Add Secret Manager
Harness offers built-in secret management for encrypted storage of sensitive information, such as access keys. Secrets are decrypted when needed, and only the private network-connected Harness Delegate has access to the key management system. You can also integrate your own secret manager. To learn more about secrets in Harness, go to Harness Secret Manager Overview.
You can only use Harness Built-in Secret Manager to store authentication credentials for access to the corresponding secret manager.
Storing credentials from one secret manager within another can result in complex and challenging situations. Moreover, these configurations might introduce vulnerabilities, posing potential security risks.
The Harness platform has several validations, including the disabling of self-references.
Configure secrets managers
Use secrets managers to safely store and access sensitive information, like API keys and credentials. Harness Secret Manager is a platform designed to securely and centrally manage secrets. It offers a unified interface to store, manage, and distribute secrets, including API keys, passwords, and certificates, used in software applications. Developers can seamlessly incorporate secrets into their applications, enforce access controls, and monitor secret usage. This system streamlines secret management and strengthens security for organizations using Harness for software development and deployment workflows.
Manage Secrets with built-in Harness Secret Manager
Google Cloud Key Management Service is the default secret manager in Harness and is named Harness Secret Manager Google KMS. To learn how to configure Harness Secret Manager Google KMS, go to how to add a Google KMS Secret Manager in Harness.
Your browser sends information securely to Harness Manager using HTTPS. Harness Manager transfers encrypted information to the Harness Delegate using HTTPS. The delegate securely exchanges a pair of keys with the secret manager through an encrypted connection. The Harness Delegate uses the encrypted key and secret, and then removes them. The keys never leave the delegate. The delegate uses the required value to deploy on the instances.
Integrate third-party secret managers
This feature is behind a Feature Flag and is available only to customers on paid plans.
Harness can integrate with third-party secrets managers, such as AWS, GCP, Hashicorp Vault, or Azure Key Vault. The basic process to add a third-party secret manager is:
- Select your Account, Organization, or Project.
- In Setup, select Connectors.
- Create a new Connector. The Connectors page appears.
- Under Secret Managers, select a secret manager type.
- Provide the account access information for the new secret manager.
- If you choose to set this secret manager as the default, select Use as Default Secret Manager.
- Select Finish.
When a new Default Secret Manager is set up, only new cloud provider and connector secret fields are encrypted and stored in the new Default Secret Manager. Cloud providers and connectors that were created before the modification, are unaffected.
The following steps provide more details on configuring specific third-party secrets managers.
- AWS KMS
- GCP KMS
- Hashicorp
- AWS Secret Manager
- GCP Secret Manager
These steps explain how use AWS KMS secrets manager. For more information, go to Add an AWS KMS Secret Manager.
Prerequisites for AWS KMS
Verify that you have the following:
- The AWS - Access Key ID from AWS
- The AWS - Secret Key ID from AWS
- The AWS ARN
- A fork of the harnesscd-example-apps repository through the GitHub website.
- For more information on forking a GitHub repository, go to forking a repository in the GitHub documentation.
- Docker. For this tutorial, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your Harness Delegate host. If you do not have the Docker runtime, use one of the following installation options:
Use AWS KMS to manage secrets
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers, such as artifacts registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure, for example, a Kubernetes cluster, and performs operations, including deployment and integration. Make sure the delegate is installed and it is connected. To learn more about delegates, go to the Delegate overview.
Create an AWS access key ID secret
To create an AWS access key, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
aws_kms_access_key. - For the secret value, paste the access token for your AWS user account. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with AWS at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
Create an AWS secret key ID secret
To create an AWS secret key ID, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
aws_kms_secret_key. - For the secret value, paste the access token for your AWS user account. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with AWS at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
Create an AWS ARN secret
To create an AWS ARN, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
aws_kms_arn. - For the secret value, paste the ARN for your AWS user account. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with AWS at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
For more information, go to find the Access key ID and ARN in the AWS documentation.
Create an AWS connector
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing authentication for operations during pipeline runtime. For instance, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. For more details, go to Connectors.
To create an AWS connector, do the following:
- Copy the contents of the aws-kms-connector.yaml file.
- In your Harness project in the Harness Manager, under Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
- Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named aws-kms-connector is successfully created.
- Select Connection Test under Connectivity Status to verify the connection is successful.
If you are NOT using the default organization and project, make sure to change the orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier in the aws-kms-connector.yaml file.
You can now use this secret manager in your pipeline.
These steps explain how use GCP KMS secrets manager. For more information, go to Add Google KMS as a Harness Secret Manager.
Prerequisites for GCP KMS
Verify that you have the following:
- The Google Cloud Symmetric Key to get values like Project ID, Region, Key Ring, Key Name for the Details page, from Google Cloud Console.
- A fork of harnesscd-example-apps repository through the GitHub website.
- For more information on forking a GitHub repository, go to forking a repository in the GitHub documentation.
- Docker. For this tutorial, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your Harness Delegate host. If you do not have the Docker runtime, use one of the following installation options:
Use GCP KMS to manage secrets
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers, such as artifacts registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure, for example, a Kubernetes cluster, and performs operations including deployment and integration. Make sure the delegate is installed and it is connected. Learn more about the delegate in the Delegate overview.
Create a GCP secret key
To create a GCP secret key, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select File.
- Enter the secret name
gcp_kms_secret_key. - For the Select File,
- Open your GCP service account's Actions ⋮ menu, then select Manage keys.
- Select ADD KEY > Create new key.
- In the resulting Create private key dialog, select JSON, create the key, and download it to your computer.
- Upload the JSON file.
- Select Save.
Create the GCP connector
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing authentication for operations during pipeline runtime. For instance, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. For more details, go to Connectors.
-
Copy the contents of gcp-kms-connector.yaml.
-
In your Harness project in the Harness Manager, under Project Setup, select Connectors.
-
Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
-
Replace
GCP PROJECT IDwith your GCP project name. -
Replace
GCP Regionwith your GCP Region. -
Replace
GCP KeyRingwith your GCP KeyRing. -
Replace
GCP KeyNamewith your GCP KeyName.You can refer Obtain Google Cloud Symmertic Key to get more information on the above parameters.
-
Select Save Changes, and verify that the new connector named gcp-kms-connector is successfully created.
-
Select Connection Test under Connectivity Status to verify the connection is successful.
If you are NOT using the default organization and project, make sure to change the orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier in the gcp-kms-connector.yaml file.
You can now use this secret manager in your pipeline.
These steps explain how use Hashicorp secrets manager. For more information, go to Add a HashiCorp Vault Secret Manager.
Prerequisites for Hashicorp Vault
Verify that you have the following:
- The Public Vault Url from Hashicorp Vault.
- The Admin Token from the Hashicorp Public vault URL.
- A fork of the harnesscd-example-apps repository through the GitHub website.
- For more information on forking a GitHub repository, go to forking a repository in the GitHub documentation.
- Docker. For this tutorial, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your Harness Delegate host. If you do not have the Docker runtime, use one of the following installation options:
Use Hashicorp to manage secrets
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers, such as artifacts registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure, for example, a Kubernetes cluster, and performs operations, including deployment and integration. Make sure the delegate is installed and it is connected. Learn more about the delegate in the Delegate overview.
Create a Hashicorp admin token
To create a Hashicorp admin token, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
hashicorp_admin. - For the secret value, paste the admin token from the Hashicorp Public vault URL. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with Hashicorp at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
Create a Hashicorp connector
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing authentication for operations during pipeline runtime. For instance, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. For more details, go to Connectors.
- Copy the contents of hashicorp_vault_connector.yaml.
- In your Harness project in the Harness Manager, under Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
- Replace the
Public Vault URLwith your public vault URL from Hashicorp Vault. - Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named hashicorp_vault is successfully created.
- Select Connection Test under Connectivity Status to verify the connection is successful.
If you are NOT using the default organization and project, make sure to change the orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier in the hashicorp_vault_connector.yaml file.
You can now use this secret manager in your pipeline.
These steps explain how use AWS secrets manager. For more information, go to Add an AWS Secrets Manager.
Prerequisites for AWS secret manager
Verify that you have the following:
- The AWS - Access Key ID from AWS
- The AWS - Secret Key ID from AWS
- A fork of the harnesscd-example-apps repository through the GitHub website.
- For more information on forking a GitHub repository, go to forking a repository in the GitHub documentation.
- Docker. For this tutorial, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your Harness Delegate host. If you do not have the Docker runtime, use one of the following installation options:
Use AWS KMS to manage secrets
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers, such as artifacts registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure, for example, a Kubernetes cluster, and performs operations, including deployment and integration. Make sure the delegate is installed and it is connected. Learn more about the delegate in the Delegate overview.
Create an AWS access key ID
To create an AWS access key ID, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
aws_secret_access_key. - For the secret value, paste the access token for your AWS user account. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with AWS at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
Create an AWS secret key ID
To create an AWS secret key ID, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
aws_secret_secret_key. - For the secret value, paste the access token for your AWS user account. The Harness Delegate uses this credential to authenticate Harness with AWS at deployment runtime.
- Select Save.
Create an AWS connector
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing authentication for operations during pipeline runtime. For instance, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. For more details, go to Connectors.
- Copy the contents of aws-secret-manager-connector.yml.
- In your Harness project in the Harness Manager, under Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
- Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named aws-secret-manager is successfully created.
- Select Connection Test under Connectivity Status to verify the connection is successful.
If you are NOT using the default organization and project, make sure to change the orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier in the aws-secret-manager-connector.yaml file.
You can now use this secret manager in your pipeline.
These steps explain how use GCP secrets manager. For more information, go to Add a Google Cloud secret manager.
Prerequisites for GCP secret manager
Verify that you have the following:
- A fork of the harnesscd-example-apps repository through the GitHub website.
- For more information on forking a GitHub repository, go to forking a repository in the GitHub documentation.
- Docker. For this tutorial, ensure that you have the Docker runtime installed on your Harness Delegate host. If you do not have the Docker runtime, use one of the following installation options:
Use GCP KMS to manage secrets
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Default Project.
The Harness Delegate is a service that runs in your local network or VPC to establish connections between the Harness Manager and various providers, such as artifacts registries, cloud platforms, etc. The delegate is installed in the target infrastructure, for example, a Kubernetes cluster, and performs operations, including deployment and integration. Make sure the delegate is installed and it is connected. To learn more about delegates, go to the Delegate overview.
Create a GCP secret key
To create a GCP secret key, do the following:
- Select New Secret, and then select File.
- Enter the secret name
gcp_secret_secret_key. - For the Select File,
- Open your GCP service account's Actions ⋮ menu, and then select Manage keys.
- Select ADD KEY > Create new key.
- In the resulting Create private key dialog, select JSON, create the key, and download it to your computer.
- Upload the JSON file.
- Select Save.
Create a GCP connector
Connectors in Harness enable integration with third-party tools, providing authentication for operations during pipeline runtime. For instance, a GitHub connector facilitates authentication and fetching files from a GitHub repository within pipeline stages. For more details, go to Connectors.
- Copy the contents of gcp-secret-manager-connector.yaml.
- In your Harness project in the Harness Manager, under Project Setup, select Connectors.
- Select Create via YAML Builder and paste the copied YAML.
- Select Save Changes and verify that the new connector named gcp-kms-connector is successfully created.
- Select Connection Test under Connectivity Status to verify the connection is successful.
If you are NOT using the default organization and project, make sure to change the orgIdentifier and projectIdentifier in the gcp-secret-manager-connector.yaml file.
You can now use this secret manager in your pipeline.
Create secrets
To create a secret, do the following:
- Sign in to Harness.
- Select Projects, and then select Secrets.
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter Name for the secret.
- For the Secret Value, enter a GitHub personal access token (PAT) with the repo scope. For more information, go to creating a personal access token in the GitHub documentation.
