Manage Harness environments and infrastructures from Git
When you create a new Harness environment or infrastructure definition, you can store it in one of the following ways:
- Inline: Harness stores the entity in its platform.
- Remote: The Harness entity is stored in Git.
You can set the entity as Inline or Remote when you create it, and then change the storage method after it is created. Changing the storage method is described in this topic.
The topic explains how to use the Remote option to store a Harness environment or infrastructure definition in your Git platform account.
Before you begin
- Make sure you have a Git repo with at least one branch.
- Make sure you have a Harness Git connector with a Personal Access Token (PAT) for your Git account.
Visual summary
Here's a quick video of how you can manage services, environments, and infrastructue definitions through Git Experience.
Create a remote environment
You can create a remote environment at the Harness account, organization, or project level. This topic explains the steps to create it at the project level. The process is the same for the other levels.
-
In your Harness account, go to a project. In Project Settings, select Environments. To learn more about creating environments, go to Create environments.
-
Select New Environment.
-
In Name, enter a name for the environment.
-
In How do you want to set up your environment, select Remote.
-
In Git Connector, select or create a Git connector to the repo for your environment. For more information, go to Code Repo Connectors.
-
In Repository, select your repository. If your repository isn't listed, enter its name. Create the repository in Git before entering it in Repository. Harness does not create the repository for you.
-
In Git Branch, select your branch. If your branch isn't listed, enter its name. Create the branch in your repository before entering it in Git Branch. Harness does not create the branch for you. You generally want to save it to the default branch on the first save. You can then create different branches in the Harness repo if you want to create different versions of your environment.
-
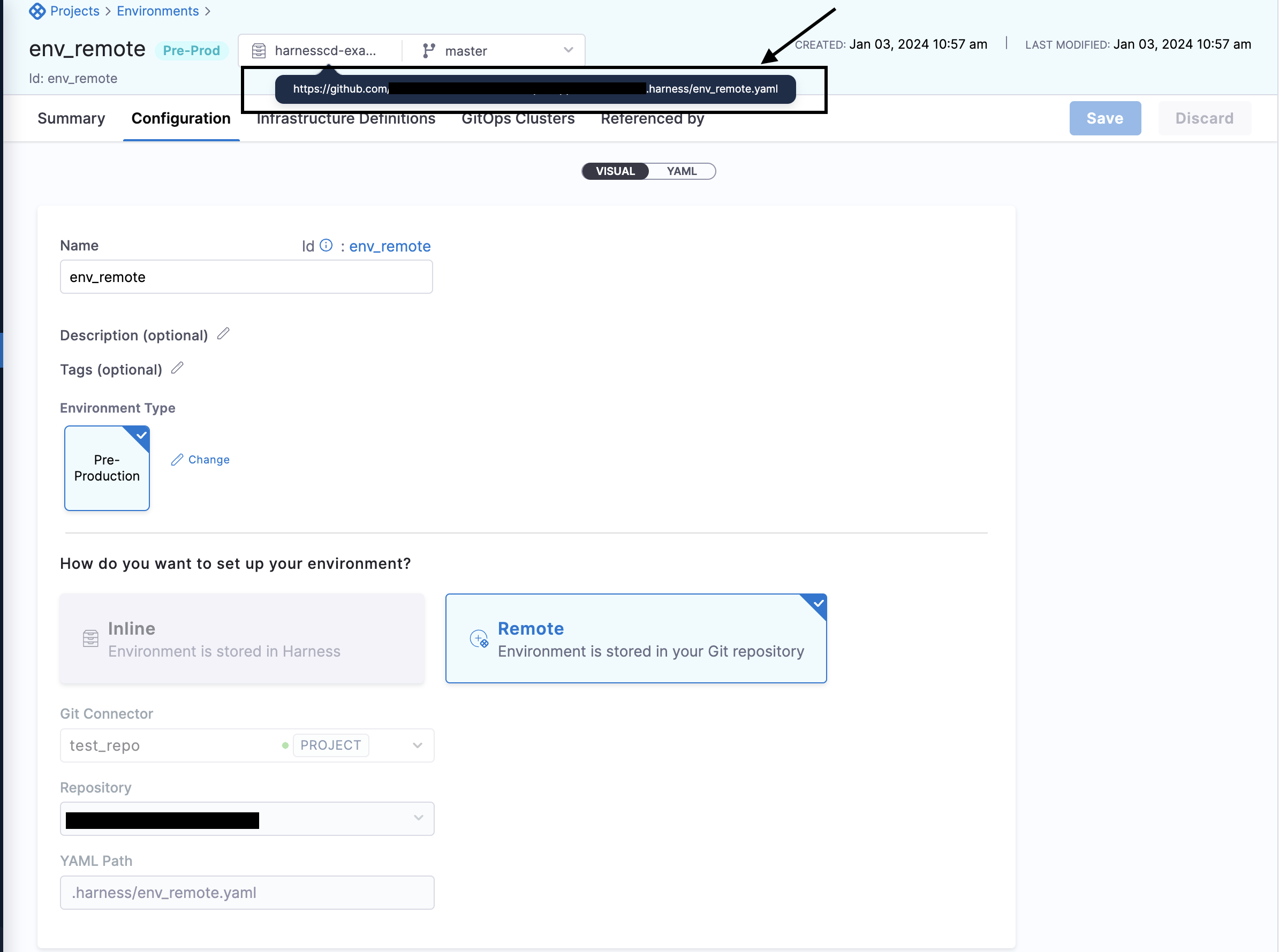
Harness Git Experience auto-populates the YAML Path. You can change this path and the file name.
-
Select Save.
-
In the new environment, click on the YAML path provided to view your new environment in your Git repo.
Create a remote infrastructure definition
-
In the remote environment, select Infrastructure Definition.
-
Select New Infrastructure Definition.
-
In Name enter name for the infrastructure definition.
-
In How do you want to set up your infrastructure, select Remote.
-
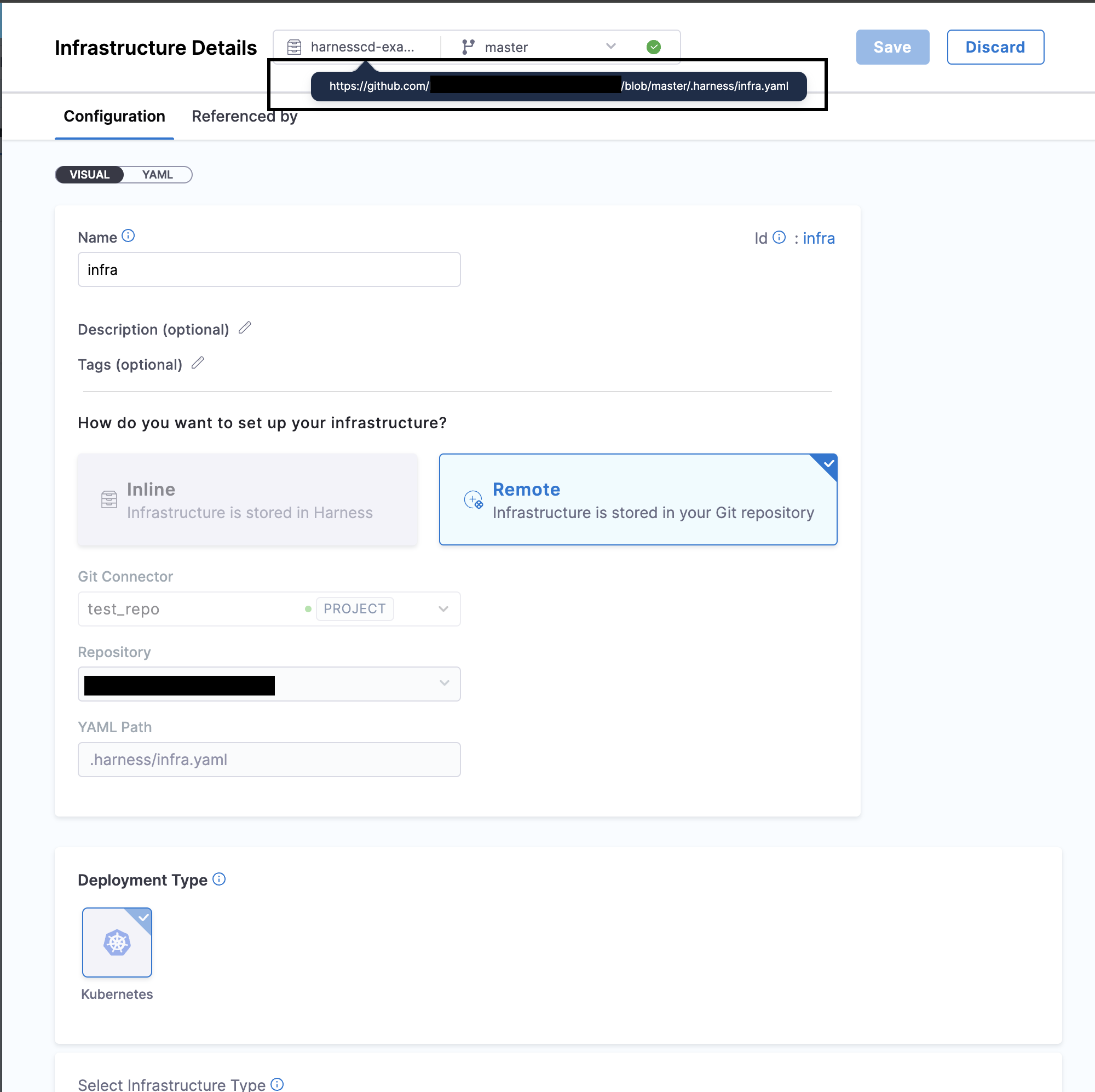
Harness will automatically populate the connector, repository, branch, and YAML path. The auto-population of the connector, branch, and repository is based on the environment configuration, specifically extracted from the Git repository where you've stored your environment details. You can change the connector as well as the branch.
-
Select the Deployment Type, Infrastructure Type, and then provide infra details. For more information, go to Create environments.
-
Select Save.
-
For the new infrastructure definition, select More Options (⋮) and then select Edit.
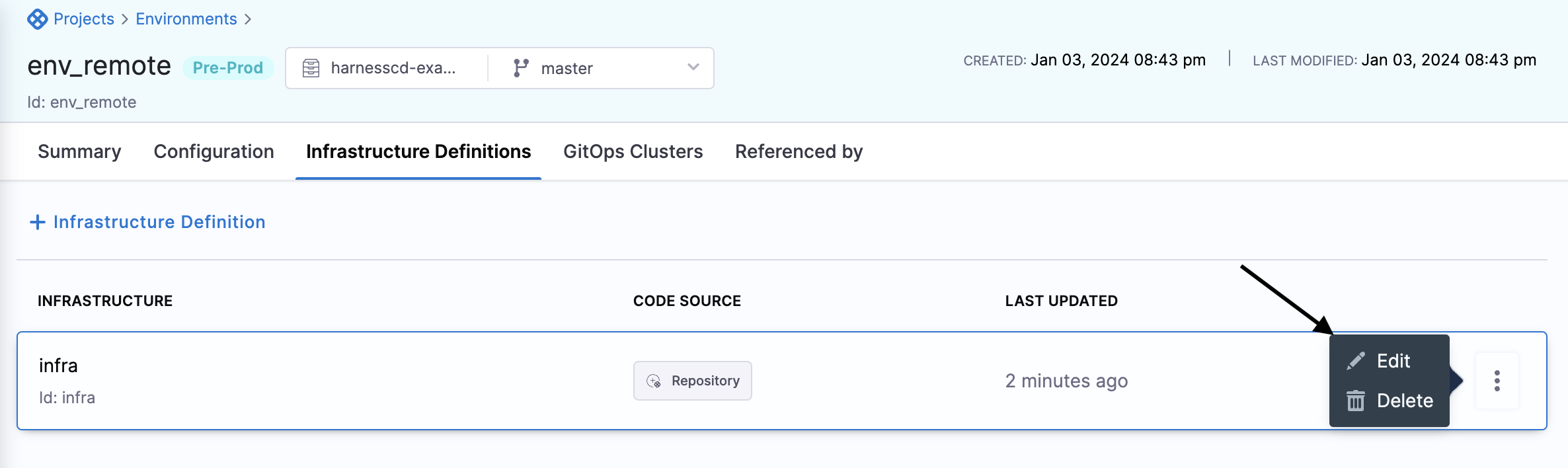
-
Click the YAML path to view your Infrastructure Definition YAML file in your Git repo.
Add a remote environment in a CD pipeline
Adding a remote environment in a CD pipeline stage is no different from adding an inline environment.
When adding a remote environment to the stage, you have the ability to choose a specific branch to determine the version of the environment you wish to utilize in your pipeline.
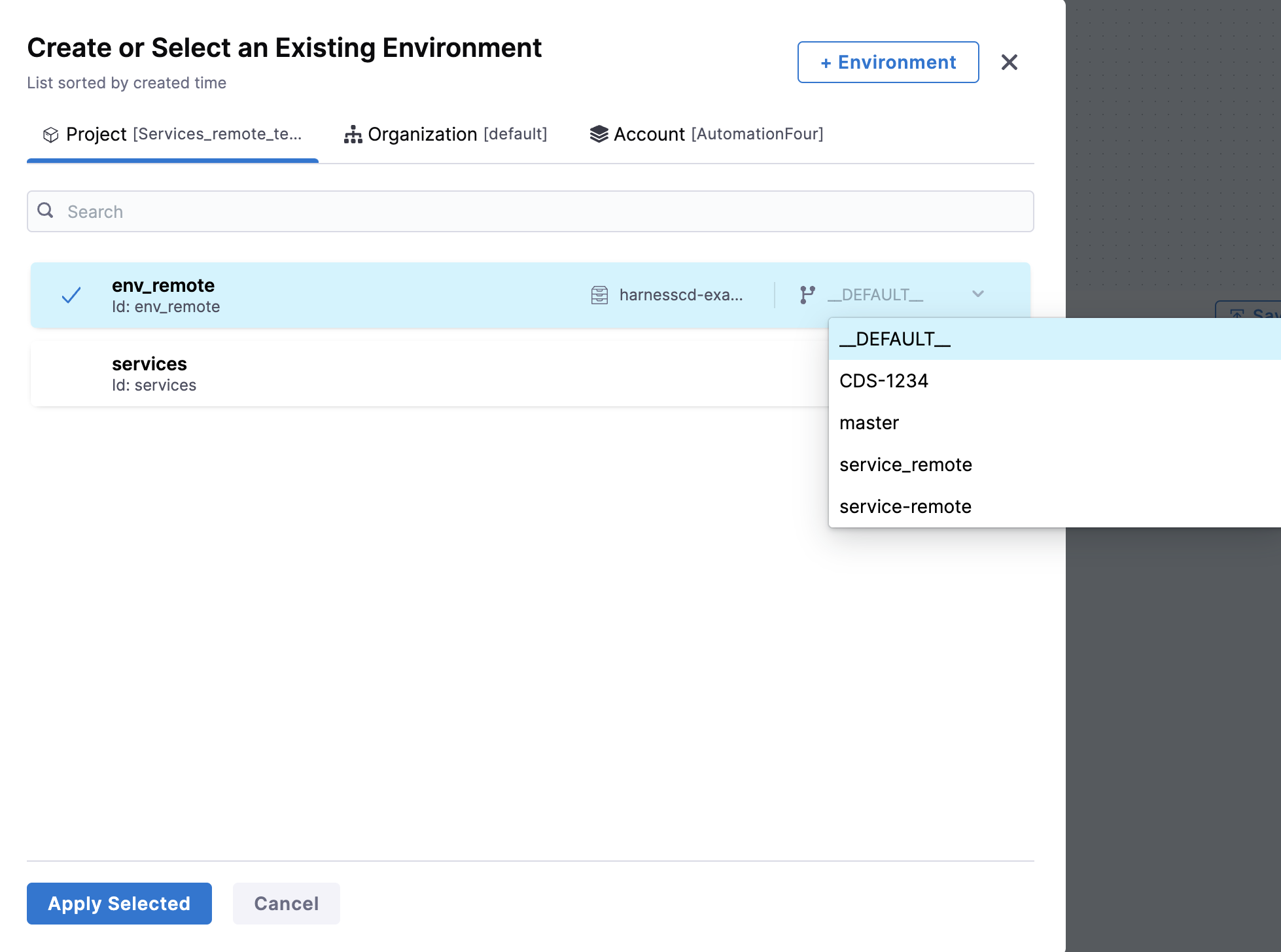
- When a remote environment is linked to a pipeline, the environment branch is displayed as
__DEFAULT__.__DEFAULT__resolves to the same branch as the pipeline when the pipeline and the environment linked to the pipeline are in the same repository. If the pipeline resides in a different repository, then DEFAULT resolves to the main branch of the repository where the linked environment resides. - Infrastructure definition takes the same branch of the environment.
- If you're using a remote stage template with a remote environment in a remote pipeline, and both are in the same repository, then the default branch is the branch where the template resides. However, if the environment is located in a different repository it will not work.
Change an inline environment to a remote environment
- In Environments, locate the environment you want to change.
- Select More Options (⋮).
- Select Move to Git.
The same settings used when creating a remote environment appear. Configure the settings just as you would for a new remote environment.
Change an inline infrastructure definition to a remote infrastructure definition
-
Select an environment, and then select the infrastructure definition you want to store in your Git repo.
-
Select More Options (⋮).
-
Select Move to Git.
The same settings used when creating a remote infrastructure definition appear. Configure the settings just as you would for a new remote infrastructure definition.