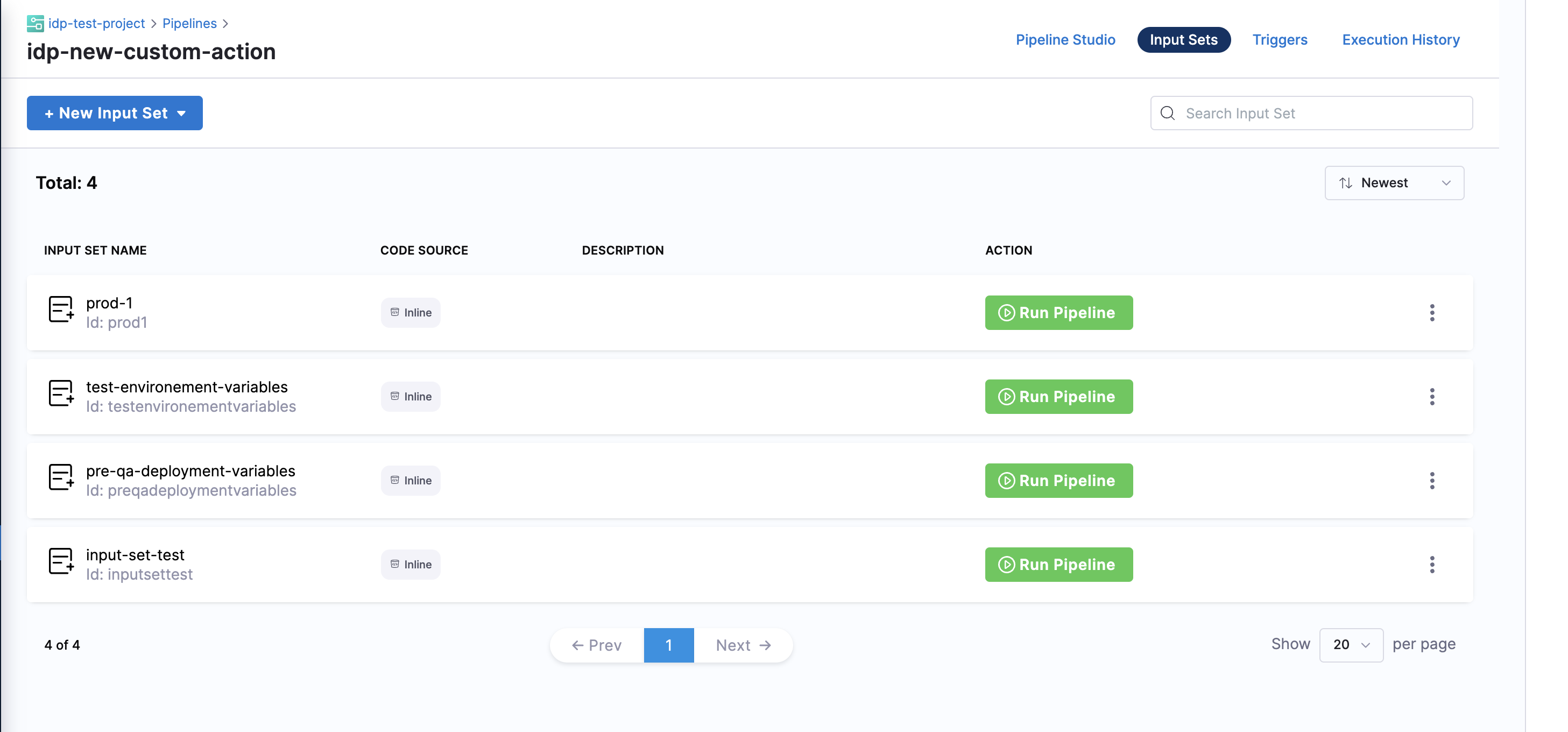
Developers need to mention the input set identifier instead of the name in the workflows input, usually identifier are names devoid of any special characters and spaces, e.g., input set-test name would have an identifier as inputsettest. It is suggested to provide all the available input-set as enums in the template to avoid any ambiguity by developers.
