Custom Scan step for supported scanners
The Custom Scan step enables you to configure supported scanners that don't yet have their own dedicated step in the Harness Step Library.
Supported scanners that use a Custom Scan step
Important notes for Custom Scan steps
- To configure a Custom Scan step, you add a set of key-value pairs in the Settings field. The key and value strings you need to specify, such as
product_nameandorchestratedScan, are case-sensitive. - You need to add a Docker-in-Docker background step if you're running an
orchestratedScanordataLoadscan in a Kubernetes or Docker build infrastructure. - You need to run the Custom Scan step with root access if you need to run a Docker-in-Docker step, or if you need to add trusted certificates to your scan images at runtime.
- The following topics contain useful information for setting up scanner integrations in STO:
Workflow descriptions
Orchestration/extraction workflows
This workflow applies to scanner integrations that support orchestratedScan or dataLoad scan modes.
-
Add a Build or Security stage to your pipeline.
-
If you're scanning a code repository, set up your codebase.
-
Add a Custom Scan step.
-
Review the Important notes for Custom Scan steps for additional requirements and relevant information.
If you're setting up a scan on a Kubernetes or Docker build infrastructure, you need to add a Docker-in-Docker background step to the stage.
-
Add the relevant
key:valuepairs to Settings.
Ingestion workflows
This workflow applies to scanner integrations that support Ingestion mode.
-
Add a Build or Security stage to your pipeline.
-
Add a Run step and set it up to save your scan results to a shared folder.
For more information, go to Run an ingestion scan in an STO Pipeline.
-
Add a Custom Scan step.
-
Review the Important notes for Custom Scan steps for additional requirements and relevant information.
-
Add the relevant
key:valuepairs to Settings.
Custom Scan settings reference
To set up a scanner, you add key-value pairs under Settings. The following sections describe the different settings and requirements.
Scanner configuration in a Custom Scan step
- Visual editor
- YAML editor
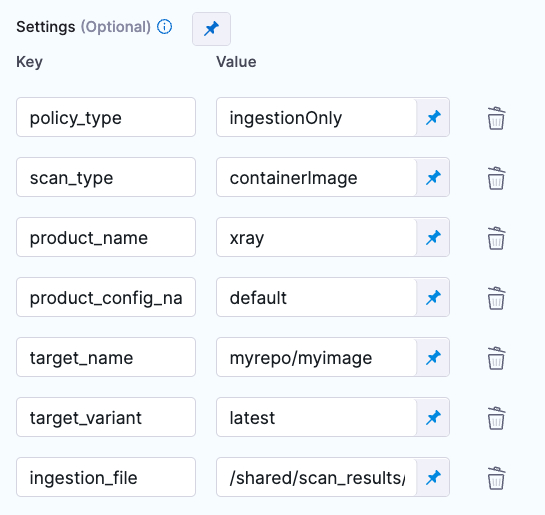
- step:
type: Security
name: custom_scan_xray
identifier: custom_scan_xray
spec:
privileged: true
settings:
policy_type: ingestionOnly
scan_type: containerImage
product_name: xray
product_config_name: default
target_name: YOUR_REPO/YOUR_IMAGE
target_variant: YOUR_TAG
ingestion_file: /shared/scan_results/xray2.json
Scanner settings
These settings are required for most scanners. For more information, go to the reference for the scanner integration you're setting up.
Supported scanners that use a Custom Scan step
Product name
The scanner name. This is required for all Custom Scan steps.
Key
product_name
Value
Go to the relevant step configuration.
Scan type
The target type to scan.
Key
scan_type
Value
Must be one of the following. For supported values, go to the relevant step configuration.
containerImage
repository
instance
configuration
Policy type
The scan mode to use.
Key
policy_type
Value
Must be one of the following. For supported values, go to the relevant step configuration.
orchestratedScan
ingestionOnly
dataLoad
Product config name
Required for most scanner integrations.
Key
product_config_name
Value
For supported values, go to the relevant step configuration.
Target and variant
Every Custom Scan step needs a target and baseline.
Target name
Key
target_name
Value
A user-defined label for the code repository, container, application, or configuration to scan. Specify a unique, descriptive name. This makes it much easier to navigate your scan results in the STO UI.
Target variant
Key
target_variant
Value
A user-defined label for the branch, tag, or other target variant to scan.
Code repositories
These settings apply to Custom Scan steps when both of these conditions are true:
- The
policy_typeisorchestratedScanordataLoad. - The
scan_typeisrepository.