- Select Save.
Where are secrets stored?
Harness stores all your secrets, including text secrets, file secrets, and SSH key secrets, in your secret manager.
The secret you use to connect Harness to your secret manager (password, etc) is stored in the Harness Default Secret Manager.
Secret manager scope
You can add secrets to the org or project scopes using a secret manager at the account or org scope. For example, you can create secrets inside a project using the secret manager configured at the org or account level.
When you create a secret, Harness shows the list of secret managers at the parent scope and up the hierarchy. If you create a secret at the project level, Harness lists all secret managers scoped at the account, org, and project levels.
If a default secret manager is updated or deleted, Harness Default Secret Manager automatically becomes the new default.
Harness creates new secrets with secret manager scope information and identifiers. Harness displays the secret manager scope on the secret list page.
Secrets and log sanitization
Harness sanitizes deployment logs and any script outputs to mask text secret values.
Follow these steps for a demo of secrets sanitization in logs.
Create a new secret
- Select New Secret, and then select Text.
- Enter the secret name
docsecret. - For the secret value, add the string
docsecret. - Select Save.
Create a pipeline
- In Default Project, select Pipelines.
- Select New Pipeline.
- Enter the name
print secret. - Select Inline to store the pipeline in Harness.
- Select Start and, in the Pipeline Studio, toggle to YAML to use the YAML editor.
- Select Edit YAML to enable edit mode. Copy the contents of the secret-sanitization.yaml file and paste it.
- Select Save to save the pipeline.
Run the pipeline
- Select Run, and then select Run Pipeline to initiate the deployment.
- Observe the execution logs as Harness runs the pipeline.
- In console logs, the secret is masked with asterisks (
*), as shown in the following image.
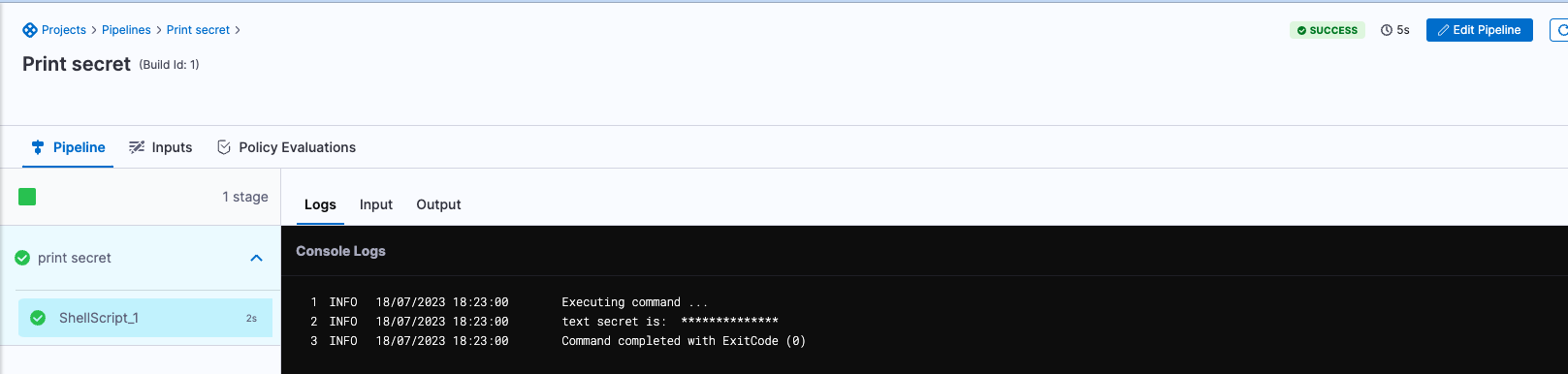
When a text secret is displayed in a deployment log, Harness substitutes the text secret value with asterisks (*) so that the secret value is never displayed. For more information, go to secrets and log-sanitization. The only exception is output variables. If an output variable value contains a secret, be aware that the secret will be visible in the build details. For more information, go to output variables.