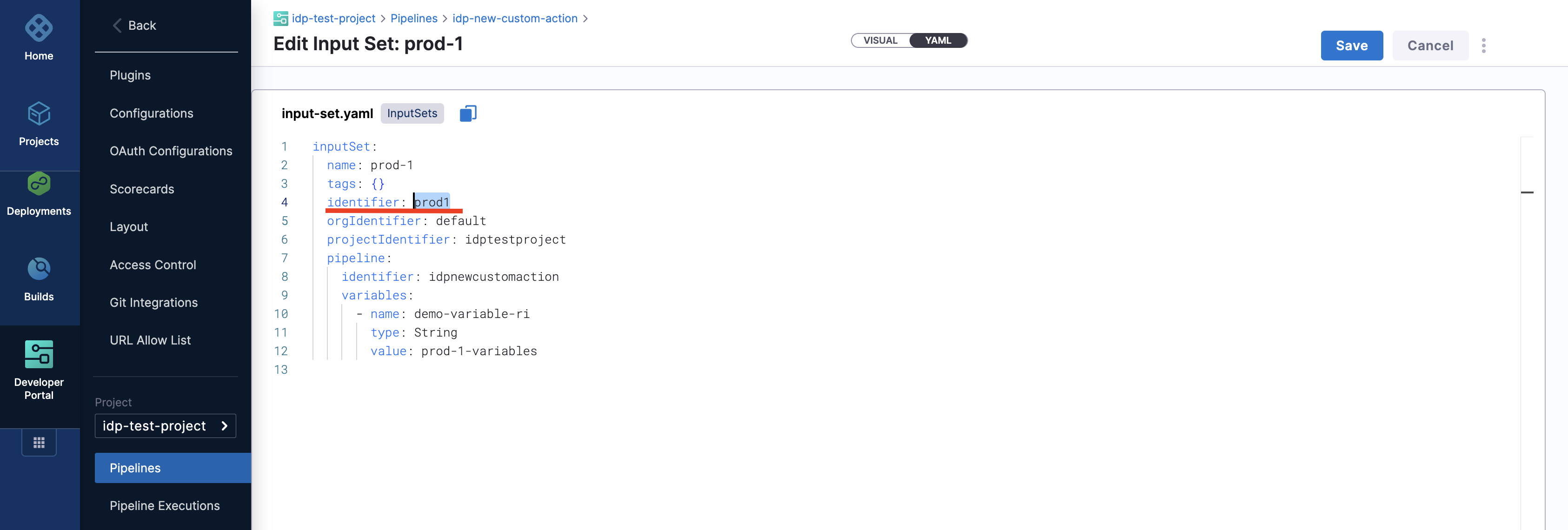
Here's an example workflow based on this source.
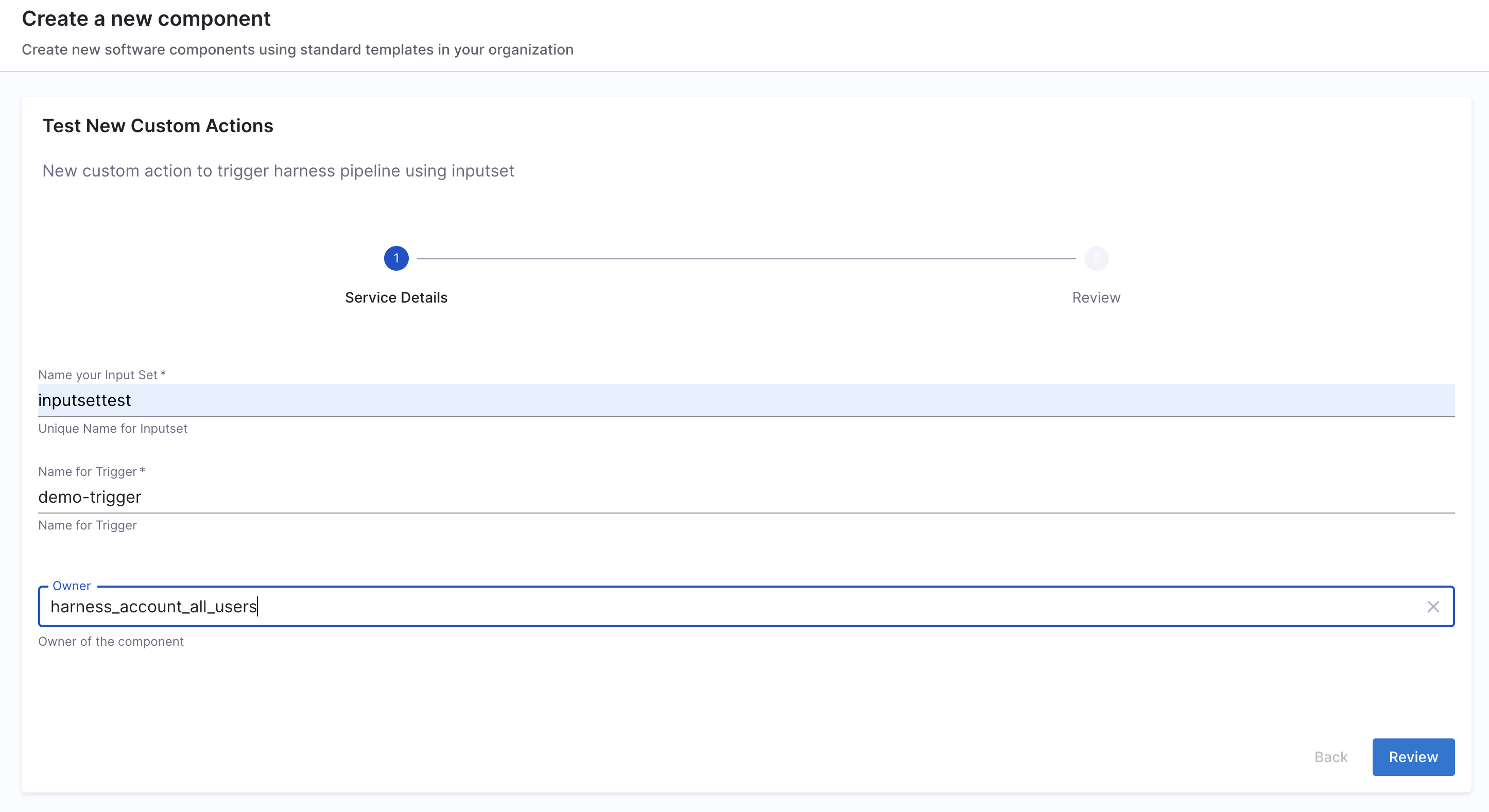
Inputs
Here's a list on inputs used for this action:
| Name | Title | Type |
|---|---|---|
| url (Mandatory) | Pipeline URL | string |
| inputSetName (Mandatory) | Input Set Name | string |
| triggerName (Mandatory) | Trigger Name | string |
| apiKey | Harness API Key | string |
Outputs
| Name | Title |
|---|---|
| API URL | Webhook URL used for execution |
| Pipeline Details | Redirects to the Harness Pipeline Editor |
| Execution URL | Recent executions of the pipeline |
Example
steps:
- id: trigger
name: Triggering pipeline via webhook
action: trigger:trigger-pipeline-with-webhook
input:
url: "YOUR_PIPELINE_URL"
inputSetName: ${{ parameters.inputSetName }}
triggerName: ${{ parameters.triggerName }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
3. harness:create-secret
This action is used to create a secret in Harness.
Inputs
Here's a list of inputs required to use the action:
| Name | Title | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| projectId (Mandatory) | Project Identifier | Project Identifier where secret will be created | string |
| orgId (Mandatory) | Organization Identifier | Organization Identifier where secret will be created | string |
| secretValue (Mandatory) | Secret Value | Secret Value | string |
| apikey | Harness x-api-key | Harness Token to Authenticate Secret Creation | string |
Output
Here's what we get as an output from the action:
| Name | Title | Type |
|---|---|---|
| secretId | Secret Identifier created | string |
4. harness:delete-secret
This action is used to delete a secret from Harness.
Inputs
Here's a list of inputs required to use the action:
| Name | Title | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| projectId (Mandatory) | Project Identifier | Project Identifier where secret will be created | string |
| orgId (Mandatory) | Organization Identifier | Organization Identifier where secret will be created | string |
| secretId (Mandatory) | Secret Identifier | Secret identifier which is to be deleted | string |
| apikey | Harness x-api-key | Harness Token to Authenticate Secret Creation | string |
5. debug:log
This action is used to write a message into the log or list all the files in your workspace.
Inputs
Here's a list of inputs required to use the action:
| Name | Title | Type |
|---|---|---|
| message | Message to output | string |
| listWorkspace | List all files in the workspace, if true | boolean |
| extra | Extra info | unknown |
Example YAML
Write a debug message:
steps:
- action: debug:log
id: write-debug-line
name: Write "Hello Harness!" log line
input:
message: Hello Harness!
List the workspace directory:
steps:
- action: debug:log
id: write-workspace-directory
name: List the workspace directory
input:
listWorkspace: true
7. debug:wait
This action is used to add a waiting period for certain time.
Inputs
Here's a list of inputs required to use this action:
| Name | Title | Type |
|---|---|---|
| minutes | Waiting period in minutes | number |
| seconds | Waiting period in seconds | number |
| milliseconds | Waiting period in milliseconds | number |
Example YAML
steps:
- action: debug:wait
id: wait-1min
name: Waiting for 1 minutes
input:
minutes: 1
Use Cases
1. Hiding Logs
To prevent displaying pipeline URLs in workflow execution logs, use hidePipelineURLLog: true.
steps:
- id: trigger
name: Create React App
action: trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
input:
url: "Pipeline URL"
hidePipelineURLLog: true
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
apikey: ${{ parameters.token }}
2. Using Parameters as Conditions
You can conditionally execute steps based on parameters.
steps:
- id: deploy
name: Deploy App
action: trigger:harness-custom-pipeline
input:
url: "YOUR_PIPELINE_URL"
inputset:
project_name: ${{ parameters.project_name }}
if: "${{ parameters.environment == 'production' }}"
Workflow Actions Usage Limitations
| Workflow Actions | Pipelines and Stages |
|---|---|
| trigger:harness-custom-pipeline | Supports only IDP Stage along with the Deploy Stage, Custom Stage(Available with Harness CD License or Free Tier usage), Pipelines using Pipeline Templates and codebase disabled Build Stage(Only Available with Harness CI License) with Run step |
| trigger:trigger-pipeline-with-webhook | Supports all the pipelines with a custom webhook based trigger |