Repository project
Key
repository_project
Value
The name of the repo to scan. To specify the repo URL, edit the Codebase Config object in the Harness pipeline.
In most cases, this should match the repo name used in your Git provider.
Repository branch
Key
repository_branch
Value
The branch that gets reported in STO for the ingested results. In most cases, this field should match the name of the Git branch that is getting scanned.
You can specify a hardcoded string or use a variable such as <+codebase.branch> to specify the branch at runtime. For more information, go to CI codebase variables reference.
Container image
These settings apply to Custom Scan steps when both of these conditions are true:
- The
policy_typeisorchestratedScanordataLoad. - The
scan_typeiscontainerImage.
- Container type
- Container domain
- Container project
- Container tag
- Container access Id
- Container access token
- AWS region
Container type
Key
container_type
Value
The registry type where the image is stored. Specify one of the following:
Scan a local image built and stored within the context of the current stage (via /var/run/docker.sock registered as a stage level volume mount).
local_image
A registry that uses the Docker Registry v2 API such as Docker Hub, Google Container Registry, or Google Artifact Registry.
docker_v2
jfrog_artifactory
aws_ecr
Container domain
Key
container_domain
Value
The URL of the registry that contains the image to scan. Examples include:
docker.io
app.harness.io/registry
us-east1-docker.pkg.dev
us.gcr.io
Container project
Key
container_project
Value
The image name. For non-local images, you also need to specify the image repository. Example: jsmith/myalphaservice
Container tag
Key
container_tag
Value
The image tag. Examples: latest, 1.2.3
Container access Id
Key
container_access_id
Value
Your access Id to the image registry.
Container access token
Key
container_access_token
Value
The password or access token used to log in to the image registry. In most cases this is a password or an API key.
You should create a Harness text secret with your encrypted token and reference the secret using the format <+secrets.getValue("container-access-id")>. For more information, go to Add and Reference Text Secrets.
AWS region
Key
container_region
Value
The region where the image to scan is located, as defined by the cloud provider such as AWS.
Application instances
These settings apply to Custom Scan steps when both of these conditions are true:
- The
policy_typeisorchestratedScanordataLoad. - The
scan_typeisinstance.
Instance domain
Key
instance_domain
Value
Domain of the application instance to scan. You can include the full path to the app in this field, or split the full path between the instance_domain and the instance_path settings. Example: https://myapp.io/portal/us
Instance path
Key
instance_path
Value
Path to append to the application instance domain, if you're splitting the full path between the instance_domain and the instance_path settings. For example, you might specify the domain as https://myapp.io and the path as /portal/us.
Instance protocol
Key
instance_protocol
Value
One of the following: HTTPS is the default.
HTTPS
HTTP
Instance port
Key
instance_port
Value
The TCP port used by the scanned app.
Instance username
Key
instance_username
Value
The username for authenticating with the scanned app.
Instance password
Key
instance_password
Value
You should create a Harness text secret with your encrypted password and reference the secret using the format <+secrets.getValue("container-access-id")>. For more information, go to Add and reference text secrets.
Configurations
The following settings apply to scanners where the scan_type is configuration.
Configuration type
Key
configuration_type
Value
aws_account
Configuration access
You can use these settings to access your configuration.
You should create Harness text secrets with your encrypted access token and access it using the format <+secrets.getValue("my-secret")>.
configuration_region
configuration_environment
configuration_access_id
configuration_access_token
Ingestion file
This setting applies to Custom Scan steps when the policy_type is ingestionOnly.
Key
ingestion_file
Value
The path to your scan results when running an Ingestion scan, for example /shared/scan_results/myscan.latest.sarif.
-
The data file must be in a supported format for the scanner.
-
The data file must be accessible to the scan step. It's good practice to save your scan results to a shared path in your stage. In the visual editor, go to the stage where you're running the scan. Then go to Overview > Shared Paths. You can also add the path to the YAML stage definition like this:
- stage:
spec:
sharedPaths:
- /shared/scan_results
Fail on Severity
If the scan finds any vulnerability with the specified severity level or higher, the pipeline fails automatically. NONE means do not fail on severity.
For more information, go to:
- STO workflows for blocking builds and PRs.
- Exemptions to override Fail on Severity thresholds for specific issues in STO
Key
fail_on_severity
Value
CRITICAL
MEDIUM
LOW
INFO
NONE
Additional Configuration
In the Additional Configuration settings, you can use the following options:
Advanced settings
In the Advanced settings, you can use the following options: